Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fully CSTR
Uploaded by
Sufian AliOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fully CSTR
Uploaded by
Sufian AliCopyright:
Available Formats
Abstract:
This experiment was performed to develop an understanding about the main principles employed in Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor (CSTR), determine the rate law and residence time for the reaction of Ethyl Acetate with Sodium Hydroxide and to investigate the effect of changing the reactants flow rate on the rate law and the residence time. This was achieved by preparing standard solutions of both reactants which were allowed to be mixed in the CSTR then titrating the resulting mixture with HCl standard solution. Results reveal that as the flow rate of a reactant increases, its conversion increases hence, the rate law increases. The experimental data were unable to predict the actual rate law as a result of some errors and assumptions.
Introduction:
The continuous stirred-tank reactor (CSTR figure (1)), also known as vat or backmix reactor, is a type of reactor used commonly in industrial processing. It is operated continuously, and is used primarily for liquid phase reactions. It is normally operated at steady state and is assumed to be perfectly mixed; consequently, there is no time dependence or position dependence of the temperature, the concentration, or the reaction rate inside the CSTR, that is, every variable is the same at every point inside the reactor. Because the temperature and concentration are identical everywhere within the reaction vessel, they are the same at the exit point as they are elsewhere in the tank. The saponification reaction between ethyl acetate and sodium hydroxide is an elementary, irreversible reaction, so it follows an elementary rate law, in which the reaction order of each species is identical to the stoichiometric coefficient in the chemical equation, thus for the following reaction: NaOH + C 2 H 5 COOCH 3 C 2 H 5 OH + COOCH 3 Na
.Figure 1: CSTR reactor
This experiment was performed to determine the kinetics and reaction rate of the saponification reaction by capacity flow method and to measure the residence time density function of the effluent stream. After that an experimental rate law is found and is compared to literature findings. Procedure included preparation of standard solutions and titration with standard prepared solutions as the reaction takes place in the CSTR. Phenolphthalein indicator was used to determine the end point of titration. Chemical Reactors are commonly classified by the three main characteristics: 1. Mode of operation (e.g., batch, continuous, semi batch) 2. Geometric configuration (e.g., tubular, agitated tank, radial flow) 3. Contacting patterns between phases (e.g., backed bed, fluidized bed, bubble column). Continuous reactor (flow reactors) is a vessel into which reactants are fed continuously and products are withdrawn continuously from it. The chemical
You might also like
- Saponification Reaction of Sodium Hydroxide An Ethyl Acetate in A Continuous-Stirred Tank Reactor (CSTR)Document21 pagesSaponification Reaction of Sodium Hydroxide An Ethyl Acetate in A Continuous-Stirred Tank Reactor (CSTR)drami94100% (13)
- Lab CSTRDocument24 pagesLab CSTRNurtasha Atikah50% (2)
- Kolej Matrikulasi Selangor: Name: Practicum: Lecturer'S Name: Date SubmittedDocument4 pagesKolej Matrikulasi Selangor: Name: Practicum: Lecturer'S Name: Date SubmittedLeevandraaNo ratings yet
- Batch Reactor (Saponification) ExptDocument3 pagesBatch Reactor (Saponification) ExptVijay Prasad0% (1)
- Kluber PresentationDocument79 pagesKluber PresentationZegera MgendiNo ratings yet
- AMS2460ADocument14 pagesAMS2460AAndres DelaCruz100% (3)
- Chlorine Institute Manual 2000Document68 pagesChlorine Institute Manual 2000Misael RamírezNo ratings yet
- Experiment CSTR 40LDocument18 pagesExperiment CSTR 40LSaber Minato Azrul100% (2)
- 1.1 AbstractDocument25 pages1.1 AbstractZati TarhiziNo ratings yet
- CSTR 40 LDocument20 pagesCSTR 40 LMuhammad NasrulNo ratings yet
- CSTRDocument19 pagesCSTRAmir Al-AimanNo ratings yet
- CSTR ManualDocument11 pagesCSTR ManualMelly FulaNo ratings yet
- PFR Lab ReportDocument16 pagesPFR Lab Reportcog0812No ratings yet
- BNBBHBHBHJBJHDocument25 pagesBNBBHBHBHJBJHZati TarhiziNo ratings yet
- CSTR 40LDocument11 pagesCSTR 40LSeiji Kyousei100% (1)
- CH142L - Experiment 1Document17 pagesCH142L - Experiment 1Allyssa BadilloNo ratings yet
- Group 4 - Report Experiment 2Document26 pagesGroup 4 - Report Experiment 2Farzanah AgeNo ratings yet
- CRE LabDocument14 pagesCRE Labahmad RaoNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 Plug FlowDocument29 pagesLab 3 Plug FlowHikaru MokaNo ratings yet
- CSTR 40LDocument16 pagesCSTR 40LhishamNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument24 pagesLab ManualAasia FarrukhNo ratings yet
- Discussion Conclusion RecommendationDocument2 pagesDiscussion Conclusion RecommendationFaiz BasriNo ratings yet
- Plug Flow ReactorDocument15 pagesPlug Flow ReactorSeiji Kyousei91% (11)
- PFR Lab ReportDocument21 pagesPFR Lab ReportValentinoDullSatin100% (1)
- Batch Reactor Manual PDFDocument4 pagesBatch Reactor Manual PDFPradeep DiwakarNo ratings yet
- CSTR Rep.Document7 pagesCSTR Rep.Mohammad MdardasNo ratings yet
- Student 4 Mini Project (Reaction Engineering)Document7 pagesStudent 4 Mini Project (Reaction Engineering)Muhammad KasyfiNo ratings yet
- Laminar Flow Reactor ProblemDocument6 pagesLaminar Flow Reactor ProblemAileen Banua Añonuevo100% (1)
- CSTR 40 LDocument28 pagesCSTR 40 LCik Tiem Ngagiman50% (2)
- Module 06 Plug Flow Reactor (PFR)Document4 pagesModule 06 Plug Flow Reactor (PFR)Farah -HNo ratings yet
- FullDocument33 pagesFullEja RotiKeju100% (2)
- CSTR 40LDocument17 pagesCSTR 40LMuhammad Affifudin100% (1)
- Saponification Reaction of Sodium Hydroxide An Ethyl Acetate in A Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor CSTRDocument21 pagesSaponification Reaction of Sodium Hydroxide An Ethyl Acetate in A Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor CSTRsyedmuhammadtarique100% (1)
- Final Report PFRDocument12 pagesFinal Report PFRmark_ancotNo ratings yet
- Abstract, Intro-Cstr in SeriesDocument2 pagesAbstract, Intro-Cstr in SerieshishamNo ratings yet
- 4 - (PFR BP101)Document15 pages4 - (PFR BP101)Aisyah Addia AzizanNo ratings yet
- Liquid Phase Chemical Reactor FinalDocument38 pagesLiquid Phase Chemical Reactor FinalToMemNo ratings yet
- Plug Flow ReactorDocument28 pagesPlug Flow ReactorNurul AinNo ratings yet
- Liquid Phase ReactorDocument22 pagesLiquid Phase Reactorkrishy19s100% (2)
- Intro Lab Report Process Modelling & SimulationDocument3 pagesIntro Lab Report Process Modelling & SimulationSelly The SpiceNo ratings yet
- LAB Plug FlowDocument24 pagesLAB Plug FlowZalina SamsuddinNo ratings yet
- Plug Flow ReactorDocument16 pagesPlug Flow ReactorN Afiqah RazakNo ratings yet
- CRE Lab ManualDocument19 pagesCRE Lab ManualMayursinh Solanki100% (1)
- CKB 20104 Reaction Engineering UniKL MICET Experiment 2a Effect of RTD On The Reaction in CSTR Full Lab ReportDocument29 pagesCKB 20104 Reaction Engineering UniKL MICET Experiment 2a Effect of RTD On The Reaction in CSTR Full Lab ReportSiti Hajar Mohamed100% (6)
- Reaction Lab Exp#1Document13 pagesReaction Lab Exp#1Muataman KhNo ratings yet
- C STR Kinetics 2012Document12 pagesC STR Kinetics 2012JpojNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Law Parameters Study of Saponification Reaction Using Integral MethodDocument5 pagesKinetic Law Parameters Study of Saponification Reaction Using Integral MethodZaid YahyaNo ratings yet
- Tubular LabDocument6 pagesTubular LabDanny NguyenNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Laboratory Ii: /DT Term Is Zero SinceDocument9 pagesChemical Engineering Laboratory Ii: /DT Term Is Zero SinceKayathre Raveendran100% (1)
- Objective Theory Apparatus Procedure Result Sample of Calculation Discussion Conclusion Recommendation Reference AppendicesDocument19 pagesObjective Theory Apparatus Procedure Result Sample of Calculation Discussion Conclusion Recommendation Reference Appendicesahmad pidotNo ratings yet
- Effect of Operating Conditions On CSTR Performance: An Experimental StudyDocument5 pagesEffect of Operating Conditions On CSTR Performance: An Experimental Studyahmed nawazNo ratings yet
- CSTR 40LDocument12 pagesCSTR 40LMohamad SyamilNo ratings yet
- KineticsDocument5 pagesKineticsCiela Jane GeraldizoNo ratings yet
- Sample Lab ReportljDocument10 pagesSample Lab ReportljDavid DavisNo ratings yet
- PFR ReactorDocument19 pagesPFR Reactorkhairi100% (1)
- A Comparative Study of Saponification Reaction in A PFR and CSTRDocument6 pagesA Comparative Study of Saponification Reaction in A PFR and CSTRAmyNo ratings yet
- 5 - (CSTR Bp143)Document12 pages5 - (CSTR Bp143)Aisyah Addia AzizanNo ratings yet
- Intro CSTRDocument6 pagesIntro CSTREmmanuel PlazaNo ratings yet
- Plug Flow ReactorDocument16 pagesPlug Flow Reactormirdza94No ratings yet
- PFRDocument19 pagesPFRKangae IlhamNo ratings yet
- Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor (40 L)Document16 pagesContinuous Stirred Tank Reactor (40 L)Mohd Zhariff75% (4)
- Batch ReactorDocument4 pagesBatch ReactorHarini BugattiveyronNo ratings yet
- Wa0002.Document78 pagesWa0002.Dipanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Comparison of The Use of Rutile and Cellulosic Electrodes - TWIDocument11 pagesComparison of The Use of Rutile and Cellulosic Electrodes - TWISumantaNo ratings yet
- Microbial Cell FactoriesDocument11 pagesMicrobial Cell FactoriesthemarkmirNo ratings yet
- Basic Molecules of LifeDocument78 pagesBasic Molecules of LifeRavi ParkheNo ratings yet
- QCR W 2001Document4 pagesQCR W 2001Madhan KannanNo ratings yet
- Understanding Oscillatory Behaviour of Gibbsite Precipitation CircuitsDocument12 pagesUnderstanding Oscillatory Behaviour of Gibbsite Precipitation CircuitsPRACHIPRAVA PRADHANNo ratings yet
- Kelvin Lau MWI +RRDocument18 pagesKelvin Lau MWI +RRUniversityJCNo ratings yet
- High Strength Precipitation Hardening and Duplex Stainless Steel Bolting For Special Purpose ApplicationsDocument6 pagesHigh Strength Precipitation Hardening and Duplex Stainless Steel Bolting For Special Purpose ApplicationsDanZel DanNo ratings yet
- Catalog AU480 1Document2 pagesCatalog AU480 1Trần Anh TuấnNo ratings yet
- Expancel Microspheres BoudDocument14 pagesExpancel Microspheres BoudChris BothaNo ratings yet
- 078-Mahoney-URANIO CALIBRACIONDocument32 pages078-Mahoney-URANIO CALIBRACIONNeider BurgosNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 4 - Module 2 - Week 2 Behavior of Gases Part 2Document20 pagesScience: Quarter 4 - Module 2 - Week 2 Behavior of Gases Part 2Mary Ann100% (1)
- US6783609Document13 pagesUS6783609ceyhun kilicNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2samy.anesuNo ratings yet
- 1st Sem Mid Term PYQs 2018&2019Document20 pages1st Sem Mid Term PYQs 2018&2019Sujeet RaiNo ratings yet
- Export Promotion Council (EPC) For LeatherDocument25 pagesExport Promotion Council (EPC) For Leathersiddharthjain9149No ratings yet
- TLC Staining Procedure TLC Stain Recipe Stain Chemistry / Physics CommentsDocument3 pagesTLC Staining Procedure TLC Stain Recipe Stain Chemistry / Physics CommentsLara DiasNo ratings yet
- Adjuvant SDocument33 pagesAdjuvant SNugroho HartonoNo ratings yet
- 4 WP 2013Document8 pages4 WP 2013TUTORKIMNo ratings yet
- Quick Guide PCRDocument78 pagesQuick Guide PCRapi-3862223No ratings yet
- Corrosion Control - Jack-Up - SP-CO-ENG-CON-06-01Document37 pagesCorrosion Control - Jack-Up - SP-CO-ENG-CON-06-01evenNo ratings yet
- Le Ngoc Lieu - Chapter 1 - DehydrationDocument117 pagesLe Ngoc Lieu - Chapter 1 - DehydrationThuỳ TrangNo ratings yet
- Indian BOE Coaching Services: Gujarat BOE-2016 Paper-2 (Boiler Engg-2) SolutionDocument7 pagesIndian BOE Coaching Services: Gujarat BOE-2016 Paper-2 (Boiler Engg-2) SolutionAlok DoshiNo ratings yet
- Class Notes of Amino Acid MetabolismDocument49 pagesClass Notes of Amino Acid MetabolismShivanand Mali100% (1)
- Chem 162 Formal Lab ReportDocument5 pagesChem 162 Formal Lab ReportLiem LimantoNo ratings yet
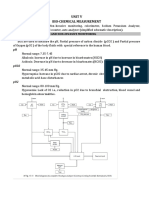
- Unit V BIO-CHEMICAL MEASUREMENTDocument8 pagesUnit V BIO-CHEMICAL MEASUREMENTAleeshaNo ratings yet