Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ECE 440L Experiment Y: M-Ary PSK Modulation and Demodulation (1 Week)
Uploaded by
Mila PlomuoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ECE 440L Experiment Y: M-Ary PSK Modulation and Demodulation (1 Week)
Uploaded by
Mila PlomuoCopyright:
Available Formats
ECE 440L Experiment Y: M-ary PSK Modulation and Demodulation (1 week)
I.
1.
OBJECTIVES
Construct and test the M-ary PSK system described in Figures 1 and 2. a. Use proper cut-off frequencies for reconstruction filters. b. Adjust system to obtain signal voltages with the appropriate amplitude and phase. Using an 8.3 kHz bit-rate and a (2048 = 211) PN Sequence as an input signal, obtain time domain displays for: QPSK = 4-PSK, 8-PSK, and 16-PSK constellations. Constellations may be displayed on the scope by i vs. q from M-Level Encoder. Using an 8.3 kHz bit-rate, a 2048 PN Sequence, and a 100 kHz Carrier, obtain time and frequency domain (PSD) displays for: a. The QPSK (= 4-PSK ) Channel. b. The output of a demodulating multiplier and its reconstruction filter. Using an 8.3 kHz bit-rate, a 2048 PN Sequence, and a 100 kHz Carrier, compare at least 16 bits of the output PN Sequence with the input. Be observant. Optional Experiments. * * * * * ** * * * * * * * * * *
Upon completion of the M-ary PSK experiment, you should be able to:
2.
3.
4.
* * * * * * ** * ** * * * * * A.
Design experiment(s) to investigate effects of whatever interests you. Keep it focused.1 a. Include: A clear objective -- sometimes, you just want to try something; An understandable procedure include sketch of set-up; Results attach print-outs if appropriate; Conclusions be concise and accurate, b. Specify the system gains and selector switch positions. (Get TA help if needed.) c. Use proper cut-off frequencies for anti-aliasing and reconstruction filters. d. Clearly specify measurements, including where measured in the system. Instead of the 2048 PN Sequence, insert a digitized audio input. Use an 8.3 kHz bit rate for the PCM Encoder and Decoder. Dont forget input and output filters. Organize your experiment to obtain some interesting results.
B.
II.
1. 2. 3.
1
PRELAB
Read your text: 8.1.1 thru 8.1.11 Visit the web-site listed in Section III. Skim this lab and try to think of an experiment you might want to do.
For example, a long PN sequence is used as an input test signal. Does the length of the input PN sequence really matter? You must have many other questions focus on one and answer it.
ECE440, Transmission of Information
Y-1
bfr05
III..
INTRODUCTION.
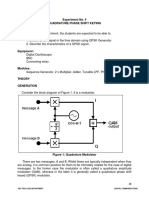
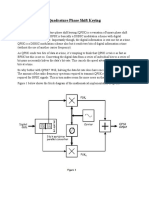
Figures 1 and 2 show the block diagram and connection diagram of the QPSK system to be investigated for this experiment. The system can be used to generate several constellations for M-ary Phase-Shift Key systems as well as generate and demodulate 4-PSK (Quadrature PSK = QPSK) signals. The carrier frequency shown is 100 kHz and the bit-rate is 8.3 kHz. On the pages following Figure 2, Table 1 and Figures 1, 3 and 7 are from: http://www.wj.com/documents/Tech_Notes_Archived/PSK_demod_part1.pdf These figures give a very quick overview of M-ary PSK.
NOTE:
In Figures 1 and 2, below, phased carriers and bit-clock are supplied to the demodulator from the generator.
SEQUENCE GENERATOR
2 sin(2 t ) 2.0 Trinary
i
M-LEVEL ENCODER
ADDER Amplifier (Inverting) QPSK Channel
BUFFER 2.0 Trinary Amplifier (Inverting)
2.0 V
2 cos(2 t )
2 sin(2 t ) 2.0 Trinary
QPSK Channel
2 cos(2 t )
K-H LPF
i
2.0 Trinary M-LEVEL DECODER INPUT SEQUENCE TTL
2.0 V
q
K-H LPF
Fig.1. Block Diagram for QPSK System.
ECE440, Transmission of Information
Y-2
bfr05
11
SW 2
SW 2
0 1 MULTIPLIER MULTIPLIER ADDER MULTIPLIER MULTIPLIER M-LEVEL DECODER
CONSTELLATION
0 1
1 2
1 2
SEQUENCE GENERATOR
M-LEVEL ENCODER
CONSTELLATION
RESET
DC AC
G
DC AC AC AC
DC
DC
4 8 16
RESET
4 - point 8 - point 16 - point
DECISION
SYNC
X
q
Z
HUNT
q g Y K XY Y K XY
B GA + gB
CLK
X-TTL
DATA
i Y K XY Y
i K XY
CLK
I
DATA
ECE440, Transmission of Information
100 k COS 100 k SIN
CLK
Y-TTL
CLK
8.3 k TTL
8.3 k TTL
QPSK CHANNEL
100 k SIN
100 k COS
8.3 k TTL
BUFFER AMPLIFIERS
Y-3
K1
BINARY OUTPUT
MASTER SIGNALS
25 kHz 100 k SIN 1/2 KROHN-HITE 100 k COS 100 k TTL
SCOPE SELECTOR A B A B OUT
A
100 kHz CARRIER
K1 A
sin(t) cos(t)
K2 TTL
LPF
8.3 k TTL 25 kHz
A
A B
K2 B
8.3 kHz SAMPLE CLOCK TTL 2 kHz MESSAGE
sin(t)
1/2 KROHN-HITE
OUT
LPF Fig. 2. Connection Diagram for . QPSK System
bfr05
ECE440, Transmission of Information
Y-4
bfr05
NOTE: The circuit of Figure 7 demodulates without a carrier from the modulating circuit. The next trick would be to steal the bit clock from the data signal.
IV.
EXPERIMENT. Perform experiments required to meet the stated objectives. Record your procedures and results.
ECE440, Transmission of Information
Y-5
bfr05
ECE440, Transmission of Information
Y-6
bfr05
You might also like
- Expt#4 - Quadrature Phase Shift KeyingDocument5 pagesExpt#4 - Quadrature Phase Shift KeyingElaiza M. PontriasNo ratings yet
- PSK Lab ManualDocument4 pagesPSK Lab ManualSakshi DewadeNo ratings yet
- A Branch-And-Bound Algorithm For The Time-Dependent Travelling Salesman ProblemDocument11 pagesA Branch-And-Bound Algorithm For The Time-Dependent Travelling Salesman ProblemDaniel FernándezNo ratings yet
- Manual Survey Pro For RangerDocument337 pagesManual Survey Pro For RangerIni ChitozNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Engineering Research and DevelopmentDocument8 pagesInternational Journal of Engineering Research and DevelopmentIJERDNo ratings yet
- WTM Microwave DigitalDocument16 pagesWTM Microwave DigitalrrohuuNo ratings yet
- PSK Qam2 PDFDocument43 pagesPSK Qam2 PDFKim Kenneth UgayNo ratings yet
- Quadrature Phase Shift Keying - 1Document15 pagesQuadrature Phase Shift Keying - 1RANA RAMEEZNo ratings yet
- Analog - Sine Wave Generation With Psoc 1 (Demonstration With CTCSS)Document11 pagesAnalog - Sine Wave Generation With Psoc 1 (Demonstration With CTCSS)Adonis LealNo ratings yet
- CDMA Baseband Processing On A TMS320C54x DSPDocument11 pagesCDMA Baseband Processing On A TMS320C54x DSPsampath5211No ratings yet
- DC Lab ManualDocument43 pagesDC Lab ManualSowmya KharviNo ratings yet
- Commn Systems Lab ManualDocument37 pagesCommn Systems Lab Manualnidheeshlal10No ratings yet
- 8 PSKDocument10 pages8 PSKJill_xyinz14589No ratings yet
- Analog Communication Lab ManualDocument60 pagesAnalog Communication Lab Manualjsingh19No ratings yet
- A New Miniaturized Electronic Pill (Epille®) For Mass Medical Application With Bi-Directional Communication SystemDocument4 pagesA New Miniaturized Electronic Pill (Epille®) For Mass Medical Application With Bi-Directional Communication SystemMarka ReddyNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 Band Pass and Band Reject Filters CompressDocument8 pagesLab 4 Band Pass and Band Reject Filters CompressAbhijith DileepkumarNo ratings yet
- QPSK Modulation and Error Correcting CodesDocument21 pagesQPSK Modulation and Error Correcting CodesSIRISHASIRIINo ratings yet
- ECET 310 ASSIST Expect Success Ecet310assistdotcomDocument14 pagesECET 310 ASSIST Expect Success Ecet310assistdotcommadelyan86No ratings yet
- Comms2 Presentation 3Document15 pagesComms2 Presentation 3James MagnataNo ratings yet
- ADC 11 Digital ModulationDocument38 pagesADC 11 Digital ModulationMehboob KhokharNo ratings yet
- A Differential QPSK Modem Using The TMS320C6711 DSKDocument5 pagesA Differential QPSK Modem Using The TMS320C6711 DSKSamia AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Phase Shift OscillatorDocument4 pagesPhase Shift OscillatorNA NANo ratings yet
- EET203 Tutorial TimerDocument2 pagesEET203 Tutorial Timerkay_rolNo ratings yet
- Analog Communication ManualDocument50 pagesAnalog Communication Manualgowrav_hassanNo ratings yet
- BPSK - Binary Phase BPSK - Binary Phase BPSK - Binary Phase BPSK - Binary Phase Shift Keying Shift Keying Shift Keying Shift KeyingDocument10 pagesBPSK - Binary Phase BPSK - Binary Phase BPSK - Binary Phase BPSK - Binary Phase Shift Keying Shift Keying Shift Keying Shift KeyingHayatun NufusNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication: Notes 2Document23 pagesWireless Communication: Notes 2mkoaqNo ratings yet
- DC Que BankDocument11 pagesDC Que BankGaurav Kumbharde0% (1)
- MV - An E-Band Low-Noise Transformer-Coupled Quadrature VCO in 40 NM CMOSDocument9 pagesMV - An E-Band Low-Noise Transformer-Coupled Quadrature VCO in 40 NM CMOSsm123ts456No ratings yet
- LabDocument9 pagesLabZuru Raya EthioNo ratings yet
- Analog Communication Manual TceDocument51 pagesAnalog Communication Manual TceDayanand Gowda KrNo ratings yet
- QDocument4 pagesQSri NikethanNo ratings yet
- DCT-6000-09 QPSK - Manual Mod Sin Sol PDFDocument25 pagesDCT-6000-09 QPSK - Manual Mod Sin Sol PDFArturo TapiaNo ratings yet
- BCS Practice Questions - 2021Document11 pagesBCS Practice Questions - 2021bharatshrawagiNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication Lab Manual For VI Semester B.Tech (Electronics Engineering)Document25 pagesDigital Communication Lab Manual For VI Semester B.Tech (Electronics Engineering)Nikolai RossanderNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Early-Late Gate Bit Synchronizer For Satellite CommunicationDocument4 pagesDesign and Implementation of Early-Late Gate Bit Synchronizer For Satellite CommunicationMatthew CarterNo ratings yet
- Digital Modulation Techniques For Mobile and Personal Communication SystemsDocument8 pagesDigital Modulation Techniques For Mobile and Personal Communication Systemsdava2007No ratings yet
- Wicomm T QPSKDocument13 pagesWicomm T QPSKvithyaNo ratings yet
- LAb 4 PSKDocument9 pagesLAb 4 PSKJoseph MagonduNo ratings yet
- 15EC306J Cycle 2 ExptsDocument28 pages15EC306J Cycle 2 ExptsSanjeev KumarNo ratings yet
- A 6.1 GS/S 52.8 MW 43 DB DR 80 MHZ Bandwidth 2.4 GHZ RF Bandpass Adc in 40 NM CmosDocument4 pagesA 6.1 GS/S 52.8 MW 43 DB DR 80 MHZ Bandwidth 2.4 GHZ RF Bandpass Adc in 40 NM Cmossohailasghar_tNo ratings yet
- Digital Communications (DCOM)Document4 pagesDigital Communications (DCOM)Mamotete MohohloNo ratings yet
- Regular Correspondence: Compact High-Frequency Output Buffer For Testing of Analog CMOS VLSI CircuitsDocument3 pagesRegular Correspondence: Compact High-Frequency Output Buffer For Testing of Analog CMOS VLSI CircuitsSaranya ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Microwave Frequency Counters: Application Note 200-1Document20 pagesFundamentals of Microwave Frequency Counters: Application Note 200-1Darshan PatelNo ratings yet
- The Quadrature FM Detector - Analysis and DesignDocument5 pagesThe Quadrature FM Detector - Analysis and DesignChristopher BrownNo ratings yet
- Hardware Implementation of 16qamDocument10 pagesHardware Implementation of 16qamChethanNo ratings yet
- AN1207 For MC145170Document6 pagesAN1207 For MC145170ftbenji123No ratings yet
- S A A O N I S C A C: Imulation ND Nalysis F Oise N Witched Apacitor Mplifier IrcuitsDocument4 pagesS A A O N I S C A C: Imulation ND Nalysis F Oise N Witched Apacitor Mplifier IrcuitsSai KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Second Order Switched Capacitors Filters With Feedback SignalDocument3 pagesImplementation of Second Order Switched Capacitors Filters With Feedback SignalInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Analog CommunicationsDocument4 pagesAnalog CommunicationsJagadeesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 TNE064 Digital Communication ElectronicsDocument4 pagesLab 1 TNE064 Digital Communication ElectronicsfwahideyNo ratings yet
- Lab MUX QPSK New2020Document4 pagesLab MUX QPSK New2020Mihai HertzNo ratings yet
- Elec4505 Exp0Document7 pagesElec4505 Exp0muafhanNo ratings yet
- DC - Experiment - No. 5Document8 pagesDC - Experiment - No. 5amol maliNo ratings yet
- Sample Question For FInal ExamDocument6 pagesSample Question For FInal ExamAmir MuzzammilNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing Using the ARM Cortex M4From EverandDigital Signal Processing Using the ARM Cortex M4Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1From EverandNewnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorFrom Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Radio Frequency Identification and Sensors: From RFID to Chipless RFIDFrom EverandRadio Frequency Identification and Sensors: From RFID to Chipless RFIDNo ratings yet
- V2X SurveyDocument37 pagesV2X SurveyAniket panditNo ratings yet
- MSC Thesis - Stock Trend Prediction Using News ArticleDocument165 pagesMSC Thesis - Stock Trend Prediction Using News ArticlepankajpandeylkoNo ratings yet
- ForestDocument2 pagesForestZINEB LAHYANo ratings yet
- M.Des IIT Delhi Brochure PDFDocument22 pagesM.Des IIT Delhi Brochure PDFAnandu KBNo ratings yet
- Virtual Classroom NetiquetteDocument10 pagesVirtual Classroom NetiquetteZylil Quila Ymir RuizNo ratings yet
- Cyinder Track CalculatorDocument3 pagesCyinder Track CalculatorSpockCritical CriticalNo ratings yet
- Annotated BibliographyDocument5 pagesAnnotated Bibliographyapi-284997804100% (1)
- DELL Latitude D420 COMPAL LA-3071P Rev 1.0 SchematicsDocument59 pagesDELL Latitude D420 COMPAL LA-3071P Rev 1.0 SchematicsviniciusvbfNo ratings yet
- Doom SourceDocument818 pagesDoom SourceEvil-Soft.comNo ratings yet
- Agc 150 Designers Handbook 4189341188 UkDocument398 pagesAgc 150 Designers Handbook 4189341188 UkMaicon ZagonelNo ratings yet
- An Acknowledgement LetterDocument1 pageAn Acknowledgement LetterGovindan PerumalNo ratings yet
- VFD Manual PDFDocument60 pagesVFD Manual PDFray1coNo ratings yet
- Haxm-Windows v6 0 1Document3 pagesHaxm-Windows v6 0 1Esteban David Ramírez EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Boundary-Scan DFT GuidelinesDocument63 pagesBoundary-Scan DFT GuidelinesSambhav VermanNo ratings yet
- StqaDocument169 pagesStqaHimanshu SinghaniNo ratings yet
- Cat CDVRDocument8 pagesCat CDVRAdeel AfzalNo ratings yet
- HWQS Intl System ArchitectureDocument1 pageHWQS Intl System Architecturereezqee100% (1)
- Industrial Report On InfosysDocument14 pagesIndustrial Report On InfosysMitesh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Integrating Security Into The IoT Strategy in The New Converged EnvironmentDocument20 pagesIntegrating Security Into The IoT Strategy in The New Converged EnvironmentSuriya RojsuriyaNo ratings yet
- Student GuideDocument342 pagesStudent GuideEduardo Velazquez MoraNo ratings yet
- Global CatalogueDocument12 pagesGlobal CatalogueSalmanNo ratings yet
- Regus Lakeview - Meeting Room Price ListDocument1 pageRegus Lakeview - Meeting Room Price ListJayaraj TNo ratings yet
- Captive Portal Troubleshooting - Basic SlidesDocument19 pagesCaptive Portal Troubleshooting - Basic SlidesEdson MouraNo ratings yet
- How To Get Unlimited Time in Internet Café's PDFDocument1 pageHow To Get Unlimited Time in Internet Café's PDFbkchoudhury1993No ratings yet
- Contents of Project ProposalDocument2 pagesContents of Project ProposalFatima Razzaq100% (1)
- Computer Basics: What Is An Application?Document4 pagesComputer Basics: What Is An Application?Ser Crz JyNo ratings yet
- JS - Map-Filter-ReduceDocument10 pagesJS - Map-Filter-ReduceJosie DeLimaNo ratings yet