Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Work Breakdown Structure
Uploaded by
Salman ShaikhOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Work Breakdown Structure
Uploaded by
Salman ShaikhCopyright:
Available Formats
Work Breakdown Structure 1) In order to successfully accomplish both contract and corporate objectives, a plan is required that defines
all effort to be expended, assigns responsibility to a specially identified organizational element, and establishes schedules and budgets for the accomplishment of the work. After project requirements definition, the first major step in the planning process is the development of the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS). 2) A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a product-oriented family tree subdivision of the hardware, services, and data required to produce the end product. The Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is structured in accordance with the way the work will be performed and reflects the way in which project costs and data will be summarized and eventually reported. 3) Preparation of the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) also considers other areas that require structured data, such as scheduling, configuration management, contract funding, and technical performance parameters. It is the single most important element because it provides a common framework from which: Total program can be described as a summation of subdivided elements Planning can be performed Costs and budgets can be established Time, cost, and performance can be tracked Objectives can be linked to company resources in a logical manner Schedules and status-reporting procedures can be established Network construction and control planning can be initiated Responsibility assignments for each element can be established
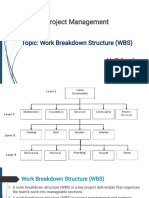
4) The Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) acts as a vehicle for breaking the work down into smaller elements, thus providing a greater probability that every major and minor activity will be accounted for. 5) Although a variety of Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) exist, the most common is the six-level indented structure shown as Figure below:
6) As the figure shows, Level 1 is the total program and is composed of a set of projects. The summation of the activities and costs associated with each project must equal
the total program. Each project, however, can be broken down into tasks, where the summation of all tasks equals the summation of all projects, which, in turn, comprises the total program. The reason for this subdivision of effort is simply ease of control. 7) The top three levels of the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) reflect integrated efforts and should not be related to one specific department. Effort required by departments or sections should be defined in subtasks and work packages. 8) At level 5, the work packages should be identifiable and homogeneous. A work package is simply a low-level task or job assignment. It describes the work to be accomplished by a specific performing organization or a group of cost centres and serves as a vehicle for monitoring and reporting progress of work. 9) Program management therefore, becomes synonymous with the integration of activities, and the project manager acts as the integrator, using the work breakdown structure as the common framework. It is important that careful consideration must be given to the design and development of the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS).
You might also like
- Work Breakdown Structure W BsDocument12 pagesWork Breakdown Structure W BsyudiNo ratings yet
- Work Breakdown Structure WBSDocument12 pagesWork Breakdown Structure WBSQamar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Work Breakdown StructureDocument3 pagesWork Breakdown Structureroshan034No ratings yet
- Work Breakdown Structure W BsDocument12 pagesWork Breakdown Structure W BsAtul JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Work Breakdown-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesWork Breakdown-WPS OfficeamanuelNo ratings yet
- Work Breakdown StructureDocument8 pagesWork Breakdown StructurerenshagullNo ratings yet
- CM 1 WBS PartthDocument21 pagesCM 1 WBS PartthPartth JayyNo ratings yet
- Project Management Systems Engineering Project: o o o o oDocument4 pagesProject Management Systems Engineering Project: o o o o okaranchouhanNo ratings yet
- Work Breakdown StructureDocument8 pagesWork Breakdown StructureYael Leví100% (1)
- Work Breakdown StructureDocument4 pagesWork Breakdown Structuregogus79No ratings yet
- Steel ManualDocument30 pagesSteel ManualMohamed AtefNo ratings yet
- Chapter-: Project PlanningDocument4 pagesChapter-: Project PlanningGolamSarwarNo ratings yet
- 2c Chapter RevisedDocument6 pages2c Chapter RevisedlehlabileNo ratings yet
- Work Breakdown Structure WBSDocument26 pagesWork Breakdown Structure WBSSiddharth SawhneyNo ratings yet
- WBS InfoDocument17 pagesWBS InfoKaren ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 23-24 F21 ReadingDocument8 pagesLecture 23-24 F21 ReadingSyedkaram AlinaqviNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 PMDocument61 pagesAssignment 2 PMInfant RajNo ratings yet
- PM Chapter-4Document4 pagesPM Chapter-4GolamSarwarNo ratings yet
- 200 Organization: Project Control System ManualDocument11 pages200 Organization: Project Control System ManualRafael Fernandez SanchezNo ratings yet
- Work Breakdown StructureDocument2 pagesWork Breakdown StructureDselvam DhanaNo ratings yet
- Work Breakdown StructureDocument9 pagesWork Breakdown StructurezubairbalochNo ratings yet
- Sadsign ReportDocument14 pagesSadsign ReportJanith SimyunnNo ratings yet
- Project Planning PDFDocument7 pagesProject Planning PDFMohammad TooneerNo ratings yet
- Work Breakdown StructureDocument3 pagesWork Breakdown Structuredonraghu07No ratings yet
- Lect3wbsobs 181128081410Document21 pagesLect3wbsobs 181128081410EstebanNo ratings yet
- PV3Pages From VisualMilestonePlanningCopy-3Document4 pagesPV3Pages From VisualMilestonePlanningCopy-3EstebanNo ratings yet
- M2 Defining The ProjectDocument22 pagesM2 Defining The ProjectMarcos JeremyNo ratings yet
- Project Cost Control Jul 02Document23 pagesProject Cost Control Jul 02Dexter DuronNo ratings yet
- Project Management: A Managerial Approach: by Lalit Kumar SharmaDocument26 pagesProject Management: A Managerial Approach: by Lalit Kumar SharmaUjjwal ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)Document15 pagesWork Breakdown Structure (WBS)Haseeb HassanNo ratings yet
- WBS Chapt 8Document21 pagesWBS Chapt 8Anjum hayatNo ratings yet
- Work Breakdown StructureDocument25 pagesWork Breakdown StructureQURAN PAK TilawatNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 5 1 NotesDocument8 pagesUnit 5 5 1 NotesSarthak kadamNo ratings yet
- Oup3 Ce159Document10 pagesOup3 Ce159richard mooreNo ratings yet
- Work Breakdown Structure - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 pagesWork Breakdown Structure - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaBaguma Grace GariyoNo ratings yet
- Cost Code & WBSDocument8 pagesCost Code & WBSsprinter792100% (1)
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) : 7:30pm-9:00pmDocument2 pagesWork Breakdown Structure (WBS) : 7:30pm-9:00pmNievesAlarconNo ratings yet
- Sap Ps End User Manual Step by StepDocument133 pagesSap Ps End User Manual Step by Stepblimao198175% (4)
- Project Management: Topic: Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) Uot AcademyDocument13 pagesProject Management: Topic: Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) Uot AcademyHAMZA ALINo ratings yet
- Module 2aDocument6 pagesModule 2afourty twoNo ratings yet
- Project ManagementDocument40 pagesProject Managementkebaman1986No ratings yet
- Using The Work Break Down Structure To Plan A ProjectDocument12 pagesUsing The Work Break Down Structure To Plan A ProjectDry IceNo ratings yet
- 5.4.1 Create WBS: Inputs 5.4.1.1 Scope Management PlanDocument8 pages5.4.1 Create WBS: Inputs 5.4.1.1 Scope Management PlanUsman GhaniNo ratings yet
- Work Breakdown Structure GuideDocument12 pagesWork Breakdown Structure GuidewajidNo ratings yet
- SMJ - PROJ - Sessions 5&6 - WBS, Gantt Chart, RACI, 6 April 2019, vFINALDocument36 pagesSMJ - PROJ - Sessions 5&6 - WBS, Gantt Chart, RACI, 6 April 2019, vFINALgazi kutub uddinNo ratings yet
- PAE Ch-3 Project-PlanningDocument39 pagesPAE Ch-3 Project-PlanningProf. Dr. Anbalagan ChinniahNo ratings yet
- Defining ProjectDocument22 pagesDefining ProjectAsif HameedNo ratings yet
- Project Management: Lecture 3 Serwan TalabaniDocument35 pagesProject Management: Lecture 3 Serwan TalabaniShkar GalalyNo ratings yet
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) : Create WBS: Inputs, Tools & Techniques, and OutputsDocument5 pagesWork Breakdown Structure (WBS) : Create WBS: Inputs, Tools & Techniques, and OutputshkaqlqNo ratings yet
- Innovation and Program Management in Aerospace and Defense IndustryDocument7 pagesInnovation and Program Management in Aerospace and Defense IndustryWajdi Jalal Osman KambalNo ratings yet
- Wbs and RbsDocument10 pagesWbs and RbsalPha BlaCkNo ratings yet
- Project PlanningDocument39 pagesProject PlanningDoc Rishibha BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Chapter5 Project PlanningDocument38 pagesChapter5 Project PlanningSanchit BatraNo ratings yet
- 5.4 Create WBS: Figure 5-9 Figure 5-10Document9 pages5.4 Create WBS: Figure 5-9 Figure 5-10Lauren RosimoNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Project Management: The Quick Reference HandbookFrom EverandIntroduction to Project Management: The Quick Reference HandbookNo ratings yet
- TOGAF® 10 Level 2 Enterprise Arch Part 2 Exam Wonder Guide Volume 2: TOGAF 10 Level 2 Scenario Strategies, #2From EverandTOGAF® 10 Level 2 Enterprise Arch Part 2 Exam Wonder Guide Volume 2: TOGAF 10 Level 2 Scenario Strategies, #2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Table CalenderDocument12 pagesTable CalenderSalman ShaikhNo ratings yet
- MLA Sea Sheep Snapshot 2017Document4 pagesMLA Sea Sheep Snapshot 2017Salman ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Kashmir Report - Pankhuri EditedDocument4 pagesKashmir Report - Pankhuri EditedSalman ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Trade GroupsDocument1 pageTrade GroupsSalman ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Life Is About ChoicesDocument3 pagesLife Is About ChoicesSalman ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Supertall Buildings BulletinDocument14 pagesSupertall Buildings BulletinSalman ShaikhNo ratings yet
- India LogisticsDocument14 pagesIndia Logisticsagupta76No ratings yet
- Amul - A Live Case of Use of ITDocument3 pagesAmul - A Live Case of Use of ITSalman ShaikhNo ratings yet
- What Do U PossesDocument1 pageWhat Do U PossesSalman ShaikhNo ratings yet
- MKTG & Biz Plan - Griffiths-3Document10 pagesMKTG & Biz Plan - Griffiths-3Salman ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Plastim Corporation Cost AccountingDocument12 pagesPlastim Corporation Cost AccountingSalman ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Numismatics Books: Indira Gandhi National Centre For The Arts, New Delhi, India 1Document1 pageNumismatics Books: Indira Gandhi National Centre For The Arts, New Delhi, India 1Salman ShaikhNo ratings yet
- In The Indian Tax StructureDocument2 pagesIn The Indian Tax StructurelovemethewayiamNo ratings yet
- Operation Research PrintoutDocument10 pagesOperation Research PrintoutSalman ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Key Constraints Analysis With Integrated Production SchedulerDocument12 pagesKey Constraints Analysis With Integrated Production SchedulerQiping DingNo ratings yet
- Deep Feed-Forward Neural NetworkDocument4 pagesDeep Feed-Forward Neural NetworkAnkit MahapatraNo ratings yet
- Unit4-MaximumPrinciple ImportantDocument18 pagesUnit4-MaximumPrinciple ImportantFathi MusaNo ratings yet
- Applications of Deep Learning For Phishing Detection A Systematic Literature ReviewDocument44 pagesApplications of Deep Learning For Phishing Detection A Systematic Literature ReviewBernardNo ratings yet
- Review: Deep Learning Methods For Cybersecurity and Intrusion Detection SystemsDocument6 pagesReview: Deep Learning Methods For Cybersecurity and Intrusion Detection SystemsChaima BelhediNo ratings yet
- Ant Colony Optimization: 22c: 145, Chapter 12Document38 pagesAnt Colony Optimization: 22c: 145, Chapter 12Binoy NambiarNo ratings yet
- PMBOK Chapter-6 Project Schedule ManagementDocument41 pagesPMBOK Chapter-6 Project Schedule ManagementPMS BDNo ratings yet
- SQA NOTES Unit 1Document16 pagesSQA NOTES Unit 1Madala GuruNo ratings yet
- Intoduction To Artificial IntelligenceDocument66 pagesIntoduction To Artificial IntelligenceDarajjee DhufeeraaNo ratings yet
- 01 - Introduction To Class - For PrintingDocument41 pages01 - Introduction To Class - For Printing小蓁No ratings yet
- Rice Syllabus - Neural ComputationDocument2 pagesRice Syllabus - Neural ComputationsurfingbananaNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence Lecture No. 5Document42 pagesArtificial Intelligence Lecture No. 5Sarmad RehanNo ratings yet
- IEC62304.2006 CheckListDocument8 pagesIEC62304.2006 CheckListJeffery Wunady0% (1)
- Chapter 12 - Information Systems DevelopmentDocument27 pagesChapter 12 - Information Systems DevelopmentSelena ReidNo ratings yet
- Cover L-NLPDocument2 pagesCover L-NLPYohannesNo ratings yet
- Dynamical Models of LoveDocument5 pagesDynamical Models of LoveJunel HerreraNo ratings yet
- Module-23 - Nyquist Stability Criterion: EE3101-Control Systems EngineeringDocument7 pagesModule-23 - Nyquist Stability Criterion: EE3101-Control Systems EngineeringhariNo ratings yet
- Total Quality ManagementDocument1 pageTotal Quality Managementanon-594335No ratings yet
- Internal Logistics Ow Simulation: A Case Study in Automotive IndustryDocument22 pagesInternal Logistics Ow Simulation: A Case Study in Automotive IndustryBranimir ZivanovicNo ratings yet
- Use of Deep Learning in Modern Recommendation System: A Summary of Recent WorksDocument6 pagesUse of Deep Learning in Modern Recommendation System: A Summary of Recent WorksJanardhan ChNo ratings yet
- CNN Building BlocksDocument14 pagesCNN Building BlocksANAND M (RA2113003011032)No ratings yet
- HOW TO LPA R2V2 31 Mar 17Document23 pagesHOW TO LPA R2V2 31 Mar 17Lotfi RaboudiNo ratings yet
- Understanding Consumer Behavior With Recurrent Neural NetworksDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Consumer Behavior With Recurrent Neural NetworksfpttmmNo ratings yet
- Software Design and Architecture: BY: Shahab Ul IslamDocument20 pagesSoftware Design and Architecture: BY: Shahab Ul IslamSyed hasan haiderNo ratings yet
- UML Activity DiagramDocument13 pagesUML Activity DiagramMuqaddas RasheedNo ratings yet
- Toyota Inventory ManagementDocument26 pagesToyota Inventory ManagementHarshGarbyal63% (16)
- Practised Test CasesDocument3 pagesPractised Test CasesDeepthireddyNo ratings yet
- SE Lecture - 1Document56 pagesSE Lecture - 1arhamNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence PDFDocument2 pagesArtificial Intelligence PDFNokiaNo ratings yet
- Orientation On Software TestingDocument37 pagesOrientation On Software TestingInfaum EduTechNo ratings yet