Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 38 Posttest
Uploaded by
Gamepage BuckOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 38 Posttest
Uploaded by
Gamepage BuckCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
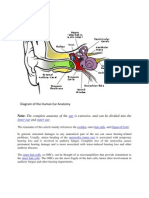
Click the thumbnail below to see a larger view of the image.
On morning rounds, the nurse is having difficulty waking a client and gets only minimal response when calling the clients name repeatedly. Using the table shown, how should the nurse report the clients status? a. Comatose b. Confused c. Disoriented d. Semicomatose Grade: User Responses: Feedback: 1 d.Semicomatose a.Rationale: A semicomatose client will minimally respond after repeated or extreme stimuli. Cognitive Level: Understanding Nursing Process: Assessment Client Need: Psychosocial Integrity 2. The nurse is planning to teach clients about how sensory information travels in the body. The information that the nurse provides should include: (Select all that apply.) Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected. a. Stimuli. b. Receptors. c. Feedback. d. Stereognosis. e. Conduction. Grade: User Responses: Feedback: 1 a.Stimuli.,b.Receptors.,e.Conduction. a.Rationale: Cognitive Level: Remembering Nursing Process: Assessment Client Need: Physiological Integrity A stimulus must stimulate a nerve receptor in order for sensory information to be perceived. Receptors are elements of the sensory-perceptual process, and convert stimuli into nerve impulses. Conduction of the impulse to the brain is a necessary step in the sensory-perceptual process. Stereognosis is a particular sense and is not part of every sensoryperceptual process. Feedback is not a part of the sensory-perceptual process.
3.
What should the nurse include when teaching about cultural differences in sensory functioning?: a. Culture determines the amount of sensory stimulation that a person considers usual or normal. b. Physiologic changes related to sensation are different from culture to culture. c. Stress levels are different depending upon the culture. d. Different cultures have different types of sensory illnesses. Grade: User Responses: Feedback: 1 a.Culture determines the amount of sensory stimulation that a person considers usual or normal. a.Rationale: Culture determines the amount of sensory stimulation that a person considers usual or normal, and also affects the amount of stimulation an individual desires and believes to be meaningful. Cognitive Level: Understanding Nursing Process: Implementation Client Need: Physiological Integrity
4.
The nurse is caring for a male client whose culture finds eye contact between men and women inappropriate. By avoiding eye contact, the nurse is attempting to prevent: a. Sensory overload. b. Anger. c. Cultural deprivation. d. Sensory deficit. Grade: User Responses: Feedback: 1 c.Cultural deprivation. a.Rationale: Cultural deprivation is the lack of culturally supportive or assistive acts in care. Cognitive Level: Understanding Nursing Process: Implementation Client Need: Safe, Effective Care Environment
5.
The nurse is assessing a client with multiple sclerosis by testing light touch, sharp and dull sensation, hot and cold sensation, vibration sense, and position sense, which are documented as testing of: a. Olfactory sense. b. Tactile sense. c. Visual acuity. d. Gustatory sense. Grade: User Responses: Feedback: 1 b.Tactile sense. a.Rationale: All of these assessment techniques test the clients tactile sense. Cognitive Level: Remembering Nursing Process: Assessment Client Need: Physiological Integrity
6.
A client has experienced a recent weight loss and notes a history of appetite changes. Which areas of sensory perceptual functioning should the nurse assess? (Select all that apply.) Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected. a. Olfactory b. Visual c. Auditory d. Gustatory e. Tactile Grade: User Responses: Feedback: 1 a.Olfactory,d.Gustatory a.Rationale: Cognitive Level: Understanding Nursing Process: Assessment Client Need: Physiological Integrity Auditory is the sense of hearing and is not directly associated with weight and appetite changes. Visual is the ability to see and does not have a direct influence on appetite or weight. The sense of taste does have an effect on appetite and could, if altered, result in weight loss. Olfactory testing evaluates the sense of smell. Sense of smell does influence appetite and the ability to maintain weight. Tactile refers to the sense of touch. It does not directly influence appetite.
7.
The nurse is caring for a client with a head injury in an intensive care unit. This client is at risk for sensory overload due to: (Select all that apply.) Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected. a. Decreased cognitive ability. b. Mobility restrictions. c. Limited social contacts. d. Discomfort. e. Close monitoring. Grade: User Responses: Feedback: 1 a.Decreased cognitive ability.,d.Discomfort.,e.Close monitoring. a.Rationale: Cognitive Level: Understanding Nursing Process: Assessment Client Need: Physiological Integrity Mobility restrictions are associated with sensory deprivation rather than sensory overload. Limitation in social contacts may cause sensory deprivation. Discomfort puts clients at risk for sensory overload. Monitoring with numerous pieces of equipment as in ICUs puts the client at risk for sensory overload. The decrease in cognitive ability associated with head injury is a risk factor for sensory overload.
8.
The nurse promotes health of the sensory system by teaching clients to: a. Wear ear protectors when watching television. b. Have their ears and eyes examined annually. c. Wear protective eye goggles when using power tools. d. Wear sunglasses at all times. Grade: User Responses: Feedback: 1 c.Wear protective eye goggles when using power tools. a.Rationale: The nurse should teach the client to wear protective eye goggles when there is risk of flying debris such as when using power tools, riding motorcycles, or spraying chemicals. Cognitive Level: Applying Nursing Process: Planning Client Need: Health Promotion and Maintenance
9.
Which of the following clients does the nurse identify as the client who is most likely to experience sensory deprivation? a. A blind 93-year-old bedridden resident of a nursing home b. A deaf 88-year-old single client with +4 edema who lives in an upstairs apartment c. A child with genetic anomalies who was abandoned in infancy, is cared for in a special needs foster home, and who attends preschool three times a week d. A premature infant transferred to a neonatal intensive care unit Grade: User Responses: Feedback: 1 b.A deaf 88-year-old single client with +4 edema who lives in an upstairs apartment a.Rationale: The deaf client with +4 edema who lives in an upstairs apartment does not have easy access to sensory stimulation and has limited potential for socialization. Cognitive Level: Analyzing Nursing Process: Assessment Client Need: Physiological Integrity
10.
Click the thumbnail below to see a larger view of the image.
The nursing student is preparing to take care of a client who has been described as having sensory deprivation. The student nurse assesses this client for: (Select all that apply.) Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected. a. Long and frequent naps. b. Periods of showing no emotion. c. Heightened ability to concentrate. d. Waking at night unaware of where he is. e. Mood alterations.
Grade: User Responses: Feedback:
1 a.Long and frequent naps.,b.Periods of showing no emotion.,d.Waking at night unaware of where he is.,e.Mood alterations. a.Rationale: Cognitive Level: Understanding Nursing Process: Assessment Client Need: Psychosocial Integrity Clinical manifestations of sensory deprivation include emotional lability. Drowsiness and excessive sleeping are signs of sensory deprivation. Nocturnal confusion is a manifestation of sensory deprivation. The clinical manifestations of sensory deprivation include apathy. Difficulty concentrating is a clinical manifestation of sensory deprivation.
11.
A client admitted to the intensive care unit complains of excessive fatigue and racing thoughts, and is moderately anxious and unable to follow instructions. The nurses assessment reveals that this client exhibits clinical signs of: a. Sensory reception. b. Sensory deprivation. c. Sensory deficit. d. Sensory overload. Grade: User Responses: Feedback: 1 d.Sensory overload. a.Rationale: Sensory overload is characterized by fatigue or sleeplessness, racing thoughts, anxiety, irritability, and reduced task performance. Cognitive Level: Analyzing Nursing Process: Assessment Client Need: Physiological Integrity
12.
The nurse is developing a care plan for the client with complete and uncorrectable deafness and assigns the nursing diagnosis Disturbed Sensory Perception (Auditory). The nurse appropriately selects what intervention for this client? a. Obtain the clients attention through touch. b. Speak at a normal pace, in a loud tone of voice. c. Move closer to the affected ear. d. Use short phrases with as few words as possible. Grade: User Responses: Feedback: 1 a.Obtain the clients attention through touch. a.Rationale: When one sense is lost, the nurse can teach the client to use other senses to supplement the loss. However, the type of stimulation needs to be adapted according to the client's specific deficit and cultural beliefs. Cognitive Level: Applying Nursing Process: Planning Client Need: Health Promotion and Maintenance
13.
When teaching a class about protecting sensory function, what instructions should the nurse provide? (Select all that apply.) Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected. a. Use protective goggles when spraying pesticides. b. Be sure that children get scheduled immunizations. c. Adults should have eye exams every 10 years. d. Always sit more than 6 feet from the television. e. Wear sunglasses when outdoors. Grade: User Responses: Feedback: 1 a.Use protective goggles when spraying pesticides.,b.Be sure that children get scheduled immunizations.,e.Wear sunglasses when outdoors. a.Rationale: Cognitive Level: Understanding Nursing Process: Implementation Client Need: Physiological Integrity The recommendation is for adults to have eye exams every 3-5 years, or more often if there is a history of glaucoma or other vision problems. There is no reason to advise sitting more than 6 feet from a television. Childhood immunizations can prevent sensory disability. Eye protection is important in preventing injury that can lead to visual problems. Protecting the eyes from UV rays is an important measure in preventing visual disturbance.
14.
The nurse determines that the child is receiving appropriate sensory input when the parents: a. Ensure regular visual screening. b. Stimulate one sense at a time and are consistent in the use of the colors and sounds. c. Provide exposure to noxious stimuli. d. Provide varied stimuli. Grade: User Responses: Feedback: 1 d.Provide varied stimuli. a.Rationale: Healthy sensory function can be promoted by providing children with appropriate sensory input by stimulating as many senses as possible and using a variety of different stimuli. Cognitive Level: Applying Nursing Process: Assessment Client Need: Health Promotion and Maintenance
15.
A nurse is providing a seminar on the confused client and explains that alertness may fluctuate at different times of the day with: a. Dementia. b. Delirium. c. Hallucinations. d. Delusions.
Grade: User Responses: Feedback:
1 b.Delirium. a.Rationale: A common characteristic, and differentiating symptom of delirium is that the level of alertness may differ at various times throughout the day. The client may be alert and oriented during the day, but become confused and disoriented at night. Cognitive Level: Understanding Nursing Process: Implementation Client Need: Psychosocial Integrity
16.
A client has been oriented to person, time, and place but becomes disoriented within 24 hours of admission to the hospital. The nurse recognizes that the most probable reason for this is: a. A normal sign of aging. b. Potential abuse. c. Chronic depression. d. Physiologic disturbances. Grade: User Responses: Feedback: 1 d.Physiologic disturbances. a.Rationale: Confusion can be caused by physiologic disturbances such as chronic medical problems. A new onset of confusion should always be seen as a symptom and not a diagnosis. Cognitive Level: Applying Nursing Process: Assessment Client Need: Physiological Integrity
17.
The nurse is developing a plan of care for a client with the nursing diagnosis Disturbed Sensory Perception (Kinesthetic). The most appropriate outcome criteria for this client is: (Select all that apply.) Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected. a. Reduce social isolation. b. Maintain function of existing senses. c. Prevent sensory deprivation. d. Prevent injury. e. Perform ADLs independently and safely. Grade: User Responses: Feedback: 1 d.Prevent injury.,e.Perform ADLs independently and safely. a.Rationale: Cognitive Level: Applying Nursing Process: Planning Client Need: Safe, Effective Care Environment Because this client lacks a sense of the position of body parts, injury prevention is an appropriate outcome criterion. Altered perception of body position makes movement a challenge, so performance of ADLs is an appropriate outcome criterion. Social interaction is not an anticipated concern for this client. This client is not at risk for sensory deprivation. There is no indication of a risk to other senses.
18.
The nurse who is caring for a newly admitted client who experienced a stroke that resulted in aphasia, develops a priority expected outcome of: a. The client will remain socially active. b. The client will move from the bed to the chair with minimal assistance. c. The client will display no symptoms of sensory deprivation. d. The client will effectively communicate needs. Grade: User Responses: Feedback: 1 d.The client will effectively communicate needs. a.Rationale: Development of an effective communication method is most important for a client with impaired verbal communication. This is necessary for safety as well as social function. The nurse needs to develop an effective communication system for this client. Cognitive Level: Applying Nursing Process: Planning Client Need: Safe, Effective Care Environment
19.
A client who had a stroke is unable to distinguish written words and symbols. The nurse determines that the most appropriate nursing diagnosis for this client is: a. Ineffective Cognition. b. Disturbed Sensory Perception. c. Acute Disorientation. d. Impaired Memory. Grade: User Responses: Feedback: 1 b.Disturbed Sensory Perception. a.Rationale: Disturbed Sensory Perception is an appropriate nursing diagnosis for this client because the client has an alteration in perceiving incoming stimuli as well as an impaired response to stimuli. The inability to recognize written words and symbols is a disturbance in the interpretation of the stimuli. Cognitive Level: Applying Nursing Process: Diagnosis Client Need: Physiological Integrity
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Clinical Refraction GuideDocument138 pagesClinical Refraction Guideyossdb100% (2)
- Vision Certificate FormatDocument1 pageVision Certificate FormatAmit SindhyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 46 PosttestDocument12 pagesChapter 46 PosttestGamepage BuckNo ratings yet
- Chapter 43 PosttestDocument6 pagesChapter 43 PosttestGamepage BuckNo ratings yet
- Chapter 45 PosttestDocument5 pagesChapter 45 PosttestGamepage BuckNo ratings yet
- Chapter 42 PosttestDocument8 pagesChapter 42 PosttestGamepage BuckNo ratings yet
- Chapter 41 PosttestDocument9 pagesChapter 41 PosttestGamepage BuckNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiment No. 2Document6 pagesLaboratory Experiment No. 2Aubrey RamiloNo ratings yet
- Annual Evidence Update On Amblyopia - 2010Document21 pagesAnnual Evidence Update On Amblyopia - 2010avram_elenaNo ratings yet
- Interpretasi Vision-Test JaegerDocument1 pageInterpretasi Vision-Test Jaegerbagol julegNo ratings yet
- Direct OphthalmoscopeDocument16 pagesDirect OphthalmoscopeMuhammed AbdulmajeedNo ratings yet
- Cerebrum MCQDocument5 pagesCerebrum MCQSrinivasa Rao BollaNo ratings yet
- Case 3:myopiaDocument24 pagesCase 3:myopiaarifamri92No ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Human EyeDocument10 pagesStructure and Function of The Human EyeSyed MujtabaNo ratings yet
- Contact Lenses Fitting GuideDocument40 pagesContact Lenses Fitting Guidemoni7777No ratings yet
- Human Eye PDFDocument13 pagesHuman Eye PDFHaidir MuhammadNo ratings yet
- AstigmatismDocument21 pagesAstigmatismSamuel PonrajNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Sense OrgansDocument39 pagesUnit 8 Sense OrgansBasant RajNo ratings yet
- Acoustic Reflex Threshold (ART) Patterns: An Interpretation Guide For Students and Supervisors: Course Material and Exam Questions Course MaterialDocument17 pagesAcoustic Reflex Threshold (ART) Patterns: An Interpretation Guide For Students and Supervisors: Course Material and Exam Questions Course Materialn_almagroNo ratings yet
- Eye Chart Template 19Document4 pagesEye Chart Template 19Bilal Hussain ShahNo ratings yet
- Special SensesDocument56 pagesSpecial SensesKhrystine VenturaNo ratings yet
- Chapter IIDocument9 pagesChapter IISunny BediNo ratings yet
- Eye RobicsDocument28 pagesEye RobicsIsmi Raudha0% (1)
- Case Based Ophthalmology GuideDocument12 pagesCase Based Ophthalmology GuideGradestack100% (2)
- Vestibular Function TestsDocument11 pagesVestibular Function TestsM. Arief Purnanta0% (1)
- Proprioception: Jussi Rantala and Jukka RaisamoDocument25 pagesProprioception: Jussi Rantala and Jukka RaisamoSai RamNo ratings yet
- Heep 116Document7 pagesHeep 116pk2varmaNo ratings yet
- Perception in ArchitectureDocument42 pagesPerception in ArchitecturePRIYANKA GREWALNo ratings yet
- My Technical Seminar PPT (Bionic Eyes)Document26 pagesMy Technical Seminar PPT (Bionic Eyes)kittyNo ratings yet
- Praktis Kendiri: Sensory Organ StimulusDocument2 pagesPraktis Kendiri: Sensory Organ Stimulusfarah6214No ratings yet
- Vision Screening - Dr. WagnerDocument37 pagesVision Screening - Dr. WagnerDien Doan QuangNo ratings yet
- Jurnal PterygiumDocument5 pagesJurnal PterygiummirafitrNo ratings yet
- Affected Anatomy: Is Extensive, and Can Be Divided Into The andDocument5 pagesAffected Anatomy: Is Extensive, and Can Be Divided Into The andKamal AhmedNo ratings yet
- PE OversimplifiedDocument4 pagesPE OversimplifiedtigorNo ratings yet
- CLP Topic 5 Rigid Gas Permeable (RGP) Lens Fitting EvaluationDocument26 pagesCLP Topic 5 Rigid Gas Permeable (RGP) Lens Fitting EvaluationRhendy 172019022No ratings yet