Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1
Uploaded by
drjonesg19585102Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1
Uploaded by
drjonesg19585102Copyright:
Available Formats
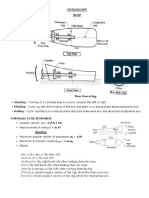
IS 15021 (Part 1) :2001 ISO 5456-1:1996
w?dkl m-w-
IndianStandard
TECHNICAL DRAWINGS PROJECTION
PART 1 SYNOPSIS
METHODS
Icsol.loo.lo
@ 61S 2001
BUREAU
MANAK
OF
IN DI AN
STAN
DARDS
ZAFAR MARG
BHAVAN,
9 BAHADUR SHAH NEW DELHI 110002
December 2001
Price Group 2
Drawings Sectional Committee,
BP 24
NATIONAL
FOREWORD
This Indian Standard (Part 1) which is identical with ISO 5456-1 : 1996 Technical drawings Projection methods Part 1: Synopsis issued by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) was adopted by the Bureau of Indian Standards on the recommendation of Drawings Sectional Committee and approval of the Basic and Production Engineering Division Council. This standard (Part 1) gives a survey of the various types of projection geometric relationships. Other parts of this series are given as follows: IS 15021 (Part 2) :2001 IS 15021 (Part 3) :2001 IS 15021 (Part 4) :2001 Technical drawings representations Technical drawings representations Projection Projection methods as well as their
methods: methods:
Part 2 Orthographic Part 3 Axonometric
Technical drawings Projection methods: Part 4 Central projection
The text of ISO Standard has been approved as suitable for publication as Indian Standard without deviations. In the adopted standard certain terminology and conventions are not identical to those used in Indian Standards. Attention is particularly drawn to the following: a) b) Wherever the words International read as Indian Standard. Standard appear referring to this standard, they should be the current
Comma (,) has been used as a decimal marker, while in Indian Standards, practice is to use a full point (.) as the decimal marker.
In this adopted standard, reference appears to certain International Standards for which Indian Standards also exist. The corresponding Indian Standards which are to be substituted in their place are listed below along with their degree of equivalence for the editions indicated : /nternationa/ Standard ISO 5456-2:1996 Corresponding Indian Standard IS 15021 (Part 2) : 2001 Technical Projection methods: Part 2 representations drawings Orthographic Degree of Equivalence Identical
1S0 5456-3:1996 ISO 5456-4:1996 IS 10209-1: 992
IS 15021 (Part 3) : 2001 Technical drawings Projection methods: Part 3 Axonometric representations drawings IS 15021 (Part 4) : 2001 Technical Projection methods: Part 4 Central projection
do do do
IS 8930 (Part 1) :1995 Technical product documentation Vocabulary: Pari 1 Terms relating to technical drawings: General and types of drawings (first revision) 8930 (Part 2): 2001 Technical Is documentation Vocabulary: Part 2 Terms projection methods product relating to
ISO 10209-2
1993
do
The concerned Sectional Committee has reviewed the provision of ISO 1503:1977 referred in this adopted standard and has decided that it is acceptable for use in conjunction with this standard. This adopted standard also gives Bibliography in Annex A which is informative. The corresponding Indian Standard against the ISO Standard is given below along with its degree of equivalence for the edition indicated: International Standard ISO 128:1982 Corresponding Indian Standard IS 10714:1983 General principles of presentation technical drawings on Degree of Equivalence Identical
IS 15021 [ Part 1 ) :2001 ISO 5456-1 :1996
hdian Standard TECHNICAL DRAWINGS PROJECTION METHODS
PART 1 SYNOPSIS
1 Scope
This part of ISO 5456 gives a survey of the various types of projection methods as well as their geometric relationships. Parts 2 to 4 specify details for the selection application of the various projection methods. and
3 Definitions
For the purposes of this part of ISO 5456, the definitions given in ISO 10209-1 and ISO 10209-2 and the following definitions apply. 3.1 pictorial representation: Parallel or central projection on a single projection plane giving a threedimensional image of an object. 3.2 true view: View of the features of an object that lie on a plane parallel to the projection plane; geometrically similar to the corresponding features of the object. 3.3 exploded view: Drawing of an assembly in pictorial representation in which all the components are drawn to the same scale and correctly orientated relative to each other, but are separated from each other in their correct sequence along common axes. NOTE 1 This term should not be confused with representations where a covering layer is removed in order to show inner portions like those presented in section (cut-away view). 3.4 principal view View of an object showing the important features, which may be chosen from the point of view of design, assembly, sales, service or maintenance,
Normative
references
The following standards contain provisions which, through reference in this text, constitute provisions of this part of ISO 5456. At the time of publication, the editions indicated were valid. All standards are subject to revision, and parties to agreements based on this part of ISO 5456 are encouraged to investigate the possibility of applying the most recent editions of the standards indicated below. Members of IEC and ISO maintain registers of currently valid International Standards. ISO 1503:1977, of movements. Geometrical orientation and directions
ISO 5456-2:1996, Technical drawings Projection methods Part 2. Orthographic representations. ISO 5456-3:1996, Technical drawings Projection methods Part 3: Axonometric representations. ISO 5456-4:1996 Technical drawings methods Part 4: Central projection. Projection
ISO 10209-1:1992, Technics/ product documentation Vocabulary Part 1: Terms relating to technical drawings: general and types of drawings. ISO 10209-2:1993, Technical product documentation Vocabulary Part 2: Terms relating to projection methods,
4 Suwey
of projection
methods
Projection methods are defined by: the type of projectors, lel or convergent; which may be either paral-
IS ISO
15021
( Part 1 ) :2001 :1996
5456-1
the position of the projection plane in relation to the projectors, either orthogonal or oblique; position of the object (its main features), which may be either parallel/orthogonal or oblique to the projection plane. and their relation-
lcodins+panxz
Coordinateplane Yz
the
A survey of the various possibilities ships is given in table 1.
5 Geometrical
orientation
Geometrical orientation in space is given by coordinate axes and coordinate planes in accordance with the arrangement given by the right-hand rule (see 1s0 1503).
Coordinatep~aneXY J
Figure2 5.1 Coordinate
axes
Invariable
Coordinate axes are imaginary lines in space which intersect at right angles to each other at the origin. There are three coordinate axes: X, Y and Z (see figure 1), to be designated by capital letters. z
Depending on the projection method chosen, certain features of the object are represented in true view as follows: 6.1 The central projection invariable is:
+ I
x
Coordinateaxis X Origin
the size of angles in planes which are parallel to the projection plane; therefore the projection plane figures lying in planes parallel to the projection plane are similar.
6.2
Oblique projection
invariable
are:
the parallelism of lines, unless they are parallel to the projection lines;
*
Figure 1
the divisional ratio of lines;
the size of angles, length of lines and all plane figures in planes parallel to the projection plane. 6.3 Orthogonal projection invariable are:
5.2
Coordinate planes
Three imaginary planes in space which intersect each other at right angles. Each of the three coordinate planes is defined by two coordinate axes and includes the origin. They are designated by capital letters XY, W and XZ (see figure 2). NOTE 2 Coordinate planes and projection planes are not always the same, therefore, if necessary, appropriate
indication (designation) should be shown on the drawing.
the parallelism of lines, unless they are parallel to
the projection lines;
the divisional ratio of lines; the size of angles, length of lines and all plane
figures in planes parallel to the projection plane;
right angles, if one side of the right angle in the
object is parallel to the projection plane.
IS ISO
15021 ( Part 1 ) :2001 5456-1 :1996
Table 1 Projectionsystems Projection
centre
Position of
projection plane to projectors
Mainfeatures of the objeot in relation to projection plane
Parallel/orthogonal
Number of projection planes One or more One One One
Type of view
Type of projection
Two-dimensional Three-dimensional Threedlmensional Three-dimensional
infinite (parallel projectors)
Orthogonal Obhque Parallel/orthogonal Oblique Oblique
Orthogonal (ISO 5456-2)
Axonometnc (ISO 5456-3)
Finite (convergent projectors) Oblique Obhque One Three-dimensional Central (ISO 5456-4)
IS 15021 ( Part 1 ) :2001 ISO 5456-1 :1996
Annex A
(informative)
Bibliography
[11 ISO 128:1982, Techmcal drawings General principles
of presentation
Bureau
of Indian Standards
BIS is a statutory institution established under the Bureau of Indian Standards Act, 1986 to promote harmonious development of the activities of standardization, marking and quallty certification of goods and attending to connected matters in the country. Copyright BIS has the copyright of all its publications. No part of these form without the prior permission in writing of BIS. This does of implementing the standard, of necessary details, such designations. Enquiries relating to copyright be addressed to Review of Indian Standards Amendments are issued to standards as the need arises on the basis of comments. Standards are also reviewed periodically; a standard along with amendments is reaffirmed when such review indicates that no changes are needed; if the review indicates that changes are needed, it is taken up for revision. Users of Indian Standards should ascertain that they are in possession of the latest amendments or edition by referring to the latest issue of BIS Catalogue and Standards: Monthly Additions. This Indian Standard has been developed from Doc : No. BP24{0140). publications may be reproduced in any not preclude the free use, in the course as symbols and sizes, type or grade the Director (Publications), BIS.
Amendments Amend No.
Issued Since Publication Date of Issue Text Affected
BUREAU OF INDIAN STANDARDS Headquarters : Telegrams : Manaksanstha (Common to all offices) Telephone 3237617 3233841
Manak Bhavan, 9 Bahadur Shah Zafar Marg, New Delhi 110002 Telephones :3230131,3233375, 3239402 Regional Central Offices : : Manak Bhavan, 9 Bahadur Shah Zafar Marg NEW DELHI 110002 : 1/14 C.I,T. Scheme Vll M, V. 1.P. Road, Kankurgachi KOLKATA 700054 : SCO 335-336, Sector 34-A, CHANDIGARH 160022
Eastern
3378499, 3378561 { 3378626,3379120 603843 602025
Northern
{ Southern : C.I.T. Campus, IV Cross Road, CHENNAI 600113
r2541216,2541442 ~2542519,2541315 8329295, 8327858 8327891,8327892
Western
: Manakalaya, E9 MlDC, Marol, Andheri (East) MUMBAI 400093
Branches
: AHMEDABAD. BANGALORE. BHOPAL. BHUBANESHWAR. COIMBATORE. FARIDABAD. GHAZIABAD. GUWAHATI. HYDERABAD. JAIPUR. KANPUR. LUCKNOW. NAGPUR. NALAGARH. PATNA. PUNE. RAJKOT. THIRUVANANTHAPURAM.
Printed at Prabhat Offset Press. New Delhi-2
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- DB 3 CH 5Document27 pagesDB 3 CH 5Anonymous f3iGLjxNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Engg DataBookIIIDocument6 pagesEngg DataBookIIIdrjonesg19585102No ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Engg Databook ch12Document21 pagesEngg Databook ch12drjonesg19585102No ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- DB 3 CH 1Document15 pagesDB 3 CH 1Dhanish KumarNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- db3ch3 DesbloqueadoDocument20 pagesdb3ch3 DesbloqueadoRoque MatienzoNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Engg Databook ch9Document38 pagesEngg Databook ch9drjonesg19585102No ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Void Fractions in Two-Phase FlowsDocument0 pagesVoid Fractions in Two-Phase FlowsMohsen AghaeiNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Engg Databook ch18Document31 pagesEngg Databook ch18drjonesg19585102No ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Engg Databook ch16Document25 pagesEngg Databook ch16drjonesg19585102No ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- Thermodynamics of Refrigerant Mixtures and Oil MixturesDocument17 pagesThermodynamics of Refrigerant Mixtures and Oil Mixturesphankhoa83No ratings yet
- Engg Databook ch13Document34 pagesEngg Databook ch13drjonesg19585102No ratings yet
- Engg Databook ch14Document28 pagesEngg Databook ch14drjonesg19585102No ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Engg Databook ch10Document26 pagesEngg Databook ch10drjonesg19585102No ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Engg Databook ch11Document22 pagesEngg Databook ch11drjonesg19585102No ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Engineering Data Book III Design Conside PDFDocument10 pagesEngineering Data Book III Design Conside PDFfoamtrailer0% (1)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Engg Databook ch8Document27 pagesEngg Databook ch8drjonesg19585102No ratings yet
- Engg Data Book Ch4Document1 pageEngg Data Book Ch4drjonesg19585102No ratings yet
- DB 3 CH 7Document39 pagesDB 3 CH 7alejodanyNo ratings yet
- Piping Systems and Microbiological ContaminationDocument18 pagesPiping Systems and Microbiological ContaminationIbrahimNo ratings yet
- Entrance Loss CoefficientsDocument13 pagesEntrance Loss CoefficientstitibiNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Epri ManualDocument62 pagesEpri Manualdrjonesg19585102No ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Fuel Property Paper DETC2006-99562Document7 pagesFuel Property Paper DETC2006-99562drjonesg19585102No ratings yet
- Epa CT Test Paper PDFDocument60 pagesEpa CT Test Paper PDFdrjonesg19585102No ratings yet
- Auto Duct User ManualDocument39 pagesAuto Duct User Manualdrjonesg19585102No ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Epri Cooling Tower Water Rfi PDFDocument4 pagesEpri Cooling Tower Water Rfi PDFdrjonesg19585102No ratings yet
- Thesis Thermal StorageDocument371 pagesThesis Thermal Storagedrjonesg19585102No ratings yet
- Duct Design ThesisDocument60 pagesDuct Design Thesisdrjonesg19585102No ratings yet
- Epri Openadr2 Software PDFDocument30 pagesEpri Openadr2 Software PDFdrjonesg19585102No ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- NASA POEGuidebookDocument172 pagesNASA POEGuidebookdrjonesg19585102No ratings yet
- Fault Level CalculationDocument43 pagesFault Level Calculationdrjonesg19585102100% (2)
- Trig Quiz ReviewDocument2 pagesTrig Quiz ReviewRajul C DasNo ratings yet
- Banach Spaces and Ramsey Theory: Some Open ProblemsDocument17 pagesBanach Spaces and Ramsey Theory: Some Open ProblemsWalner Mendonça SantosNo ratings yet
- Practical Analytic Geometry With Applications To Aircraft 1Document366 pagesPractical Analytic Geometry With Applications To Aircraft 1eventnow100% (1)
- Lectures On BuildingsDocument8 pagesLectures On Buildingschaoxian82416No ratings yet
- Grade 12 Trigonometry Worksheets PDFDocument3 pagesGrade 12 Trigonometry Worksheets PDFCordell100% (1)
- CH 6 NotesDocument34 pagesCH 6 NotesKris ANo ratings yet
- Angles and Circles Geometry ProblemsDocument8 pagesAngles and Circles Geometry Problemsgobinda prasad barmanNo ratings yet
- PHYS 342 - Lecture 3 Notes - F12Document9 pagesPHYS 342 - Lecture 3 Notes - F12John DoeNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus (History of Mathematics)Document10 pagesCourse Syllabus (History of Mathematics)Jomel Tapayan Famoso50% (2)
- ProjectileDocument40 pagesProjectileSweet EmmeNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Basic Calculus-Quarter 3: Asseeement # 1Document6 pagesBasic Calculus-Quarter 3: Asseeement # 1Aiyu ChiseeNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Notes and Past PapersDocument38 pagesKinematics Notes and Past PapersSuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan Basic Calculus May 12 2020Document13 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan Basic Calculus May 12 2020Leah Mae FranceNo ratings yet
- CNC - Chapter 11 - Offsets & Polar Coordinate SystemDocument10 pagesCNC - Chapter 11 - Offsets & Polar Coordinate Systembarbu ioanNo ratings yet
- Representing Temperature Data on a Number LineDocument17 pagesRepresenting Temperature Data on a Number Linesoundu ranganathNo ratings yet
- Periodical Test q3 EADocument5 pagesPeriodical Test q3 EAJake Lester DafangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 TEST BANKDocument19 pagesChapter 23 TEST BANKAli AlhammadiNo ratings yet
- Molecular Geometries and Bonding Theories: Theodore L. Brown, H. Eugene Lemay, JR., and Bruce E. BurstenDocument30 pagesMolecular Geometries and Bonding Theories: Theodore L. Brown, H. Eugene Lemay, JR., and Bruce E. BurstenPablo BarriosNo ratings yet
- Inmo PreparationDocument2 pagesInmo PreparationVinay KumarNo ratings yet
- Math 131-Spring 13-Course Outline PDFDocument3 pagesMath 131-Spring 13-Course Outline PDFShravan PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Combinatorial Group Theory Magnus PDFDocument2 pagesCombinatorial Group Theory Magnus PDFGlenn0% (3)
- Gyroscope Effects on Ship Steering, Pitching & RollingDocument29 pagesGyroscope Effects on Ship Steering, Pitching & RollingEssKayNo ratings yet
- GeometryDocument3 pagesGeometryFaith Joyrish DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 ReviewerDocument3 pagesPhysics 2 Reviewersamantha cabreraNo ratings yet
- Encyclopedia of Mathematical Physics Vol 1 A C Ed Fran Oise Et Al PDFDocument726 pagesEncyclopedia of Mathematical Physics Vol 1 A C Ed Fran Oise Et Al PDFASARSAT100% (3)
- Cet Vectors 40 With SolutionsDocument5 pagesCet Vectors 40 With SolutionsHNo ratings yet
- Name: Teacher: Date: Score:: Compound ShapesDocument2 pagesName: Teacher: Date: Score:: Compound ShapesMinchi ChiNo ratings yet
- 7464 - Summative Assessment MemorandumDocument8 pages7464 - Summative Assessment MemorandumForbetNo ratings yet
- Derivative FormulasDocument4 pagesDerivative FormulassimomaigaNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Math Curriculum Map for 2nd QuarterDocument3 pagesGrade 10 Math Curriculum Map for 2nd QuarterMary Grace FresnediNo ratings yet
- To Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignFrom EverandTo Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (137)
- Pocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataFrom EverandPocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (22)
- Advanced Modelling Techniques in Structural DesignFrom EverandAdvanced Modelling Techniques in Structural DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)