Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Invertebrate Zoology
Uploaded by
Edelyn ArguellesOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Invertebrate Zoology
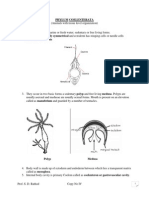
Uploaded by
Edelyn ArguellesCopyright:
Available Formats
Invertebrate Zoology a. Zoology: the study of anim als b. Kingdom : Anim alia i. Invertebrates and Chordates c.
As we exam ine invertebrates and vertebrates, notice how each successive phylum becom es m ore advanced in one way or another 2. Invertebrate Zoology Evolution a. One such trend in the body cavity or coelom i. Acoelom ates: solid body, no cavity ii. Pseudocoelom ates: body cavity not com pletely lined by m esoderm iii. Coelom ates: body cavity com pletely lined with m esoderm 3. Anim al Characteristics a. Heterotrophic b. Multicellular c. Eukaryotic 4. Advantage of Being Multicellular a. allows cells to specialize b. allows division of labor 5. 14 Invertebrate Phyla Here are a few... a. Porifera - sponges i. collectively known as the Parazoa ii. from the Greek poros L passage iii. m ostly m arine (1) only 100 out of 8000 different species live in fresh water iv. why an anim al??? (1) m ulticellular eukaryotic heterotroph with no cell walls 6. Porifera 7. Porifera 8. Cnidaria a. collectively known as the Radiata b. soft bodied anim als with stinging tentacles arranged in circles around their m outh c. com es from Greek word nettle d. m ostly m arine i. only 50 out of 11,000 species live in fresh water 9. Cnidaria a. gastrovascular cavity i. only one opening b. nem atocysts i. coiled, dart like, poisonous stingers 10. Cnidaria: Hydra a. Class: Hydrozoa b. reproduction i. budding and herm aphrodites 11. Cnidaria: Jellyfish a. Class: Scyphozoa b. 1 cm to 6 m in diam eter and tentacles > 50 m in length c. nem atocysts of m ost are harm less to hum ans i. som e painful...som e deadly 12. Cnidaria: Jellyfish 13. Cnidaria: Sea Anem one a. Class: Anthozoa b. m utalism with Clownfish 14. Cnidaria: Coral/polyps a. Class: Anthozoa i. highly productive ecosystem s 15. Bilateral Sym m etry
a. b. c. d. e. 16. 17.
two sided dorsal: top ventral: bottom anterior: head (front) posterior: tail
18.
19.
20.
21. 22. 23.
24.
25.
26.
Bilateral Sym m etry a. ...but also with bilateral invertebrates Platyhelm inthes a. flatworm s b. collectively known as the Acoelom ates c. truly free living i. first anim als that can dictate their m ovem ent d. anterior head i. sim ple nervous system e. still only one opening Platyhelm inthes a. Class: Turbellaria b. Planaria i. regeneration ii. non-polluted waters Platyhelm inthes a. Class: Trem atoda b. Flukes i. all parasitic ii. usually develop in an interm ediate, i.e. a snail, before infecting host Platyhelm inthes a. Class: Cestoidea b. Tapeworm s i. cows, fish, pigs...drink infected water or eat infected food (1) cysts in m uscle of host (2) we get tapeworm from im properly cooked m eat ii. dieting?! Platyhelm inthes a. Scolex Tapeworm Life Cycle Rotifera: rotifers a. Pseudocoelom ates b. Cilia, but also jaws c. Parthenogenesis i. No m ales...only fem ales (1) Males only live long enough to m ake sperm ...then die ; Nem atoda a. Roundworm s: Pseudocoelom ates i. sim plest anim al that has double opening digestive system ii. non-segm ented iii. som e free living iv. found in m ost aquatic habitats, m oist soil, plant and anim al tissues Nem atoda a. m ostly decom posers, but som e are parasitic i. Trichinella spiralis trichinosis (1) undercooked pork ii. River Blindness Mollusca a. From here on we deal with Coelom ates b. Soft bodied anim als that have an internal or external shell c. a lot of diversity within the phyla i. > 150,000 known species ii. snails, slugs, octopuses, squid, clam s, oysters, scallops,
chitons... Cephalopods (squid, octopuses...) i. well developed nervous system and brain ii. closed circulatory system 27. Mollusca Classes a. Bivalvia i. 2 shells (1) clam s, oysters, m ussels, scallops b. Gastropoda i. snails, slugs c. Polyplacophora i. chitons d. Cehphalopoda i. octopuses, squid, nautilus, cuttlefish 28. Mollusca 29. Annelida a. segm ented worm s b. well developed digestive tract and closed circulatory system i. blood with O 2 carrying hem oglobin c. Classes: i. Oligochaeta L earthworm s ii. Hirudinea L leeches 30. Annelida 31. Arthropoda a. largest phylum i. 1 x 10 6 known possibly > 10 x 10 6 ii. includes spiders, ticks, scorpions, insects, shrim p, crabs, centipedes... b. tough exoskeleton - chiton c. jointed appendages d. segm ented body 32. Arthropoda a. open circulatory system with heart b. well developed nervous system i. sensory system including eyes, olfactory (sm ell), antennae also for touch and sm ell ii. m ostly located at anterior end L head c. well developed gas exchange system i. gills, tracheal system s with branched air ducts 33. Arthropoda Classes a. Arachnida i. spiders, scorpions, ticks, m ites b. Diplopoda i. m illipedes c. Chilopoda i. centipedes d. Insecta i. insects (1) rem em ber the orders?!!! e. Crustacea i. crabs, lobsters, crayfish, shrim p 34. Arthropoda 35. Echinoderm ata a. 5 part radial sym m etry i. 5 parts organized sym m etrically around the center b. internal skeleton c. tube feet 36. Echinoderm ata Class: Asteroidea a. Starfish 37. Echinoderm ata Class: Echinoidea 38. Echinoderm ata d.
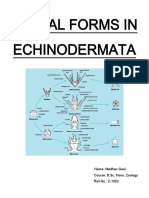
Class: Holothuroidea a. Sea Cucum bers 39. Chordata a. Characteristics i. Notochord (1) flexible supporting rod (a) usually dorsal (b) runs along nerve chord (2) in vertebrates, notochord is replaced by backbone ii. Pharyngeal (throat) slits (1) used to breath with (2) precursor to gills or lungs 40. Chordata a. Characteristics: i. Hollow dorsal nerve chord (1) runs along and above notochord (2) anterior end is usually the brain (3) branches off at various places to different parts of the body ii. Post anal tail iii. Includes tunicates and lancelets iv. Also includes vertebrates, but thats for the next unit............
You might also like
- Comparative Anatomy of Respiratory SystemDocument129 pagesComparative Anatomy of Respiratory Systemgerman guazaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Vertebrate Anatomy Lecture Notes - Digestive SystemDocument14 pagesComparative Vertebrate Anatomy Lecture Notes - Digestive SystemMielah Ruth100% (1)
- Cnidaria SummaryDocument12 pagesCnidaria SummaryJose ArroyoNo ratings yet
- Zoology Project of ZrsaDocument4 pagesZoology Project of ZrsaZotei RawihteNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SurfacesDocument11 pagesRespiratory SurfacesNitesh KotianNo ratings yet
- Locomotion ZoologyDocument12 pagesLocomotion Zoologyadithya4rajNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument138 pagesRespiratory SystemJosefantastic 75No ratings yet
- Organ Systems 1 NBC ReviewerDocument39 pagesOrgan Systems 1 NBC ReviewerJames ChavezNo ratings yet
- 4 Porifera Spicules & Canal SystemDocument34 pages4 Porifera Spicules & Canal Systemapi-3732735100% (2)
- Chordate Origin and EvolutionDocument3 pagesChordate Origin and Evolutionmonique100% (2)
- Phylum PoriferaDocument30 pagesPhylum PoriferaEloisa Lopez100% (2)
- Composite Fish Culture in HillsDocument20 pagesComposite Fish Culture in HillsSullip MajhiNo ratings yet
- Practical XII TH STD Zoology EMDocument24 pagesPractical XII TH STD Zoology EMsanthoshsivanandam SivanandamNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Genome Complexity - Learn Science at ScitableDocument4 pagesEukaryotic Genome Complexity - Learn Science at ScitableAnder ManaresNo ratings yet
- Ento231 PDFDocument151 pagesEnto231 PDFMunna GuptaNo ratings yet
- Zoology PresentationDocument8 pagesZoology Presentationਰੋਹਿਤ ਕੁਮਾਰNo ratings yet
- Economic ZoologyDocument47 pagesEconomic ZoologyAntony SebastianNo ratings yet
- CH 26 Phylum PoriferaDocument51 pagesCH 26 Phylum Poriferaapi-244168124No ratings yet
- Roles of Insects For HumanDocument58 pagesRoles of Insects For Humannovita manaluNo ratings yet
- Wetlands of AssamDocument7 pagesWetlands of AssamHasibuddin AhmedNo ratings yet
- Dheeraj BishtDocument38 pagesDheeraj Bishtdheeraj bishtNo ratings yet
- India Quiz QuestionsDocument12 pagesIndia Quiz Questionsankur0708No ratings yet
- Human Digestive SystemDocument29 pagesHuman Digestive SystemRagini Dubey100% (1)
- NWIA National BrochureDocument32 pagesNWIA National BrochureSaurabh SinghviNo ratings yet
- Abstracts For 32nd Congrass of ZoologyDocument350 pagesAbstracts For 32nd Congrass of ZoologySaima WaseemNo ratings yet
- 005-Phylum CnidariaDocument24 pages005-Phylum CnidariacoraNo ratings yet
- Farooq Ali: Presented byDocument22 pagesFarooq Ali: Presented byFarooq AliNo ratings yet
- Phylum CnidariaDocument26 pagesPhylum CnidariaAbby SangualNo ratings yet
- Phylum PoriferaDocument5 pagesPhylum Poriferastudent10100No ratings yet
- ZOO301 Parade of VertebratesDocument14 pagesZOO301 Parade of VertebratesPatricia Hariramani100% (1)
- FishesDocument74 pagesFishesLophyn UmarNo ratings yet
- History of ZoologyDocument4 pagesHistory of ZoologyBen Gabriel MaghuyopNo ratings yet
- Notes On The Phylum PORIFERADocument20 pagesNotes On The Phylum PORIFERAnoblefx100% (1)
- Archaeozoology: Camelopardalis Brisson, From The Prehistoric Site of Susunia, District BankuraDocument7 pagesArchaeozoology: Camelopardalis Brisson, From The Prehistoric Site of Susunia, District BankuraDibyendu DasNo ratings yet
- Lec4 SocialInsects TheSociety NotesDocument3 pagesLec4 SocialInsects TheSociety NotesAlexandra LvNo ratings yet
- Pests of PaddyDocument19 pagesPests of PaddyPurushotham PaspuletiNo ratings yet
- Metamorphism in InsectsDocument24 pagesMetamorphism in Insectsyayeg raja100% (1)
- Describe The Taxonomical of Identification of Cultivable FishesDocument5 pagesDescribe The Taxonomical of Identification of Cultivable FishesNarasimha MurthyNo ratings yet
- Nieves - An Assessment of Macro-Invertebrate Gleaning in Fisheries On The Albay GulfDocument9 pagesNieves - An Assessment of Macro-Invertebrate Gleaning in Fisheries On The Albay GulffurkonableNo ratings yet
- Cnidaria: Body Cavity Known As The CoelenteronDocument21 pagesCnidaria: Body Cavity Known As The CoelenteronLakshya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Bernays & Chapman 1994Document325 pagesBernays & Chapman 1994Alexandre Pimenta100% (2)
- Phylum PoriferaDocument2 pagesPhylum PoriferayashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- General Classification (All Phylum)Document16 pagesGeneral Classification (All Phylum)kiran PoudelNo ratings yet
- Transcription: RNA Polymerases and General Transcription FactorsDocument77 pagesTranscription: RNA Polymerases and General Transcription FactorsmluluNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Pediculosis Capitis - A Critical Appraisal of The Current LiteratureDocument12 pagesTreatment of Pediculosis Capitis - A Critical Appraisal of The Current Literaturejft842No ratings yet
- Zoology CH 8 Animal Like Pro TistsDocument103 pagesZoology CH 8 Animal Like Pro TistsTHUNDERCLASH_SILVEREYES139100% (3)
- Phylum HemichordataDocument61 pagesPhylum Hemichordatakingbanakon0% (1)
- Lecture III Insect Orders PDFDocument57 pagesLecture III Insect Orders PDFLouella ArtatesNo ratings yet
- Phylum Porifera PDFDocument17 pagesPhylum Porifera PDFkingNo ratings yet
- 09 Vertebrate Digestive SystemDocument74 pages09 Vertebrate Digestive SystemJohn Andre CruzNo ratings yet
- Phylum PoriferaDocument17 pagesPhylum PoriferaRhiZhal SquDetto FrizTalNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom: Basis of ClassificationDocument15 pagesAnimal Kingdom: Basis of ClassificationChaitali Deshmukh100% (1)
- CnidariaDocument48 pagesCnidariaMafe CabilesNo ratings yet
- TOrsionDocument19 pagesTOrsionDrSneha VermaNo ratings yet
- Translation in Prokaryotes: NEET 2020Document1 pageTranslation in Prokaryotes: NEET 2020ADIKKI ANOOHYANo ratings yet
- Echinoderm Larvae PDFDocument15 pagesEchinoderm Larvae PDFMadhav GoelNo ratings yet
- Phylum Coelenterata ClassificationDocument3 pagesPhylum Coelenterata ClassificationSudesh Rathod100% (1)
- Bor Et Al., 2003Document3 pagesBor Et Al., 2003Sergio LlorenteNo ratings yet
- Spiders of AustraliaDocument265 pagesSpiders of AustraliaDouglas Carvalho100% (3)
- List of Students of 5 SEM CBCS (Medical)Document11 pagesList of Students of 5 SEM CBCS (Medical)Emraan EmmiNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument9 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsMlshin LaoNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell and Animal CellDocument12 pagesPlant Cell and Animal CellKimverheart Dennisse NavalNo ratings yet
- Science Quest 8 AC 3E c04 PDFDocument94 pagesScience Quest 8 AC 3E c04 PDFmaxx100% (1)
- Testicles Research by Deez Part 1Document23 pagesTesticles Research by Deez Part 1Dark flame masterNo ratings yet
- 309 Lab 2Document5 pages309 Lab 2SanahKumarNo ratings yet
- Presentation: Behind Bars at The Zoo (PAGE 179-180)Document11 pagesPresentation: Behind Bars at The Zoo (PAGE 179-180)Mohd Fandi OsmanNo ratings yet
- Sean Burke - Online Crayfish DissectionDocument10 pagesSean Burke - Online Crayfish Dissectionapi-386190429No ratings yet
- Animal ClassificationDocument17 pagesAnimal ClassificationAyesha ShaikhNo ratings yet
- An Overview of The Dragonflies and Damselflies of The Maltese Islands (Central Mediterranean) (Odonata)Document123 pagesAn Overview of The Dragonflies and Damselflies of The Maltese Islands (Central Mediterranean) (Odonata)Ram LeeNo ratings yet
- Science Support & MovementDocument4 pagesScience Support & MovementElen UningNo ratings yet
- Past Papers: Human PhysiologyDocument2 pagesPast Papers: Human PhysiologyMalavikaN100% (1)
- Amazing Animals - InteriorDocument31 pagesAmazing Animals - InterioralexandraNo ratings yet
- In Ovo Feeding in PoultryDocument46 pagesIn Ovo Feeding in Poultrysarang82% (11)
- Anatomy and Physiology of Digestive SystemDocument34 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Digestive SystemIan IsidroNo ratings yet
- Project Report ON Endangered Species of Animals in India: Vishal ThakurDocument7 pagesProject Report ON Endangered Species of Animals in India: Vishal ThakurShubham BayasNo ratings yet
- Chap004 Test Bank Tank PDFDocument53 pagesChap004 Test Bank Tank PDFHeraNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Marine Parasite in Malaysia: Prepared by Mohd Adib Fadhil Mohd Arif Bin Mohammad Nor Mohd Hafidz AidzatDocument28 pagesIntroduction of Marine Parasite in Malaysia: Prepared by Mohd Adib Fadhil Mohd Arif Bin Mohammad Nor Mohd Hafidz AidzatmadibfadhilNo ratings yet
- WoRMS - World Register of Marine Species - Anadara Gray, 1847Document5 pagesWoRMS - World Register of Marine Species - Anadara Gray, 1847DesyanitaNo ratings yet
- Some Characteristics of The Phylum CnidariaDocument5 pagesSome Characteristics of The Phylum CnidariaTI Journals PublishingNo ratings yet
- Supplement To Apoidea (Insecta Hymenoptera) of Uttarakhand StateDocument1 pageSupplement To Apoidea (Insecta Hymenoptera) of Uttarakhand StateJournal of Environment and Bio-SciencesNo ratings yet
- Putri - Report TextDocument2 pagesPutri - Report TextAziz Rifianda0% (1)
- Tissues ReviewerDocument5 pagesTissues ReviewerJoannah MarieNo ratings yet
- 0610 s17 QP 31Document24 pages0610 s17 QP 31BioScMentor-1No ratings yet
- Vertebrates WorksheetDocument2 pagesVertebrates WorksheetAvanti CBNo ratings yet
- Pup Rearing: The Role of Mothers and Allomothers in Free-Ranging Domestic DogsDocument13 pagesPup Rearing: The Role of Mothers and Allomothers in Free-Ranging Domestic DogsLucy LinNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Physiology Syllabus - LabDocument7 pagesAnatomy Physiology Syllabus - Labapi-321286607No ratings yet
- NeurulationDocument9 pagesNeurulationaesha890% (1)