Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH 38: Antiviral Drugs I: Depression and Suicidal Thoughts
Uploaded by
sarah_smith1Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CH 38: Antiviral Drugs I: Depression and Suicidal Thoughts
Uploaded by
sarah_smith1Copyright:
Available Formats
Pharmacology II
CH 38: Antiviral Drugs I
Study Guide
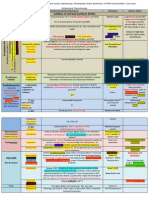
TREATMENT OF RESPIRATORY VIRUS INFECTIONS
Treatments only exist for Influenza A and B and RSV Neuraminidase inhibitors Oseltamivir Tamiflu Zanamivir Relenza -influenzaorthomyoxovirus; contain neuroamidinase enzymes -prevents release of new virons and their spread from cell to cell -effective against Influenza A and B -Administered PRIOR to exposure prevent infection -Administered WITHIN 24-48 hrs after onset of infection reduces intensity and duration of Sx MOA -osteltamivir is a transition state analog of salic acid substrate and serves as INHIBITORS of enzyme activity -inhibits viral neuroamidase OsteltamivirOral prodrug Zanamivir inhaled or activated by liver intranasal Ribavirin Virazole
General
Pharmokinetics
Adverse Effects
Osteltamivir -GI discomfort -Nausea **TAKE WITH FOOD
Zanamivir -irritation to respiratory tract -AVOID in pts with SEVERE REACTIVE ASTHMA or COPD broncospasm can occur w/ fatality
-synthetic guanosine analog -tx of infants and young children with SEVERE RSV infection -NOT FOR ADULTS -effective in chronic hep C when combined w/ interferon-a-2b -may reduce mortality and viremia of Lassa fever -prevents viral mRNA capping and blocking RNA-dependent RNA polymerase -INTERFERES w/ protein synthesis -Oral and IV absorption increased w/ fatty meal -Aerosol used in certain respiratory viral conditions -Dose dependent transient anemia w/ IV -AEROSOL MAY BE SAFERbut respiratory function can deteriorate quickly after initiation of aerosol tx -CONTRAINDICATED in pregnancy
TREATMENT of HEPATIC VIRAL INFECTIONS
Hep B and C are most common causes chronic hep, cirrhosis, hepatocellular carcinoma Only hepatic viral infxns with tx available
Interferon IFN General
-inducible glycoproteins interferes w/ ability of virus to infect cell -interferon--2a approved for tx of hep B and C, condylomata acuminata, cancers (hairy cell leukemia and Kaposis sarcoma)
pegylated formulations (Pegasys) bismonomethoxy polyethylene glycol covalently attached to increase size of molecule -decreases rate of absorption -decreases renal clearance -decreased immunogenicity -LENGTHENS DURATION OF ACTION
MOA Pharmokinetics Adverse Effects
-degradation of viral mRNA and tRNA -SubQ -cellular uptake and metabolism by liver and kidneyno active compound in plasma -flu-like sx on injection (myalgias, arthralgias, GI *BLACK BOX WARNING*DISCONTINUE DRUG IF disturbances, fever, chills) worsening of: -FATIGUE and DEPRESSION COMMONdecrease with -autoimmune disorders subsequent injections -thyroiditis -Bone marrow Suppression -TTP -ITP *BLACK BOX WARNING*may cause severe -RA depression and suicidal thoughts -Interstitial nephritis -SLE -Psorias
Interferon IFN Drug Interactions
-interferes w/ hepatic drug metabolism -toxic accumulations of thiophylline reported
Lamivudine Epivir General -inhibitor of HBV DNA polymerase (Hbv Epivir) and HIV reverse transcriptase (Epivir) -inexpensive -high rate of drug resistance -role diminishing due to new drugs MOA -competitively at concentrations that have negligible to host DNA polymerase -inhibits reverse transcriptase Pharmokinetics -intracellular half-life much longer than plasma half-lifeINFREQUENT dosing -absorbed orally -excreted unchanged in urine Adverse Effects -WELL TOLERATED -HA and dizziness
TREATMENT of HERPESVIRUS INFECTIONS
Includes: cold sores, viral encephalitis, genital infxns, Drugs exert actions during acute phase NO EFFECT during LATENT phase (except for foscarnet) inhibits HBV polyermase
Acyclovir Zovirax General -prototypic antiherpetic therapeutic agent -DRUG OF CHOICE for HSV encephalopathy -effective against HSV 1 & 2, VZV, some Esptein-commonly used in GENITAL HERPES Barr virus-mediated infxns MOA -guanisine analong lacks true sugar moiety -causes premature DNA-chain termination -virus-infected cells most susceptible Pharmokinetics -IV, oral, topical -accumulates in pts w/ renal failure Adverse Effects -depend on route -Oral HA, diarrhea, N/V -Topicallocal irritation -IV transient renal dysfunction in high doses or in dehydrated pt Resistance -usually found in HIV pts -cross-resistance w/ other cyclovirs Foscarnet General
Pharmokinetics
Adverse Effects Resistance
-NOT purine and pyrimidine analog -Phosphonoformate (physrophosphate derivative) -broad in vitro antiviral activity -approved for CMV retinitis in immunocompromised hosts and acyclovir-resistant HSV and herpes zoster infxns -must be injected IV -must be given frequently to avoid relapse when plasma levels fall -excreted through glomerular filtration and tubular secretion into urine -Nephrotoxicity -nausea -anemia -fever -cross-resistance btwn foscarnet and ganciclovir or acyclovir is UNCOMMON
Ganciclovir Cytovene (or Valganciclovir) General -analog of acyclovir 8-20x greater activity against CMV (only approved for CMV) -tx of CMV retinitis in immunocompromised pts and CMV prophylaxsis in transplant pts MOA -nucleotide competitively inhibits viral DNA polymerase and can be incorporated into the DNA (decreases rate if chain elongation) Pharmokinetics -Gangciclovir IV; accumulates in pts w/ renal failure -Valganciclovir Oral Adverse Effects -dose dependent neutropenia -carcinogenic, embryotoxic, teratogenic in experimental animals
General
MOA Pharmokinetics
Penciclovir (Denavir) -acyclic guanosine nucleoside derivative active against HSV-1, HSV-2, VZV - Cold sores and labialis -inhibits HSV DNA polymerase - topical -Bone pain and healing shortened approx. day in duration
Famiciclovir (Famvir) -prodrug of penciclovir -approved for tx of acute herpes zoster -metabolized to active penciclovir -orally
Adverse Effects
-HA -nausea
You might also like
- ANTIBIOTICS CLASS MECHANISMS USES SIDE EFFECTSDocument4 pagesANTIBIOTICS CLASS MECHANISMS USES SIDE EFFECTSJoão Paulo MaresNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics for Urinary Tract Infections - Treatment GuideDocument45 pagesAntibiotics for Urinary Tract Infections - Treatment GuideMelinda FiskaNo ratings yet
- Antiviral Drugs Classification and MechanismsDocument56 pagesAntiviral Drugs Classification and MechanismsciccianoNo ratings yet
- DR - Saleh-26 March 2013-Farmakologi (Anti Jamur, Anti Virus, Anti Parasit, DLL)Document72 pagesDR - Saleh-26 March 2013-Farmakologi (Anti Jamur, Anti Virus, Anti Parasit, DLL)jeinpratpong100% (4)
- 'Mbbs Lecture Note Malaria - pptx2021-1Document56 pages'Mbbs Lecture Note Malaria - pptx2021-1Noah OlumideNo ratings yet
- Fulminant Hepatic FailureDocument53 pagesFulminant Hepatic FailureAR KarthickNo ratings yet
- 4 Beta-lactam antibiotics overviewDocument4 pages4 Beta-lactam antibiotics overviewVladimir GurjanovNo ratings yet
- Inhibitor of Cell Wall Synthesis (ICWS) : Proteus ComboDocument12 pagesInhibitor of Cell Wall Synthesis (ICWS) : Proteus Comboflomax23100% (1)
- Antimalarial Drugs: Mechanisms of Action, Clinical Uses and Adverse EffectsDocument61 pagesAntimalarial Drugs: Mechanisms of Action, Clinical Uses and Adverse EffectsMewael TesfamichaelNo ratings yet
- PANRE and PANCE Review Antimicrobial PharmacologyDocument27 pagesPANRE and PANCE Review Antimicrobial PharmacologyThe Physician Assistant Life100% (2)
- Drug Therapy of Viral Hepatitis 1-Hepatitis A: Passive ImmunityDocument4 pagesDrug Therapy of Viral Hepatitis 1-Hepatitis A: Passive ImmunityOsama El ShfieNo ratings yet
- Antifungal Agents: EchinocandinsDocument2 pagesAntifungal Agents: EchinocandinsCourtney TownsendNo ratings yet
- Antiparasitic Medications: Dr. Meera Ababneh, Pharm.D, PHDDocument39 pagesAntiparasitic Medications: Dr. Meera Ababneh, Pharm.D, PHDSaddamix AL OmariNo ratings yet
- afb5_1.-antimalarials-medicalDocument63 pagesafb5_1.-antimalarials-medicalAx D98No ratings yet
- Mksap 16Document3 pagesMksap 16Wade BullockNo ratings yet
- Drug Treatment of Pulmonary Tuberculosis: 4 Medical Year PharmacologyDocument30 pagesDrug Treatment of Pulmonary Tuberculosis: 4 Medical Year PharmacologyRuchi KholiyaNo ratings yet
- Anti - TB DrugsupdatedDocument35 pagesAnti - TB DrugsupdatedgNo ratings yet
- Anti-Malarial DrugsDocument58 pagesAnti-Malarial Drugs88AKKNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Lecture 6Document3 pagesPharmacology Lecture 6John Harvey PerezNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics F MCP 1Document37 pagesAntibiotics F MCP 1Mohamed ElraiyNo ratings yet
- KANAMYCIN - Kanamycin Injection, S Olution Fres Enius Kabi USA, LLCDocument15 pagesKANAMYCIN - Kanamycin Injection, S Olution Fres Enius Kabi USA, LLCheristiana pratiwiNo ratings yet
- Antimalarial DrugsDocument53 pagesAntimalarial DrugsAmitKumarNo ratings yet
- Anti Fungal AgentsDocument44 pagesAnti Fungal Agentsqruz Mohamed DiisNo ratings yet
- Anti Protozoal Agents (Antimalarials)Document30 pagesAnti Protozoal Agents (Antimalarials)srank gamerNo ratings yet
- MalariaDocument45 pagesMalariaSiya PatelNo ratings yet
- Year Two Drugs OverviewDocument4 pagesYear Two Drugs OverviewCaine ReganNo ratings yet
- PEDIADRUGDocument6 pagesPEDIADRUGPatrice LimNo ratings yet
- Fluimucil TabletDocument21 pagesFluimucil TabletJammilaKateDakayNo ratings yet
- SULPHONAMIDES & CO- TRIMOXAZOLE BAMSDocument46 pagesSULPHONAMIDES & CO- TRIMOXAZOLE BAMSKasturiRangan SrivatsaNo ratings yet
- Quinolones, Folic Acid Antagonist, and Urinary Tract AntisepticsDocument29 pagesQuinolones, Folic Acid Antagonist, and Urinary Tract AntisepticsAliImadAlKhasakiNo ratings yet
- Cephalosporins, Flouroquinolones and SulfonamidesDocument7 pagesCephalosporins, Flouroquinolones and SulfonamidesErum JanNo ratings yet
- Metronidazole: Mechanism of Antibacterial Action Is Unclear, But NeedsDocument60 pagesMetronidazole: Mechanism of Antibacterial Action Is Unclear, But NeedsmmydungNo ratings yet
- Myasthenia Gravis TransDocument2 pagesMyasthenia Gravis Trans2013SecBNo ratings yet
- MedSurg Medication Study Guide Test 1Document12 pagesMedSurg Medication Study Guide Test 1Sarah PlunkettNo ratings yet
- Antiviral Drugs: Ana Khusnul Faizah Farmasi FK Uht 2020Document24 pagesAntiviral Drugs: Ana Khusnul Faizah Farmasi FK Uht 2020Muhammad Iqbal DarmansyahNo ratings yet
- Management of Uncomplicated Urinary Tract InfectionDocument38 pagesManagement of Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infectionhuddy101No ratings yet
- Cephalosporins ReportDocument24 pagesCephalosporins ReportPhoenixNo ratings yet
- IMMUNOMODULATORSDocument44 pagesIMMUNOMODULATORSMaria khurshidNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 2 Kegawatan Asthma, Pneumonia CopdDocument53 pagesKuliah 2 Kegawatan Asthma, Pneumonia CopdtrianaamaliaNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy of TuberculosisDocument23 pagesChemotherapy of TuberculosisIman SaksoukNo ratings yet
- Ph119.1 Final NotesDocument13 pagesPh119.1 Final NotesANDREA GAIL ANONUEVONo ratings yet
- Antiviral: Anggelia Puspasari, MD Dept. Pharmacology and Therapeutic Medical Faculty University of JambiDocument30 pagesAntiviral: Anggelia Puspasari, MD Dept. Pharmacology and Therapeutic Medical Faculty University of JambieldiNo ratings yet
- Antimalarial Drug CologyDocument15 pagesAntimalarial Drug CologyManthan ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Crystal Induced Arthropathies: BY: DR Mehrunnisa Umar Assisstant Profesor Department of MedicineDocument25 pagesCrystal Induced Arthropathies: BY: DR Mehrunnisa Umar Assisstant Profesor Department of MedicinedrusmanjamilhcmdNo ratings yet
- Question 21c. Classification of Immunosuppressive and Imunomodulating Agents Including Cytokines and Clinical Uses.Document4 pagesQuestion 21c. Classification of Immunosuppressive and Imunomodulating Agents Including Cytokines and Clinical Uses.wanichysonlyNo ratings yet
- Hello Everyone: Prof. (DR.) Akhilesh ShrivastavaDocument19 pagesHello Everyone: Prof. (DR.) Akhilesh Shrivastavaarpitagupta28No ratings yet
- Antiparasitic Drugs (Antiprotozoal: DR John EgbagbaDocument37 pagesAntiparasitic Drugs (Antiprotozoal: DR John EgbagbaPrincewill SeiyefaNo ratings yet
- Antiprotozoals Part IDocument46 pagesAntiprotozoals Part IAYO NELSONNo ratings yet
- Sulfonamides, TMP, QuinolonesDocument4 pagesSulfonamides, TMP, QuinolonesMello DiaxNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of ENT InfectionsDocument86 pagesPharmacotherapy of ENT InfectionsHoque Mohammed Newaz ShorifulNo ratings yet
- Pharma-URO-CYCLIC LIPOEPETIDES (Vancomycin)Document6 pagesPharma-URO-CYCLIC LIPOEPETIDES (Vancomycin)Hussein AlhaddadNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CaseDocument9 pagesDrug Study - CaseMay EvelynNo ratings yet
- Farmaco 1Document12 pagesFarmaco 1Raluca IchimNo ratings yet
- Preventing and Treating Malaria NaturallyDocument7 pagesPreventing and Treating Malaria NaturallyGifanichan MvpshawolandromedaNo ratings yet
- IMMUNOSUPPRESANTSDocument13 pagesIMMUNOSUPPRESANTSasriNo ratings yet
- HESI MED SURG STUDY GUIDE ANTIBIOTICSDocument1 pageHESI MED SURG STUDY GUIDE ANTIBIOTICSGeorgeNo ratings yet
- Adult Infectious Disease Bulletpoints HandbookFrom EverandAdult Infectious Disease Bulletpoints HandbookRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- CMS Geriatrics NotesDocument2 pagesCMS Geriatrics Notessarah_smith1No ratings yet
- Otology 2011Document178 pagesOtology 2011sarah_smith1No ratings yet
- History ChecklistDocument10 pagesHistory Checklistsarah_smith1No ratings yet
- Micro Test 3 Study GuideDocument29 pagesMicro Test 3 Study Guidesarah_smith1No ratings yet
- Micro - Key PlayersDocument23 pagesMicro - Key Playerssarah_smith1No ratings yet
- Case Group 1Document10 pagesCase Group 1JASMEEN RAVALNo ratings yet
- AKIDocument23 pagesAKInadddNo ratings yet
- Innovations in Medical ElectronicsDocument10 pagesInnovations in Medical Electronicsapi-3837905100% (5)
- Iontophoresis Definition and PrinciplesDocument4 pagesIontophoresis Definition and PrinciplesSiva Shanmugam100% (1)
- Nursing History Part 1. Demographic InformationDocument6 pagesNursing History Part 1. Demographic InformationAngelica VillalonNo ratings yet
- Formulasi Tablet VaginalDocument9 pagesFormulasi Tablet VaginalnatinlalaNo ratings yet
- Women in Business GuideDocument20 pagesWomen in Business GuidewednesdayjournalNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation BSMMU As 3rd AuthorDocument4 pagesCase Presentation BSMMU As 3rd AuthorGovind ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Related Coverage: Stigma Experienced by Children and Adolescents With Obesity Use Neutral WordsDocument5 pagesRelated Coverage: Stigma Experienced by Children and Adolescents With Obesity Use Neutral WordsSlaghard AnerajNo ratings yet
- Development Economics II Summary: Health, Calories, and ProductivityDocument9 pagesDevelopment Economics II Summary: Health, Calories, and Productivityshabrina larasatiNo ratings yet
- Classification Criteria For SLE PDFDocument4 pagesClassification Criteria For SLE PDFCocea MihaiNo ratings yet
- Cervical Dystonia Supplement - Summer 08Document8 pagesCervical Dystonia Supplement - Summer 08Kelly PhillipsNo ratings yet
- Health Related Millennium Development Goals Part IDocument24 pagesHealth Related Millennium Development Goals Part IGudegna GemechuNo ratings yet
- MYOPIA REDUCTION... A View from the InsideDocument6 pagesMYOPIA REDUCTION... A View from the InsidePierre RodulfoNo ratings yet
- Trauma FocusedCognitive BehavioralTherapy (TF CBT)Document2 pagesTrauma FocusedCognitive BehavioralTherapy (TF CBT)Joel RamosNo ratings yet
- Atrial FibrillationDocument14 pagesAtrial FibrillationNur Atiqah ZainalNo ratings yet
- Yakima Co (WA) Protocols 2010Document117 pagesYakima Co (WA) Protocols 2010Anthony James-Hartwell100% (1)
- Practical Radiotherapy Planning, Fourth EditionDocument477 pagesPractical Radiotherapy Planning, Fourth EditionMehtap Coskun100% (12)
- Sulfonamide Drug StudyDocument1 pageSulfonamide Drug StudyMenard VelascoNo ratings yet
- For Older People, Medications Are Common AGS Beers Criteria Aims To Make Them Appropriate, TooDocument3 pagesFor Older People, Medications Are Common AGS Beers Criteria Aims To Make Them Appropriate, TooindriNo ratings yet
- Hemolytic DiseaseDocument10 pagesHemolytic DiseaseChino Paolo SamsonNo ratings yet
- An Update On The Management of Endometrial HyperplasiaDocument5 pagesAn Update On The Management of Endometrial Hyperplasiafitrah fajrianiNo ratings yet
- How To Boost Your Immune System - Harvard HealthDocument6 pagesHow To Boost Your Immune System - Harvard HealthAnonymous 0qsjVfQtLNo ratings yet
- Access Medicine - TableDocument2 pagesAccess Medicine - Tablecode-24No ratings yet
- Sandip Das Naukri CVDocument3 pagesSandip Das Naukri CVShreya SinghNo ratings yet
- Ramos vs. CADocument20 pagesRamos vs. CAWilfredNo ratings yet
- Shigella: The Organism/ToxinDocument3 pagesShigella: The Organism/ToxinEduardo Ramirez LasoNo ratings yet
- CrohnsDocument19 pagesCrohnsLauren LevyNo ratings yet
- Obesity and HomoeopathyDocument15 pagesObesity and HomoeopathyDr. Rajneesh Kumar Sharma MD Hom100% (2)
- Addicts - Road To Financial Recovery Facilitator GuideDocument7 pagesAddicts - Road To Financial Recovery Facilitator Guiden3f32010No ratings yet