Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP Copd
Uploaded by
joeletteOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCP Copd
Uploaded by
joeletteCopyright:
Available Formats
NURSING CARE PLAN
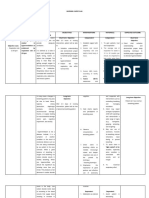
Nursing Diagnosis Subjective Impaired gas Cues: exchange related to Upon arrival decreased at the ventilation and emergency mucus plugs room, the client verbalized that: Hindi ako makahinga. Bakit ba ang tagal naman ng mga doctor? Dalawang taon na akong may Emphysema, madalas hirap ako huminga pero mas matindi ngayon. When asked by the Cues Analysis Inflammation of the bronchial walls causes them to thicken. This thickening, together with excessive mucus, blocks the airways and hinders gas exchange. Reference: MedicalSurgical Nursing: A Psychophysiolo gic Approach, 4th Ed., Palandri, et. al, pp. 151-152 . Goals and Objectives After 4 hours of nursing intervention, the client will be able to maintain adequate gas exchange as evidenced by stable blood gas values and normal respirations. Objectives: 1) The client will be able to maintain patent airway and normal breathing patterns. Interventions Rationale Evaluation
1) Regularly monitor respiratory rate and pattern, ABG results, and signs of hypoxia or hypercapnia. Report significant changes promptly.
Prompt recognition of deteriorating respiratory function can reduce potentially lethal outcomes.
2) Administer
low-flow oxygen therapy (1-3 L/min 24-31% FIO2) as needed via nasal prongs or high-flow venture mask (24-41% FIO2).
Reference: Medical-Surgical Nursing, Luckmann, pp. Efficiency 1997 Were the resources available to the nurse Oxygen corrects existing nd the client hypoxemia. Excessive maximized? increases in oxygen (55- _Yes _No 70% FIO2) may diminish Why? respiratory drive and further increase carbon Appropriateness dioxide retention. Were interventions
Adequacy Was the client able to maintain patent airway and normal breathing patterns? _Yes _No Why?
physician on how frequent he experiences dyspnea, the client answered, Always. Objective Cues: - 67% oxygen saturatio n - Dyspn ea - Shortn ess of breath - Nasal flaring - Produc tive cough - Client looks fatigued when breathin g
appropriate to client Reference: situation? Medical-Surgical _Yes _No Nursing, Luckmann, pp. Why? 1997 Acceptability 3) Assist client into high The upright position Were the Fowlers position. allows full lung interventions excursion and enhances acceptable to the air exchange. client and significant others? Reference: _Yes _No Medical-Surgical Why? Nursing, Luckmann, pp. 4) Administer 1997 Adequacy bronchodilators as Were the ordered. Monitor for side Bronchiodilators relax interventions effects. bronchial smooth adequate to address muscle, facilitating the clients needs and airflow. Common side problem? effects include tremor, _Yes _No tachycardia and other Why? cardiac dysrhythmias. Reference: Medical-Surgical 5) Use caution when Nursing, Luckmann, pp. administering narcotics, 1997 sedatives and tranquilizers. These medications are respiratory depressants and can further impair ventilation.
- Hyperv entilation - Presen ce of barrel chest - Raised acromion processe s and use of accessor y muscles for breathin g
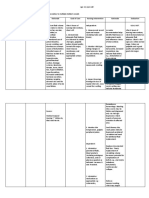
2) The client will be able to demonstrate modified breathing techniques that facilitate ventilator capacity.
Reference: Medical-Surgical Adequacy 1) Assess the ventilation: Nursing, Luckmann, et. Was the client able to a) Weakness and tiring in al, pp. 1997 maintain patent relation to attempts to airway and normal breathe. Information is gained breathing patterns? b) Breathing pattern, about the effectiveness _Yes _No rate, rhythm, and of the treatment plan Why? depth; chest and the need for its expansion, presence modification. Efficiency of respiratory distress Were the resources (shortness of breath, Reference: available to the nurse wheezing or dyspnea), Medical-Surgical nd the client nasal flaring, pursed- Nursing: A Nursing maximized? lip breathing, Process Approach, _Yes _No prolonged expiratory Ignatavicius, et. al, 580 Why? phase, use of accessory muscles. Appropriateness Were interventions 2) Instruct client in appropriate to client techniques of breathing situation? such as: _Yes _No a) Pursed-lip breathing Breathing techniques Why? b) Diaphragmatic facilitate exhalation of breathing stagnant, trapped air Acceptability c) Relaxation therapy and are beneficial during Were the d) Coughing and deep dyspneic episodes. interventions breathing acceptable to the Reference: client and significant Medical-Surgical others? Nursing: A Nursing _Yes _No Process Approach, Why?
3) Assist client in maintaining proper positioning during dyspneic episodes: a) Sitiing up and leaning on over-bed table (orthopneic position) b) Sitting up and resting with elbows on knees c) Standing and leaning against wall
Ignatavicius, et. al, 580 Adequacy Use of accessory Were the muscles is facilitated by interventions supporting arms and adequate to address shoulders, and thoracic the clients needs and cavity is enlarged for problem? increased lung _Yes _No expansion. Why?
Reference: Medical-Surgical Nursing: A Nursing 4) Maximize the effect of Process Approach, medical interventions by Ignatavicius, et. al, 580 proper sequencing of respiratory treatments Work of breathing is and by judicious use of reduced by decreasing bronchodilators and inflammatory processes steroids (IV, oral, or and through inhaled). bronchodilation. Reference: Medical-Surgical Nursing: A Nursing 5) Assess the quality and Process Approach, quantity of sputum: color, Ignatavicius, et. al, 580 consistency, amount, and odor. These characteristics may indicate pulmonary infection. Adequacy Was the client able to
3) The client will be able to modify
behaviors conserve energy.
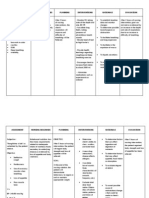
to
Reference: 1) Refer client to Medical-Surgical rehabilitation programs Nursing: A Nursing for general body Process Approach, exercises. Ignatavicius, et. al, 580 Exercises improve overall muscle function and allow more efficient use of oxygen by the muscles. 2) Formulate a plan with the client for pacing activities of daily living. a) Encourage sitting for most activities, such as peeling potatoes or talking on the telephone. b) Teach the client to always breathe during an activity and never to hold his breath. c) Be aware that activities involving the arms consume the most energy. d) Plan rest periods during more strenuous activities. 3) Evaluate nutritional state of the client and
maintain patent airway and normal breathing patterns? _Yes _No Why? Efficiency Were the resources available to the nurse nd the client maximized? _Yes _No Why?
Reference: Medical-Surgical Nursing, Luckmann, et. Appropriateness al, pp. 1998 Were interventions appropriate to client Pacing conserves energy situation? that is needed for _Yes _No breathing. Why?
Reference: Acceptability Reference: Were the Medical-Surgical interventions Nursing, Luckmann, et. acceptable to the al, pp. 1997 client and significant others? _Yes _No Why? Adequacy Were interventions the
offer support. a) Compare baseline weight to present weight. b) Evaluate laboratory data: serum total protein and albumin levels. c) Assist the client in choosing foods that are easy to chew and swallow and that are high in calories. d) Assist the client by cutting food and feeding if the client tires easily. e) Suggest that the client eats small, frequent meals.
adequate to address the clients needs and problem? Eating consumes energy _Yes _No needed for breathing; Why? clients whi have increased work of breathing have higher calorie requirements. Reference: Reference: Medical-Surgical Nursing, Luckmann, et. al, pp. 1997
You might also like
- NCP PTBDocument6 pagesNCP PTBJay Dela VegaNo ratings yet
- Causes and Nursing Care of Pleural EffusionDocument4 pagesCauses and Nursing Care of Pleural EffusionHania Polangi100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Interaction Immediate Cause Goal: Effectivenes SDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan: Interaction Immediate Cause Goal: Effectivenes SCatherine Kaye Marquez RoxasNo ratings yet
- NCP Copd4Document15 pagesNCP Copd4Alessa Marie Crisostomo Salazar100% (1)
- NCP For Tuberculosis.Document7 pagesNCP For Tuberculosis.Kirstie ClaireNo ratings yet
- NCP BMDocument1 pageNCP BMSourabh MehraNo ratings yet
- Assessing and Managing Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument3 pagesAssessing and Managing Ineffective Airway ClearanceNelle Agni100% (1)
- Asthma Care PlanDocument3 pagesAsthma Care PlanSam ParkNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related To HyperventilationDocument4 pagesIneffective Breathing Pattern Related To HyperventilationVanessa Charlotte LagunayNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan for Impaired Gas ExchangeCuttie Anne GalangNo ratings yet
- NCP CopdDocument14 pagesNCP CopdJanine ClaudeNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPMark Benedict Ocampo VelardeNo ratings yet
- Acute Respiratory FailureDocument25 pagesAcute Respiratory FailurejohnleeeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis: Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument4 pagesNursing Diagnosis: Impaired Gas ExchangeShen Paril0% (1)
- Asthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressDocument2 pagesAsthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressMargarette GeresNo ratings yet
- Managing COPD ExacerbationDocument17 pagesManaging COPD ExacerbationSean Menard Flores100% (1)
- Nursing ManagementDocument16 pagesNursing ManagementNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- NCP CopdDocument4 pagesNCP CopdJoshua ValdrizNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument14 pagesNursing Care PlanVin Landicho100% (1)
- Concept Map - Abby !Document2 pagesConcept Map - Abby !Abegail Abaygar100% (3)
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Document1 pageChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Bheru LalNo ratings yet
- ANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationEdrianne Tui100% (2)
- NCP1 CHFDocument2 pagesNCP1 CHFapi-27015740100% (5)
- NCP PTBDocument2 pagesNCP PTBKath TalubanNo ratings yet
- Student NurseDocument2 pagesStudent NurseTAYABAN, KENNETH JAKE, Q.No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for PneumoniaDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for PneumoniaFARAH MAE MEDINANo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan for Impaired Gas ExchangePrincess Andrea Bulatao100% (1)
- Case Report On Bipolar Affective Disorder: Mania With Psychotic SymptomsDocument2 pagesCase Report On Bipolar Affective Disorder: Mania With Psychotic SymptomskslhfwoiebvNo ratings yet
- Copd NCPDocument16 pagesCopd NCPSuperMaye100% (1)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjennelyn losantaNo ratings yet
- Assessing and Treating Pneumonia Through Respiratory Monitoring and InterventionsDocument3 pagesAssessing and Treating Pneumonia Through Respiratory Monitoring and InterventionsDyanne BautistaNo ratings yet
- (Patho) PTB COPDDocument1 page(Patho) PTB COPDKyle HannahNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care Planrois romaNo ratings yet
- Case Study Pleural EffusionDocument4 pagesCase Study Pleural EffusionKhristine Anne FabayNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term Goal: IndependentDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term Goal: IndependentNinaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPPrincess Camille ArceoNo ratings yet
- III. Nursing Care Plan Nursing Priority No. 1: Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Excessive Accumulation of Secretions Secondary To PneumoniaDocument6 pagesIII. Nursing Care Plan Nursing Priority No. 1: Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Excessive Accumulation of Secretions Secondary To PneumoniaRae Marie Aquino100% (1)
- MCN NCPDocument4 pagesMCN NCPPEARL CHRISTINE CUDALNo ratings yet
- Focus Charting (F-DAR) : How To Do Focus Charting or F-DAR: Notes Fundamentals of NursingDocument6 pagesFocus Charting (F-DAR) : How To Do Focus Charting or F-DAR: Notes Fundamentals of NursingMichael Angelo SeñaNo ratings yet
- Discharge Planning PaperDocument5 pagesDischarge Planning Paperapi-283173905No ratings yet
- Drug Study Lab, NCP - Bronchial AsthmaDocument6 pagesDrug Study Lab, NCP - Bronchial AsthmaRichelle Sandriel C. de CastroNo ratings yet
- Assessment Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation: Mechanism of ActionDocument2 pagesAssessment Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation: Mechanism of ActionNicole CalpoturaNo ratings yet
- Managing Impaired Gas Exchange and Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument27 pagesManaging Impaired Gas Exchange and Ineffective Airway ClearancecuakialyannaNo ratings yet
- Pleural EffusionDocument5 pagesPleural EffusionTerizla MobileNo ratings yet
- NCP HemothoraxDocument3 pagesNCP Hemothoraxroseonabreeze0% (2)
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPNikki del Rosario100% (2)
- NCP PneumoniaDocument2 pagesNCP Pneumonia_garonNo ratings yet
- Manage Bronchiectasis Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesManage Bronchiectasis Nursing Care PlanPaola Marie VenusNo ratings yet
- Impaired Breathing PatternDocument1 pageImpaired Breathing PatternHanya Bint PotawanNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation GoalDocument4 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation GoalKei Cruz100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument10 pagesNursing Care PlanElijah S GomezNo ratings yet
- Reflective SkillDocument9 pagesReflective Skillmiss tinkerbella83% (6)
- NFDN 2003 Assignment 1Document8 pagesNFDN 2003 Assignment 1Courtney Robinson100% (2)
- Test Bank For Nursing A Concept Based Approach To Learning Volume I Pearson Full DownloadDocument86 pagesTest Bank For Nursing A Concept Based Approach To Learning Volume I Pearson Full Downloadedgarwilsonmqdnjkatbp100% (24)
- Mechanical Ventilation: Standard Weaning Criteria (Respiratory Therapy)Document6 pagesMechanical Ventilation: Standard Weaning Criteria (Respiratory Therapy)S3DOSHA osmanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument10 pagesNursing Care PlanmariasomorayNo ratings yet
- (Osborn) Chapter 41: Learning Outcomes (Number and Title)Document19 pages(Osborn) Chapter 41: Learning Outcomes (Number and Title)KittiesNo ratings yet
- Indian Journal of Nursing SciencesDocument5 pagesIndian Journal of Nursing Sciencesmadhu.BNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 031.bridge To NCLEX Review Question AnswersDocument7 pagesChapter - 031.bridge To NCLEX Review Question AnswersJackie JuddNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPAbegail Abaygar100% (1)
- Form 4 Additional Mathematics Revision PatDocument7 pagesForm 4 Additional Mathematics Revision PatJiajia LauNo ratings yet
- Done - NSTP 2 SyllabusDocument9 pagesDone - NSTP 2 SyllabusJoseph MazoNo ratings yet
- United States Bankruptcy Court Southern District of New YorkDocument21 pagesUnited States Bankruptcy Court Southern District of New YorkChapter 11 DocketsNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Final TestDocument3 pagesAssignment - Final TestbahilashNo ratings yet
- Corporate Governance, Corporate Profitability Toward Corporate Social Responsibility Disclosure and Corporate Value (Comparative Study in Indonesia, China and India Stock Exchange in 2013-2016) .Document18 pagesCorporate Governance, Corporate Profitability Toward Corporate Social Responsibility Disclosure and Corporate Value (Comparative Study in Indonesia, China and India Stock Exchange in 2013-2016) .Lia asnamNo ratings yet
- Ecc Part 2Document25 pagesEcc Part 2Shivansh PundirNo ratings yet
- USDA Guide To CanningDocument7 pagesUSDA Guide To CanningWindage and Elevation0% (1)
- 2020 Global Finance Business Management Analyst Program - IIMDocument4 pages2020 Global Finance Business Management Analyst Program - IIMrishabhaaaNo ratings yet
- Dep 32.32.00.11-Custody Transfer Measurement Systems For LiquidDocument69 pagesDep 32.32.00.11-Custody Transfer Measurement Systems For LiquidDAYONo ratings yet
- Applied Statics and Strength of Materials 6th Edition Ebook PDFDocument61 pagesApplied Statics and Strength of Materials 6th Edition Ebook PDFteri.sanborn87695% (44)
- Typical T Intersection On Rural Local Road With Left Turn LanesDocument1 pageTypical T Intersection On Rural Local Road With Left Turn Lanesahmed.almakawyNo ratings yet
- AA ActivitiesDocument4 pagesAA ActivitiesSalim Amazir100% (1)
- Prac Res Q2 Module 1Document14 pagesPrac Res Q2 Module 1oea aoueoNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles ColoringDocument2 pagesCell Organelles ColoringThomas Neace-FranklinNo ratings yet
- Rubric 5th GradeDocument2 pagesRubric 5th GradeAlbert SantosNo ratings yet
- The Service Marketing Plan On " Expert Personalized Chef": Presented byDocument27 pagesThe Service Marketing Plan On " Expert Personalized Chef": Presented byA.S. ShuvoNo ratings yet
- 2021 JHS INSET Template For Modular/Online Learning: Curriculum MapDocument15 pages2021 JHS INSET Template For Modular/Online Learning: Curriculum MapDremie WorksNo ratings yet
- Physioex 9.0 Exercise 1 Act 1Document5 pagesPhysioex 9.0 Exercise 1 Act 1Adela LhuzNo ratings yet
- Week 15 - Rams vs. VikingsDocument175 pagesWeek 15 - Rams vs. VikingsJMOTTUTNNo ratings yet
- Flowmon Ads Enterprise Userguide enDocument82 pagesFlowmon Ads Enterprise Userguide ennagasatoNo ratings yet
- Dance Appreciation and CompositionDocument1 pageDance Appreciation and CompositionFretz Ael100% (1)
- Tutorial 1 Discussion Document - Batch 03Document4 pagesTutorial 1 Discussion Document - Batch 03Anindya CostaNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet: 3 Quarter Week 1 Mathematics 2Document8 pagesLearning Activity Sheet: 3 Quarter Week 1 Mathematics 2Dom MartinezNo ratings yet
- Kathy Davis - Dancing Tango - Passionate Encounters in A Globalizing World-New York University Press (2015)Document236 pagesKathy Davis - Dancing Tango - Passionate Encounters in A Globalizing World-New York University Press (2015)Csongor KicsiNo ratings yet
- Masteringphys 14Document20 pagesMasteringphys 14CarlosGomez0% (3)
- Prasads Pine Perks - Gift CardsDocument10 pagesPrasads Pine Perks - Gift CardsSusanth Kumar100% (1)
- CS210 Lecture 32 Magical Application Binary Tree IIIDocument38 pagesCS210 Lecture 32 Magical Application Binary Tree IIIOshoNo ratings yet
- Easa Management System Assessment ToolDocument40 pagesEasa Management System Assessment ToolAdam Tudor-danielNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis of Wipro LTDDocument101 pagesFinancial Analysis of Wipro LTDashwinchaudhary89% (18)