Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pacemaker 7-20-2011
Uploaded by
Jean PiagetOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pacemaker 7-20-2011
Uploaded by
Jean PiagetCopyright:
Available Formats
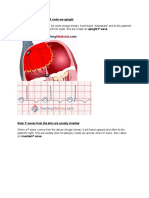
Venticle is paced but no QRS follows! Only stimulation spike is recorded with no QRS following 1.
Capture failure if QRS rate is slow, pacing threshold is too low. Heart is stimulated on demand but QRS is not triggered. Pacing threshold = amplitude (volts) x pulse duration 2. Undersencing if QRS rate is not slow, sensitivity (detection level, sencing level, sencing thresold) is too high. Heart is stimulated competitively at an inappropriate timing during refractory period. 3. Isoelectric fusion beat QRS complex happens to be so small as to resemble a stimulus only. Look at different lead. 4. In DDD, atrium sensed QRS (far-field sensing), and gave a V stimuli after AVI or URI (upper rate interval), when ventricule is in still refractory period.
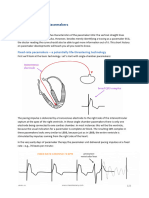
No V pace! Pacemaker does not stimulate ventricle no matter what! V stimulation appears inhibited by something. In DDD mode, if there is only A stilulation and no V stimulation, and there is patients own QRS or ventricular asystole. Self inhibition = Cross talk Ventricle is sensing Atrial activity. Venticules oversensing. Solution: Reduce A output pulse. Reduce ventricular sensitivity. Set PAVB (ventricular blanking). PAVB can prevent crosstalk. Set VSP. PAVB (Postatrial ventricular blanking period) = short interval after A atrial pace stimulus during which ventricle cannot sense the activity. Postatrial ventricular blanking. PAVB does not occur after spontaneous P (atrial activity). VSP (Vensricular safety pacing) = If ventricle sensed some activity right after A atrial (or you may say, if cross talk happens), the pacemaker will give V stimuli faster than AVI without waiting until it comes on T. The pacemaker will drop a spike after VSP peroid after the sensing.
Pacemaker drops a spike on QRS or T wave.! The pacemaker can overlook a true QRS during PAVB period and will provide V stimulus sometimes on T wave.
VSP (Vensricular safety pacing) = If ventricle sensed own QRS right after A atrial, the pacemaker will give V stimuli on top of QRS without waiting AVI and therefore it would come on T. The pacemaker will drop a spike after VSP peroid after A atrial.
AVI appears Shorter than you set. Cross talk is occurring on VSP setting.
Appears VOO. Pacemaker stimulates ventricle regardless of atrial activity. Atrium is senseing some noise.Far-field sensing Atriaum senses ventricular activity. Solution: Reduce atrial sensing. Set PVARP. PVARP - Prevent far field sensing. Also prevent sensing retrograde P. DDD pacemaker cannot initiate a new AVI during PVARP. Caution: This can cause atrial undersensing, however.
Endless loop tachycardia. Far-field sensing Atriaum senses ventricular activity. Retrograde P (outside the PVARP) is sensed by pacemaker. Retrograde P is sensed by atrium and starts AVI. RR interval is usually equal to URI but can be longer as URI + AVI. Cannot be shorter than URI. Appears AVNRT
Atrium does not capture! Retrograde P is making atrium refractory, but ventricle is successfully paced after AVI. RNRVAS (retrograde P is inside the PVARP) CL = LRI Appears no sinus activity. Appears capture failure of atrium.
Because of Retrograde P, Atrium is in refractory period, when pacemaker provides A stimuli. P wave does not follow A pace stimuli, but ventricle is paced after AVI. The ventricle activity produce retrograde P again.
Sudden reduction of HR to half. -- Spontaneous P: pacing V stimuli = 2:1 Tachycardia indused 2:1 block. Ventricular paced interval (VPI) = 2x spontaneous atrial P interval. This is caused because URI is shorter than TARP. Tx : Set longer URI to ensure a Wencheback URI. Wenckeback UR response makes the patient maintain the URI (fastest HR).
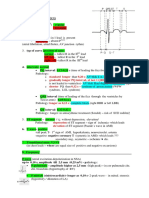
Automatic interval = Basic lower rate interval (LRI) = pVRP + Escape interval = sVRP +
LRI = determines the lowest ventricular rate. (longest interval) URI = fastest ventricular rate. DDD mode does not have atrial rate. DDD mode does reset the rate by atrial activity and ventricular activity. If it sensed an atrial activity, it will provides V slimulation after AVI. AVI = AV interval.
Hysteresis = Escape interval longer than LRI Pacemaker does not see its own stimulous and resultant QRS-T = (almost the same as Blanking period) = VRP (pacemaker ventricular refractory period)
Higher definiton VRP = short interval after stumulus or spontaneous QRS. Pacemaker will not sense ventricular activity during this period, and wait to start counting LRI during this period.
PVARP = short interval after stumulus or spontaneous QRS. Pacemaker will not sense atrial activity during this period. Prevent far field sensing. Also prevent sensing retrograde P. DDD pacemaker cannot initiate a new AVI during PVARP. Caution: This can cause atrial undersensing, however.
superior QRS vector RV apical pacing normal vector RVOT pacing lead is moving toward pulmonary valve! RAD ECG lead is too high or, unintended LV pacing pacing wire cross the PFO or coronary sinus!
T wave maybe inverted after long period of pacing = memory effect
Retrograde P causes the following problems. Endless loop tachycardia (retrograde P is outside the PVARP) CL= URI (or <URI +AVI) Appears AVNRT Retrograde P is sensed by atrium and starts AVI. RR interval is usually equal to URI but can be longer as URI + AVI. Cannot be shorter than URI.
RNRVAS (retrograde P is inside the PVARP) CL = LRI Appears no sinus activity. Appears capture failure of atrium. Because of Retrograde P, Atrium is in refractory period, when pacemaker provides A stimuli. P wave does not follow A pace stimuli, but ventricle is paced after AVI. The ventricle activity produce retrograde P again.
AV dissociation
due to VVI No p wave or there is a retrograde p VVI Fusion beat VVI
You might also like
- TelemetryDocument3 pagesTelemetryKelly PrattNo ratings yet
- 04 - Dual Chamber TimingDocument138 pages04 - Dual Chamber TimingMihir RavalNo ratings yet
- Understanding ECG's 2Document41 pagesUnderstanding ECG's 2Ben HarperNo ratings yet
- Rule: P Waves From The SA Node Are UprightDocument13 pagesRule: P Waves From The SA Node Are UprightredroseeeeeeNo ratings yet
- Pacemakers - Fact SheetDocument7 pagesPacemakers - Fact Sheettalha.k.rajpootNo ratings yet
- ECG at A GlanceDocument53 pagesECG at A Glancenurliah armandNo ratings yet
- Basics and Interpretation: Sif HansdottirDocument65 pagesBasics and Interpretation: Sif Hansdottirwenny1186100% (1)
- Cardiac RhythmsDocument12 pagesCardiac RhythmsPete Cobra CobraitiNo ratings yet
- Definition ECGDocument8 pagesDefinition ECGMelody BoadoNo ratings yet
- EKG RhythmsDocument71 pagesEKG RhythmsalexaNo ratings yet
- Understanding ECG's KingsholmDocument53 pagesUnderstanding ECG's KingsholmBen HarperNo ratings yet
- Ecg Criteria SVT Vs VT: DR - Vinoth Kumar PostgraduateDocument48 pagesEcg Criteria SVT Vs VT: DR - Vinoth Kumar Postgraduatelichumo murryNo ratings yet
- ECG Arrhythmia2006Document28 pagesECG Arrhythmia2006aris rifkhiNo ratings yet
- ECG Arrhythmia2006Document28 pagesECG Arrhythmia2006rickyfauzanNo ratings yet
- Avnrt AvrtDocument21 pagesAvnrt AvrtRima Rovanne Wenas100% (1)
- How To: Read ECG?Document63 pagesHow To: Read ECG?Let BNo ratings yet
- Normal Sinus RhythmDocument97 pagesNormal Sinus RhythmNatasha LiberisNo ratings yet
- ArrhytmiaDocument70 pagesArrhytmiaAfied FitrahNo ratings yet
- Ecg RhythmsDocument9 pagesEcg RhythmsNoreena PrincessNo ratings yet
- Learning ECGDocument187 pagesLearning ECGPhysiology by Dr Raghuveer100% (2)
- I.Sinus Rhythms and Sinus ArrhythmiasDocument64 pagesI.Sinus Rhythms and Sinus ArrhythmiashirschmedNo ratings yet
- Raza's ECGDocument45 pagesRaza's ECGcozmoxxxNo ratings yet
- Supraventricular Tachycardia - Life in The Fast Lane ECG LibraryDocument29 pagesSupraventricular Tachycardia - Life in The Fast Lane ECG LibraryYehuda Agus SantosoNo ratings yet
- Supraventricular TachyarrythmiasDocument172 pagesSupraventricular TachyarrythmiasAbnet WondimuNo ratings yet
- ECG ReadingDocument11 pagesECG ReadingSuresh Shrestha100% (1)
- Unit 7 ArrhythmiaDocument32 pagesUnit 7 ArrhythmiaJack TomarNo ratings yet
- 2017 - Pocket Guide ECG InterpretationDocument21 pages2017 - Pocket Guide ECG InterpretationmariaNo ratings yet
- ECG TutorialDocument40 pagesECG TutorialAnonymous HAbhRTs2TfNo ratings yet
- PG - Quick Look On Arrhythmia in ED - JCU 2021Document71 pagesPG - Quick Look On Arrhythmia in ED - JCU 2021Afied FitrahNo ratings yet
- Pacemaker Timing & IntervalsDocument124 pagesPacemaker Timing & IntervalsNiranjan Reddy100% (1)
- Cheat ECGDocument3 pagesCheat ECGNeil Emman BotardoNo ratings yet
- Rhythm Interpretation and Its ManagementDocument6 pagesRhythm Interpretation and Its Managementjh_ajjNo ratings yet
- EKG Interpretation Lecture 1 - Identifying The Squiggles, Developing A System For ReadingDocument6 pagesEKG Interpretation Lecture 1 - Identifying The Squiggles, Developing A System For Readingkcargen100% (1)
- 5 Steps To Rhythm Strip InterpretationDocument2 pages5 Steps To Rhythm Strip Interpretationjosh082572No ratings yet
- NCM 103 (LEC) : Electrocardiogram (ECG) ElectrocardiogramDocument10 pagesNCM 103 (LEC) : Electrocardiogram (ECG) ElectrocardiogramJohn Protacio50% (2)
- ECG InterpretationDocument83 pagesECG InterpretationJuana Maria Garcia Espinoza100% (2)
- RhythmDocument8 pagesRhythmparkmickyboo100% (1)
- Module7b Reading12lead EcgDocument43 pagesModule7b Reading12lead EcgTakpire DrMadhukarNo ratings yet
- Dr. Adeel Ahmed Waheed: House Officer M-4Document84 pagesDr. Adeel Ahmed Waheed: House Officer M-4Hussain AzharNo ratings yet
- Irama JunctionalDocument18 pagesIrama JunctionalTaufik Nur YahyaNo ratings yet
- Kuliah EKG II Unswagati 2016Document77 pagesKuliah EKG II Unswagati 2016iikNo ratings yet
- Suatu Alat Laboratoris Alat Bantu DiagnosisDocument78 pagesSuatu Alat Laboratoris Alat Bantu DiagnosisMohammad AlmuhaiminNo ratings yet
- Ecg enDocument12 pagesEcg enKeep smileNo ratings yet
- Basics of Ep and AvnrtDocument59 pagesBasics of Ep and Avnrtbharath kumar sNo ratings yet
- Recognizing Normal ECGDocument50 pagesRecognizing Normal ECGJosiephine Bucalon100% (3)
- Heart RhythmsDocument3 pagesHeart RhythmsjimmybonserNo ratings yet
- Suatu Alat LaboratorisDocument78 pagesSuatu Alat LaboratorisHematology 2016No ratings yet
- Basic Ecg From FastlanDocument125 pagesBasic Ecg From Fastlanomarfaruque7807No ratings yet
- Arrythmia Recognition Lecture FinalDocument54 pagesArrythmia Recognition Lecture FinalFlorencio D. Santos IVNo ratings yet
- EcgDocument18 pagesEcgDelyn Gamutan MillanNo ratings yet
- How To Read An ECGDocument15 pagesHow To Read An ECGCFTCNo ratings yet
- ECG Made Easy - RevisedDocument114 pagesECG Made Easy - RevisedenoNo ratings yet
- Interpretasi Elektrokardiografi: Dr. Erlina Marfianti, MSC, SPPD Departemen Ilmu Penyakit Dalam Fakultas Kedokteran UiiDocument60 pagesInterpretasi Elektrokardiografi: Dr. Erlina Marfianti, MSC, SPPD Departemen Ilmu Penyakit Dalam Fakultas Kedokteran UiiArif Zulfian MubarokNo ratings yet
- Membaca EkgDocument90 pagesMembaca EkgDwi S WijayaNo ratings yet
- Beta's Short RP.: Click Here To ViewDocument1 pageBeta's Short RP.: Click Here To ViewLwin Maung Maung ThikeNo ratings yet
- 11 AvrtDocument32 pages11 AvrtthetlwinagNo ratings yet
- How To Read An ECGDocument24 pagesHow To Read An ECGredroseeeeeeNo ratings yet
- Quick Ekg ReferenceDocument23 pagesQuick Ekg Referencekowaikowar100% (2)
- Tachycardia Which Fast Is Too FuriousDocument79 pagesTachycardia Which Fast Is Too FuriousEstiningtiyas RahayuNo ratings yet
- 28,29 Management of Cardiac ArrhythmiasDocument41 pages28,29 Management of Cardiac ArrhythmiasSL Dr ChEMiSNo ratings yet
- Schwartzs Principles of Surgery Absite and Board Review 11E Nov 8 2022 - 1260469751 - Mcgraw Hill Timothy Billiar All ChapterDocument68 pagesSchwartzs Principles of Surgery Absite and Board Review 11E Nov 8 2022 - 1260469751 - Mcgraw Hill Timothy Billiar All Chapterroy.nogle598100% (11)
- Chapter 24 - Alterations of Cardiovascular Function in Children - Nursing Test BanksDocument19 pagesChapter 24 - Alterations of Cardiovascular Function in Children - Nursing Test BanksNeLNo ratings yet
- Max Heindel - The Web of Destiny PDFDocument32 pagesMax Heindel - The Web of Destiny PDFYoudont CareatallNo ratings yet
- Summative Test in Science 6 (Circulatory)Document3 pagesSummative Test in Science 6 (Circulatory)ronaldodigma97% (33)
- Bed Side Assessment of Adult PatientDocument60 pagesBed Side Assessment of Adult PatientDheeraj RaiNo ratings yet
- Manual of Canine and Feline Cardiology PDFDocument450 pagesManual of Canine and Feline Cardiology PDFNovanAndrian100% (1)
- Mrs. Maria Eloisa Lim Chu Gungon: When You Reach Age 75 When You Reach Age 75 If The Insured Passes Away at Age 75Document11 pagesMrs. Maria Eloisa Lim Chu Gungon: When You Reach Age 75 When You Reach Age 75 If The Insured Passes Away at Age 75John Philip TiongcoNo ratings yet
- PacemakersDocument8 pagesPacemakersVIVEK Kumar Prajapati 72No ratings yet
- Safri 2018 IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 125 012125Document7 pagesSafri 2018 IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 125 012125Renoldy PapilayaNo ratings yet
- ICD9CMDocument470 pagesICD9CMBayyinah ArdianNo ratings yet
- Crazy BusyDocument55 pagesCrazy BusyDarenNo ratings yet
- Gr. 7 PE LM (Q1) PDFDocument46 pagesGr. 7 PE LM (Q1) PDFOm NamaNo ratings yet
- QP Code:111010 Reg. No: ........................ First Year B.SC Nursing Degree Examinations October 2017 Anatomy (2016 Scheme) Model Question PaperDocument6 pagesQP Code:111010 Reg. No: ........................ First Year B.SC Nursing Degree Examinations October 2017 Anatomy (2016 Scheme) Model Question PaperdrsNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary Syndrome, STEMI, Anterior Wall, Killips - 1, DM Type II - UncontrolledDocument61 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome, STEMI, Anterior Wall, Killips - 1, DM Type II - UncontrolledJai - Ho100% (5)
- Diagnosis: Imaging of Valvular Heart Disease in Heart FailureDocument9 pagesDiagnosis: Imaging of Valvular Heart Disease in Heart FailureAudini BerbasariNo ratings yet
- Las Science4 q2w2Document2 pagesLas Science4 q2w2Annabelle Poniente HertezNo ratings yet
- Evaluation MyocarditisDocument5 pagesEvaluation MyocarditisRaidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- The Heart Circulatory System AS Biology Answers AQA OCR EdexcelDocument3 pagesThe Heart Circulatory System AS Biology Answers AQA OCR Edexcellászló_kocsis_6No ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter ScienceDocument3 pages2nd Quarter Sciencesusan h. bucasasNo ratings yet
- Histo CompilationDocument217 pagesHisto CompilationNico LokoNo ratings yet
- Nanda 2021 2023Document6 pagesNanda 2021 2023Khimberly UmbaoNo ratings yet
- Pacemaker Learning Package: Paula Nekic CNE Liverpool Hospital ICU January 2016Document46 pagesPacemaker Learning Package: Paula Nekic CNE Liverpool Hospital ICU January 2016Zahangir Kabir AshikNo ratings yet
- I. Bacteria: Chapter 1 Gram Positive CocciDocument20 pagesI. Bacteria: Chapter 1 Gram Positive CocciRahul B100% (1)
- Exercise Physiology Lab ReportDocument11 pagesExercise Physiology Lab Reportapi-253201402No ratings yet
- (Case Digest) People v. UlepDocument1 page(Case Digest) People v. UlepTricia Mae TolentinoNo ratings yet
- DiscussionDocument26 pagesDiscussionCHARMAINE ORUGANo ratings yet
- Physio 2 - NotesDocument157 pagesPhysio 2 - NotesSivaranjini BhalaNo ratings yet
- ICF-CY Developmental Code Sets: Birth-2 Years: Ellingsen, K. M. & Simeonsson, R.J. (2011)Document2 pagesICF-CY Developmental Code Sets: Birth-2 Years: Ellingsen, K. M. & Simeonsson, R.J. (2011)Kristina TabaresNo ratings yet
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)From EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (31)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (404)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (82)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlFrom EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (60)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (170)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (46)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- Empath: The Survival Guide For Highly Sensitive People: Protect Yourself From Narcissists & Toxic Relationships. Discover How to Stop Absorbing Other People's PainFrom EverandEmpath: The Survival Guide For Highly Sensitive People: Protect Yourself From Narcissists & Toxic Relationships. Discover How to Stop Absorbing Other People's PainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (95)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesFrom EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (1412)