Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Building A Regulated 5V DC Power Supply
Uploaded by
Prasanna Man RajbanshiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Building A Regulated 5V DC Power Supply
Uploaded by
Prasanna Man RajbanshiCopyright:
Available Formats
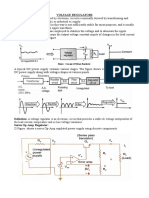
Building a Regulated 5V DC power supply,
A regulated 5 volt DC supply is essential for powering micro-controller and TTL based circuits. The output of most wall-warts and adapters is to rippled and impure for use in digital circuits. Lets build an inexpensive power supply using some discrete components and a fixed voltage regulator IC.
You will need:
a step down transformer [12V] four silicon diodes [1N4007] a resistor [47] capacitors [2 x 220F, 0.3F and 0.1F] three terminal voltage regulator IC [LM7805] a small general propose PCB, some wires, and a suitable output port (I use a audio connector).
The circuit of the supply is as given below:
Fig: Circuit Diagram, click to expand.
A Picture of all components you will need, a resistor, capacitors, a regulator and diodes:
Fig: Components, click to enlarge. The circuit consists of three main blocks, the rectifier, filter and regulator. The rectifier is used to transform the mains AC voltage to a suitable DC voltage. The output of the rectifier is however an impure DC signal so we use a filter to clean the signal and finally a regulator to deliver precisely 5 volts, irrespective of the load connected to the output.
Rectifier
It consists of a transformer and a diode bridge. The diodes are standard silicon 1N4007 diodes. We have chosen a 12V transformer because the regulator IC needs at-least 7.5V of input voltage to function properly.
Filter
We use a pi-filter here. The two 220F capacitors and resistor form the filter. Pi-filters are great for light load applications like digital circuits. Be sure to check the polarity of the capacitors before connecting them. The resistor shown above is one rated to dissipate up-to 5W of power across it. You may use smaller 3W resistors, but availability may be an issue. Don't use the tiny 0.25 W or 0.5W ones though.
Regulator
The voltage is regulated by three terminal voltage regulator IC LM7805. This regulator provides stable 5V DC output against large fluctuations in input voltage and load. It also has internal protection circuits which 'brownout' the device when overloaded. To decide the pin-outs, hold the regulator with its face towards you and legs pointing upward, the pin to the right is the input, middle pin is ground and left most pin is output.
Construction Tips
The transformer can be made to snugly fit onto the PCB by bending the screw mounts under and around the board as shown in the picture below.
A 6.3mm or 3.5mm female mono TRS connector (tip, ring, sleeve), also known as an 'audio jack' serves as a great output port. The power can then be delivered via standard audio cables. Since the power resistors is quite large, solder it vertically to save space on the board. Mount the entire board on thermocol when finished to prevent accidental short circuits. The finished circuit fits neatly into a 2 by 1.5 PCB, excluding the output jack and plug. You can also include a small switch at the out-put for easy operation. The IC can be heatsink-ed on multiple layers of aluminum foil to dissipate the heat, or if you are enclosing this in a metal box, pin the IC to the sides of the box. This is not entirely necessary though.
Fig: The finished circuit,
You might also like
- This Is 20 Watt Power Audio Amplifier Which Use IC LM1875 As Main ComponentDocument14 pagesThis Is 20 Watt Power Audio Amplifier Which Use IC LM1875 As Main ComponentJc LastaNo ratings yet
- Regulated Power SupplyDocument6 pagesRegulated Power Supplypandadillipkumar26No ratings yet
- Single Transistor 12v To 230v InverterDocument7 pagesSingle Transistor 12v To 230v Inverteryr48No ratings yet
- Transformerless Power SupplyDocument3 pagesTransformerless Power SupplyRafael Vazquez VillamarNo ratings yet
- Datasheet 4051Document6 pagesDatasheet 4051Jui KulkarniNo ratings yet
- 3 Phase Voltage FolumarsDocument12 pages3 Phase Voltage FolumarsrocaoNo ratings yet
- Lic Report 14 - 4 Final2Document12 pagesLic Report 14 - 4 Final2Harshvardhan MishraNo ratings yet
- A. ResistorDocument5 pagesA. ResistorErwin AhmadNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of SpreadsheetsDocument5 pagesA Brief History of SpreadsheetsDexter CastilloNo ratings yet
- Edc Lab ManualDocument70 pagesEdc Lab ManualreneeshczNo ratings yet
- DC Power Supply: King Abdulaziz University Electronics IDocument20 pagesDC Power Supply: King Abdulaziz University Electronics IMohannad S. AlghamdiNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.02 To Observe The Characteristics of A Half Wave RectifierDocument4 pagesExperiment No.02 To Observe The Characteristics of A Half Wave RectifierWaqas MughalNo ratings yet
- +zener Voltage RegulationDocument4 pages+zener Voltage RegulationtrshaaaNo ratings yet
- 30 LED Projects PDFDocument46 pages30 LED Projects PDFalexandre38650% (2)
- Chapter 8. Switched-Inductor Supplies With Design Insight and Intuition (Power IC Design)Document29 pagesChapter 8. Switched-Inductor Supplies With Design Insight and Intuition (Power IC Design)Minh Hai RungNo ratings yet
- Manual de Reparacion MCR Serie 32-33Document34 pagesManual de Reparacion MCR Serie 32-33Fernando Tapia Gibson100% (2)
- 555 TimerDocument76 pages555 TimerSai Krishna KodaliNo ratings yet
- Two Point StarterDocument4 pagesTwo Point StarterudhayabarathiNo ratings yet
- Variador VT DeiverDocument194 pagesVariador VT DeivercesarNo ratings yet
- Government Polytechnic, Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Electrical Workshop LabDocument15 pagesGovernment Polytechnic, Muzaffarpur: Name of The Lab: Electrical Workshop LabTapobroto Chatterjee100% (1)
- 5v DC SupplyDocument19 pages5v DC SupplyDev Agarwal100% (1)
- EC6361 Electronics LaboratoryDocument97 pagesEC6361 Electronics LaboratoryBaskarNo ratings yet
- Electronics Lab Exp3 PDFDocument17 pagesElectronics Lab Exp3 PDFgacc4sitesNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 Half Wave and Full WaveDocument8 pagesLab 4 Half Wave and Full WaveRashid Rind Rashid Rind100% (1)
- Brake Load Test of Squirel Cage Induction Motor 3 PhaseDocument7 pagesBrake Load Test of Squirel Cage Induction Motor 3 Phasejassisc100% (1)
- Transformer Less POWER SUPPLY REPORTDocument7 pagesTransformer Less POWER SUPPLY REPORTضياء بن احمد الكباري67% (3)
- Short Transmission LineDocument18 pagesShort Transmission LineNaga AnanthNo ratings yet
- Hopkinson Test On DC Shunt MotorDocument5 pagesHopkinson Test On DC Shunt MotorVarun VadluriNo ratings yet
- Bridge Rectifier - Definition, Construction and WorkingDocument14 pagesBridge Rectifier - Definition, Construction and WorkingRamKumarNo ratings yet
- MCB-Miniature Circuit BreakerDocument6 pagesMCB-Miniature Circuit BreakerVannak CHenNo ratings yet
- Static RelaysDocument11 pagesStatic RelaysBharathwaj SreedharNo ratings yet
- NRI Discovery LabDocument19 pagesNRI Discovery Labden headNo ratings yet
- AC Electrical Machines Lab Manual 3 - 1Document65 pagesAC Electrical Machines Lab Manual 3 - 1Rockstar RichNo ratings yet
- Car Battery Charger Circuit DiagramDocument3 pagesCar Battery Charger Circuit DiagramJaiNo ratings yet
- The Phase Control Circuit The TC787Document10 pagesThe Phase Control Circuit The TC787nansusanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 For B.electronicDocument12 pagesExperiment 4 For B.electronicUmmu Umar Wa AisyahNo ratings yet
- AC Voltage Measurement Using PIC16F877A MicrocontrollerDocument15 pagesAC Voltage Measurement Using PIC16F877A Microcontrollervallery1No ratings yet
- 48 Volt Battery ChargerDocument5 pages48 Volt Battery ChargerpradeeepgargNo ratings yet
- Full-Wave Bridge RectifierDocument26 pagesFull-Wave Bridge RectifierSmallhorse1984No ratings yet
- BEE LAB MANUAL FINAL1st SemesterDocument38 pagesBEE LAB MANUAL FINAL1st SemesterSaif KhanNo ratings yet
- On IgbtDocument19 pagesOn IgbtSayanta Saha100% (1)
- Precision Rectifier CircuitsDocument13 pagesPrecision Rectifier CircuitsWaqas PervaizNo ratings yet
- Ee105 Fet LectDocument61 pagesEe105 Fet LectKahMun LimNo ratings yet
- Design of Regulated Power SupplyDocument18 pagesDesign of Regulated Power SupplyDanish KhanNo ratings yet
- Tube Light ManualDocument2 pagesTube Light ManualSwaroop MallickNo ratings yet
- Diodes: Symbol Name DescriptionDocument7 pagesDiodes: Symbol Name DescriptionKepin'z TsAx PAweheNo ratings yet
- TTL LOGIC Family - Hariram-1Document16 pagesTTL LOGIC Family - Hariram-1Hari RamNo ratings yet
- Voltage RegulatorsDocument3 pagesVoltage RegulatorsNisha Kotyan G R100% (1)
- Presentation 1Document15 pagesPresentation 1Ajay Talajiya0% (1)
- Dual Variable Power SupplyDocument13 pagesDual Variable Power SupplyMayank SainiNo ratings yet
- 16X2 LCD Basics:: LCD Pin Description: Pin No Symbol I/O DescriptionDocument33 pages16X2 LCD Basics:: LCD Pin Description: Pin No Symbol I/O DescriptionvaralakshmikrNo ratings yet
- Summing AmplifierDocument6 pagesSumming AmplifierAhmed ShaabanNo ratings yet
- Experiment # 09: Objective: To Study The Over Voltage Protection of DC Power Supply System (CLO 1) ApparatusDocument20 pagesExperiment # 09: Objective: To Study The Over Voltage Protection of DC Power Supply System (CLO 1) ApparatusRasheed Shah100% (1)
- Enerzio Product Catalog 2019-2020 New PDFDocument16 pagesEnerzio Product Catalog 2019-2020 New PDFHarvinder Singh HarryNo ratings yet
- 45 - 60055 - EE512 - 2015 - 5 - 2 - 1 - Experiment 2 PLC PDFDocument7 pages45 - 60055 - EE512 - 2015 - 5 - 2 - 1 - Experiment 2 PLC PDFkrishnandrkNo ratings yet
- GE8261-Engineering Practices Lab - EEEDocument21 pagesGE8261-Engineering Practices Lab - EEEAdnan KNo ratings yet
- DC Servo Motor - MalDocument6 pagesDC Servo Motor - Malapi-19787379100% (1)
- Ec8361-Adc Lab ManualDocument118 pagesEc8361-Adc Lab ManualmuminthajNo ratings yet
- FRENIC Solar Pump Controller: Compatible With Induction and PMSM PumpsDocument4 pagesFRENIC Solar Pump Controller: Compatible With Induction and PMSM PumpsGibbs PerNo ratings yet
- How To Build Your Own 10WPAmpDocument31 pagesHow To Build Your Own 10WPAmpJose C. Lita JrNo ratings yet
- 1) Smps Using Viper22A: Circuit DiagramDocument6 pages1) Smps Using Viper22A: Circuit DiagramBhadreshkumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- How To Configure An Anybus Controlnet Adapter/Slave Module With Rsnetworx For ControlnetDocument26 pagesHow To Configure An Anybus Controlnet Adapter/Slave Module With Rsnetworx For ControlnetEcaterina IrimiaNo ratings yet
- Type 2625 and 2625NS Volume BoostersDocument4 pagesType 2625 and 2625NS Volume Boostershamz786No ratings yet
- Hex Inverter: BU4069UB / BU4069UBF / BU4069UBFVDocument4 pagesHex Inverter: BU4069UB / BU4069UBF / BU4069UBFVjose omañaNo ratings yet
- IPLOOK SMS Product Information V1.3Document14 pagesIPLOOK SMS Product Information V1.3IPLOOK TechnologiesNo ratings yet
- Samco CarryallDocument4 pagesSamco CarryallbillNo ratings yet
- System and Standard Functions For S7-300 and S7-400Document586 pagesSystem and Standard Functions For S7-300 and S7-400orgil02220100% (1)
- CV Iqbal 2016Document3 pagesCV Iqbal 2016Muhammad Iqbal ImaduddinNo ratings yet
- M1 Section 1. Assignment 1 Metacognitive Reading ReportDocument2 pagesM1 Section 1. Assignment 1 Metacognitive Reading ReportLandThere100% (1)
- InstallDocument6 pagesInstallDebangshu KumarNo ratings yet
- OpTransactionHistory02 12 2019Document4 pagesOpTransactionHistory02 12 2019Vijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Course Outline: ABE 105 - AB Power EngineeringDocument2 pagesCourse Outline: ABE 105 - AB Power EngineeringKaren Joy BabidaNo ratings yet
- Race and Gender in Silicon Valley - SyllabusDocument2 pagesRace and Gender in Silicon Valley - SyllabusCampus ReformNo ratings yet
- 8a. Scratch-3.0-for-Inclusive-LearningDocument31 pages8a. Scratch-3.0-for-Inclusive-LearningAvram MarianNo ratings yet
- Veko Brand VFD Inverter Basic Default Settings and Adjusting InstructionsDocument4 pagesVeko Brand VFD Inverter Basic Default Settings and Adjusting InstructionsNuhj OsohcidNo ratings yet
- Gei 100727 PDFDocument26 pagesGei 100727 PDFMohd Khairul AshrafNo ratings yet
- CyberOps Skills Assessment - Student TRNG - ExamDocument4 pagesCyberOps Skills Assessment - Student TRNG - ExamIsabella Leon67% (3)
- AaiPe NeoBankingDocument17 pagesAaiPe NeoBankingPuneet SethiNo ratings yet
- Harvey Newman Receives Department of Energy, Office of High Energy Physics Lifelong Achievement AwardDocument2 pagesHarvey Newman Receives Department of Energy, Office of High Energy Physics Lifelong Achievement AwardMaria SpiropuluNo ratings yet
- 德勤 - 数字化精益制造工业4.0技术改变了精益流程,从而推动企业发展 -DI Digital Lean DSNDocument20 pages德勤 - 数字化精益制造工业4.0技术改变了精益流程,从而推动企业发展 -DI Digital Lean DSNxiao pengNo ratings yet
- 30 Rat BCU TechsheetDocument2 pages30 Rat BCU TechsheetBryan OngNo ratings yet
- Pbdocs Traktoren Zetor 117 41 Forterra eDocument1 pagePbdocs Traktoren Zetor 117 41 Forterra eZoran RajčevićNo ratings yet
- Scope of Work of Non IBR Boiler InspectionDocument1 pageScope of Work of Non IBR Boiler InspectionShailendra BoroleNo ratings yet
- AWM UL - CertificateofComplianceDocument1 pageAWM UL - CertificateofCompliancesamirNo ratings yet
- Cosivis eDocument208 pagesCosivis eZadiel MirelesNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility PDFDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic Compatibility PDFRedouane NaceriNo ratings yet
- Webhook With WhatsappDocument11 pagesWebhook With WhatsappsarasasasaNo ratings yet
- Onto 1Document16 pagesOnto 1DavidTumini Ogolo100% (1)
- Spencer Kane Kennelly, Exp. Associate: Data Standardization and Master/Reference Data ManagementDocument1 pageSpencer Kane Kennelly, Exp. Associate: Data Standardization and Master/Reference Data ManagementArjun GhattamneniNo ratings yet