Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Self-Quiz: in Your Notebook, Record The Letter of The Choice That Best Answers Each Question
Uploaded by
moe_lol99Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Self-Quiz: in Your Notebook, Record The Letter of The Choice That Best Answers Each Question
Uploaded by
moe_lol99Copyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 10
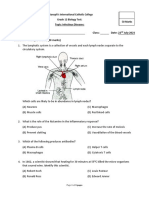
SELF-QUIZ
7. What is an important defence against invading
Unit 3
In your notebook, record the letter of the choice that best answers each question.
1. Which of the following characteristics of an invader
can be recognized by antibodies of the immune system? (a) nuclear material (b) cell membrane shape (c) cell size (d) the electrical charge of the cell
2. What is an antibody?
(a) a white blood cell that engulfs an invading microbe (b) a protein that reacts with an antigen (c) a white blood cell that identifies a foreign invader (d) a protein that is attached to the cell membrane of a microbe (e) a protein that is always attached to the cell membrane of an antibody-producing cell
3. Which of the following is the cellular component
responsible for antibody production? (a) B cell (d) platelet (b) T cell (e) mast cell (c) macrophage
4. Which part of your immune system is charged with
recognition of invading pathogens? (a) antibodies (d) phagocyte (b) B cell lymphocyte (e) all of the above (c) T cell lymphocyte
5. Which of the following is sometimes a glycoprotein
microbes that can be found in tears? (a) Macrophages from the tears engulf foreign invaders by phagocytosis. (b) Lysozyme, special enzymes secreted in tears and sweat, destroy bacteria by dissolving their cell walls. (c) Mucus produced by tears adheres to microbes and targets them for antibody production. (d) Cilia, found along the eyelashes, sweeps microbes from the eye. (e) Water washes away the microbes, preventing them from entering the tear duct. 8. Which of the following does not describe the action of complement proteins produced by the immune system? (a) Some of the proteins act as markers by causing antigens to aggregate. (b) Some of the proteins attach themselves to the cell membrane of the antigen, immobilizing the antigen. (c) Some of the proteins engulf the foreign invader by phagocytosis. (d) Some of the proteins form a protective coating around the microbe. (e) Some of the proteins dissolve or puncture the cell membrane of bacterial invaders.
9. Why is the transplantation of donor organs affected
complex found on the surface of cell membranes that is not found in ones body? (a) a toxin (d) a virus (b) an antibody (e) a prion (c) an antigen
6. When do B cells turn into super antibody-producing
cells? (a) when macrophages engulf foreign invading materials (b) when T cells identify the invader and release lymphokine (c) when B cells identify the invader and release histamine (d) when plasma proteins identify the invader and release lymphokine (e) when platelets identify the invader and release histamine
by the immune response? (a) Transplanted organs contain antigens that T cells recognize as harmful. (b) Transplanted organs contain antibodies that recognize cells in your body as being harmful. (c) Transplanted organs contain antigens that stimulate the production of antigens in your own body. (d) Transplanted organs contain antibodies that stimulate the production of antigens in your own body. (e) Transplanted organs contain antibodies that B cells recognize as harmful.
10. How can transplant rejection be reduced?
(a) Keep the area clean to prevent microbe infections. (b) Transplant organs with a close tissue match. (c) Inject antibodies into the recipients body for the first few weeks after the operation. (d) Choose transplanted organs from an entirely different species so that they cannot be recognized by the immune system. (e) Either (c) or (d).
NEL
An interactive version of the quiz is available online.
GO
The Maintenance of Balance by the Immune System 495
www.science.nelson.com
You might also like
- Spare Part PhilosophyDocument27 pagesSpare Part Philosophyavaisharma50% (2)
- Quiz ImmunologyDocument50 pagesQuiz ImmunologyMedShare97% (39)
- Fundamentals of Molecular Virology 2nd Edition Acheson Test BankDocument8 pagesFundamentals of Molecular Virology 2nd Edition Acheson Test BankBrandonGillespieofjt100% (8)
- Current Trends and Issues in Nursing ManagementDocument8 pagesCurrent Trends and Issues in Nursing ManagementMadhu Bala81% (21)
- Immunology MCQDocument50 pagesImmunology MCQAbdallah Essam Al-Zireeni96% (131)
- Sanskrit Subhashit CollectionDocument110 pagesSanskrit Subhashit Collectionavinash312590% (72)
- MicroDocument7 pagesMicroAbdulrahmanMohammedNo ratings yet
- McqsDocument21 pagesMcqsOsama Bakheet100% (2)
- Levenson MCQDocument55 pagesLevenson MCQZainab Hasan100% (1)
- Test QuestionsDocument14 pagesTest QuestionsMohammad Usman QureshiNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Midterm ExamDocument8 pagesMicrobiology Midterm Examslg23350% (2)
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Heredity And Molecular GeneticsFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers: Heredity And Molecular GeneticsNo ratings yet
- The First Voyage Round The World by MageDocument405 pagesThe First Voyage Round The World by MageGift Marieneth LopezNo ratings yet
- Immunology MCQDocument51 pagesImmunology MCQLouise Marie Palamos DamascoNo ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument55 pagesImmunologyW.F KareemNo ratings yet
- 1Document5 pages1Ahmad Shboul100% (1)
- ImmunologyDocument3 pagesImmunologyEkta MenghaniNo ratings yet
- Sample Exams To Post 2019 PDFDocument32 pagesSample Exams To Post 2019 PDFDustin SuttonNo ratings yet
- Immunology Exam November 2019Document13 pagesImmunology Exam November 2019Vuyo TunesNo ratings yet
- Infectious DiseaseDocument8 pagesInfectious DiseaseGeorge TarraNo ratings yet
- Study Guide For Lecture Exam 2 Biol 1407 03.12.2010Document50 pagesStudy Guide For Lecture Exam 2 Biol 1407 03.12.2010Erica MizzIndependent BubuchuNo ratings yet
- Soal MCQ 1Document14 pagesSoal MCQ 1RahmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 43 The Immune SystemDocument13 pagesChapter 43 The Immune System蔡旻珊No ratings yet
- Question - Tutorial 5 - Immune SystemDocument2 pagesQuestion - Tutorial 5 - Immune SystemNur AthirahNo ratings yet
- Innate ImmunityDocument21 pagesInnate ImmunityAdel AlomarNo ratings yet
- 43Document15 pages43raynahollanderNo ratings yet
- WK10 AnswersDocument6 pagesWK10 AnswersaskldhfdasjkNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesFinal Exam Anatomy and PhysiologyAlibasher MacalnasNo ratings yet
- Exam 3 Topics Guide MicrobiolgyDocument11 pagesExam 3 Topics Guide MicrobiolgyZubaida MohammadNo ratings yet
- Human Health and DiseaseDocument4 pagesHuman Health and DiseasesunilsigmaNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Eligibility Test (BET) For DBT-JRF Award (2010-11)Document20 pagesBiotechnology Eligibility Test (BET) For DBT-JRF Award (2010-11)Nandakumar HaorongbamNo ratings yet
- 1st YearDocument5 pages1st Yeararhamrafique42No ratings yet
- BiochemDocument8 pagesBiochemVijaaynranNo ratings yet
- Biomentors (MCDB 1B) - Immunology Quiz (ANSWERS)Document2 pagesBiomentors (MCDB 1B) - Immunology Quiz (ANSWERS)Tiff VoNo ratings yet
- 免疫猜题Document15 pages免疫猜题limengdi0269No ratings yet
- Clinical Laboratory Immunology 1st Edition Maahon Tice Test BankDocument8 pagesClinical Laboratory Immunology 1st Edition Maahon Tice Test BankBrian Craig100% (37)
- Bio PDFDocument4 pagesBio PDFlina atyaniNo ratings yet
- Essential Cell Biology Alberts 3rd Edition Test BankDocument13 pagesEssential Cell Biology Alberts 3rd Edition Test Bankmeaganstephensonmdbapgcjfezt100% (45)
- Biology Chapter 6 Solution Paper Grade 11 Advanced 2021-2022Document8 pagesBiology Chapter 6 Solution Paper Grade 11 Advanced 2021-2022mallmazNo ratings yet
- Review General & USMLE Microbiology MCQsDocument51 pagesReview General & USMLE Microbiology MCQsM7md AllahhamNo ratings yet
- DPP - Human Health & Disease by Seep PahujaDocument11 pagesDPP - Human Health & Disease by Seep PahujamilanbhongadeNo ratings yet
- Immunology MCQ ReviewDocument5 pagesImmunology MCQ ReviewAnuradha NanayakkaraNo ratings yet
- Test 1Document1 pageTest 1UzochukwuNo ratings yet
- Essential Cell Biology Alberts 3rd Edition Test BankDocument13 pagesEssential Cell Biology Alberts 3rd Edition Test Bankvenerealembolism93fNo ratings yet
- TUGAS BIOMEDIS 2022 - Immune SystemDocument3 pagesTUGAS BIOMEDIS 2022 - Immune SystemabirackshaanwirajayaNo ratings yet
- LYMPHATIC Also Called IMMUNE SYSTEMDocument13 pagesLYMPHATIC Also Called IMMUNE SYSTEMBai Rihan PangolimaNo ratings yet
- A.Ince - Lab 3 (Immunology Review Quiz)Document8 pagesA.Ince - Lab 3 (Immunology Review Quiz)ameeraNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology QuizDocument8 pagesPathophysiology QuizTanya ViarsNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Unit 7 Study Guide Chapter 43Document7 pagesAP Bio Unit 7 Study Guide Chapter 43Huma KhanNo ratings yet
- Virology Mcqs PDocument16 pagesVirology Mcqs PDavid lufafaNo ratings yet
- Mock Ospe AmsaDocument25 pagesMock Ospe AmsasahirbuleNo ratings yet
- File HandlerDocument15 pagesFile Handlercyberdexter450No ratings yet
- Worksheet Immune Response (2) ElyDocument7 pagesWorksheet Immune Response (2) Elylina atyaniNo ratings yet
- Microbiology and Immunology Questions and Past PapersDocument82 pagesMicrobiology and Immunology Questions and Past PapersNkululeko SinethembaNo ratings yet
- اهم اسئلة 2Document32 pagesاهم اسئلة 2Adam JerusalemNo ratings yet
- STD Xii Biology Set Ii QPDocument8 pagesSTD Xii Biology Set Ii QPUnna K BNo ratings yet
- Microbiology An Introduction 11th Edition Tortora Test BankDocument21 pagesMicrobiology An Introduction 11th Edition Tortora Test Bankheathercamposnwqbyitgsc100% (30)
- MB115 2020 Final Exam 2020Document26 pagesMB115 2020 Final Exam 2020Milimo MweembaNo ratings yet
- Cancer Gene Therapy by Viral and Non-viral VectorsFrom EverandCancer Gene Therapy by Viral and Non-viral VectorsMalcolm BrennerNo ratings yet
- Natural Hosts of SIV: Implication in AIDSFrom EverandNatural Hosts of SIV: Implication in AIDSAftab A. AnsariNo ratings yet
- Lesser Known Homoeopathic Medicines of Alopecia Areata.20200718115446Document9 pagesLesser Known Homoeopathic Medicines of Alopecia Areata.20200718115446BruntNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Q3 Figure Life DrawingDocument10 pagesLesson 1 Q3 Figure Life DrawingCAHAPNo ratings yet
- EX200Document7 pagesEX200shubbyNo ratings yet
- Loop Types and ExamplesDocument19 pagesLoop Types and ExamplesSurendran K SurendranNo ratings yet
- Group 2 ITI Consensus Report: Prosthodontics and Implant DentistryDocument9 pagesGroup 2 ITI Consensus Report: Prosthodontics and Implant DentistryEsme ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Additional Article Information: Keywords: Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma, Cribriform Pattern, Parotid GlandDocument7 pagesAdditional Article Information: Keywords: Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma, Cribriform Pattern, Parotid GlandRizal TabootiNo ratings yet
- An Eastern Orthodox Understanding of The Dangers of Modernity and TechnologyDocument10 pagesAn Eastern Orthodox Understanding of The Dangers of Modernity and TechnologyTimothy ZelinskiNo ratings yet
- Lenovo NotebooksDocument6 pagesLenovo NotebooksKamlendran BaradidathanNo ratings yet
- Seizure Control Status and Associated Factors Among Patients With Epilepsy. North-West Ethiopia'Document14 pagesSeizure Control Status and Associated Factors Among Patients With Epilepsy. North-West Ethiopia'Sulaman AbdelaNo ratings yet
- EP001 LifeCoachSchoolTranscriptDocument13 pagesEP001 LifeCoachSchoolTranscriptVan GuedesNo ratings yet
- Aero Ebook - Choosing The Design of Your Aircraft - Chris Heintz PDFDocument6 pagesAero Ebook - Choosing The Design of Your Aircraft - Chris Heintz PDFGana tp100% (1)
- First - Second and Third Class Levers in The Body - Movement Analysis in Sport - Eduqas - Gcse Physical Education Revision - Eduqas - BBC BitesizeDocument2 pagesFirst - Second and Third Class Levers in The Body - Movement Analysis in Sport - Eduqas - Gcse Physical Education Revision - Eduqas - BBC BitesizeyoyoyoNo ratings yet
- Term Paper Inorganic PolymersDocument24 pagesTerm Paper Inorganic PolymersCasey Karua0% (1)
- Drager Narkomed 6400 Field Service Procedure Software Version 4.02 EnhancementDocument24 pagesDrager Narkomed 6400 Field Service Procedure Software Version 4.02 EnhancementAmirNo ratings yet
- Guided-Discovery Learning Strategy and Senior School Students Performance in Mathematics in Ejigbo, NigeriaDocument9 pagesGuided-Discovery Learning Strategy and Senior School Students Performance in Mathematics in Ejigbo, NigeriaAlexander DeckerNo ratings yet
- Concrete Specification (BS8500)Document3 pagesConcrete Specification (BS8500)teh100% (1)
- Tyler Nugent ResumeDocument3 pagesTyler Nugent Resumeapi-315563616No ratings yet
- DNA Vs RNA - Introduction and Differences Between DNA and RNADocument10 pagesDNA Vs RNA - Introduction and Differences Between DNA and RNAKienlevyNo ratings yet
- Module-29A: Energy MethodsDocument2 pagesModule-29A: Energy MethodsjhacademyhydNo ratings yet
- Classification of Books Using Python and FlaskDocument5 pagesClassification of Books Using Python and FlaskIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Coal Bottom Ash As Sand Replacement in ConcreteDocument9 pagesCoal Bottom Ash As Sand Replacement in ConcretexxqNo ratings yet
- Angel C. Delos Santos: Personal DataDocument8 pagesAngel C. Delos Santos: Personal DataAngel Cascayan Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Marion Nicoll: Life & Work by Catharine MastinDocument147 pagesMarion Nicoll: Life & Work by Catharine MastinArt Canada InstituteNo ratings yet
- Consent Form: Republic of The Philippines Province of - Municipality ofDocument1 pageConsent Form: Republic of The Philippines Province of - Municipality ofLucette Legaspi EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Soundarya Lahari Yantras Part 6Document6 pagesSoundarya Lahari Yantras Part 6Sushanth Harsha100% (1)
- The Rock Reliefs of Ancient IranAuthor (Document34 pagesThe Rock Reliefs of Ancient IranAuthor (mark_schwartz_41No ratings yet