Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Soviet Russia: Perestroika Glasnost
Uploaded by
Hayley WelshOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Soviet Russia: Perestroika Glasnost
Uploaded by
Hayley WelshCopyright:
Available Formats
The Russian Revolution of 1917 caused the downfall of the Russian Empire.
Following the Russian Revolution, there was a struggle for power between the Bolshevik party, led by Vladimir Lenin, and the anti-communist White movement. In December 1922, the Bolsheviks won the civil war, and the Soviet Union was formed with the merger of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, the Transcaucasian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic, the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic and the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic. Following the death of Vladimir Lenin in 1924, Joseph Stalin took power,[2] leading the USSR through a large-scale industrialization program. Stalin established a planned economy and suppressed political opposition to him and the Communist party.[2][3] In June 1941, Nazi Germany and its allies invaded the Soviet Union, breaking the nonaggression pact, which the latter had signed in 1939. After four years of brutal warfare, the Soviet Union emerged victorious as one of the world's two superpowers, the other being the United States. The Soviet Union and its Eastern European satellite states engaged in the Cold War, a prolonged global ideological and political struggle against the United States and its Western Bloc allies, which it ultimately abandoned in the face of economic troubles and both domestic and foreign political unrest.[4][5] In the late 1980s, the last Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev tried to reform the state with his policies of perestroika and glasnost, but the Soviet Union collapsed and was formally dissolved in December 1991 after the abortive August coup attempt.[6] The Russian Federation assumed its rights and obligations.[7]
Soviet Russia
Main articles: Soviet Union, History of the Soviet Union, and Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic
The symbols of the early Soviet era: Tatlin's Tower project and the giant Worker and Kolkhoz Woman sculpture group. Following the October Revolution, a civil war broke out between the anti-communist White movement and the new regime with its Red Army. Russia lost its Ukrainian, Polish,
Baltic, and Finnish territories by signing the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk that concluded hostilities with the Central Powers in World War I. The Allied powers launched an unsuccessful military intervention in support of anti-Communist forces, while both the Bolsheviks and White movement carried out campaigns of deportations and executions against each other, known respectively as the Red Terror and White Terror. By the end of the civil war the Russian economy and infrastructure were heavily damaged. Millions became White migrs,[60] and the Povolzhye famine claimed up to 5 million victims.[61] The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (called Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic at the time) together with three other Soviet republics formed the Soviet Union, or USSR, on 30 December 1922. Out of the 15 republics of the USSR, the Russian SFSR was the largest in terms of size, and making up over half of the total USSR population, dominated the union for its entire 69-year history. Following Lenin's death in 1924, Joseph Stalin, an elected General Secretary of the Communist Party, managed to put down all opposition groups within the party and consolidate much power in his hands. Leon Trotsky, the main proponent of the world revolution, was exiled from the Soviet Union in 1929, and Stalin's idea of socialism in one country became the primary line. The continued internal struggle in the Bolshevik party culminated in the Great Purge, a period of mass repressions in 193738, in which hundreds of thousands of people were executed, including military leaders convicted in coup d'tat plots.[62] The government launched a planned economy, industrialisation of the largely rural country, and collectivization of its agriculture. During this period of rapid economical and social changes, millions of people were sent to penal labor camps,[63] including many political convicts, and millions were deported and exiled to remote areas of the Soviet Union.[63] The transitional disorganisation of the country's agriculture, combined with the harsh state policies and a drought, led to the famine of 193233.[64] However, though with a heavy price, the Soviet Union was transformed from a largely agrarian economy to a major industrial powerhouse in a short span of time.
The Appeasement policy of Great Britain and France towards Adolf Hitler's annexations of Ruhr, Austria and finally of Czechoslovakia enlarged the might of Nazi Germany and put a threat of war to the Soviet Union. Around the same time the German Reich allied with the Empire of Japan, a rival of the USSR in the Far East and an open enemy in the SovietJapanese Border Wars in 193839. In August 1939, after another failure of attempts to establish a counter-Nazism alliance with Britain and France, the Soviet government agreed to conclude the MolotovRibbentrop Pact with Germany, pledging non-aggression between the two countries and dividing their spheres of influence in Eastern Europe. While Hitler conquered Poland, France and other countries acting on single front at the start of the World War II, the USSR was able to build up its military and regain some of the former territories of the Russian Empire during the Soviet invasion of Poland and the Winter War.
On 22 June 1941, Nazi Germany broke the non-aggression treaty and invaded the Soviet Union with the largest and most powerful invasion force in human history,[65] opening the largest theater of the Second World War. Although the German army had considerable success early on, their onslaught was halted in the Battle of Moscow. Subsequently the Germans were dealt major defeats first at the Battle of Stalingrad in the winter of 1942 43,[66] and then in the Battle of Kursk in the summer of 1943. Another German failure was the Siege of Leningrad, in which the city was fully blockaded on land between 1941 44 by German and Finnish forces, suffering starvation and more than a million deaths, but never surrendering.[67] Under Stalin's administration and the leadership of such commanders as Georgy Zhukov and Konstantin Rokossovsky, Soviet forces drove through Eastern Europe in 194445 and captured Berlin in May 1945. In August 1945 the Soviet Army ousted Japanese from China's Manchukuo and North Korea, contributing to the allied victory over Japan.
First human to travel into space, Yuri Gagarin The 194145 period of World War II is known in Russia as the Great Patriotic War. In this conflict, which included many of the most lethal battle operations in human history, Soviet military and civilian deaths were 10.6 million and 15.9 million respectively,[68] accounting for about a third of all World War II casualties. The full demographic loss to the Soviet peoples was even greater.[69] The Soviet economy and infrastructure suffered massive devastation[70] but the Soviet Union emerged as an acknowledged superpower. The Red Army occupied Eastern Europe after the war, including East Germany. Dependent socialist governments were installed in the Eastern bloc satellite states. Becoming the world's second nuclear weapons power, the USSR established the Warsaw Pact alliance and entered into a struggle for global dominance, known as the Cold War, with the United States and NATO. The Soviet Union exported its Communist ideology to newly formed People's Republic of China and North Korea, and later into Cuba and many other countries. Significant amounts of the Soviet resources were allocated in aid to the other socialist states.[71]
After Stalin's death and a short period of collective rule, new leader Nikita Khrushchev denounced the cult of personality of Stalin and launched the policy of de-Stalinization. Penal labor system was reformed and many prisoners were released and rehabilitated (lots of them posthumously).[72] The general easement of repressive policies became known later as the Khrushchev thaw. At the same time, tensions with the United States heightened when the two rivals clashed over the deployment of the U.S. Jupiter missiles in Turkey and Soviet missiles in Cuba.
Soviet and Russian space station Mir In 1957 the Soviet Union launched the world's first artificial satellite, Sputnik 1, thus starting the Space Age. Russian cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin became the first human to orbit the Earth aboard Vostok 1 manned spacecraft on 12 April 1961. Following the ousting of voluntarist and erratic Khrushchev in 1964, another period of collective rule ensued, until Leonid Brezhnev became the leader. The era of 1970s and the early 1980s was designated later as the Era of Stagnation, a period when the economic growth slowed and social policies became static. The Kosygin reform, aimed into partial decentralization of the Soviet economy and shifting the emphasis from heavy industry and weapons to light industry and consumer goods, was stifled by the conservative Communist leadership. In 1979 the Soviet forces entered Afghanistan at the request of its communist government. The occupation drained economic resources and dragged on without achieving meaningful political results. Ultimately the Soviet Army was withdrawn from Afghanistan in 1989 because of international opposition, persistent anti-Soviet guerilla warfare (enhanced by the U.S.), and a lack of support from Soviet citizens. From 1985 onwards, the last Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev introduced the policies of glasnost (openness) and perestroika (restructuring) in an attempt to modernize the country and make it more democratic. However, this led to the rise of strong nationalist and separatist movements. Prior to 1991, the Soviet economy was the second largest in the world,[73] but during its last years it was afflicted by shortages of goods in grocery stores, huge budget deficits, and explosive growth in money supply leading to inflation.[74]
In August 1991, a coup d'tat attempt by members of Gorbachev's government, directed against Gorbachev and aimed at preserving the Soviet Union, instead led to the end of socialist rule. The USSR was dissolved into 15 post-Soviet states in December 1991.
You might also like
- THE STATE OF THE REPUBLIC: How the misadventures of U.S. policy since WWII have led to the quagmire of today's economic, social and political disappointments.From EverandTHE STATE OF THE REPUBLIC: How the misadventures of U.S. policy since WWII have led to the quagmire of today's economic, social and political disappointments.No ratings yet
- Geoffrey BawaDocument37 pagesGeoffrey BawaPriyasha AgnihotriNo ratings yet
- Mmlb2 Derrick WebDocument16 pagesMmlb2 Derrick WebPerfect ParsonsNo ratings yet
- The Spell of JapanDocument178 pagesThe Spell of JapanCalioFlacoNo ratings yet
- Japan TimelineDocument9 pagesJapan TimelineAyanami FaerudoNo ratings yet
- VILLAGEDocument52 pagesVILLAGEJosé Ignacio GonzálezNo ratings yet
- EtrDicAmm 06Document6 pagesEtrDicAmm 06api-3812626No ratings yet
- Microprocessor and Microcontroller Module 3Document91 pagesMicroprocessor and Microcontroller Module 3dshyam1991No ratings yet
- Algebra1 FormulasheetDocument1 pageAlgebra1 Formulasheetapi-268582979No ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Japan Under The ShogunsDocument20 pagesChapter 15 Japan Under The ShogunsmwmorenoNo ratings yet
- Ortega - Cuban Merchants, Slave Trade Knowledge and The Atlantic World, 1790s-1820sDocument29 pagesOrtega - Cuban Merchants, Slave Trade Knowledge and The Atlantic World, 1790s-1820sLeonardo MarquesNo ratings yet
- Rogue of The Week: Sen. Gordon Smith Two Blind Dates, Soul-Style Miss Dish: Pop Quiz!Document8 pagesRogue of The Week: Sen. Gordon Smith Two Blind Dates, Soul-Style Miss Dish: Pop Quiz!mary engNo ratings yet
- EtrDicAmm 01Document6 pagesEtrDicAmm 01api-3812626No ratings yet
- No One Can Rajni CanDocument15 pagesNo One Can Rajni CanChandra SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter One, Section One: Early PeoplesDocument16 pagesChapter One, Section One: Early PeoplesmissseesNo ratings yet
- The Berlin-Tokyo Axis and Japanese Military InitiativeDocument29 pagesThe Berlin-Tokyo Axis and Japanese Military InitiativeLorenzo Fabrizi100% (1)
- Unesco ListDocument26 pagesUnesco ListMagdalena PaduchNo ratings yet
- Johanna Granville. History of The Russian Pacific FleetDocument3 pagesJohanna Granville. History of The Russian Pacific FleetJohanna Granville100% (4)
- List of Directors of The Federal Reserve Bank of New York (1914-2011)Document45 pagesList of Directors of The Federal Reserve Bank of New York (1914-2011)juliusevola1No ratings yet
- Topographic Map of DickinsonDocument1 pageTopographic Map of DickinsonHistoricalMapsNo ratings yet
- Popov: Mixed Fortunes (2014)Document206 pagesPopov: Mixed Fortunes (2014)dusan.pavlovicNo ratings yet
- Rastafari Calendar Quick Reference List Print ReadyDocument2 pagesRastafari Calendar Quick Reference List Print ReadyyadonNo ratings yet
- Golden Age of FraternalismDocument31 pagesGolden Age of FraternalismDauradeNo ratings yet
- Operation Barbarossa - The Invasion of The Soviet UnionDocument59 pagesOperation Barbarossa - The Invasion of The Soviet UnionMichael MauldwinNo ratings yet
- Walter Phillips - The Confederation of EuropeDocument344 pagesWalter Phillips - The Confederation of EuropeDubravko AladicNo ratings yet
- Primary Sources On Indian RemovalDocument5 pagesPrimary Sources On Indian RemovalIvan GlinskiNo ratings yet
- Catalog Keeler BulbsDocument1 pageCatalog Keeler BulbsEDRAES17No ratings yet
- Niles - The Complete Geography. Mathematical, Physical, Political (1889)Document152 pagesNiles - The Complete Geography. Mathematical, Physical, Political (1889)caegeospNo ratings yet
- Russo-Japanese War, (1904-05), Military Conflict in Which ADocument29 pagesRusso-Japanese War, (1904-05), Military Conflict in Which AApril SilangNo ratings yet
- Complete List of 344 Drugs Banned From Today in The MarketDocument10 pagesComplete List of 344 Drugs Banned From Today in The Marketfreelancer800100% (1)
- China and The Geneva Conference of 1954Document20 pagesChina and The Geneva Conference of 1954Thư BùiNo ratings yet
- The Ottoman Emigration To America, 1860-1914Document36 pagesThe Ottoman Emigration To America, 1860-1914aejandro16No ratings yet
- London Gazette 38183 Despatch On The Far East 1940 Oct. 17-1941 Dec. 27, by Air Chief Marshal Sir Robert Brooke-Popham, Commander-in-Chief, Far East PDFDocument42 pagesLondon Gazette 38183 Despatch On The Far East 1940 Oct. 17-1941 Dec. 27, by Air Chief Marshal Sir Robert Brooke-Popham, Commander-in-Chief, Far East PDFxib4esalesNo ratings yet
- 5 GenocidesDocument16 pages5 Genocidesapi-487698885No ratings yet
- World War IDocument61 pagesWorld War IThunder ChimpNo ratings yet
- Tomita-Government Bonds in The Meiji Restoration PeriodDocument22 pagesTomita-Government Bonds in The Meiji Restoration Periodmesato1971No ratings yet
- The Crisis o The Enemies of America Unmasked PDFDocument326 pagesThe Crisis o The Enemies of America Unmasked PDFAnnaliza BendalNo ratings yet
- Funderburk - Betrayal of America - Bush's Appeasement of Communist Dictators Betrays American Principles (1991)Document138 pagesFunderburk - Betrayal of America - Bush's Appeasement of Communist Dictators Betrays American Principles (1991)user1776No ratings yet
- Unit 371Document9 pagesUnit 371DivertikerNo ratings yet
- Aid and Transition in TajikistanDocument16 pagesAid and Transition in Tajikistannagendrar_2No ratings yet
- A Collection of Reports On Bolshevism in Russia-No-1 - 1919 PDFDocument118 pagesA Collection of Reports On Bolshevism in Russia-No-1 - 1919 PDFVZZNo ratings yet
- Pujo Committee 2Document3 pagesPujo Committee 2Keith KnightNo ratings yet
- Buddhist Temple Names in JapanDocument29 pagesBuddhist Temple Names in JapanchnnnnaNo ratings yet
- Deaths and Cases Nycha NYC As of 11may20 - Final v2Document6 pagesDeaths and Cases Nycha NYC As of 11may20 - Final v2Matt Troutman100% (1)
- 8th Grade U S History Ngsss-Ss Pacing Guide Year at A GlanceDocument1 page8th Grade U S History Ngsss-Ss Pacing Guide Year at A Glanceapi-366325761No ratings yet
- History of The Communist Party USA - WikipediaDocument12 pagesHistory of The Communist Party USA - WikipediakevinmichaelsNo ratings yet
- What Was The Cold War?: (3) How Do These Tensions Immediately Start Forming After WW2?Document3 pagesWhat Was The Cold War?: (3) How Do These Tensions Immediately Start Forming After WW2?lindsey2aNo ratings yet
- SAR Medals and Order of PrecedenceDocument17 pagesSAR Medals and Order of PrecedenceAlan SeeNo ratings yet
- Bible SealedBookDocument7 pagesBible SealedBookdnou812No ratings yet
- Harlem BrochureDocument2 pagesHarlem Brochurelilymcap2017No ratings yet
- History of Russia - From Peter The Great To GorbachevDocument4 pagesHistory of Russia - From Peter The Great To GorbachevartistjsbNo ratings yet
- TtimboxcDocument13 pagesTtimboxcjimmyNo ratings yet
- Missiong Pages of The Civil Rights Movement 4-13-16Document49 pagesMissiong Pages of The Civil Rights Movement 4-13-16Beloved Community Center of Greensboro100% (1)
- White Mans Burden&CivilizationDocument103 pagesWhite Mans Burden&CivilizationVijay DhuriNo ratings yet
- Japanes e Mythol OgyDocument45 pagesJapanes e Mythol OgymagnumsilentiumNo ratings yet
- Chicago Park Map PDFDocument1 pageChicago Park Map PDFAmanda ZimmermanNo ratings yet
- French DirectoryDocument9 pagesFrench Directoryjojo632810100% (1)
- POLITICAL CULTURE PS 109 Topic 3 PDFDocument21 pagesPOLITICAL CULTURE PS 109 Topic 3 PDFJopoy CapulongNo ratings yet
- Union of Soviet Socialist RepublicsDocument3 pagesUnion of Soviet Socialist RepublicsελληνγιωργοςκομαντοNo ratings yet
- History of The USSRDocument1 pageHistory of The USSRKavish GargNo ratings yet
- Internal Medicine NotesDocument54 pagesInternal Medicine NotesHayley Welsh75% (4)
- Perio Notes CombinedDocument71 pagesPerio Notes CombinedHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- You Are A Paediatric Registrar at GCUH and Judy, Has Brought Her Son Dylan, Age 3, To See You With Concerns of Delayed DevelopmentDocument2 pagesYou Are A Paediatric Registrar at GCUH and Judy, Has Brought Her Son Dylan, Age 3, To See You With Concerns of Delayed DevelopmentHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Cerebellum ExamDocument2 pagesCerebellum ExamHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- General Medicine ScenarioDocument8 pagesGeneral Medicine ScenarioHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Gamsat Sample Preview 7Document11 pagesGamsat Sample Preview 7Hayley Welsh100% (1)
- Prepoll TimesDocument68 pagesPrepoll TimesHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Physiology Practice QuestionsDocument4 pagesCardiovascular Physiology Practice QuestionsHayley Welsh100% (1)
- PharmacologyDocument48 pagesPharmacologyHayley Welsh90% (10)
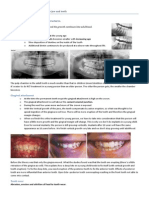
- Maturational Changes in The Jaw and TeethDocument4 pagesMaturational Changes in The Jaw and TeethHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Geometric Outlines of Permanent TeethDocument1 pageGeometric Outlines of Permanent TeethHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Mandibular Permanent Lateral IncisorDocument4 pagesMandibular Permanent Lateral IncisorHayley WelshNo ratings yet
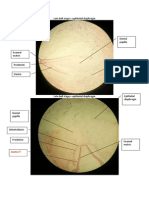
- Microscope Slides - Decalcified Sections Tooth DevelopmentDocument3 pagesMicroscope Slides - Decalcified Sections Tooth DevelopmentHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Mandibular First PremolarDocument5 pagesMandibular First PremolarHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Direct Factors Affecting The PeriodontiumDocument4 pagesDirect Factors Affecting The PeriodontiumHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Mandible at Birth: Anatomical Features of MandibleDocument5 pagesMandible at Birth: Anatomical Features of MandibleHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Neural Crest Cell: As The Groove Gets Deeper, Neural Crest. After The Neural Fold Meet andDocument4 pagesNeural Crest Cell: As The Groove Gets Deeper, Neural Crest. After The Neural Fold Meet andHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Mandibular Permanent Second MolarDocument1 pageMandibular Permanent Second MolarHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive SystemsDocument8 pagesMale Reproductive SystemsHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Amalgam 10Document5 pagesAmalgam 10Hayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Permanent Upper Canine NotesDocument5 pagesPermanent Upper Canine NotesHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Lower CentralDocument1 pageLower CentralHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Uses: - Resin Denture Teeth - Soft Lining Material (Desirable Property)Document1 pageUses: - Resin Denture Teeth - Soft Lining Material (Desirable Property)Hayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Feature On Bone Structures AssociatedDocument4 pagesFeature On Bone Structures AssociatedHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Pulp Cavity of Permanent TeethDocument1 pagePulp Cavity of Permanent TeethHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy: Why Do We Use Alloys?Document8 pagesMetallurgy: Why Do We Use Alloys?Hayley WelshNo ratings yet
- 10 Steps of GlycolysisDocument3 pages10 Steps of GlycolysisHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Summary Branchial ArchDocument2 pagesSummary Branchial ArchHayley WelshNo ratings yet
- Arn30053 TC - 3 09.8 001 Web 1Document34 pagesArn30053 TC - 3 09.8 001 Web 1SOKUEN JUNGNo ratings yet
- Parasite Eve - Ultimate Weapon DetailsDocument1 pageParasite Eve - Ultimate Weapon DetailsDemetrio Gutierrez EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Army - Shoulder RanksDocument2 pagesPhilippine Army - Shoulder Ranksjb2ookworm75% (8)
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument3 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentOm Pratap TomarNo ratings yet
- Macross VFDocument38 pagesMacross VFHijiMayoNo ratings yet
- Clad in Steel - The Evolution of Plate Armor in Medieval EuropeDocument42 pagesClad in Steel - The Evolution of Plate Armor in Medieval EuropeRWWT RWWTNo ratings yet
- Test of A Man, TheDocument209 pagesTest of A Man, TheElFinDelFinNo ratings yet
- Mearsheimer - Better To Be Godzilla Than BambiDocument2 pagesMearsheimer - Better To Be Godzilla Than BambiFilipe MSNo ratings yet
- Maac BrochureDocument7 pagesMaac BrochureKanti ModhwadiaNo ratings yet
- Stalin Hitler Bullock ArticleDocument8 pagesStalin Hitler Bullock ArticleIoana PataleNo ratings yet
- Element Leaders GuideDocument4 pagesElement Leaders GuideErnest CastleNo ratings yet
- Circular 13 2019Document2 pagesCircular 13 2019Tejindar SinghNo ratings yet
- Bonifacio Newer InfoDocument5 pagesBonifacio Newer InfoAivi VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Airbus Defence & Space Military Aircraft: Product ReviewDocument24 pagesAirbus Defence & Space Military Aircraft: Product ReviewJacob Jack YoshaNo ratings yet
- New Markup Rates PDFDocument2 pagesNew Markup Rates PDFVickyJeeNo ratings yet
- Vietnam Solitaire RulesDocument7 pagesVietnam Solitaire RulesRobbieTaylorNo ratings yet
- Marassa Jumeaux CosmasDocument3 pagesMarassa Jumeaux CosmasAshura MarshNo ratings yet
- Introduction History AaDocument28 pagesIntroduction History Aasamarth agrawalNo ratings yet
- Somalia ReconsideredDocument16 pagesSomalia ReconsideredIbrahim Abdi GeeleNo ratings yet
- Paper 18 PDFDocument197 pagesPaper 18 PDFRashni B RanjanNo ratings yet
- Commonly Used Maritime TermsDocument18 pagesCommonly Used Maritime TermsAlina BarbuNo ratings yet
- Bolt Action Errata - March 2022Document34 pagesBolt Action Errata - March 2022deltateam0004197No ratings yet
- Tag LinesDocument19 pagesTag Linesakm14366No ratings yet
- Statement by The Ukrainian Canadian CongressDocument1 pageStatement by The Ukrainian Canadian CongressLevon SevuntsNo ratings yet
- USO Show ScriptDocument3 pagesUSO Show ScriptMelina WorthingtonNo ratings yet
- Whole PDFDocument317 pagesWhole PDFIrfan FazailNo ratings yet
- Bato The Daesitiate After The WarDocument9 pagesBato The Daesitiate After The WarsalmedinmesihovicNo ratings yet
- Plano Hidráulico Cargador 988GDocument13 pagesPlano Hidráulico Cargador 988Ggerardo100% (1)
- Annex On NormalizationDocument1 pageAnnex On NormalizationAdam HaneyNo ratings yet
- Shirō IshiiDocument3 pagesShirō IshiiDylan Paul DeweeseNo ratings yet