Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Separation
Uploaded by
Johnny YuillOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Separation
Uploaded by
Johnny YuillCopyright:
Available Formats
SEPARATION Q: Ask the candidate to draw a three-phase separator including internals and associated Safety and control equipment.
1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9)
Deflector Plates/diverters & Inlet Momentum Breakers Mist Pads Coalescing Pads Straightening Vanes Weir Centrifugal Devices Horizontal baffles Vortex Breaker Water/Sand Jets
Q:
What executive action would you expect to take place on Low low oil/water interface level on 3 phase separator? Produced water outlet v/v will shut in.
Q:
What does either increasing or lowering the pressure in a separator do to Oil and Gas flows? Lowering the pressure will increase the gas flow and also increase the oil flow due to the higher. D.P. between the choke and the separator. Increasing the pressure will reduce both the gas and oil flows.
Q:
What are typical chemicals you can find injected into the separation stream? Corrosion inhibitor will be injected at or as close to the wellhead as possible. (Continual injection). The process fluids have corrosive properties to the dissolved CO2, H2S in the process fluids. These contaminants make the fluids more corrosive and as the fluids enter the process pipework the systems become subject to corrosion under the correct process conditions. Scale inhibitor is injected either down-hole as part of a squeeze treatment (batch treatment) or as close to the wellhead as possible (continual injection). The produced water has scaling potential due to changes in temperature and pressure. Demulsifier is injected at the oil manifolds upstream of the separators (continual injection). This is to assist separation of the produced water from the oil in the separation train. De-oiler (reverse demulsifier) is injected (intermittently) into the produced water directly downstream of the separators. This is to gather the oil particles entrained in the produced water into larger particles to assist oil separation from the produced water. Generally there should be no requirement for de-oiler but is required on some occasions. I.e. tight emulsions. Scale inhibitor is also often injected into the process system downstream of the separation train or at intervals interstage continual injection). The requirement depends upon the type and scaling tendency expected, i.e. there may be a requirement to protect the crude coolers from scale formation due to temperature and pressure drop across the coolers. Corrosion inhibitor is also often injected into the downstream process system to protect the export pipeline from corrosion (continual injection). What effects has the heating or cooling of oil have in the separation train? Heating the oil will improve separation. Cooling the oil will impede the separation process and could lead to wax problems. What is the purpose of interlocks on PSVs and how would you expect to see them controlled? Interlocks are there to ensure that the correct PSVs are on line and that the manual block Valves are in the correct position. E.G. the offline PSV will have the upstream block valve Locked closed and the downstream block valve locked open (spec break). The system will be controlled by the interlock register. Describe the operation of an electrically driven centrifugal pump, its main parts and signs of mechanical wear and tear. This type of pump is perhaps one of the most simple elements of mechanical hardware, consisting of one rotating part, the impeller, housed in a stationary casing (the spiral casing, or volute). The sole purpose of the pump is to increase the static pressure of the liquid being transported and this is achieved by energy input via the pump drive shaft. In passing through the impeller vanes, the fluid undergoes a pressure rise, partly due to centrifugal forces, and partly due to the flow into an ever-increasing cross-sectional area. The major energy transfer, however, is manifested in a dramatic rise in the kinetic energy of the fluid at the impeller blade exits. The spiral casing serves to reconvert some of this kinetic energy into additional pressure energy. If extremely high pressures are required, then the overall compression can be conveniently carried out over a number of impeller stages. Such multistage pumps usually have a series of impellers "ganged" on to a single drive shaft, which then constitutes a reasonably compact unit. Thus, multistage machines can give us the high flow rates of the centrifugal pump, but also provide a high-pressure rise over as many stages as are required. Some reservoir water injection pumps can have as many as 27 impeller stages.
Q:
Q:
Q:
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- USA v. Sussmann - Durham Filing - Motion On Potential Conflicts of InterestDocument13 pagesUSA v. Sussmann - Durham Filing - Motion On Potential Conflicts of InterestWashington Examiner100% (3)
- Code of Ethics Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument4 pagesCode of Ethics Multiple Choice QuestionsGideon P. Casas88% (24)
- Coreapb3: Nivin PaulDocument19 pagesCoreapb3: Nivin PaulNivin PaulNo ratings yet
- 4-Sided Planer & Moulder Operation Manual: For Spares and Service ContactDocument48 pages4-Sided Planer & Moulder Operation Manual: For Spares and Service ContactAlfred TsuiNo ratings yet
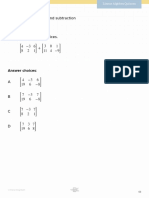
- Topic: Matrix Addition and SubtractionDocument6 pagesTopic: Matrix Addition and SubtractionAnonyNo ratings yet
- Supplier Relationship Management As A Macro Business ProcessDocument17 pagesSupplier Relationship Management As A Macro Business ProcessABCNo ratings yet
- 2019 - All Heads of Bureaus & Offices - Disconnection of Old Dti Telephone Lines - 64562Document8 pages2019 - All Heads of Bureaus & Offices - Disconnection of Old Dti Telephone Lines - 64562dannalauraNo ratings yet
- UTAR Convocation Checklist For Graduands Attending Convocation (March 2019) - 1Document5 pagesUTAR Convocation Checklist For Graduands Attending Convocation (March 2019) - 1JoyleeeeeNo ratings yet
- JKBMS Tutorial SetupDocument7 pagesJKBMS Tutorial SetupFabricio Varovsky Muñiz ArteagaNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Climate Change in NigeriaDocument9 pagesLiterature Review On Climate Change in Nigeriac5rn3sbr100% (1)
- CS8792 CNS Unit5Document17 pagesCS8792 CNS Unit5024CSE DHARSHINI.ANo ratings yet
- GSM Controlled RobotDocument33 pagesGSM Controlled RobotAbhishek KunalNo ratings yet
- Operating Instruction PMD55Document218 pagesOperating Instruction PMD55Dilip ARNo ratings yet
- Operations Management: Green Facility Location: Case StudyDocument23 pagesOperations Management: Green Facility Location: Case StudyBhavya KhattarNo ratings yet
- Java 9 Real - TimeDocument57 pagesJava 9 Real - TimeDiego AmayaNo ratings yet
- D Fwxfs Fzô Fee F Fs Wû Àfiy°Ff WX' Af° F Ff°Fe W F FF 21 D F°Ff Izy QZVF FWX A FZ Afz FF FF 23Document24 pagesD Fwxfs Fzô Fee F Fs Wû Àfiy°Ff WX' Af° F Ff°Fe W F FF 21 D F°Ff Izy QZVF FWX A FZ Afz FF FF 23Govind Chandra DwivediNo ratings yet
- Service Laws ProjectDocument4 pagesService Laws ProjectRaman PatelNo ratings yet
- Bank Details and Payment MethodsDocument1 pageBank Details and Payment Methodsetrit0% (1)
- Aquamimicry: A Revolutionary Concept For Shrimp FarmingDocument5 pagesAquamimicry: A Revolutionary Concept For Shrimp FarmingMarhaendra UtamaNo ratings yet
- 04 HSE Inspection ChecklistDocument2 pages04 HSE Inspection ChecklistAjay Hazarika100% (2)
- Tan vs. CincoDocument2 pagesTan vs. CincoKing Badong67% (3)
- Tower BridgeDocument6 pagesTower BridgeCalvin PratamaNo ratings yet
- Learning Dynamics and Vibrations by MSC AdamsDocument80 pagesLearning Dynamics and Vibrations by MSC AdamsFrancuzzo DaniliNo ratings yet
- December + Yearly ReviewDocument2 pagesDecember + Yearly ReviewNick FabrioNo ratings yet
- Case Study: PointDocument1 pageCase Study: PointprasadzinjurdeNo ratings yet
- Fly The Maddog X User Manual MSFS 2020Document15 pagesFly The Maddog X User Manual MSFS 2020KING OF NOOBSNo ratings yet
- TIAPortalOpennessenUS en-USDocument656 pagesTIAPortalOpennessenUS en-USskyttt135No ratings yet
- Lua ApiDocument176 pagesLua Apiyaotl albores tecuautzinNo ratings yet
- 201805graphene PDFDocument204 pages201805graphene PDFMohammad RezkyNo ratings yet
- in The Matter of The Estate of Remigia SaguinsinDocument3 pagesin The Matter of The Estate of Remigia SaguinsinAila AmpieNo ratings yet