Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Traing and Development
Uploaded by
Bini MathewOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Traing and Development
Uploaded by
Bini MathewCopyright:
Available Formats
INTRODUCTION
If you don't know where you are going, any road will take you there. - Lewis Carroll in Alice's Adventure in Wonderland (1865).
Give a man a fish, and you have given him meal. Teach man to catch fish, and you have given him a livelihood. This ancient Chinese proverb seems to describe the underlying rationale of all training and development programme. No industrial organization can long ignore the training and development needs of its employees without seriously inhibiting its performance. Even the most careful selection does not eliminate the need for training, since people are not moulded to specifications and rarely meet the demands of their jobs adequately. Poverty stricken India spends $45 billion on training each year. Expenditures of such magnitudes call for a periodic sharp look. Training in particular needs such scrutiny. TRAINING It refers to the acquisition of knowledge, skills, and competencies as a result of the teaching of vocational or practical skills and knowledge that relates to specific useful skills. It forms the core of apprenticeships and provides the backbone of content at technical colleges and polytechnics. Today it is often referred to as professional development. Training is primarily concerned with preparing people for certain activities delineated by technology and by the organization and settings in which they work. Education helps students to choose their activities. Training helps participants to improve their performance. Education deals mostly knowledge and understanding. Training deals mostly with understanding, skill and action. Training embraces an understanding of the complex processes by which various factors that make up a situation interact. Training is the most important activity or plays an important role in the development of human resources. To put the right man at the right place with the trained personnel has now become essential in todays globalize market. No organization has a choice on whether or not to develop employees. Therefore training has nowadays become an important and required factor for maintaining and improving interpersonal and inter- group collaboration. Human resource is the life blood of any organization. Only through well-trained personnel, can an organization achieve its goals.
Training is defined as learning that is provided in order to improve performance on the present job. A person's performance is improved by showing her how to master a new or established technology. The technology may be a piece of heavy machinery, a computer, a procedure for creating a product, or a method of providing a service. Training is provided for the present job. This includes training new personnel to perform their job, introducing a new technology, or bringing an employee up to standards. Training is mainly concerned with the meeting of two of these inputs -- people and technology. That is, having people learn to master a given technology. DEVELOPMENT This term is often viewed as a broad, ongoing multi-faceted set of activities (training activities among them) to bring someone or an organization up to another threshold of performance. This development often includes a wide variety of methods, e.g., orienting about a role, training in a wide variety of areas, ongoing training on the job, coaching, mentoring and forms of self-development. Some view development as a life-long goal and experience. Training & Development is the field concerned with workplace learning to improve performance. Such training can be generally categorized as on-the-job or off-the-job. On-the-job describes training that is given in a normal working situation, using the actual tools, equipment, documents or materials that they will use when fully trained. On-the-job training is usually most effective for vocational work. Off-the-job training takes place away from normal work situation which means that the employee is not regarded as productive worker when training is taking place. An advantage of off-the-job training is that it allows people to get away from work and totally concentrate on the training being given. This type of training is most effective for training concepts and ideas. At a glance, we find that training gives the following results: 1) 2) Growth, expansion and modernization cannot take place without trained manpower. It increases productivity and profitability, reduces cost and finally enhances skill and
knowledge of the employee. 3) 4) 5) Prevents obsolescence. Helps in developing a problem solving attitude. Gives people awareness of rules and procedures.
6) 7) 8) 9) 10) 11)
Builds better communications skills. Develops hidden talent. Ensures consistent quality. Provides greater focus. Produces more effective/productive efforts. Clarifies the concept of marketing as a business process.
TYPICAL REASONS FOR EMPLOYEE TRAINING AND DEVELOPMENT Training and development can be initiated for a variety of reasons for an employee or group of employees, e.g. When a performance appraisal indicates performance improvement is needed. To "benchmark" the status of improvement so far in a performance improvement effort. As part of an overall professional development program. As part of succession planning to help an employee be eligible for a planned change in role
in the organization. To "pilot", or test, the operation of a new performance management system. To train about a specific topic.
GENERAL BENEFITS FROM EMPLOYEE TRAINING AND DEVELOPMENT There are numerous reasons for supervisors to conduct training among employees. These reasons include: Increased job satisfaction and morale among employees Increased employee motivation Increased efficiencies in processes, resulting in financial gain Increased capacity to adopt new technologies and methods Increased innovation in strategies and products Reduced employee turnover Enhanced company image, e.g., conducting ethics training. Risk management, e.g., training about sexual harassment, diversity training
DETERMINATION OF TRAINING NEEDS In order to determine the training needs of an organization the HRD manager should seek information on the following points: a) b) c) Whether training is needed? Where training is needed? Which training is needed?
Whether training is needed? Training result from problems such as: Standards of work performance not being met; Accidents; Excessive scrap; High rate of transfer and turnover; Too many low ratings on employee evaluation reports; Many people using different methods to do the same job; Excessive fatigue, fumbling, struggling with the job; Bottlenecks and deadlines not being met;
In many organizations the determination of training needs is predominantly done through observations. One common method for recording observations is the check- list of training needs. It provides for indicating by a Yes or No check. Where training is needed? After determining the need for training the manager should determine where the organization training emphasis can and should be placed. This involves a detailed analysis of the following factors: i. ii. iii. iv. Structure of the organization, Objectives, Human resource and future plans, and Cultural milieu.
Which training is needed? The last question to be answered by the personnel manager is about the type of training needed. This involves determining what knowledge, skills or attitudes each individual employee should develop to be able to perform his task in an effective way. The three major skills which the employees of any organization need to successfully discharge their duties are: the conceptual skill, the human relations skill and the technical skill. Conceptual skill deals with ideas, technical skill with things and human skill with people. WHAT IS GOOD TRAINING The three typical beneficiaries of a training programme are the managers and supervisors of trainees, trainees themselves and external customers. Each beneficiary has his own requirements and perception of what is good training. Thus, the senior managers and supervisors want training to be low in cost, to increase employees job performance, to improve their attitudes and morale and to be minimally disruptive to the work in terms of promotion or compensation. Trainees want the training to be of high quality which can be easily transferred to the job. They want the training venue to be more pleasant than the job venue and expect training work place to benefit them personally. Last, though not the least important are external beneficiaries who want the training to result into high quality products and services, but do not want training to interfere with the fulfillment of their needs for example, a bank customer wants high quality customer service from tellers but does not want a trainee teller to take a few moments longer than usual with a transaction. The HRD manager must address all the above needs of different beneficiaries throughout the training process. METHODS OF TRAINING No simple formula defines the form of training to be used for a given purpose. The skills needs of operatives, the size and traditions of the company, the abilities of trainers, the time and the money available for training and the experience of the company about the training activities that have been carried on in the past, will affect the type of training that will be most successful in a given situation. Nevertheless it will be helpful to indicate briefly the principal alternatives from which the manager may choose:1) On- the- job training The most important type of training is On- the job training. The
experience of actually doing something makes a lasting impression and has a reality that other types of training cannot provide. The worker in this method learns to master the operations involved on
the actual job situation under the supervision of his immediate boss. Some important advantages of this type of training are as follows :a) b) c) It can be learned in a relatively short period of time, say, a week or two. It is highly economical. It is not located in an artificial situation, either physically or psychologically and, therefore,
eliminates the possible problem of transfer of learning. There are several types of training programmes which make use of on-the-job training concept. Some of them are described below: 2) Job rotation Internship training Apprenticeship Vestibule Training: - This method attempts to duplicate on the job situation in a company
classroom training, which is often imparted with the help of equipment and machines, which are identical with those in use in the place of work. It is very efficient method of training semiskilled personnel, particularly when many employees have to be training for the same kind of work. 3) Learning by seeing or demonstration method :- In this method , the trainer describes and
display something ,as when he teaches an employee how to do something by actually performing the activity himself and by going through step by step explanation of why and how he is doing . Demonstration are very effective in teaching because it is much easier to show a person how to do a job then ask him to gather instructions from the reading materials, discussion etc. 4) Simulation: - Simulation is a technique, which duplicates, as nearly as possible, the actual
conditions encountered on the job. The training is essential in cases which actual on the job practice might result in a serious injury, a costly error, or the destruction of valuable materials or resources. 5) Class-room or off-the-job training: - Off-the job training is not a part of everyday job
activity. The actual location may be in the company classroom or in places which are owned by the company. These methods consists of : Lectures Conferences Group discussions Case studies
Role-playing Programmed instructions Laboratory trainings
TRAINING PLAYS THE FOLLOWING ROLES IN AN ORGANIZATION 1) Increase in efficiency: Training plays active role in increasing efficiency of employees in an
organization. Training increases skills for doing a job in better way. Though an employee can learn many things while he is put on a job, but he can do much better if he learns how to do the job. This becomes more important specially in the context of changing technology because the old method working may not be relevant. 2) Increase in morale of employees: - Morale is a mental condition of an individual or group,
which determines the willingness to cooperate. High morale is evidenced by employee enthusiasm voluntary conformation with regulations and willingness to cooperate with others to achieve organizational objectives. Training increases employee morale by relating their skills with their job requirements. Trained employees can see job in more meaningful ways because they are able to relate their kills with job. 3) Reduced Supervision: Trained employees require less supervision. They require more
autonomy and freedom. Such autonomy and freedom can be given if the employees are trained properly to handle their jobs without the help of supervision. 4) Increased organizational viability and flexibility: Trained people are necessary to maintain
organizational viability and flexibility. Viability relates to survival of the organization during bad days, and flexibility relates to sustain its effectiveness despite the loss of its key personnel and making short-term adjustment with the existing personnel. Such adjustment is possible if the organization has trained people who can occupy the positions vacated by key personnel.
BENEFITS OF TRAINING Training benefits the organization in manifold ways: 1. Benefits to organization: Leads to improved profitability and more positive attitudes toward profit orientation. Improves the job knowledge and skills at all levels of the organization.
Improves the morale of the workforce. Helps people identify with organizational goals. Helps create a better corporate image. Fosters authenticity, openness, and trust. Aids in organizational development. Learns from the training. Helps keep costs down in many areas, example production, personnel, administration etc. Develops a sense of responsibility to the organization for being competent and
knowledgeable. 2. Improves labour management relations. Helps employee adjust to change. Aids in handling conflict, thereby helping to prevent stress and tension. Benefits to the individual which in turn ultimately benefit the organization: Helps the individual in making better decisions an effective problem solving. Through T&D, motivational variables of recognition, achievement, growth, responsibility and
advancement are internalized and operationalized. Aids in encouraging and achieving self development and self confidence. Helps a person handle stress, tension, frustration and conflict. Provides information for improving leadership knowledge, communication skills and
attitudes. 3. Increase job satisfaction and recognition. Satisfy personal needs of the trainer. Helps eliminate fear in attempting new task. Benefits in personnel and human resources: Improves communication between groups and individual. Aids in orientation for new employees and those taking new jobs through transfer and
promotion. Provides information on equal opportunity and affirmative action.
Improves inter personal skills. Improves morale. Builds cohesiveness in groups. Provides a good climate for learning, growth and co ordination. Makes organization policies, rules and regulations viable. Makes the organization a better place to work and live.
TRAINING PROCEDURE 1) Identify training needs: - These are certain steps that are performed for training the
employees. The first step is to identify T&D needs. In this step we arrange and obtain support for the contribution of T&D to organizational strategy. Then we identify organizational T&D needs. Thereafter we agree priorities for developing the T&D function. These sub steps are followed by identifying the current competence of individuals of individuals and agreeing individuals and group priorities or learning. 2) Design T&D strategies and plans: - The second step is to design T&D strategies and plans. In
this step first we identify resources required to implement a strategic plans and specify an operational plan that meets organizational requirements and further designing learning programs that meet learning needs and test, adapt and agree learning program designs. 3) Provide learning opportunities resources and support: - The third step is to provide learning
opportunities resources and support. In this we obtain and allocate resources to meet the requirement of Training and development plans. Then prepare and present demonstrations and information to co-ordinate and assist the preparation and delivery of learning opportunities. 4) Evaluate effectiveness of T&D:-Fourth step in training is to evaluate the effectiveness of
T&D, which involves plan setup, evaluate, and modify the learning plans. Then assess, co-ordinate, verify and identify previously acquired competence. 5) Support T&D advances and practice: - And last step is to support T&D advances and practice.
This includes evaluating and disseminating advances in T&D. Then we administer training facilities and after that establish and maintain information system.
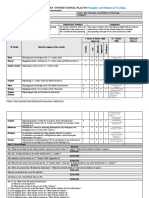
BLOCK DIAGRAM OF TRAINING PROCEDURE
You might also like
- Training and DevelopmentDocument21 pagesTraining and DevelopmentJohn Mutyiri100% (1)
- HRM - 5th Week - Lecture HandoutDocument8 pagesHRM - 5th Week - Lecture HandoutProf. Jomar MariquitNo ratings yet
- BBCT 3023 Asgmt 2Document16 pagesBBCT 3023 Asgmt 2Ammd noorNo ratings yet
- Employee Training: DefinitionsDocument19 pagesEmployee Training: DefinitionsHari NaghuNo ratings yet
- Nature of Training and DevelopmentDocument6 pagesNature of Training and DevelopmentMd Iqbal Hossen Shemul100% (1)
- Human Resource DevelopmentDocument21 pagesHuman Resource DevelopmentsmitNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 Theoritical Frame WorkDocument22 pagesChapter - 3 Theoritical Frame WorkNarasimhaPrasadNo ratings yet
- Training at ONGCDocument33 pagesTraining at ONGCNaveen Poonia100% (2)
- Training and Development HotelDocument57 pagesTraining and Development Hoteljassi nishad100% (1)
- Training and Development Hotel VelenDocument57 pagesTraining and Development Hotel VelenSalman Raza100% (1)
- R of LDocument33 pagesR of LRaja SekharNo ratings yet
- Training and Development in NALCO (Final Report)Document76 pagesTraining and Development in NALCO (Final Report)subhashree688% (8)
- Training and DevelopmentDocument36 pagesTraining and DevelopmentManishaNo ratings yet
- Training and Development Activities at BrandixDocument87 pagesTraining and Development Activities at Brandixfaisal gazi89% (9)
- Training and DevelopmentDocument25 pagesTraining and DevelopmentamrithNo ratings yet
- Training and Devlopment Voltas Ltd. Final PrintDocument81 pagesTraining and Devlopment Voltas Ltd. Final PrintPrabhat SharmaNo ratings yet
- Training & Development Short NoteDocument13 pagesTraining & Development Short NoteloharsudhakarNo ratings yet
- TRAINING AND DEVELOPMENT - JerseyDocument66 pagesTRAINING AND DEVELOPMENT - JerseyVenugopal VutukuruNo ratings yet
- HRM - 5th Week - Lecture NotesDocument15 pagesHRM - 5th Week - Lecture NotesProf. Jomar MariquitNo ratings yet
- Training and Development in InfosysDocument34 pagesTraining and Development in Infosyskrupamayekar92% (13)
- Employee Training and DevelopmentDocument12 pagesEmployee Training and DevelopmentHạnh NguyênNo ratings yet
- 489 Ea 2 A 2602 C 432Document57 pages489 Ea 2 A 2602 C 432Gautham BgmNo ratings yet
- Project Report Employees Training AND DevelopmentDocument28 pagesProject Report Employees Training AND DevelopmentSahil MahajanNo ratings yet
- Leson 3Document28 pagesLeson 3ladosehrawatNo ratings yet
- HRM ProjectDocument26 pagesHRM Projectguptasoniya247No ratings yet
- Impotance of TrainingDocument25 pagesImpotance of TrainingDANIEL CHEKOL100% (1)
- Training and DevelopmentDocument6 pagesTraining and Developmentbhagathnagar100% (1)
- Study On Training and Development in INFOSYSDocument34 pagesStudy On Training and Development in INFOSYSPrateek Maratha100% (1)
- Literature Review On Employee Training and DevelopmentDocument13 pagesLiterature Review On Employee Training and DevelopmentMizanur Rahman Peash100% (1)
- Chapter 1Document31 pagesChapter 1Kiran kumar SahuNo ratings yet
- Importance of Training and DevelopmentDocument4 pagesImportance of Training and DevelopmentAnnaIzzatNo ratings yet
- Strategic/ Systematic Approach To Training For Human Resource DevelopmentDocument18 pagesStrategic/ Systematic Approach To Training For Human Resource DevelopmentSapna RaiNo ratings yet
- HRDDocument102 pagesHRDhakimmajidabbas6706No ratings yet
- 2.0 Training, Development and Education (T&D)Document6 pages2.0 Training, Development and Education (T&D)NANTHININo ratings yet
- HRM Training & DevelopmentDocument47 pagesHRM Training & DevelopmentGosai JaydeepNo ratings yet
- Gopi ProjectDocument33 pagesGopi ProjectlooserNo ratings yet
- Training and DevelopmentDocument18 pagesTraining and Developmentsimply_cooolNo ratings yet
- Training & Development ProjectDocument22 pagesTraining & Development ProjectRagucharan RajNo ratings yet
- Bhawna Singh FileDocument72 pagesBhawna Singh FileMayankRohillaNo ratings yet
- The Need For Employees Training and Development in An OrganizationDocument17 pagesThe Need For Employees Training and Development in An OrganizationTom NaveenNo ratings yet
- Training Need IdentificationDocument11 pagesTraining Need IdentificationSukhdev Sharma100% (1)
- Training and DevelopmentDocument19 pagesTraining and Developmentsavita100% (1)
- Importance of Training and DevelopmentDocument14 pagesImportance of Training and DevelopmentAXian TanveerNo ratings yet
- Tand D 2Document68 pagesTand D 2Hari NaghuNo ratings yet
- Lesson 01 Introduction To Training Development & EducationDocument25 pagesLesson 01 Introduction To Training Development & EducationAnne Proffitt100% (2)
- Sobika Project 1Document99 pagesSobika Project 1Lingeswaran PNo ratings yet
- Training and DevelopmentDocument46 pagesTraining and DevelopmentAbhijeet DeyNo ratings yet
- MCOMDocument15 pagesMCOMmadhudubey011981No ratings yet
- Training and DevelopmentDocument3 pagesTraining and DevelopmentM RABOY,JOHN NEIL D.No ratings yet
- Training: Place of Training in Company ManagementDocument10 pagesTraining: Place of Training in Company ManagementThariqAhammedNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology Company Profile 4) Data Analysis 5) Findings 6) RecommendationDocument70 pagesResearch Methodology Company Profile 4) Data Analysis 5) Findings 6) RecommendationJohnNo ratings yet
- Definition of Training DevelopmentDocument15 pagesDefinition of Training DevelopmentBlizkriegNo ratings yet
- M M M MDocument36 pagesM M M MPriyanka Rutul PatelNo ratings yet
- Training and DevelopmentDocument18 pagesTraining and Developmenteldhopaul19894886No ratings yet
- Complete Training and Development Notes For MBA HRDocument206 pagesComplete Training and Development Notes For MBA HRJames Ross100% (1)
- Project On Training & Development in HBLDocument61 pagesProject On Training & Development in HBLPinnam MallikarjunaNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Employee Training Guide- Training Today, Leading TomorrowFrom EverandThe Ultimate Employee Training Guide- Training Today, Leading TomorrowNo ratings yet
- Certified Training Instructor ProfessionalFrom EverandCertified Training Instructor ProfessionalRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Modern Methods of Vocational and Industrial TrainingFrom EverandModern Methods of Vocational and Industrial TrainingNo ratings yet
- Learning and Development: How To Close The Skills Gap in Your OrganizationFrom EverandLearning and Development: How To Close The Skills Gap in Your OrganizationNo ratings yet
- The Employment Market in IndiaDocument2 pagesThe Employment Market in IndiaBini MathewNo ratings yet
- Balance of Payments AccountingDocument6 pagesBalance of Payments AccountingBini MathewNo ratings yet
- Recent Development in Global Financial MarketDocument8 pagesRecent Development in Global Financial MarketBini MathewNo ratings yet
- Exchange Rate DeterminationDocument18 pagesExchange Rate DeterminationBini MathewNo ratings yet
- 20150306110342assignment Instructions (PPB3143 - 1 2014 2015)Document3 pages20150306110342assignment Instructions (PPB3143 - 1 2014 2015)Seth HowardNo ratings yet
- Independent StudyDocument1 pageIndependent Studyapi-217676054No ratings yet
- Research On Student EmploymentDocument434 pagesResearch On Student EmploymentKheng VichetNo ratings yet
- Annual ReportDocument69 pagesAnnual Reportkathir_adminNo ratings yet
- IEP Format SampleDocument10 pagesIEP Format SampleChristine Joy PamaNo ratings yet
- Social Work 2011 2016Document10 pagesSocial Work 2011 2016Joseph MalelangNo ratings yet
- The Almost Blanks SlateDocument10 pagesThe Almost Blanks SlateMateo AcostaNo ratings yet
- FET Oral RubricsDocument4 pagesFET Oral RubricsRonald PresherNo ratings yet
- A Profile of Elementary Social Studies Teachers and Their ClassroomsDocument9 pagesA Profile of Elementary Social Studies Teachers and Their ClassroomsMhin MhinNo ratings yet
- Platos Prayer To Pan PDFDocument12 pagesPlatos Prayer To Pan PDFAlex MadisNo ratings yet
- Master of Management in EU Funds DMWDocument12 pagesMaster of Management in EU Funds DMWAzoska Saint SimeoneNo ratings yet
- Impact of Emotional Intelligence On Employees PerformanceDocument24 pagesImpact of Emotional Intelligence On Employees Performancedanamaria13100% (2)
- Sample Demo Lesson Plan in Principles and Methods of TeachingDocument3 pagesSample Demo Lesson Plan in Principles and Methods of TeachingJun PontiNo ratings yet
- Freshman Orientation AgendaDocument2 pagesFreshman Orientation Agendaapi-257131514No ratings yet
- What Objective TestsDocument3 pagesWhat Objective TestsVanessa Gabica TaliNo ratings yet
- Individual Performance Commitment and Review Form Ipcrf 2018-2019Document2 pagesIndividual Performance Commitment and Review Form Ipcrf 2018-2019OLIVIA C.NERONANo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document7 pagesChapter 3Rico Jon Hilario Garcia100% (1)
- Philippine Christian University: Reflection On BehaviorismDocument5 pagesPhilippine Christian University: Reflection On BehaviorismJem AguilarNo ratings yet
- General PhysicsDocument6 pagesGeneral PhysicsCris CarriedoNo ratings yet
- DREYFUS, Hubert L. Heidegger, Authenticity and Modernity - Essays in Honor of Hubert L. Dreyfus V1Document424 pagesDREYFUS, Hubert L. Heidegger, Authenticity and Modernity - Essays in Honor of Hubert L. Dreyfus V1Guilherme Pereira100% (5)
- Cpa 7 - 1Document4 pagesCpa 7 - 1api-584365435No ratings yet
- Inventories For Diagnosing School CultureDocument30 pagesInventories For Diagnosing School CultureJutamanee Ae KraikunasaiNo ratings yet
- George Couros' CVDocument5 pagesGeorge Couros' CVGeorge CourosNo ratings yet
- Adorno On EducationDocument24 pagesAdorno On Educationintern980No ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Chemistry For Examination From 2023Document4 pagesCambridge O Level: Chemistry For Examination From 2023Syed AsharNo ratings yet
- Steppingstones 2Document2 pagesSteppingstones 2api-350726106No ratings yet
- Culturally Relevant UsaDocument14 pagesCulturally Relevant UsaNitin BhardwajNo ratings yet
- CBRC CertificateDocument1 pageCBRC CertificateAlanlovely Arazaampong AmosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Lesson 3 School and Community Relations: CTP 106: The Teaching Profession Submitted By: Janis Ian S. DelfinoDocument5 pagesChapter 2 - Lesson 3 School and Community Relations: CTP 106: The Teaching Profession Submitted By: Janis Ian S. Delfinoᜐᜋᜒ ᜀᜈᜓNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal PresentationDocument51 pagesProject Proposal PresentationVina Dapog100% (1)