Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH11 Notes
Uploaded by
Ross Collier0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views4 pagesCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views4 pagesCH11 Notes
Uploaded by
Ross CollierCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
Ch.
11 notes 07/05/2007 12:53:00
Macroeconomics focuses on the overall performance of the economy- the
structure of econ. Activity in a region
• Econ. Track production, income and consumption in the nation’s
econ.
• The most commonly used measure of this is the gros product+
market value of production in a geographic region in a given period,
usually one year
-The gross domestic product (GDP) measures the market value of all final
goods and services produced in the us in 1 year.
• Measures production from individuals and businesses
• Includes all business located in the us even foreign business EX.
Mercedes plant in Tuscaloosa.
• Excludes US products produced in foreign countries EX: Coke plant
in mex.
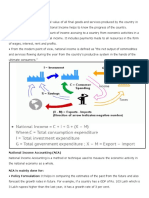
National Income Accounts
• Tracking process that provides information about economic activity
• Keeps track of final goods and services= sold to the end, final use
o EX: tree cut down to make furni, only counts the furni sold in
the end, not all the sales in bet.
• This is done to avoid double counting so the sale of intermediate
goods and sevides is not counted (things that are used for
additional processing or that go into making something) EX sale of
the piece of lumber made from tree)
• GDP also ignores secondhand value – sale of used goods – this is
because the GDP measures production, not sales
• These products would have already been counted when they were
first produced and sold
Calculating GDP
• Natl. income accounts based on idea that one person’s spending is
another person’s income
• So GDP can be measured 2 ways- calculating total spending on US
production, or by total income earned from US population.
Expenditure Approach
• Adds up spending on all final goods in one year
• 4 components: consumption ©, Investment (I), government
purchases (G), and Net exports of goods minus imports (x-m)
• Consumption: purchases of final goods -makes up 2/3 of all us
spending
o Includes durable goods- TV (takes a long time)
o And nondurable goods- soap/shampoo (will run out)
• Investment- use of money to produce new capital goods
o Most important part = physical capital- spending on things
like buildings, equipment, etc. that is used to produce goods
o Also includes inventory investment- stock of goods in process
or finished goods to be sold
o Doesn’t include buying existing buildings or used equipment
already been counted
• Gov. purchaces- federal, state, and local expenditures on goods and
services= building roads, public edu, ect.
o Gov. transfer payments don’t count – expenditures for which
the gov. receives no goods in exchange= SS, welfare, FEMA
aid
• Net Exports- total US exports minus total US imports
• GDP measures goods produced within national borders, so it
includes things produced domestically and sold abroad, but
excludes products made in other countries and sold in the US.
Expenditure Approach considers aggregate (total spending) =
C + I + G + (X-M) =GDP
Income Approach
• Adds up the income earned from production
• The aggregate income= the sum of all income earned by resource
suppliers
• To avoid double counting- calculate the value added at each stage
of production
o EX: each stage of making a table is paid for along the way so
calculate the value added at each stage (the amt paid for the
intermediate good)
• Add up the sum of all VALUE ADDED = 20 + 30+50+100=200$
same as final selling price)
07/05/2007 12:53:00
07/05/2007 12:53:00
You might also like
- Unit 2 National Income AccountingDocument83 pagesUnit 2 National Income Accountingbrianmfula2021100% (1)
- GDPDocument43 pagesGDPAbdullahNo ratings yet
- Gross Domestic ProductDocument18 pagesGross Domestic ProductABBAS ANo ratings yet
- GDP Measurement - Identities - Session3Document37 pagesGDP Measurement - Identities - Session3Haardik GandhiNo ratings yet
- Discussion B-3Document64 pagesDiscussion B-3Tahfim KhanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.2 National Income AccountingDocument8 pagesLesson 1.2 National Income AccountingJael Cris JavierNo ratings yet
- Measuring The EconomyDocument40 pagesMeasuring The EconomyTiffany Gayle bNo ratings yet
- GDP:two Measures of National Product Flow of Product Approach. Earning and Cost ApproachDocument53 pagesGDP:two Measures of National Product Flow of Product Approach. Earning and Cost ApproachUmer Farooq MirzaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20: The Measurement of National Income: National Output and Value AddedDocument4 pagesChapter 20: The Measurement of National Income: National Output and Value AddedSaaki GaneshNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomic IndicatorsDocument27 pagesMacroeconomic Indicatorsanjali mishraNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Economic ActivitiesDocument17 pagesMeasurement of Economic ActivitiesDeepak SethiaNo ratings yet
- 1618398280-2. National Income AccountingDocument4 pages1618398280-2. National Income AccountingKuldeep SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lecture CHR 10-02 Appendix Measurement of GDPDocument80 pagesLecture CHR 10-02 Appendix Measurement of GDPhushx2821No ratings yet
- Econ 111 Extended 24 - Summer 17Document48 pagesEcon 111 Extended 24 - Summer 17FatmahNo ratings yet
- Economic Environment of Business-GdpDocument42 pagesEconomic Environment of Business-GdpBalajiNo ratings yet
- ch-7 NewDocument16 pagesch-7 NewSAKIB MD SHAFIUDDINNo ratings yet
- GDP and GNPDocument27 pagesGDP and GNPKeerthikanthGubbalaNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument16 pagesNational IncomeSamia Irshad ullahNo ratings yet
- Basic Economic Terms and DefinitionsDocument22 pagesBasic Economic Terms and DefinitionsNathalie OlivaNo ratings yet
- National Income AccountingDocument23 pagesNational Income AccountingAmit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- The Components of The Macroeconomy: The Three Market ArenasDocument7 pagesThe Components of The Macroeconomy: The Three Market ArenasCorin Ahmed CorinNo ratings yet
- PGDM (2019-21) Term 2 (September-December) : Dr. Kalpana TokasDocument30 pagesPGDM (2019-21) Term 2 (September-December) : Dr. Kalpana Tokasv_amyNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument29 pagesNational IncomegipaworldNo ratings yet
- National Income and Occupational Structure in IndiaDocument45 pagesNational Income and Occupational Structure in IndiaakshatNo ratings yet
- Topic 2: National Income AccountingDocument46 pagesTopic 2: National Income AccountingSakshi VermaNo ratings yet
- Mee - 2 - Data of Macro (2013) - ClassDocument60 pagesMee - 2 - Data of Macro (2013) - Classsnata92No ratings yet
- Unit 5 NewDocument94 pagesUnit 5 NewrajapatnaNo ratings yet
- Economics IDocument34 pagesEconomics IKevin kayNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Chapter20Document49 pagesWeek 4 Chapter20elserry.comNo ratings yet
- Gross Domestic ProductDocument13 pagesGross Domestic ProductLakshmiNo ratings yet
- Gross Domestic ProductDocument13 pagesGross Domestic ProductsaiNo ratings yet
- National Income Accounting (NIA)Document8 pagesNational Income Accounting (NIA)Mamta VermaNo ratings yet
- 7C PDFDocument3 pages7C PDFReinaNo ratings yet
- Expentidure Method-1Document5 pagesExpentidure Method-1HimanshuChorasamaNo ratings yet
- National IncomeDocument49 pagesNational IncomeStive JohnNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Part 1Document14 pagesModule 2 Part 1Pratyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Concept of National IncomeDocument12 pagesConcept of National Incomevishal111089100% (1)
- CH 2 MacroeconomicsDocument63 pagesCH 2 MacroeconomicsYidid GetachewNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics S2 (Pertemuan 2.1)Document30 pagesMacroeconomics S2 (Pertemuan 2.1)Muhammad Faizal AkbarNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomic Analysis For Management 1 - Chapter 3Document21 pagesMacroeconomic Analysis For Management 1 - Chapter 3dawsonNo ratings yet
- POE2 - Week 2Document19 pagesPOE2 - Week 2엄소빈No ratings yet
- Unit 5 NewDocument94 pagesUnit 5 NewrajapatnaNo ratings yet
- Module - 4 National IncomeDocument64 pagesModule - 4 National Incomelakshmi dileepNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Macroeconomics - Lec 5 and 6 - Chapter20Document40 pagesWeek 3 - Macroeconomics - Lec 5 and 6 - Chapter20elserry.comNo ratings yet
- National Income Concept and MeasurementDocument33 pagesNational Income Concept and Measurementriteshlal100% (1)
- 8.2 IB Economics SLDocument6 pages8.2 IB Economics SLEman DhaifNo ratings yet
- Measuring Economic Activity and WelfareDocument22 pagesMeasuring Economic Activity and WelfareVilly CenitaNo ratings yet
- HE9091 Lecture 7Document60 pagesHE9091 Lecture 7XL TNo ratings yet
- National Income AnalysisDocument25 pagesNational Income Analysisvaibhav001988No ratings yet
- 2023 Chap19Document86 pages2023 Chap19wannafadedNo ratings yet
- PBD Module 1 NotesDocument13 pagesPBD Module 1 Notesafshots422No ratings yet
- Session 3Document19 pagesSession 3Ramji TripathyNo ratings yet
- ECON1102 Complete NotesDocument60 pagesECON1102 Complete NotesJustin100% (1)
- National Income PPT 1Document34 pagesNational Income PPT 1Maanya SharmaNo ratings yet
- National Income Accounting Reference - Chapter 5Document13 pagesNational Income Accounting Reference - Chapter 5hannah_clariceNo ratings yet
- The National Income Accounting 1Document15 pagesThe National Income Accounting 1Kyle Kenneth GarciaNo ratings yet
- Nations WealthDocument49 pagesNations WealthwomabaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Business Economics Study Resource: CIMA Study ResourcesFrom EverandFundamentals of Business Economics Study Resource: CIMA Study ResourcesNo ratings yet
- Business Economics: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageFrom EverandBusiness Economics: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageNo ratings yet
- Art102notes8 23 07Document1 pageArt102notes8 23 07Ross CollierNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Notes 4-12-07Document2 pagesReproductive Notes 4-12-07Ross Collier100% (3)
- SixflagsDocument1 pageSixflagsRoss CollierNo ratings yet
- A Separate Peace Webquest A+Document5 pagesA Separate Peace Webquest A+Ross Collier100% (2)
- Biology Notes 3Document2 pagesBiology Notes 3Ross CollierNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes 3Document2 pagesBiology Notes 3Ross CollierNo ratings yet
- Poetry AnalysisDocument3 pagesPoetry AnalysisRoss Collier100% (2)
- Biology Notes 3Document2 pagesBiology Notes 3Ross CollierNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes 3Document2 pagesBiology Notes 3Ross CollierNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Notes 4-12-07Document2 pagesReproductive Notes 4-12-07Ross Collier100% (3)
- Reproductive Notes 4-12-07Document2 pagesReproductive Notes 4-12-07Ross Collier100% (3)
- Biology Notes 3Document2 pagesBiology Notes 3Ross CollierNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Notes 4-12-07Document2 pagesReproductive Notes 4-12-07Ross Collier100% (3)
- Reproductive Notes 4-12-07Document2 pagesReproductive Notes 4-12-07Ross Collier100% (3)
- Chapter 13Document4 pagesChapter 13Ross CollierNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Notes EconomicsDocument1 pageChapter 10 Notes EconomicsRoss CollierNo ratings yet
- CH11 NotesDocument4 pagesCH11 NotesRoss Collier100% (2)
- BellringersDocument1 pageBellringersRoss Collier100% (1)
- Chapter 10 Notes EconomicsDocument1 pageChapter 10 Notes EconomicsRoss CollierNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document4 pagesChapter 13Ross CollierNo ratings yet
- Year-Round School Persuasive PaperDocument1 pageYear-Round School Persuasive PaperRoss Collier100% (5)
- Us Partner 2Document10 pagesUs Partner 2seemabNo ratings yet
- 5 Symbolic Frame Worksheet Ogl481Document3 pages5 Symbolic Frame Worksheet Ogl481api-572981123No ratings yet
- Introduction To: - Pinkal Deore 20190301007Document6 pagesIntroduction To: - Pinkal Deore 20190301007Pinkal DeoreNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Review of Supply and Demand TheoryDocument69 pagesModule 2 - Review of Supply and Demand TheoryRegina LintuaNo ratings yet
- How To Use Commodity Code (HS Code) in SAP AFSDocument8 pagesHow To Use Commodity Code (HS Code) in SAP AFSGeshan Weerasinghe100% (3)
- Introduction Incoterms 2010 RulesDocument17 pagesIntroduction Incoterms 2010 RulesSudershan ThaibaNo ratings yet
- Business Planning For AgribusinessDocument26 pagesBusiness Planning For Agribusinesshussen seidNo ratings yet
- JK PrawnManufacfuringCorporationDocument47 pagesJK PrawnManufacfuringCorporationAlmadin KeñoraNo ratings yet
- How Retailers Can Build Resilience Ahead of A Recession v4Document4 pagesHow Retailers Can Build Resilience Ahead of A Recession v4Deepak SharmaNo ratings yet
- KIA InvoiceDocument1 pageKIA InvoiceScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Miss Marians Disordered OrganizationDocument1 pageMiss Marians Disordered OrganizationVince SebugueroNo ratings yet
- Exercises Tax2Document9 pagesExercises Tax2Helen Faith EstanteNo ratings yet
- Avon: International Business Case Study (CIA) : Saurav Bhattacharjee Roll No: 1928928Document7 pagesAvon: International Business Case Study (CIA) : Saurav Bhattacharjee Roll No: 1928928sauravsNo ratings yet
- Chopra3 PPT ch01Document25 pagesChopra3 PPT ch01osama haseebNo ratings yet
- Beechy7e Vol 1 SM Ch08Document59 pagesBeechy7e Vol 1 SM Ch08Aayush AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Assumption and LimitationDocument4 pagesAssumption and LimitationDM MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- Hush Money ReportDocument23 pagesHush Money ReportHariNo ratings yet
- Strategic Performance Measurement: Transfer PricingDocument2 pagesStrategic Performance Measurement: Transfer Pricingtaxathon thaneNo ratings yet
- A Case Study in Results AnalysisDocument7 pagesA Case Study in Results AnalysissampathNo ratings yet
- Kellogg 2004 Rotisserie RanchDocument8 pagesKellogg 2004 Rotisserie RanchWen KangNo ratings yet
- Services Marketing Notes PDFDocument283 pagesServices Marketing Notes PDFakhil89% (108)
- Inventory QuestionsDocument2 pagesInventory QuestionsJoseph CameronNo ratings yet
- Ibo 2Document33 pagesIbo 2Charan SinghNo ratings yet
- Comfort Shoes: Udhaya Chandran S. B Rakesh G. RDocument19 pagesComfort Shoes: Udhaya Chandran S. B Rakesh G. RRakesh GrrNo ratings yet
- Acc111 (412) Activity27 MarimonDocument2 pagesAcc111 (412) Activity27 MarimonDonabelle MarimonNo ratings yet
- Revenue (Ifrs 15)Document43 pagesRevenue (Ifrs 15)Sherlock HomlesNo ratings yet
- Girdharilal Case StudyDocument1 pageGirdharilal Case StudySandipan DawnNo ratings yet
- Business Simulation Group 2 Section B - Assessee (10th Nov)Document7 pagesBusiness Simulation Group 2 Section B - Assessee (10th Nov)mahapatrarajeshranjanNo ratings yet
- Marketing Canadian 10th Edition Crane Test Bank DownloadDocument43 pagesMarketing Canadian 10th Edition Crane Test Bank DownloadPamela Starling100% (22)
- Reviewer in Revenue and Expense RecognitionDocument7 pagesReviewer in Revenue and Expense RecognitionPaupauNo ratings yet