Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TN06004 LPC2000 Adc
Uploaded by
linhdanhbom6Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TN06004 LPC2000 Adc
Uploaded by
linhdanhbom6Copyright:
Available Formats
TN06004
LPC2000 ADC code example
Paul Seerden 2006 March 27
Technical note
Introduction
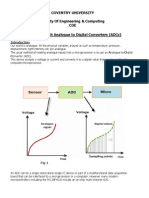
This technical note gives two software examples showing the use the 10-bit A/D converter of the Philips Semiconductors LPC2000 microcontroller family. The examples are written for the LPC2129 (and tested on an MCB2100 board), but are valid for all earlier Philips ARM devices (without individual result registers).
Software controlled start Polling mode
In the first software example all four analog inputs are converted sequentially. UART0 is used to send the conversion results to a PC running a terminal emulator program (for example HyperTerminal). The UART driver routines are not shown in this note. The function ADC_Read() initializes the AD converter, selects the right channel and starts the conversion. Next, it waits for the conversion to be completed and it returns the 10-bit ADC value.
#include <LPC21xx.H>
// LPC21xx definitions
extern void UART0_Init(void); extern void Print12B(unsigned short w); extern void PrintString(const char *s);
static unsigned short ADC_Read(unsigned char ch) { unsigned int i; ADCR = ADCR |= do { i = } while 0x00200300 | ch; 0x01000000; ADDR; ((i & 0x80000000) == 0); // Init ADC (Pclk = 12MHz) and select channel // Start A/D Conversion // Read A/D Data Register // Wait for end of A/D Conversion // bit 6:15 is 10 bit AD value
return (i >> 6) & 0x03FF; } int main(void) { UART0_Init();
// Initialize UART0
PrintString("\nLPC2129 ADC test:\n\n" "AIN0 AIN1 AIN2 AIN3\n\n"); while (1) { Print12B(ADC_Read(1)); PrintString(" "); Print12B(ADC_Read(2)); PrintString(" "); Print12B(ADC_Read(4)); PrintString(" "); Print12B(ADC_Read(8)); PrintString("\r"); } }
// convert and print channel AIN0 // convert and print channel AIN1 // convert and print channel AIN2 // convert and print channel AIN3
Philips Semiconductors
TN06004
LPC2000 ADC code example
Burst mode Interrupt driven
The second example shows the conversion results using the same UART0 (send output) routines. The AD converter however, is now initialized in burst - and interrupt driven mode. In burst mode the AD converter does repeated conversions scanning the input channels selected by the SEL field of the A/D control register ADCR (in our case all four channels of an LPC2129). After every conversion an interrupt (VIC channel 0) is generated. Inside the interrupt handler the CHN (channel) bits of the data register are used to determine which input channel was converted.
#include <LPC21xx.H>
// LPC21xx definitions
extern void UART0_Init(void); extern void Print12B(unsigned short w); extern void PrintString(const char *s); static unsigned short ADCresult[4];
void ADC_Isr(void) __irq { unsigned int r,ch; r = ADDR; ch = (r >> 24) & 0x07; ADCresult[ch] = (r>>6) & 0x03FF; VICVectAddr = 0; } int main(void) { VICVectAddr0 = (unsigned int) &ADC_Isr; VICVectCntl0 = 0x32; // Channel0 on Source#18 ... enabled VICIntEnable |= 0x40000; // 18th bit is the ADC ADCR = 0x0020780F; ADCR |= 0x00010000; UART0_Init(); // Init ADC (Pclk = 12MHz) // start burst mode now, see errata ADC.2 // Initialize UART0 // // // // Read Data Register and clear DONE flag which channel was converted bit 6:15 is 10 bit AD value reset VIC
PrintString("\nLPC2129 ADC test:\n\n" "AIN0 AIN1 AIN2 AIN3\n\n"); while (1) { Print12B(ADCresult[0]); PrintString(" "); Print12B(ADCresult[1]); PrintString(" "); Print12B(ADCresult[2]); PrintString(" "); Print12B(ADCresult[3]); PrintString("\r"); } }
// print result channel AIN0 // print result channel AIN1 // print result channel AIN2 // print result channel AIN3
Philips Electronics N.V. 2006
Application information Applications that are described herein for any of these products are for illustrative purposes only. Philips Semiconductors make no representation or warranty that such applications will be suitable for the specified use without further testing or modification.
You might also like
- Projects With Microcontrollers And PICCFrom EverandProjects With Microcontrollers And PICCRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The I2C Bus SpecificationsDocument46 pagesThe I2C Bus Specificationsshrivastav.ajay100% (14)
- CANopenDocument23 pagesCANopenvdevarajsaran100% (1)
- !! Memory Management Algorithms and Implementation in C C++Document392 pages!! Memory Management Algorithms and Implementation in C C++Anonymous gptX7l0ARXNo ratings yet
- Serial ProgrammingDocument177 pagesSerial ProgrammingkristofwoutersNo ratings yet
- Experiment 10 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) in PIC18F452 ObjectiveDocument10 pagesExperiment 10 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) in PIC18F452 Objectivehira NawazNo ratings yet
- Exp 8Document5 pagesExp 8Ashwini KothavaleNo ratings yet
- LPC1768 ADC Programming TutorialDocument11 pagesLPC1768 ADC Programming Tutorialsiva kumaarNo ratings yet
- ADC Measurement DetailDocument9 pagesADC Measurement DetailMuhammad SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Adc Lab Pic18Document23 pagesAdc Lab Pic18Bolarinwa Joseph100% (1)
- Analog Comparator: PE2 PE3Document16 pagesAnalog Comparator: PE2 PE3Arup NayakNo ratings yet
- Fa20-Bee-150 MP Lab Report - 07Document5 pagesFa20-Bee-150 MP Lab Report - 07Saadat KhanNo ratings yet
- Exploreembedded Com PDFDocument7 pagesExploreembedded Com PDFGonzalo ViñamaguaNo ratings yet
- Fa20-Bee-150 MP Lab Report - 07Document5 pagesFa20-Bee-150 MP Lab Report - 07Saadat KhanNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital Conversion: IntroductionDocument8 pagesAnalog To Digital Conversion: IntroductionKeyur ParekhNo ratings yet
- Data Acq SystemDocument8 pagesData Acq SystemAnonymous kT0ONWNo ratings yet
- Technoblogy - ATtiny85 Bargraph VoltmeterDocument6 pagesTechnoblogy - ATtiny85 Bargraph VoltmeterreynielNo ratings yet
- Analog-to-Digital Conversion: Industrial Embedded SystemsDocument14 pagesAnalog-to-Digital Conversion: Industrial Embedded Systemschandramohan muruganNo ratings yet
- How Do I Use An ADC Peripheral?: HI or LO. For Example, The Button Is Pushed and TheDocument37 pagesHow Do I Use An ADC Peripheral?: HI or LO. For Example, The Button Is Pushed and ThepatelgausNo ratings yet
- ADC PPTDocument28 pagesADC PPTDuoDrenchNo ratings yet
- Topic 13 - ATMega32 ADC in C (ISMAIL - SKE - UTM 2021)Document39 pagesTopic 13 - ATMega32 ADC in C (ISMAIL - SKE - UTM 2021)Aya AmirNo ratings yet
- PIC18f452: Course: ContactDocument13 pagesPIC18f452: Course: ContactMalik Adil FarooqNo ratings yet
- STM32 ADC Tutorial Complete Guide With ExamplesDocument18 pagesSTM32 ADC Tutorial Complete Guide With Examplessuper_faca100% (1)
- Chapter 7 - ADC ModuleDocument17 pagesChapter 7 - ADC ModuleBùi Tùng DươngNo ratings yet
- Assignment Number 2 MPIDocument4 pagesAssignment Number 2 MPISidra AkramNo ratings yet
- United International University: EEE 424: Microprocessor and Interfacing Laboratory Experiment#5Document7 pagesUnited International University: EEE 424: Microprocessor and Interfacing Laboratory Experiment#5Nura Alam ProtikNo ratings yet
- ADC Programming: Va (Vref/2) DvalDocument25 pagesADC Programming: Va (Vref/2) DvalAditya AgarwalNo ratings yet
- T19 AdcDocument11 pagesT19 AdcReyes Benitez LuisNo ratings yet
- Avr AdcDocument6 pagesAvr AdcMohamed SaadNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital Convertor: PIC18f452Document13 pagesAnalog To Digital Convertor: PIC18f452ranaNo ratings yet
- ADC - Eplination and CodeDocument11 pagesADC - Eplination and Codeexcelsis_No ratings yet
- EEET2096 Tutorial Exercises - wk10Document2 pagesEEET2096 Tutorial Exercises - wk10Tyler PetersNo ratings yet
- L7. PIC16F877:ADC MODULE: Lab Notes 7 Mechatronics Lecture Notes by Dr. Can U. DogruerDocument3 pagesL7. PIC16F877:ADC MODULE: Lab Notes 7 Mechatronics Lecture Notes by Dr. Can U. DogruerDomingo Dominguez GonzalezNo ratings yet
- ADC in AVR ATmega16Document7 pagesADC in AVR ATmega16Gaurav Shinde100% (1)
- Lesson Adc PWMDocument36 pagesLesson Adc PWMDavidRubeomNo ratings yet
- ADC Interfacing With MicrocontrollersDocument9 pagesADC Interfacing With MicrocontrollersLuis MezaNo ratings yet
- EST ManualDocument125 pagesEST ManualanandjothimanijothimNo ratings yet
- RM0090 Analog-To-Digital Converter (ADC)Document66 pagesRM0090 Analog-To-Digital Converter (ADC)Hieu PhamNo ratings yet
- Adc Pic18f452Document8 pagesAdc Pic18f452Muhammad Ummair100% (1)
- ADC TutorialDocument58 pagesADC TutorialveerakumarsNo ratings yet
- ADC TutorialDocument12 pagesADC TutorialSathiya NathanNo ratings yet
- PLEASE (NEATLY) SHOW ALL WORK! Comment All Code Well. Do Not Make TheDocument4 pagesPLEASE (NEATLY) SHOW ALL WORK! Comment All Code Well. Do Not Make TheengshimaaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 5 - AnswerDocument32 pagesTutorial Chapter 5 - AnswerHanadia HapendiNo ratings yet
- AdcDocument2 pagesAdcAlex YanzaNo ratings yet
- CED19I032Document20 pagesCED19I032Pranavram VNo ratings yet
- ADC Module: VoltageDocument5 pagesADC Module: VoltageAmmar AlkindyNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller BasicsDocument14 pagesMicrocontroller BasicsholaNo ratings yet
- Embedded C ProgramDocument7 pagesEmbedded C ProgramLucifer100% (1)
- Avr TutorialDocument53 pagesAvr TutorialRakesh Kumar100% (1)
- AVRDocument20 pagesAVRAhsan KhanNo ratings yet
- PIC18F4550 ADC - PIC ControllersDocument9 pagesPIC18F4550 ADC - PIC ControllersKrishanu Modak100% (1)
- 2 AdcDocument13 pages2 AdcM.i. RehmanNo ratings yet
- AVR ADC Interrupt FeatureDocument2 pagesAVR ADC Interrupt FeatureAdrianMartinezMendezNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 3 AdcDocument8 pagesExperiment No 3 AdcDakshata WaghNo ratings yet
- ADC Program For LPC2138Document8 pagesADC Program For LPC2138hypernuclide100% (1)
- A - D ConverterDocument19 pagesA - D Converterask4imadeosas9393No ratings yet
- Course On Microcontrollers (IICT - BUET)Document109 pagesCourse On Microcontrollers (IICT - BUET)Sahariar Bin ShafiqueNo ratings yet
- ADC12Document17 pagesADC12vmtstemorNo ratings yet
- TMS320F2812-Analogue To Digital ConverterDocument26 pagesTMS320F2812-Analogue To Digital ConverterPantech ProLabs India Pvt LtdNo ratings yet
- Development Board For Stm8S003F3: by Nitin Chand M S (2018H1400171P), Rohith Krishnan P (2018H1400180P)Document13 pagesDevelopment Board For Stm8S003F3: by Nitin Chand M S (2018H1400171P), Rohith Krishnan P (2018H1400180P)Thông NguyễnNo ratings yet
- 21 Adc2Document9 pages21 Adc2vishnuksNo ratings yet
- roject mẫu AVR2Document58 pagesroject mẫu AVR2luuvuduc81No ratings yet
- CPR E 381x/382x Lab11aDocument10 pagesCPR E 381x/382x Lab11aHelenNo ratings yet
- Device DriversDocument120 pagesDevice Driversapi-3721578100% (2)
- Distribution of Marks For The Evaluation of Hardware Assignments (Total 40)Document5 pagesDistribution of Marks For The Evaluation of Hardware Assignments (Total 40)api-3721578No ratings yet
- ELF FormatDocument60 pagesELF Formatapi-3721578100% (3)
- C++ Tutorial For C UsersDocument48 pagesC++ Tutorial For C Usersapi-3721578100% (2)
- Device DriverDocument114 pagesDevice Driverapi-3721578100% (2)
- RTOS KernelDocument73 pagesRTOS Kernelapi-3721578100% (4)
- FT01Document4 pagesFT01api-3721578100% (1)
- C/OS-II Reference Manual: #DefineDocument128 pagesC/OS-II Reference Manual: #DefineVramesh4545No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document39 pagesChapter 1api-3721578100% (2)
- Ti Jtag SeminarDocument7 pagesTi Jtag Seminarapi-3721578100% (1)
- Tech Serial v1r0c0 PDFDocument15 pagesTech Serial v1r0c0 PDFsalehimohsen13514969100% (1)
- uCOS ViewDocument48 pagesuCOS Viewapi-3721578No ratings yet
- JTAGDocument124 pagesJTAGshankar1505No ratings yet
- Efficient Programming Techniques For ARMDocument18 pagesEfficient Programming Techniques For ARMapi-3802111100% (1)
- Jtag CableDocument1 pageJtag Cableapi-3721578100% (2)
- Interfacing A MAX6902 RTC With An 8051-Type Microcontroller: DescriptionDocument8 pagesInterfacing A MAX6902 RTC With An 8051-Type Microcontroller: Descriptionapi-3721578100% (3)
- Designing With The Advanced+ Boot Block Flash Memory ArchitectureDocument17 pagesDesigning With The Advanced+ Boot Block Flash Memory Architectureapi-3721578100% (1)
- Interfacing The PC Serial Port RS232Document40 pagesInterfacing The PC Serial Port RS232Sneetsher Crispy100% (16)
- Wriring A KernelDocument32 pagesWriring A Kernelapi-3701437100% (1)
- WP Arm 0103Document7 pagesWP Arm 0103api-3721578No ratings yet
- Compiler Design in CDocument55 pagesCompiler Design in Capi-3825528No ratings yet
- What Is Device DriverDocument8 pagesWhat Is Device Driverapi-26349602No ratings yet
- Real-Time and Embedded GuideDocument177 pagesReal-Time and Embedded Guideapi-3827556100% (3)
- 12 CanDocument39 pages12 Canapi-3721578100% (2)
- Introduction To The Controller Area Network (CAN) : Steve Corrigan HPLDocument17 pagesIntroduction To The Controller Area Network (CAN) : Steve Corrigan HPLRiyas VhNo ratings yet