Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 8
Uploaded by
Juni FarhanaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 8
Uploaded by
Juni FarhanaCopyright:
Available Formats
1. 2. 3.
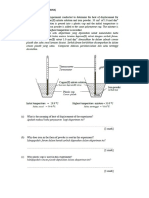
CHAPTER 8: SALTS WHO IS SALT ? WHAT IS SALT ? WHO IS SALT ? Ionic compound formed when the hydrogen ion, H+ from an acid is replaced by a metal ion or an ammonium ion, NH4+
4.
REFER TEXT BOOK : PAGE 138 EXAMPLE : replace Na+ Na+ ClMetal ions Sodium chloride H Cl replace NH4+ NH4+ ClAmmonium ion Ammonium chloride
5.
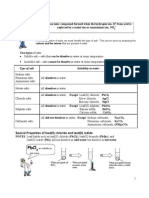
SALTS CONSIST ANION PART COMES FROM THE ACID WHILE CATION PART COMES FROM BASES Common anions (parent acids) Common cations HCl Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Fe2+ HNO3 K+ Cu2+ Al3+ Zn2+ H2CO3 NH4+ Fe3+ Pb2+ H2SO4
6. 7. 8.
METAL ION DISPLACE H+ ION IN ACIDS
All nitrate salts ; soluble salts ALL NO3-
9.
SOLUBLE SALT All Na+, K+, NH4+ salts ; soluble salts ALL
Na+, K+, NH4+ SOLUBLE SALT 10. All carbonate salts ; insoluble salts EXCEPT CO32ALL INSOLUBLE SALT EXCEPT Na+, K+, NH4+ 11. All SO42-, Cl- salts ; soluble salts EXCEPT EXCEPT EXCEPT ALL ALL Pb2+ Ag+ Hg2+ Pb2+ Ca 2+ Ba2+ ClSO42SOLUBLE SALT SOLUBLE SALT 12. 13. INSOLUBLE SALT SOLUBLE SALT PbSO4 ALL SO42CaSO4 ALL BaSO4 ALL NO3CO32ALL ClAgCl ALL PbCl2 Na+, K+, NH4+ CLASSIFICATION OF SALTS 14. PREPARATION OF SALTS SOLUBLE SALTS INSOLUBLE SALTS NEUTRALISATION
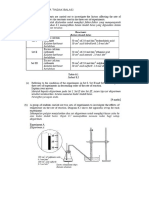
OTHER METHOD PRECIPITATION ACID + METAL ACID + ALKALI SOLUBLE SALT + SOLUBLE SALT ACID + METAL OXIDE [SPA] Sodium ,Na+ salts Potassium, K+ salts Ammonium, NH4+ salts INSOLUBLE SALT & SOLUBLE SALT ACID + METAL CARBONATE OTHER SOLUBLE SALTS 15. PREPARATION OF SOLUBLE SALTS [ SODIUM SALTS / POTASSIUM SALTS / AMMONIUM SALTS ] NEUTRALISATION REACTION EXAMPLE PREPARATION OF POTASSIUM CHLORIDE K OH H Cl Cl K H2O ALKALI ACID SALTS TITRATION METHOD FIND OUT THE EXACTLY VOLUME OF ACID REQUIRED TO NEUTRALISE ALKALI. END POINT POINT WHEN INDICATOR CHANGES COLOUR DURING TITRATION NOTE : CONCENTRATION AND VOLUME OF ALKALI ARE KNOWN. 16. LET DO THIS: PREPARATION OF POTASSIUM CHLORIDE APPARATUS : Pipette 25mL, Burette 50mL, Conical Flask 250 mL MATERIALS : Potassium hydroxide 1.0 M, Hydrochloric acid 1.0 M, Phenolphthalein Use a pipette to transfer 25.0 cm3 of potassium hydroxide solution to a conical flask. Add 2 to 3 drops of phenolphthalein Fill a burette with hydrochloric acid and record the initial burette reading. Slowly adding the acid into the conical flask and swirls- until the indicator turns from pink to colourless. Record the volume of acid used. (V cm3) Record the final burette reading in 2d.p Colourless KOH turn to pink. Record the burette reading in 2d.p 17. PREPARATION OF POTASSIUM CHLORIDE START OVER AGAIN BUT WITHOUT INDICATOR : To get the pure and neutral salt solution
Pipette 25.0 cm3 of the same potassium hydroxide solution into a conical flask. Do not add any indicator. From the burette, add exactly V cm3 of hydrochloric acid to the alkali and swirls and shake well. RECRYSTALLISATION PROCESS [PURIFIED SOLUBLE SALTS] HEATING/EVAPORATE COOLING FILTRATION DRY Solution salt contains impurities continuous with recrystallisation process CRYSTAL SALT 18. PREPARATION OF SOLUBLE SALTS [ OTHER SALTS EXCEPT Na+, K+, NH4+] OTHER METHOD : DISSOLVE METAL IN ACID Pour 50 cm3of sulphuric acid into a beaker. Warm the acid Use a spatula to add copper(II) oxide powder bit by bit into the acid. Stir the mixture well. Continue adding copper(II) oxide until some of it no longer dissolves(excess unreacted metal Metal/ metal oxide/ metal carbonate Excess unreactedmetal (residue) Glass rod Acid Evaporating basin with salt solution (filtrate) Solution salt contains impurities continuous with recrystallisation process See the change of metal solid colour and dissolve 19. RECRYSTALLISATION PROCESS [PURIFIED SOLUBLE SALTS] HEATING/EVAPORATE COOLING Salt solution Evaporating basin Crystal salt 20. RECRYSTALLISATION PROCESS [PURIFIED SOLUBLE SALTS] FILTRATION DRY CRYSTAL SALT These physical characteristics:
o o o
Regulars geometry shapes, such as cubic or hexagonal. Flat faces, straight edges and sharp angles. Same angle between adjacent faces. Glass rod Rinse with distilled water Filter Paper Salt Cystals The crystals are filtered and rinsed with a little cold distilled water.
21. DISSOLVE SOLUTE IN ACID PREPARATION OF SOLUBLE SALTS
NEUTRALISATION REACTION 1ST TITRATION WITH INDICATOR FIND VOLUME OF ACID HEATING DISSOLVE METAL IN ACID TRANSFER TO EVAPORATING BASIN EXCESS METAL NOT DISSOLVE COMPLETE REACT 2ND TITRATION NO INDICATOR GET PURE SALT recrystalisation HEATING/EVAPORATE COOLING FILTRATION DRY CRYSTAL SALT 22. PREPARATION OF INSOLUBLE SALTS [ ALL CARBONATE SALTS except Na+/K+/NH4+ ] PbSO4 / CaSO4/ BaSO4/PbCl2/ AgCl] PRECIPITATION REACTION PREPARATION OF LEAD(II) CHLORIDE EXAMPLE Pb NO3 Na Cl Cl2 Pb NO3 Na SOLUBLE SALTS SOLUBLE SALTS INSOLUBLE SALTS DOUBLE DECOMPOSITION METHOD TWO AQUOUES SOLUTIONS/SOLUBLE SALTS WERE MIX TOGETHER INTERCHANGE TO PRODUCE TWO NEW COMPOUND WHICH IS INSOLUBLESALT OR PRECIPITATE, AND AQUEOUS SOLUTION/SOLUBLE SALTS 23. PRECIPITATION REACTION two aquoues solutions/soluble salts were mix together [one of the solutions contains the cations of the insoluble salt] [one of the solutions contains the anions of the insoluble salt] the ions of the two aqueous solutions above interchange to produce two new compound which is insoluble salt or precipitate, and aqueous solution 24. PRECIPITATION REACTION Glass rod Glass rod Distilled water Mixture solutions
Filter paper Precipitate (residue) Precipitate (residue) Filter funnel Retort stand Aqueous Solution (filterate) Rinse : remove other ions from precipitate Filtration : Remove solution from precipitate FILTRATION RINSE 25. PRECIPITATION REACTION FLOW CHART : PREPARATION OF INSOLUBLE SALTS Precipitate/Soluble salts Filter paper MIX - STIR TWO SOLUBLE SALTS Dry : Dried by pressing between two pieces of filter paper. FILTRATION REMOVE FILTRATE RINSE REMOVE OTHER IONS DRY PRESS BETWEEN FILTER PAPER 26. PREPARATION OF SALTS REMEMBER : METAL ION DISPLACE HYDROGEN ION IN ACID TO FORMED SALTS HCl [H+/Cl-] Hydrochloric acid METAL / AMMONIUM ION Na+ Ca2+ Zn2+ HNO3 [H+/NO3-] Nitric Acid K+ Al3+ Pb2+ H2SO4 [2H+/SO42-] Nitric Acid NH4+ Mg2+ Cu2+ H2CO3 [2H+/CO32-] Nitric Acid Fe2+ Fe3+ 27. SUMMARIES OF REACTION
28. EXTRA INFO : REMEMBER Reactive metal is magnesium, aluminium, and zinc. Unreactivemetal is iron, lead, silver Metal that is less reactive from hydrogen such as copper, lead and silver did not react with dilute acid. Soluble salts of sodium, potassium and ammonium can be prepared by the reaction between an acid and alkali. 29. EXTRA INFO : REMEMBER Metal, metal oxide and metal carbonate is a solid that cannot dissolves in water, hence during reaction that solid must be added excessively to make sure all hydrogen ions in acid is completely reacted. Excess solid can be expelling through filtration. Unreactive metal such as lead (Pb), copper (Cu), and silver (Ag) cannot react with dilute acid. So to prepare salt contains lead ions (Pb2+), copper ions (Cu2+) or silver ions (Ag+), we must use either oxide powder or carbonate powder only. Impure soluble salt can be purified through crystallization process 30. Copyright 2010 AlchemistFreestyle.blogspot.com
Andromendas Rizal + FOLLOW
2006 views, 4 favs, 2 embeds more
Related
Salts460 views
Acids And Bases8034 views
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- SLB Dowel Drilling FluidsDocument27 pagesSLB Dowel Drilling FluidsMohamed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Batch Manufacturing RecordDocument7 pagesBatch Manufacturing RecordAnu JoshiNo ratings yet
- Salt Reduction Guide For The Food Industry PDFDocument82 pagesSalt Reduction Guide For The Food Industry PDFperunikicaNo ratings yet
- H&M Lab ManualDocument220 pagesH&M Lab ManualDyeing Dyeing91% (11)
- Consumer-Chem Q1 Mod2 Properties-of-Common-Chemicals v3Document16 pagesConsumer-Chem Q1 Mod2 Properties-of-Common-Chemicals v3Shane TabalbaNo ratings yet
- Latihan Gabungan Alkana N AlkenaDocument6 pagesLatihan Gabungan Alkana N AlkenaJuni FarhanaNo ratings yet
- Sodium Chloride - CrystallizationDocument8 pagesSodium Chloride - CrystallizationVatra ReksaNo ratings yet
- Struk TurDocument38 pagesStruk TurJuni FarhanaNo ratings yet
- Struk TurDocument38 pagesStruk TurJuni FarhanaNo ratings yet
- Modul Ulangkaji Form 4Document69 pagesModul Ulangkaji Form 4KHARTHIKA78% (9)
- CHAPTER 6 +chapter 7Document5 pagesCHAPTER 6 +chapter 7Juni FarhanaNo ratings yet
- Graf Fungsi 5k2 GalusDocument2 pagesGraf Fungsi 5k2 GalusJuni FarhanaNo ratings yet
- Paper 3 SPM 2011 Mastery PracticesDocument31 pagesPaper 3 SPM 2011 Mastery PracticesJuni FarhanaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 +chapter 7Document5 pagesCHAPTER 6 +chapter 7Juni FarhanaNo ratings yet
- ANALISIS PAPER 3 CHEMISTRY - Docx 10'4Document14 pagesANALISIS PAPER 3 CHEMISTRY - Docx 10'4Juni FarhanaNo ratings yet
- ANALISIS PAPER 3 CHEMISTRY - Docx 10'4Document14 pagesANALISIS PAPER 3 CHEMISTRY - Docx 10'4Juni FarhanaNo ratings yet
- Modul Amali Kertas 3 F4 2015Document9 pagesModul Amali Kertas 3 F4 2015acik5596No ratings yet
- ElectroplatingDocument3 pagesElectroplatingJuni FarhanaNo ratings yet
- Esei F5 Trial SPM 2015Document34 pagesEsei F5 Trial SPM 2015Juni FarhanaNo ratings yet
- An Experiment Is Conducted To Determine The Rate of Reaction Between 25 CMDocument3 pagesAn Experiment Is Conducted To Determine The Rate of Reaction Between 25 CMJuni FarhanaNo ratings yet
- Modul Galus Chem 2014Document83 pagesModul Galus Chem 2014Juni Farhana100% (2)
- Pecutan Sebatian Karbon SPM 2016Document8 pagesPecutan Sebatian Karbon SPM 2016Juni FarhanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Acids N BasesDocument6 pagesChapter 7 Acids N BasesJuni FarhanaNo ratings yet
- Quiz MathematicsDocument2 pagesQuiz MathematicsJuni FarhanaNo ratings yet
- Preparation and Purification of Soluble SaltsDocument12 pagesPreparation and Purification of Soluble SaltsJuni FarhanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document7 pagesChapter 8Juni FarhanaNo ratings yet
- Chap 05Document4 pagesChap 05Jamaliah Daud100% (5)
- Chapter 8 SaltDocument2 pagesChapter 8 SaltJuni FarhanaNo ratings yet
- Notes Updates Salts2Document33 pagesNotes Updates Salts2Juni FarhanaNo ratings yet
- Topik 7 Kertas 1Document34 pagesTopik 7 Kertas 1Arbayana AmbranNo ratings yet
- Desalination of Wall Painting in The Kaiserdom in Koenigslutter FinalDocument10 pagesDesalination of Wall Painting in The Kaiserdom in Koenigslutter FinalCamelia CostinNo ratings yet
- The Synthesis of Azo DyesDocument12 pagesThe Synthesis of Azo DyesJaveed GanaieNo ratings yet
- Review of RL or Rs FinalDocument3 pagesReview of RL or Rs FinalAllen Rod CuesoNo ratings yet
- 4ch0 w19 QP 1cDocument28 pages4ch0 w19 QP 1cTamannaNo ratings yet
- IS 9000 Part 11Document13 pagesIS 9000 Part 11Suvro ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Kubota 2420Document70 pagesKubota 2420Dodik E. Prasetyo100% (1)
- Drilling Fluids Inc Brine FluidsDocument19 pagesDrilling Fluids Inc Brine FluidsAgum Gumelar SoinandiNo ratings yet
- Original Evercrete Formula: PropertiesDocument2 pagesOriginal Evercrete Formula: PropertiesJose AndreNo ratings yet
- Experiment 9-Ion Exchange ChromatographyDocument2 pagesExperiment 9-Ion Exchange ChromatographyAlma Pabilane100% (3)
- CL FE HandoutsDocument59 pagesCL FE HandoutsweldsvNo ratings yet
- Salts in Crude Oil (Electrometric Method) : Standard Test Method ForDocument6 pagesSalts in Crude Oil (Electrometric Method) : Standard Test Method ForDennise ChicaizaNo ratings yet
- Pre-Test 1Document6 pagesPre-Test 1Jenelyn Lanang DiariosNo ratings yet
- Utilization of Brine Sludge in Non-Traffic Paver Blocks: by Gaurav PathakDocument21 pagesUtilization of Brine Sludge in Non-Traffic Paver Blocks: by Gaurav PathakgauravNo ratings yet
- Study On Preparation & Development of Cookies Enriched With Mint Leaf (Mentha) PowderDocument7 pagesStudy On Preparation & Development of Cookies Enriched With Mint Leaf (Mentha) PowderHasib HasanNo ratings yet
- Procederes For Cleaning and DisinfectionDocument14 pagesProcederes For Cleaning and DisinfectionBayu KristyonoNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Acids and Alkalis Information SheetsDocument22 pages7.1 Acids and Alkalis Information Sheetsdana hadadNo ratings yet
- English Trenton Wax Tape SystemsDocument16 pagesEnglish Trenton Wax Tape SystemsTaylorNo ratings yet
- 2012 TrialDocument9 pages2012 TrialCin D NgNo ratings yet
- Water Salinity Detection Using A Smartphone: February 2017Document10 pagesWater Salinity Detection Using A Smartphone: February 2017Difa LaudzaNo ratings yet
- Guide To Selecting Salt Tolerant PlantsDocument40 pagesGuide To Selecting Salt Tolerant PlantsfaafoNo ratings yet
- Measurement Uncertainty Evaluation of Salinity Sensing Through Water Electrical Conductivity Method by Gravimetric ValidationDocument10 pagesMeasurement Uncertainty Evaluation of Salinity Sensing Through Water Electrical Conductivity Method by Gravimetric ValidationAriska AnjalniNo ratings yet