Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Telecommunication Engineering
Uploaded by
Asadul HoqueOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Telecommunication Engineering
Uploaded by
Asadul HoqueCopyright:
Available Formats
What is Telecommunication Engineering?
A telecommunication engineer is responsible for designing and overseeing the installation of telecommunications equipment and facilities, such as complex electronic switching systems, copper telephone facilities, and fiber optics. Telecom engineering also overlaps heavily with broadcast engineering. Broadcast engineering is the field of electrical engineering, and now to some extent computer engineering and information technology, which deals with radio and television broadcasting. What is Telecommunication Network? A telecommunications network is a collection of terminals, links and nodes which connect together to enable telecommunication between users of the terminals. Networks may use circuit switching or message switching. What is called Inlets and outlets? Inlets and outlets: A major component of a switching system or am exchange is the set of input and output circuits called inlets and outlets. What is Switching network? Switching network: The primary function of a switching system is to establish an electrical path between a given inlets-outlets pair. The hardware used for establishing such a connection is called switching matrix or switching network. What is side tone? Side tone: Side tone is the effect of sound that is picked up by the telephone's mouthpiece and in real-time introduced at a low level into the earpiece of the same handset, acting as controlled feedback. What is Subscriber? Subscriber: In telephone conversation, the one who initiate the calls referred to as the calling subscriber and the one for whom the call is destined is the called subscriber. What is called Control functions? Control functions: The functions performed by a switching system in establishing and releasing connection are known as control functions. What is called trunk and subscriber line? The links that rub between the switching systems are called trunks and those that run to the subscriber premises are known as subscriber lines.
Define the classification of switching system.
Switching System
Manual Switching
Electromechanical
Strowger or Stepby-Step
Space Division
Automatic Switching
Electronics
Crossbar
Switching
Time Division Switching
Digital
Analog
Space Switch
Time Switch
Combination Switch
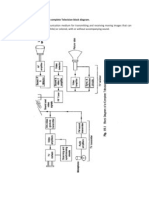
How many types of connections need to establish with a switching system? o Local call connection between two subscribers in the system. o Outgoing call connection between a subscriber and an outgoing trunk. o Incoming call connection between an incoming trunk and a local subscriber. o Transits call connection between an incoming trunk and an outgoing trunk. Describe the Telecommunication Network Subscribers all over the world cannot be connected to a single switching system unless we have a gigantic switching system in the sky and every subscriber has a direct access to the same. The major part of the telecommunication networks is still ground based, where subscribers are connected to the switching system via copper wires. The links that rub between the switching systems are called trunks and those that run to the subscriber premises are known as subscriber lines.
Model of a Switching network with N inlets and M outlets.
When N=M, the switching network is called a symmetric network.
When all the inlets/outlets are connected to the subscriber lines, the logical connection appears as
In this case, the output lines are folded back to the input and hence the network is called a folded network.
Define the Advantages of Automatic Switching System. The operation of an automatic exchange is language independent. A greater degree of privacy is obtained in automatic exchanges as no operator is normally involved in setting up and monitoring a call. Establishment and release of calls are faster I automatic exchanges. It is not unusual in a manual exchange. The time required to establish and release a call remains more or less of the same order irrespective of the load on the system or the time of the day. In a manual system, this may not be true A rotary dial telephone uses the following for implementing pulse dialing: o Finger plate and spring, o Shaft, gear and pinion wheel, o Pawl and ratchet mechanism, o Impulsing cam and suppressor cam or a trigger mechanism, o Impulsing contact, o Centrifugal governor and worm gear, o Transmitter, receiver and bell by pass circuits. Five subscribers related signaling functions are involved (performed by operator) in establishing, maintaining, and releasing a telephone conversation. o Respond to the calling subscriber to obtain the identification of the called party o Inform the calling subscriber that the call is being established o Ring the bell of the called party, o Inform the calling subscriber, if the called party is busy, o Inform the calling subscriber, if the called party line is unobtainable for some reason. Define the Classification of signaling tone. Dial Tone: This is send by the local exchange service to the calling subscriber to indicate that the exchange is ready to receive the caller number. The dial tone is 33 Hz or 50 Hz.
Ringing Tone: This is a forward signal send by the exchange to the called subscriber to indicate the arrival call. Simultaneously this tone is received by the calling party. The frequency of the ringing tone is 133 Hz or 400 Hz.
Busy Tone: This is sent by the local exchange that the serves the called subscriber when that subscriber not available or called party is attending another call then a busy tone is sent to calling party. The busy tone has same length of 0.75 seconds or 0.375 seconds.
Call-in-progress Tone: This is a 400 Hz or 800 Hz having 0.1 seconds on/off periods. This indicates that the dialed number that means call is in progress.
Number unobtainable tone: A tone played out to indicate that the dialed number is not in service. The tone may precede an announcement.
Describe Strowger Switching Components In the strowger system, there are two types of selectors which form the building blocks for the switching system: Uniselector, Two-motion Selector. A uniselector is one which has a single rotary switch with a bank of contacts. Typically, there are four bank of which three are used for switching and the fourth one is used for homing. o The three switching banks have 25 or 10 contracts each. o The first contact in each bank is known as the home contact and the remaining as switching contact. o The homing bank has only two contacts: one at the first position corresponding to the home contacts of the other banks. o Depending on the number of switching contacts, uniselectors are identified as 10-outlets or 24outlets uniselectors.
Design Parameters to characterize the Switching Systems 1. Number of subscriber lines, N 2. Total number of switching elements, S 3. Cost of the Switching System, C S Cs Cc Cch Cs=cost per switching elements Cc= cost of the common control system Cch= cost of the common hardware 4. Switching capacity, SC, 5. Traffic handling capacity, 6. Equipment Utilization factor, 7. Number of switching stages, K 8. Average switching time per stages, Tst. 9. Call setup time, Ts=Tst X K X T0 10. . Cost capacity index, CCI=
100-Line Switching System
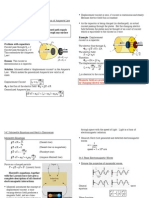
Describe Touch Tone dialing process. Touch Tone Dialing: The touch tone dialing scheme is shown in Figure-1D. The rotary dial is replaced by a push button keyboard. Touching a button generate a tone which a combination of two frequency, one from the lower band and other from the upper band. For example pressing the push button 9 transmit 852Hz and 1477Hz. An extended design provides for an additional frequency 1633 Hz in the upper band, and can produce 16 distinct signals. This design is used only in military and other special applications.
Figure 1D
Describe the Principle of Crossbar Switching The foundational concept of crossbar switching that it is use common control networks. The common control networks enable to perform event monitoring, call processing, charging, operation and maintenance. The common control method of switching overcomes the disadvantage of step by step switching. It receives all the number, stores, and then establishes connection. The basic Crossbar matrix required at least M X N sets of contacts and M+N or less activator to select no of the connection. In Figure-2D is showing a 3X4 crossbar switching. It contains an array of horizontal and vertical wires. Both wires are connected to initially separated contact point of switches. Horizontal and vertical bars are mechanic ally connected to these contact points and attached to the electromagnets. When both horizontal and vertical bars connected to the electromagnet are activated, the contact of the intersection of the two bars will close together. Thus the connection is made and continuous to hold.
Figure 2D
When the electromagnets are de-energized both horizontal and vertical bars are released from the contact. In order to prevent the catching of different crosspoint in the same circuit, a procedure is followed to establish a connection. Accordingly, horizontal bar is energized first and then vertical bar is energized to make contact or in reverse. But while removing contact horizontal bar is de-energized first and then the vertical bar is de-energized.
The process of crossbar switching can be summarized as Energise horizontal bar or Energise vertical bar Energise vertical bar of Energise horizontal bar De-energise horizontal bar or De-energise vertical bar Crossbar Switching Configuration: Diagonal crosspoint matrix: A diagonal matrix for 5 subscribers is shown in Fig: a. The number of crosspoints are reduced to N (N-1)/2, where N is the number of subscribers. It is also called triangle matrix or two way matrix.
The diagonal matrix is fully connected. When subscriber C initiates a call, his horizontal bar is energized first and then the appropriate bar. The diagonal crosspoint matrix is nonblocking configuration. The difficulty is that the failure of a signal switch will make some subscribers inaccessible. Blocking configuration: In blocking crossbar switches the number of vertical bars is less than the number of subscribers and determines the number of simultaneous calls that can be put through the switch. Consider the below figure the 8 X 3 switch.
Figure 3D Let a connection consider be required to be established between the subscriber A and B. 1st the horizontal bar A is energized. Then one of the free vertical bars says P is energized. The crosspoint AP latched, now if we energise the horizontal bar B, BP will not be latched, as the P vertical is energized before B was energized. In order to be able to connect A to B, we need another vertical crossbar which should electrically correspond to the vertical bar P. In this case, the vertical P is associate with the same electrically correspond to the vertical bat P. When P is energized after B, the crosspoint BP is latchedand and a connection between A and B is established. The sequence we can may be summarized as: Energise horizontal A Energise free vertical P De-energise horizontal A Energise horizontal B Energise vertical P De-energise horizontal B
You might also like
- Electronics IIDocument12 pagesElectronics IIAsadul HoqueNo ratings yet
- Radio and Television EngineeringDocument10 pagesRadio and Television EngineeringAsadul Hoque100% (1)
- Programm Code For Final ExamDocument9 pagesProgramm Code For Final ExamAsadul HoqueNo ratings yet
- Com Bi National Logic CircuitDocument9 pagesCom Bi National Logic CircuitAsadul HoqueNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal ProcessingDocument12 pagesDigital Signal ProcessingAsadul Hoque100% (1)
- What Is TelevisionDocument2 pagesWhat Is TelevisionAsadul HoqueNo ratings yet
- Analog Communication Part 2Document8 pagesAnalog Communication Part 2Asadul HoqueNo ratings yet
- Analog CommunicationDocument10 pagesAnalog CommunicationAsadul HoqueNo ratings yet
- CSE-267 Microprocessor and InterfacingDocument8 pagesCSE-267 Microprocessor and InterfacingAsadul HoqueNo ratings yet
- Measurement N InstrumentDocument5 pagesMeasurement N InstrumentAsadul HoqueNo ratings yet
- Data Communication and NetworkingDocument10 pagesData Communication and NetworkingAsadul HoqueNo ratings yet
- Electrical Measurements LabDocument40 pagesElectrical Measurements Labmdayyub100% (4)
- Analog CommunicationDocument10 pagesAnalog CommunicationAsadul HoqueNo ratings yet
- Internship ReportDocument83 pagesInternship ReportAsadul Hoque100% (1)
- Chapter 34Document6 pagesChapter 34mmsaleem1967No ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- VDP08 Technical CatalogueDocument47 pagesVDP08 Technical CatalogueAdal VeraNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing Level 2 MCQsDocument8 pagesUltrasonic Testing Level 2 MCQspandab BkNo ratings yet
- Picador Vegetales HCM450Document20 pagesPicador Vegetales HCM450javier vilchez romeroNo ratings yet
- Previews AGA XQ9902 PreDocument6 pagesPreviews AGA XQ9902 PreAldrin HernandezNo ratings yet
- Structural Systems Engineering GuideDocument67 pagesStructural Systems Engineering Guidejucar fernandezNo ratings yet
- HalideDocument195 pagesHalidejadecolourNo ratings yet
- YCMOU-6th Semester Question Papers-7Document5 pagesYCMOU-6th Semester Question Papers-7phase_shekhar21No ratings yet
- Using Electricity SafelyDocument1 pageUsing Electricity SafelymariaNo ratings yet
- SRSUNTOUR General Fork GlossaryDocument23 pagesSRSUNTOUR General Fork GlossaryThomas JunkersfeldNo ratings yet
- Micron Ezeprox Access Control KeypadDocument4 pagesMicron Ezeprox Access Control KeypadThuy VuNo ratings yet
- The Sperry Bombsight: A Pioneering Rival to NordenDocument6 pagesThe Sperry Bombsight: A Pioneering Rival to NordenPaul DupontNo ratings yet
- Hanson G209 (SW Valves)Document12 pagesHanson G209 (SW Valves)AKSHEYMEHTANo ratings yet
- Hino 500S Catalog LR PDFDocument8 pagesHino 500S Catalog LR PDFZulNo ratings yet
- Bilge Alarm Monitor OMD 11Document22 pagesBilge Alarm Monitor OMD 11Lucian Iftemie100% (3)
- Pen Holder SHSDocument16 pagesPen Holder SHSabhijeetbose1No ratings yet
- Studio4 - LEED - Green - Associate - Study - Guide - Master 2nd Edition PDFDocument310 pagesStudio4 - LEED - Green - Associate - Study - Guide - Master 2nd Edition PDFyu zhangNo ratings yet
- 01-01 Boltec S - SafetyDocument30 pages01-01 Boltec S - SafetyALVARO ANTONIO SILVA DELGADONo ratings yet
- Dimensions of Physical Quantities DensityDocument100 pagesDimensions of Physical Quantities DensityGerman Rincon UrregoNo ratings yet
- 1999 System Wiring Diagrams. Chevrolet - SuburbanDocument1 page1999 System Wiring Diagrams. Chevrolet - SuburbanJimmy Perera BurgosNo ratings yet
- Network What To ReadDocument2 pagesNetwork What To ReadTauseef AhmadNo ratings yet
- Engine & Transmission ToolsDocument45 pagesEngine & Transmission Toolsabduallah muhammad100% (1)
- Course OutlineDocument14 pagesCourse OutlineTony SparkNo ratings yet
- Ea80 Series PDFDocument82 pagesEa80 Series PDFAnca MunteanuNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0038080612000790 Main PDFDocument16 pages1 s2.0 S0038080612000790 Main PDFJuanSebastianGamezNo ratings yet
- Revision of Bs 8002, 8004, AND 8081Document34 pagesRevision of Bs 8002, 8004, AND 8081Rupesh Kaushik100% (1)
- Foundation LayoutDocument1 pageFoundation LayoutrendaninNo ratings yet
- Setting vpn1Document10 pagesSetting vpn1Unink AanNo ratings yet
- Diffraction of Laser Beam Using Wire Mesh, Cross Wire and GratingDocument2 pagesDiffraction of Laser Beam Using Wire Mesh, Cross Wire and GratingPriyesh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Calgon Tech SpecDocument4 pagesCalgon Tech SpecDanStratoNo ratings yet
- Unit Conversion Heat TransferDocument5 pagesUnit Conversion Heat TransferFamela GadNo ratings yet