Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PDF Document
Uploaded by
Ben ChanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PDF Document
Uploaded by
Ben ChanCopyright:
Available Formats
Printed by Jouve, 75001 PARIS (FR)
(19)
E
P
2
0
7
2
3
9
3
A
1
1111111L1L111
(11) EP 2 072 393 A1
(12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION
(43) Date of publication:
24.06.2009 Bulletin 2009/26
(21) Application number: 07024939.6
(22) Date of filing: 21.12.2007
(51) Int Cl.:
B63H 23/24
(2006.01)
H02H 9/00
(2006.01)
H02J 4/00
(2006.01)
H02H 9/08
(2006.01)
(84) Designated Contracting States:
AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR
HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MT NL PL PT RO SE
SI SK TR
Designated Extension States:
AL BA HR MK RS
(71) Applicant: SIEMENS AKTIENGESELLSCHAFT
80333 Mnchen (DE)
(72) Inventor: Van Ravens, Rune
0566 Oslo (NO)
(54) Electrical system for floating installation, in particular offshore vessel, with a feeding
comprising a combined transformer for resistance grounding and transformer pre-
magnetization
(57) Electrical system for floating installation, in par-
ticular offshore vessel, with combined transformer feed-
ing for resistance grounding and transformer pre-mag-
netization
EP 2 072 393 A1
2
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
55
Description
[0001]
1. Which technical problem or which problem
that can be solved with technical means is the
basis for the invention?
1. On floating installations, in particular on off-
shore vessels, earthing of the onboard electrical
system is frequently achieved through high re-
sistance (HR) grounding. i.e. having a resistor
between the system and ground (the steel struc-
ture of the floating installation, e.g. the vessel,
defined as "earth". Resistors can be connected
at the neutral point of one or more generators.
If the quantity of generators is high, it is prefer-
able to connect the resistors to the main switch-
gear via a special transformer. Contrary to a nor-
mal three phase transformer, such HR ground-
ing transformers has a fourth iron core "legs".
This is to allow return path of zero sequence
earth current.
Modern vessels with electrical propulsion power
have increased installed power and resulting distri-
bution transformers that may cause problems of "in
rush" current when connecting "large" transformers.
Separate transformers are been used to pre-mag-
netize transformers from their secondary side prior
to connecting to the main switchgear. Worst case,
one pre-magnetization transformer would be re-
quired for each different secondary side voltage level
of the transformers to be pre-magnetized.
2. How has this problem been solved up to now?
2. As noted above, each main switchboard
would normally require as a minimum one (1)
pre-magnetization transformer with separate
feeder and cables, and one (1) HR grounding
transformers with separate feeder and cables.
On a "dynamically positioned" (DP) vessel (i.e.
keeping at positing with thrusters/ propellers
during operation), one set of feeders and cables
is required per main switchboard (normally 3-4
switchboards).
3. By which technical features of the invention
is the problem named under point 1 solved?
One or more pre-magnetization transformers and
one HR grounding transformer are combined into
one (transformer) unit.
Also one or more pre-magnetization transformers
and more than one HR grounding transformers can
be combined into one (transformer) unit.
In a preferred embodiment, for each main switch-
board, one or more pre-magnetization transformers
and one (or more) HR grounding transformers are
combined into one (transformer) unit.
4. Which advantages are gained by the technical
features of the invention indicated under point
3?
The invention reduces the required main switchgear
feeders and cabling by 50% or better. The reduced
installed equipment results in:
- Reduced procurement cost (CAPEX) for trans-
formers, main switchgear (feeders) and cables.
- Reduced installation as a result of less equip-
ment and cables.
- Reduced weight and space required on the ves-
sel
5. Drawing(s) of example(s) or alternative solu-
tion(s)
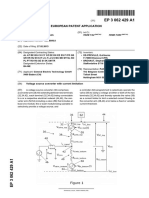
Principal sketch
Fig.1 - Siemens enhanced configuration, yet
separate feeders for HR earthing and pre-mag-
netization
Fig.2 - Configuration with invention, combined
feeders for HR earthing and pre-magnetization
[0002] Abbreviations used in the figures:
HR = High Resistance Resistor
GT = Grounding transformer
PMT = Pre-Magnetization Transformer
(G + PM) T = Combined Grounding + Pre-Magneti-
zation Transformer
Claims
1. Electrical system for floating installation, in particular
offshore vessel, with combined transformer feeding
for resistance grounding and transformer pre-mag-
netization.
1 2
EP 2 072 393 A1
3
EP 2 072 393 A1
4
EP 2 072 393 A1
5
EP 2 072 393 A1
6
EP 2 072 393 A1
7
You might also like
- The Grey Nomads Guide To AustraliaDocument3 pagesThe Grey Nomads Guide To AustraliaFreerangecamping60% (5)
- Cutter Wheel - H1140Document4 pagesCutter Wheel - H1140Sebastián Fernando Canul Mendez100% (2)
- Testatika Princip PDFDocument0 pagesTestatika Princip PDFmanos306No ratings yet
- A Foil Winding Pulse Transformer EP1929489B1Document15 pagesA Foil Winding Pulse Transformer EP1929489B1ourbobbyNo ratings yet
- TEPZZ 9 8Z 8A - T: European Patent ApplicationDocument23 pagesTEPZZ 9 8Z 8A - T: European Patent ApplicationCammy KohNo ratings yet
- SubstationDocument12 pagesSubstationalnemerjassemNo ratings yet
- Railway electrification systems and traction transformationDocument7 pagesRailway electrification systems and traction transformationAry PutraNo ratings yet
- Traction TransformationDocument7 pagesTraction TransformationdabrevipulNo ratings yet
- Power Electronic TransformerDocument7 pagesPower Electronic TransformerNarendra TrivediNo ratings yet
- Capacitor Voltage TransformerDocument12 pagesCapacitor Voltage TransformerThangco HutNo ratings yet
- High Power Frequency Converters For Industrial and Power Plant DrivesDocument11 pagesHigh Power Frequency Converters For Industrial and Power Plant DrivesAminMoghadasiNo ratings yet
- Abb GCB Chapter 9Document9 pagesAbb GCB Chapter 9RagsNo ratings yet
- LHS White Paper Rev ADocument51 pagesLHS White Paper Rev AsemercaNo ratings yet
- Phenomena FerroresonanceDocument7 pagesPhenomena FerroresonanceFarekh HuzairNo ratings yet
- A New High-Efficiency Single-Phase Transformerless PV Inverter TopologyDocument8 pagesA New High-Efficiency Single-Phase Transformerless PV Inverter TopologyMohamed SaidNo ratings yet
- An9506 PDFDocument16 pagesAn9506 PDFAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- Arc Suppression Coils PDFDocument11 pagesArc Suppression Coils PDFmc315895No ratings yet
- HyundaiDocument42 pagesHyundaiwindaidenNo ratings yet
- EP21191279NWA1Document39 pagesEP21191279NWA1NISHANNo ratings yet
- 1MW 20kHz Isolated Bidirectional DC-DC Converter for Renewable EnergyDocument8 pages1MW 20kHz Isolated Bidirectional DC-DC Converter for Renewable EnergyJonxa BalenziagaNo ratings yet
- Scott Conected Power TransformerDocument61 pagesScott Conected Power TransformermanosNo ratings yet
- Ep 15275056 Nwa 1Document53 pagesEp 15275056 Nwa 1Stephane Brehaut PhD Ceng SMIEEENo ratings yet
- Testing of FlybackDocument21 pagesTesting of Flybackdexterconexion1312No ratings yet
- 1mrk513011-Ben en Auxiliary Current Transformer For Radss 1-Phase and 3-Phase Slce 12 Slce 16 Slxe 4Document4 pages1mrk513011-Ben en Auxiliary Current Transformer For Radss 1-Phase and 3-Phase Slce 12 Slce 16 Slxe 4GustavoForsterNo ratings yet
- TRANSFORMER WITH REDUCED HEIGHT, VOLUME AND WEIGHT - European Patent Office - EP 3048623 B1Document6 pagesTRANSFORMER WITH REDUCED HEIGHT, VOLUME AND WEIGHT - European Patent Office - EP 3048623 B1Gokhan KalkanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Propulsion Systems GuideDocument21 pagesElectrical Propulsion Systems GuideAlina NastasaNo ratings yet
- Examples Ferroresonance in High Voltage Power System: N. Jacobson, Membec IEEEDocument7 pagesExamples Ferroresonance in High Voltage Power System: N. Jacobson, Membec IEEE_FlyMan_No ratings yet
- Reliability Main TransformatorDocument18 pagesReliability Main TransformatorSiswoyo SuwidjiNo ratings yet
- 3-Phase AC-Drives With Passive Front-Ends With Focus On The Slim DC-Link TopologyDocument7 pages3-Phase AC-Drives With Passive Front-Ends With Focus On The Slim DC-Link TopologyFrançois SteinmetzNo ratings yet
- Single Phase To Three Phase ConverterDocument5 pagesSingle Phase To Three Phase ConverterGabriel MejiaNo ratings yet
- Transformer - NTDocument108 pagesTransformer - NTSaurabh DubeyNo ratings yet
- 04302522Document6 pages04302522proteccionesNo ratings yet
- VDF CableDocument27 pagesVDF CableENSERZA1No ratings yet
- Alone, FCG-Driven High Power Microwave SystemDocument5 pagesAlone, FCG-Driven High Power Microwave SystempauljansonNo ratings yet
- v42 63Document5 pagesv42 63Bala KumarNo ratings yet
- Workhorses of Industry: Industrial Transformers in A DC EnvironmentDocument7 pagesWorkhorses of Industry: Industrial Transformers in A DC Environmentreza515heiNo ratings yet
- Transformer Design Consideration For Off Line Flyback Converters Using Fairchild Power Switch (FPS™)Document10 pagesTransformer Design Consideration For Off Line Flyback Converters Using Fairchild Power Switch (FPS™)StefanvnvNo ratings yet
- 01 - Wk10 APM Handout Part 1 of 4Document9 pages01 - Wk10 APM Handout Part 1 of 4Iancu DorelNo ratings yet
- United States: (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0313948 A1Document28 pagesUnited States: (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2013/0313948 A1salvor00No ratings yet
- 2010 23 Supercond SC Tech Superconductur Transformer 0953 2048 23-1-014025Document6 pages2010 23 Supercond SC Tech Superconductur Transformer 0953 2048 23-1-014025Sandra ZitzNo ratings yet
- Ece Vii Power Electronics (06ec73) SolutionDocument77 pagesEce Vii Power Electronics (06ec73) SolutionVijay SaiNo ratings yet
- 300 W MOSFET 144 MHZ PA - Final VersionDocument41 pages300 W MOSFET 144 MHZ PA - Final Versionxe1kyaNo ratings yet
- Difference between single and three-phase transformersDocument1 pageDifference between single and three-phase transformersjay shahNo ratings yet
- Final 1Document78 pagesFinal 1Steve JantzenNo ratings yet
- EP2541363B1Document17 pagesEP2541363B1IulianCioarcaNo ratings yet
- Impulse Generator DatasheetDocument4 pagesImpulse Generator DatasheetaprilswapnilNo ratings yet
- Powering Large Scale HFC NetworksDocument8 pagesPowering Large Scale HFC NetworkssshytiNo ratings yet
- IJREAT - Bridgeless Cuk RectifiersDocument11 pagesIJREAT - Bridgeless Cuk RectifiersLeeladhar KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Flyback Transformer - WikipediaDocument5 pagesFlyback Transformer - WikipediaqqazertyNo ratings yet
- Specifications of HV SwitchgearDocument61 pagesSpecifications of HV Switchgeardeepthik27No ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering GuideDocument124 pagesElectrical Engineering GuidesselmtpdrNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Converter Transformer Failure in HVDC SystemsDocument8 pagesAnalysis of Converter Transformer Failure in HVDC Systemshaha2012No ratings yet
- 3 - A - Novel - Nine-Level - Inverter - Employing - One - Voltage - Source - and - Reduced - Components - As - High-Frequency - AC - Power - SourceDocument9 pages3 - A - Novel - Nine-Level - Inverter - Employing - One - Voltage - Source - and - Reduced - Components - As - High-Frequency - AC - Power - Sourcer.ebrahimi1993No ratings yet
- A Guide to Vintage Audio Equipment for the Hobbyist and AudiophileFrom EverandA Guide to Vintage Audio Equipment for the Hobbyist and AudiophileNo ratings yet
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)From EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)No ratings yet
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 3: Switching Power SuppliesFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 3: Switching Power SuppliesNo ratings yet
- It Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingFrom EverandIt Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Influence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesFrom EverandInfluence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Simple StressDocument5 pagesLesson 1 - Simple StressJohn Philip NadalNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual: E2M40 and E2M80 Rotary Vacuum PumpsDocument46 pagesInstruction Manual: E2M40 and E2M80 Rotary Vacuum PumpsVicki NugrohoNo ratings yet
- IIT2019 RIT-1-CPM Chemistry TestDocument15 pagesIIT2019 RIT-1-CPM Chemistry TestPRAKHAR GUPTANo ratings yet
- Binge-Eating Disorder in AdultsDocument19 pagesBinge-Eating Disorder in AdultsJaimeErGañanNo ratings yet
- Technote Torsional VibrationDocument2 pagesTechnote Torsional Vibrationrob mooijNo ratings yet
- 4608 Eed 01Document29 pages4608 Eed 01NickNo ratings yet
- Tyfo SDocument2 pagesTyfo SAndi AsNo ratings yet
- Hedging Techniques in Academic WritingDocument11 pagesHedging Techniques in Academic WritingÛbř ÖňNo ratings yet
- ARES SC4 Service Manual (HP-300UA)Document20 pagesARES SC4 Service Manual (HP-300UA)mike_net8903No ratings yet
- NASA Technical Mem Randum: E-Flutter N78Document17 pagesNASA Technical Mem Randum: E-Flutter N78gfsdg dfgNo ratings yet
- Is Revalida ExamDocument11 pagesIs Revalida ExamRodriguez, Jhe-ann M.No ratings yet
- Uji Deteksi Biofilm Dari Isolat Klinik Kateter Urin Bakteri Entercoccus Dibandingkan Dengan Tube MethodDocument27 pagesUji Deteksi Biofilm Dari Isolat Klinik Kateter Urin Bakteri Entercoccus Dibandingkan Dengan Tube MethodIyannyanNo ratings yet
- G 26 Building Using ETABS 1673077361Document68 pagesG 26 Building Using ETABS 1673077361md hussainNo ratings yet
- 35.2 - ING - El Puente NewsletterDocument13 pages35.2 - ING - El Puente NewsletterIrmali FrancoNo ratings yet
- Revised fire drill performance standardsDocument47 pagesRevised fire drill performance standardsKartikeya GuptaNo ratings yet
- IruChem Co., Ltd-Introduction of CompanyDocument62 pagesIruChem Co., Ltd-Introduction of CompanyKhongBietNo ratings yet
- Sanchez 07 Poles and Zeros of Transfer FunctionsDocument20 pagesSanchez 07 Poles and Zeros of Transfer FunctionsYasmin KayeNo ratings yet
- Surgical InstrumentsDocument4 pagesSurgical InstrumentsWafa L. AbdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- Wirkungen FlechtenstoffeDocument21 pagesWirkungen FlechtenstoffeLogge UliNo ratings yet
- 2021 - Tet Purchase Behavior Report - INFOCUSDocument15 pages2021 - Tet Purchase Behavior Report - INFOCUSGame AccountNo ratings yet
- SSX Diaphragm: Truextent® Replacement Diaphragms For JBL and RADIANDocument2 pagesSSX Diaphragm: Truextent® Replacement Diaphragms For JBL and RADIANIvica IndjinNo ratings yet
- Hot Tub BrochureDocument124 pagesHot Tub BrochureMai Tuan AnhNo ratings yet
- Flame Configurations in A Lean Premixed Dump Combustor With An Annular Swirling FlowDocument8 pagesFlame Configurations in A Lean Premixed Dump Combustor With An Annular Swirling Flowعبدالله عبدالعاطيNo ratings yet
- Synopsis - AVR Based Realtime Online Scada With Smart Electrical Grid Automation Using Ethernet 2016Document19 pagesSynopsis - AVR Based Realtime Online Scada With Smart Electrical Grid Automation Using Ethernet 2016AmAnDeepSinghNo ratings yet
- Hexagon MI GLOBAL S DataSheet Letter EN NAFTA Rel5Document22 pagesHexagon MI GLOBAL S DataSheet Letter EN NAFTA Rel5dudecastro1542No ratings yet
- State of The Art Penelitian - Chat GPT 2023Document137 pagesState of The Art Penelitian - Chat GPT 2023restyNo ratings yet
- GERD – Definition, pathophysiology, epidemiology and diagnostic investigationsDocument132 pagesGERD – Definition, pathophysiology, epidemiology and diagnostic investigationsSorana VasilescuNo ratings yet
- Vishwabhanu Oct '18 - Jan '19Document26 pagesVishwabhanu Oct '18 - Jan '19vedicvision99100% (3)