Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture 2.5 Transistor Applications
Uploaded by
Aids SumaldeCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture 2.5 Transistor Applications
Uploaded by
Aids SumaldeCopyright:
Available Formats
2/6/2012
1
Transistor Applications
EE 21 Fundamentals of Electronics
Outline
Current mirror circuits
Constant current circuits
Transistor Switching and Logic gates
Voltage-controlled resistor
Timer Network
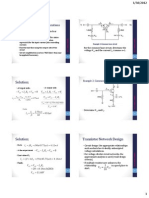
Current Mirror Circuits
Provides constant
current
Used primarily in
integrated circuits
Requires identical
transistors,
fabricated near each
other on the same
chip.
Current Mirror Circuits
The two transistor
currents are
approximately
And for each
transistor,
| |
E E
B
I I
I ~
+
=
1
E C
I I ~
Current Mirror Circuits
The current through
resistor Rx is given
by
Simplifying,
| |
|
E E
X
I I
I
2
+ =
| |
|
E E
X
I I
I
2
+ =
Current Mirror Circuits
Finally,
In summary, the
constant current at
Q2 mirrors that of
Q1, given by
E E X
I I I ~
+
=
|
| 2
X
BE CC
X
R
V V
I I
= =
2/6/2012
2
Current Mirror Circuits
Another type of
current mirror
circuit involves a
JFET, with the
mirrored current
being its I
DSS
.
Constant Current Source (CCS)
Assumption: base
input impedance >
R
1
or R
2
.
By VDR,
Also,
The current is now
given by
2 1
1
R R
R V
V
EE
B
+
=
V V V
B E
7 0. =
C
E
EE E
E
I
R
V V
I ~
=
) (
CCS with Zener Diode
Zener diode allows
for an improved
current source.
VEE serves only to
turn the zener diode
on.
KVL gives us
C
E
BE Z
E
I
R
V V
I ~
=
Transistor Switching
Basis for switching in the concept of saturation
and cutoff.
Involves the switching (or moving) of the Q-
point from cut-off to saturation along the load
line.
Ideal assumptions: I
C
= 0 (cutoff) when I
B
=
0, V
CEsat
= 0. (saturation)
Saturation and Cutoff
At saturation, the current I
C
is high and voltage
V
CE
very low.
Thus, ideal resistance at saturation 0
At cutoff, V
CE
= V
CC
= high and I
C
is very low.
Thus ideal resistance at cutoff .
Logic Gates using BJTs
Inverter / NOT Gate
AND Gate
OR Gate
2/6/2012
3
Inverter Gate
If a low input is
impressed, the
output is high, while
if a high input (5 V)
is impressed, the
output is low.
AND Gate
The output C = AB
requires that both
inputs A and B be
turned on (high) in
order for the input
to be high.
OR Gate
The output C = A + B
requires that only
either one of the
two inputs A or B be
high in order for the
output to be high.
Voltage Controlled Resistor
Follows the equation given
by the ohmic region
of the FET.
In the ohmic region,
the FET curve can be
likened to that of a resistor (linear).
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
P
GS
o
d
V
V
r
r
1
JFET Timer
INITIAL:
When power is first
applied, capacitor
shorts out.
With Vc = 0, V
GS
= 0
initially, thus I
D
=
I
DSS
and the bulb
lights up.
JFET Timer
While this is
happening,
capacitor charges
up to -9 V.
When capacitor
reaches pinch-off
level (-6V), I
D
= 0
and bulb turns off.
2/6/2012
4
JFET Timer
TIMING FUNCTION
When switch is
closed, capacitor is
shorted and V
GS
= 0,
thus I
D
= I
DSS
and the
lamp lights up.
When switch is
released, capacitor
charges to -9V.
JFET Timer
The bulb dims until
turned-off when Vc
= Vp.
The length of the
light-on time is
determined by the
RC network, with
=(R
1
+R
2
)C, and the
pinch-off voltage Vp.
JFET Timer
R
1
helps limit initial
surge current
R
2
is the variable
resistance to modify
R
3
limits the
discharge current
when the switch is
closed.
JFET Timer
Note that the JFET
has a very high
input impedance
and thus, will not
affect the of the RC
network (due to it
being connected in
parallel).
You might also like
- Unit IDocument156 pagesUnit IrevathianuNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Bias Transistor1Document46 pagesBias Transistor1angel larasatiNo ratings yet
- 2006 Hyundai Elantra GLS 2.0L Engine SpecsDocument277 pages2006 Hyundai Elantra GLS 2.0L Engine SpecsSergio Roca100% (1)
- DC BIASING - BJTs: Key ConceptsDocument44 pagesDC BIASING - BJTs: Key ConceptsUgeswran ThamalinggamNo ratings yet
- Dynatech T56 Repair Capabilities ListDocument6 pagesDynatech T56 Repair Capabilities ListrizkyNo ratings yet
- P3-No.10.9 TBEA Power Transformer BrochureDocument28 pagesP3-No.10.9 TBEA Power Transformer Brochurehamza shahzadNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5 Goals Chapter 4 Small-Signal Modeling and Linear AmplificationDocument9 pagesChapter-5 Goals Chapter 4 Small-Signal Modeling and Linear AmplificationSachithHiroshanaWijethungaNo ratings yet
- MANUAL eFLOW EN 24.12.15Document86 pagesMANUAL eFLOW EN 24.12.15Andrey100% (1)
- SpeedAC NXT - Bagging - Operating Manual - Revision 1 11Document150 pagesSpeedAC NXT - Bagging - Operating Manual - Revision 1 11Nijam Jabbar100% (7)
- Transistors: Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT)Document32 pagesTransistors: Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT)Praveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Analog Fault DerivationDocument89 pagesAnalog Fault DerivationSachidananda SwarNo ratings yet
- Lec 7Document36 pagesLec 7Ahmed Abdelaziz AtallahNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv Wave Shaping CircuitsDocument42 pagesUnit Iv Wave Shaping Circuitsyuktha venkatesanNo ratings yet
- Module1 BJTDocument47 pagesModule1 BJTsoulriders07No ratings yet
- Transistors 02Document10 pagesTransistors 02Anel BalićNo ratings yet
- EMT 369 Wk1 Introduction To Power ElectronicsDocument25 pagesEMT 369 Wk1 Introduction To Power ElectronicsgurdianskyNo ratings yet
- Transient Pspice Analysis (7.4) : Dr. Holbert April 26, 2006Document22 pagesTransient Pspice Analysis (7.4) : Dr. Holbert April 26, 2006karlrodNo ratings yet
- CH 7Document53 pagesCH 7Gautam TamangNo ratings yet
- Transistor Switching LEDDocument8 pagesTransistor Switching LEDKashish JainNo ratings yet
- Svetlece DiodeDocument11 pagesSvetlece DiodemikcomiNo ratings yet
- JurnalDocument46 pagesJurnalHasmar HuseinNo ratings yet
- EDC - Unit 3 FinalDocument118 pagesEDC - Unit 3 FinalDr UmapathyNo ratings yet
- Es2c0 SlidesDocument108 pagesEs2c0 SlidesNamita GeraNo ratings yet
- CAPACITORSDocument23 pagesCAPACITORSmaprofNo ratings yet
- EE42 100 Wb-Lecture16 073113-FDocument42 pagesEE42 100 Wb-Lecture16 073113-FozanistzNo ratings yet
- Types of Voltage Regulator and DC Power Supply NotesDocument23 pagesTypes of Voltage Regulator and DC Power Supply NotesSorry studyNo ratings yet
- Study Zener Diode Voltage RegulationDocument12 pagesStudy Zener Diode Voltage RegulationViraj PatvaNo ratings yet
- Week 6 ReviewDocument32 pagesWeek 6 ReviewVRAJ PRAJAPATINo ratings yet
- Differential Amplifiers: Topologies, Operation, and ApplicationsDocument64 pagesDifferential Amplifiers: Topologies, Operation, and ApplicationsjinenmokNo ratings yet
- EE 306 ManualDocument55 pagesEE 306 Manualzain khuramNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Tuned OscillatorsDocument25 pagesLesson 3 Tuned OscillatorsOdoch HerbertNo ratings yet
- 1, Penguat Sinyak Kecil1Document36 pages1, Penguat Sinyak Kecil1Alex AndriaNo ratings yet
- Investigate CE Amplifier CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesInvestigate CE Amplifier Characteristicsfedley sikoliaNo ratings yet
- Differential and Multistage Amplifiers: The Most Widely Used Circuit Building Block in Analog Integrated CircuitsDocument19 pagesDifferential and Multistage Amplifiers: The Most Widely Used Circuit Building Block in Analog Integrated CircuitsRakeshSoniNo ratings yet
- Bipolar-Junction Transistor: Mrinmoy Kundu, Lecturer Dept. of EEE, BUET Date: 4/2/2024Document22 pagesBipolar-Junction Transistor: Mrinmoy Kundu, Lecturer Dept. of EEE, BUET Date: 4/2/2024Tasnim TishaNo ratings yet
- EE Course Notes: BJTs Chapter 5 SummaryDocument7 pagesEE Course Notes: BJTs Chapter 5 SummarybkrebtelNo ratings yet
- Ch7 Power Amps6 v2Document73 pagesCh7 Power Amps6 v2sadyehclenNo ratings yet
- Dasar Elektronikaa BJT BiasingDocument10 pagesDasar Elektronikaa BJT Biasingremember sundayNo ratings yet
- Differential AmplifierDocument42 pagesDifferential AmplifierJanardhan ChNo ratings yet
- ProblemsDocument18 pagesProblemsShrutJainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document45 pagesChapter 5Alwani IzzatiNo ratings yet
- Wave Shaping CircuitsDocument55 pagesWave Shaping Circuitsramakris79No ratings yet
- L10 BJT Applications and BiasingDocument23 pagesL10 BJT Applications and BiasingpojanopeNo ratings yet
- Differential and Multistage AmplifiersDocument85 pagesDifferential and Multistage AmplifiersShino JosephNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuits I Lab ManualDocument44 pagesElectronic Circuits I Lab Manualkunaraj100% (7)
- Mechatronics: Application of TransistorsDocument33 pagesMechatronics: Application of TransistorsKARTHIK S SNo ratings yet
- Transistor Bias CircuitsDocument29 pagesTransistor Bias CircuitsbruhNo ratings yet
- Transistor Amplifier Biasing and GainDocument10 pagesTransistor Amplifier Biasing and GainAshkarali KottakkalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ElectronicsDocument78 pagesChapter 1 ElectronicsBenjaminNo ratings yet
- BJT Written Report Group 8Document11 pagesBJT Written Report Group 8Jayvee GusenalemNo ratings yet
- Transistor Biasing2Document17 pagesTransistor Biasing2Anant UpadhiyayNo ratings yet
- EN564 Analogue Electronics and InstrumentationDocument46 pagesEN564 Analogue Electronics and InstrumentationAl AidenNo ratings yet
- Mod 1Document110 pagesMod 1somus3971No ratings yet
- EE 21-Lecture 2 - Diode Construction & CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesEE 21-Lecture 2 - Diode Construction & CharacteristicsAids Sumalde100% (1)
- Transistor As A SwitchDocument7 pagesTransistor As A SwitchS GNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document31 pagesLecture 5Ali MustafaNo ratings yet
- Ic 2Document30 pagesIc 2Radhie NoahNo ratings yet
- Wave Shaping CircuitsDocument56 pagesWave Shaping CircuitsWaltas KariukiNo ratings yet
- EE 21 Sample ProblemsDocument1 pageEE 21 Sample ProblemsAids SumaldeNo ratings yet
- Single-Phase Transformer DesignDocument7 pagesSingle-Phase Transformer DesignAids SumaldeNo ratings yet
- EE 21 Op Amp ExamplesDocument3 pagesEE 21 Op Amp ExamplesJohn Karlo ReynanteNo ratings yet
- EE 120 - Interfacing With The Analog WorldDocument8 pagesEE 120 - Interfacing With The Analog WorldAids SumaldeNo ratings yet
- EE 120 Logisim Constructed CountersDocument3 pagesEE 120 Logisim Constructed CountersAids SumaldeNo ratings yet
- EE 120 Project GuidelinesDocument1 pageEE 120 Project GuidelinesAids SumaldeNo ratings yet
- EE 120 - Integrated Circuit FamiliesDocument15 pagesEE 120 - Integrated Circuit FamiliesAids SumaldeNo ratings yet
- EE 120 Mini Project GuidelinesDocument2 pagesEE 120 Mini Project GuidelinesAids SumaldeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2.2 Add-On: Miscellaneous Bias SolutionsDocument2 pagesLecture 2.2 Add-On: Miscellaneous Bias SolutionsAids SumaldeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Small Signal Analysis (2 SPP PDFDocument47 pagesLecture 3 - Small Signal Analysis (2 SPP PDFAids Sumalde100% (2)
- EE 21 AssignmentDocument1 pageEE 21 AssignmentAids SumaldeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2.2 BJT DC BiasingDocument8 pagesLecture 2.2 BJT DC BiasingAids SumaldeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2.4: FET DC Biasing & Combination NetworksDocument4 pagesLecture 2.4: FET DC Biasing & Combination NetworksAids Sumalde0% (1)
- Lecture 3 - Small Signal Analysis (2 SPP PDFDocument47 pagesLecture 3 - Small Signal Analysis (2 SPP PDFAids Sumalde100% (2)
- Lecture 2.3: FET IntroductionDocument3 pagesLecture 2.3: FET IntroductionAids Sumalde0% (1)
- EE 21 - Lecture 4 LEDs and Voltage MultipliersDocument2 pagesEE 21 - Lecture 4 LEDs and Voltage MultipliersAids SumaldeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2.1 Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument6 pagesLecture 2.1 Bipolar Junction TransistorAids SumaldeNo ratings yet
- EE 21 Solution To Quiz #3Document1 pageEE 21 Solution To Quiz #3Aids SumaldeNo ratings yet
- EE 21-Lecture 1-Semiconductor TheoryDocument5 pagesEE 21-Lecture 1-Semiconductor TheoryAids SumaldeNo ratings yet
- EE 120 Sample Problems - Boolean Algebra and Canonical FormsDocument1 pageEE 120 Sample Problems - Boolean Algebra and Canonical FormsAids SumaldeNo ratings yet
- EE 21-Lecture 3.5 Power Supply DesignDocument4 pagesEE 21-Lecture 3.5 Power Supply DesignAids SumaldeNo ratings yet
- EE 21-Lecture 2 - Diode Construction & CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesEE 21-Lecture 2 - Diode Construction & CharacteristicsAids Sumalde100% (1)
- EE 21-Lecture 3 - Diode ApplicationsDocument12 pagesEE 21-Lecture 3 - Diode ApplicationsAids SumaldeNo ratings yet
- Western Digital JumperDocument3 pagesWestern Digital JumperNeyder Jose ColoradoNo ratings yet
- RT310i FULL MANUAL UK V005-Revied-1 PDFDocument23 pagesRT310i FULL MANUAL UK V005-Revied-1 PDFsekula_zrNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Threaded Fasteners and JointsDocument41 pagesDesign and Analysis of Threaded Fasteners and JointsRa Balamurugan67% (3)
- UM9401 / UM9402 / UM9415: Key Features DescriptionDocument7 pagesUM9401 / UM9402 / UM9415: Key Features DescriptionRafael CamposNo ratings yet
- Operational Write Up - SCRDocument10 pagesOperational Write Up - SCRZahoor AhmedNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Closed Loop Control of Buck Converter Fed DC Motor DriveDocument4 pagesSimulation of Closed Loop Control of Buck Converter Fed DC Motor DriveIJSTENo ratings yet
- DTV2760C 3Document17 pagesDTV2760C 3plasmapeteNo ratings yet
- 4 SQ - MM Spring Clamp Feed Through Compact Terminal Blocks: Images Cat. No. Description Std. PackDocument2 pages4 SQ - MM Spring Clamp Feed Through Compact Terminal Blocks: Images Cat. No. Description Std. PackNitinNo ratings yet
- Microwave Solid State DevicesDocument12 pagesMicrowave Solid State DevicesFaisal KhanNo ratings yet
- PM5X4Document2 pagesPM5X4Sergio Sosa NavaNo ratings yet
- ELEC PANEL LISTDocument21 pagesELEC PANEL LISTjsrplc7952No ratings yet
- C LIFEsaver BBS Observations TopicsDocument5 pagesC LIFEsaver BBS Observations Topicsheikal hajazieNo ratings yet
- CR420Document56 pagesCR420Gikcoklat AmuntaiNo ratings yet
- Powerrex BulletPro-BP40M-2-post-clear-floor-lift-4-ton-240V-user-manualDocument18 pagesPowerrex BulletPro-BP40M-2-post-clear-floor-lift-4-ton-240V-user-manualCykhong KhongNo ratings yet
- RPM Measurement (Tachometer)Document10 pagesRPM Measurement (Tachometer)19E45A0229 SDESEEENo ratings yet
- Pilot CartridgeDocument2 pagesPilot CartridgeJosé Alberto RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Oneac EDP90Document117 pagesOneac EDP90Ardiansyah NewNo ratings yet
- Magco - CatalogDocument37 pagesMagco - CataloglifttecNo ratings yet
- Embedded System ManualDocument74 pagesEmbedded System ManualMuhammad Zeeshan SaeedNo ratings yet
- McCloskey J40v2 Track Crusher SpecsDocument5 pagesMcCloskey J40v2 Track Crusher Specsмаргарита100% (1)
- Montageanleitung Cycle R: Art.-Nr. 07986-996Document14 pagesMontageanleitung Cycle R: Art.-Nr. 07986-996Beth KananiaNo ratings yet
- Manual de FrenoDocument145 pagesManual de Frenofabian bazanNo ratings yet
- Infusomat Space P: B. Braun Space Infusion SystemsDocument2 pagesInfusomat Space P: B. Braun Space Infusion SystemsNurhidayah AyuNo ratings yet
- Differential Pressure Recorder Data SheetDocument8 pagesDifferential Pressure Recorder Data SheetEdmund LimNo ratings yet
- Electrician Certification PreparationDocument52 pagesElectrician Certification PreparationcsgonzNo ratings yet