Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Standard Costing (Compatibility Mode)
Uploaded by
sugambordoloiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Standard Costing (Compatibility Mode)
Uploaded by
sugambordoloiCopyright:
Available Formats
9/23/2011
Standard Costs and Variance Analysis
Meaning of Standard Costing
According to CIMA London, Standard Costing is, the preparation and use of standard costs, their comparison with actual costs, and the analysis of variances to their causes and points of incidence. Standard Costing discloses the cost of deviations from standard and classifies these as to their causes, so that management is immediately informed of the sphere of operations in which remedial action is necessary. Thus Standard Costing is a method of ascertaining costs whereby statistics are prepared to show : The standard costs The actual costs The difference between these costs which is termed as variance
2
9/23/2011
Standard Costing As A Management Tool
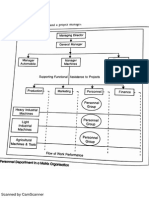
Delegation of Authority and Responsibility :The sphere of :The operation of adverse variations is disclosed and particular production department or centre can be held accountable. The delegation of responsibility and authority can be made by the management to control the affairs in different departments. Management by Exception: Management by exception can be made applicable in the business and the management can concentrate on cases which are off standard. Better Economy, Efficiency and Productivity: Managerial review of costs is more effective as the operations are scrutinized carefully and inefficiencies are disclosed.
Limitations of Standard Costing
Heavy costs :Fixation of standards may be costly and may :Fixation require high skill and competence. Frequent Revision Required :Revision of standards is a :Revision tedious and costly process. Unsuitable for Non-standardized Products: Industries Nondealing in non- standardized products may find the system nonunsuitable and costly. Fixation of Responsibility Difficult: Responsibility can be fixed only when controllable and non controllable factors are distinctly known Adverse Psychological Effects: Standards may be fixed at a high level which is unachievable, resulting in frustration or building up of resistance.
4
9/23/2011
Standard costs may be: (i) IDEAL, (ii) Expected, and (iii) Normal/Attainable.
Ideal standard cost The ideal standard cost refers to estimates of costs under ideal or perfect conditions. The assumption would be that there would be no waste, no scrap, no idle items, no machine breakdown, and so on. Expected Standard Cost The expected standard cost is based upon the most likely attainable result. Technically, it means what can happen and not what should happen. Normal Standard Costs Normal standard costs are costs which are attainable if operations/activities are efficient.
Determination of Standard Costs
Preliminaries to setting of Standards: Establishment of Cost Centres : Though all the processes combined together manufacture the final product, but for measuring productivity and controlling labour and overheads, classification into cost centres becomes necessary. Classification and Codification of Accounts: Helps in quick Accounts: collection and analysis of cost information. Period of Use: This involves the length of the operating Use: period for which standards are to be used. The standards, which may be long term or short term, may be categorized as : a) Basic Standards: Not altered over a long period of time, Standards: revisions are not frequent and there is a stability and stagnancy in standards fixed. fixed. b) Current Standards: These are short term standards. 6
9/23/2011
Determination of Standard Costs ( Contd )
Reasonable or Desired Level of Attainment :Standards are :Standards to be set assuming efficient working conditions and reasonable good performance. Active Level: The level of activity or performance required must be decided upon before establishing any standards. It should be computed keeping in mind the capacity of the plant and the marketability of the products.
Cost Variances
The deviation of the actual from the standard is known as variance. Variance may be favourable or adverse. Cost Variance may be depicted in the following manner: Cost Variances
Direct Material Cost Variance
Direct Labour Cost Variance
Over Head Cost Variance
9/23/2011
Direct Material Variance
Direct Material Cost Variance Direct Material Price Variance Direct Material Mix Variance
Direct Material Usage Variance Direct Material Yield Variance
Direct Material Cost Variance: It is the difference between the standard cost of direct material specified for the output achieved and the actual cost of direct material used. = (Total Standard cost for actual output) Total Actual Cost = ( Std. Price x Std Quantity for _ ( Actual Price x Actual actual output) quantity)
9
Direct Material Variance ( Contd )
Direct Material Price Variance : That portion of direct material cost variance which is due to the difference between the standard price specified and actual price paid. = ( Actual Qty used) x ( Std Price Actual Price ) Direct Material Usage Variance : That portion of direct material cost variance which is due to the difference between the standard quantity specified and the actual quantity used. = ( Std. Rate ) x ( Std. qty for actual output Actual qty ) Direct Material Mix Variance: That portion of direct material Variance: usage variance which is due to the difference between the standard and actual composition of a mixture. = ( Std. Price ) x (Revised Std. Qty Actual Qty)
10
9/23/2011
Direct Material Variance ( Contd )
where, Revised Std Qty = (Total weight of Actual Mix) x Std. Qty ( Total Weight of Std. Mix ) Material Yield Variance : It is that portion of direct material usage variance which is due to the difference between the standard yield specified and the actual yield obtained. = ( Std. Cost per unit ) x ( Std. Output for Actual Mix - Actual Output )
11
Direct Labour Variance
Direct Labour Cost Variance Direct Labour Rate Variance Direct Labour Mix Variance
Direct Labour Efficiency Variance Direct LabourYield Variance
Direct Labour Cost Variance: It is the difference between standard direct wages specified for the activity achieved and the actual direct wages paid. = ( Std. cost for actual output ) - ( Actual Cost ) = ( Std rate x Std Time for Actual Output) ( Actual rate Actual Time )
12
9/23/2011
Direct Labour Variance ( Contd )
Direct Labour Rate Variance : That portion of direct labour cost variance which is due to the difference between the standard rate of pay specified and the actual rate paid. = Actual Time x ( Std. Rate Actual Rate ) Direct Labour Efficinecy Variance: That portion of direct Variance: labour cost variance which is due to the difference between the standard labour hours specified for the activity achieved and the actual labour hours expended. = Std Rate x ( Std. Time for Actual Output Actual Time) Direct Labour Mix Variance : This variance arises if during a particular period, the grades of labour used in production are different from those budgeted. = Std. Rate x ( Revised Std. Time Actual Time )
13
Direct Labour Variance ( Contd )
where, Revised Std. Time = (Total Actual Time ) x Std. Time ( Total Std. Time) Direct Labour Yield Variance : It is the variance in labour cost on account of increase or decrease in yield or output as compared to the relative standard. = Std. Cost per unit x ( Std. Output of _ Actual Actual mixture output ) Total Direct Labour Efficiency Variance : In those cases where there is an idle time variance ; Total Direct Labour efficiency variance = ( Idle Time variance )+ (Direct Labour efficiency variance) Idle Time Variance = Idle Time x Std. Rate
14
9/23/2011
Overhead Variances
Certain Important terms related to Overhead Variances: Standard Overhead rate per unit = Budgeted Overheads Budgeted Output Standard Overhead rate per hr = Budgeted Overheads Budgeted Hours Standard hrs for Actual Output = Budgeted hrs x Actual Output Budgeted Output Standard Output = Budgeted Output x Actual Hrs Budgeted hrs Recovered Overheads = (Std rate per hr) x (Std hrs for actual output) Budgeted Overheads = (Std. Rate per unit) x (Budgeted Output) Standard Overheads = (Std. rate per unit) x (Std. Output for actual time) Actual Overheads = (Actual rate per unit) x (Actual output)
15
Overhead Variance ( Contd )
Overhead Cost Variance Variable Overhead Cost Variance Fixed Overhead Expenditure Variance Fixed Overhead Efficiency Variance
Fixed Overhead Cost Variance Fixed Overhead Volume Variance Fixed Overhead Capacity Variance
Overhead Cost Variance = Recovered Overheads Actual Overheads Variable Overhead Cost Variance: Variance: = Recovered Variable Overheads Actual Variable Overheads
16
9/23/2011
Variable Overheads ( Contd )
Fixed Overhead Cost Variance : = Recovered fixed Overheads Actual Fixed Overheads Fixed Overhead Expenditure Variance: Variance: = Budgeted Fixed Overheads Actual Fixed Overheads Fixed Overhead Volume Variance : = Recovered Fixed Overheads Budgeted Fixed Overheads Fixed Overhead Efficiency Variance : = Std Fixed Overhead x ( Std. Hrs for _ Actual rate per hour Actual production Hours ) Fixed Overhead Capacity Variance : = Std Fixed Overhead x ( Actual Hrs _ Budgeted Rate per hr Worked Hours )
17
Sales Variance
Sales Variance With Reference to Turnover With Reference to Profit
Value Variance Price Mixture Volume Quantity
With Reference to Turnover: Value Variance = Budgeted Sales Actual Sales Price Variance = Actual Qty Sold x ( Std. Price Actual price) = (Standard Sales Actual Sales) Volume Variance = Std. Price x ( Budgeted Qty Actual Qty ) = Budgeted Sales Standard Sales
18
9/23/2011
Sales Variance ( Contd )
-
Mix Variance : Based On Quantity : Mix Variance = Std. Price x ( Revised Std. Qty Actual Qty.) = Revised Std. Sales Std. Sales Based on Value : Mix Variance = Revised Std. Sales Std. Sales where, Revised Std. Sales = Budgeted Ratio of Sales x Std. Sales where, Budgeted Ratio of Sales = Budgeted Sales of a Product Total Budgeted Sales Quantity Variance = Budgeted Sales Revised Std. Sales
19
Sales Variance ( Contd )
With Reference to Profit : Value Variance = Budgeted profit Actual Profit Price Variance = Std. Profit Actual Profit = Actual Qty Sold x ( Std. Profit Actual Profit per unit ) Volume Variance = Budgeted Profit Standard Profit = Std. Rate of Profit x ( Budgeted Qty Actual Qty ) Mix Variance = Revised Std. Profit Std. Profit Quantity Variance = Budgeted profit Revised Std. Profit
20
10
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Delhi Gang Rape: 5 Accused Summoned Cops Refute Charges: M&M Re-Enters 2-Wheeler Space With Pantero & CenturoDocument1 pageDelhi Gang Rape: 5 Accused Summoned Cops Refute Charges: M&M Re-Enters 2-Wheeler Space With Pantero & CenturosugambordoloiNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Policing Social Media Isn't A Smart Policy - BL - 17aug10 PDFDocument2 pagesPolicing Social Media Isn't A Smart Policy - BL - 17aug10 PDFPrudhvinadh KopparapuNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Paint IndustryDocument4 pagesPaint IndustrysugambordoloiNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Sony Xperia Z - Assemble Your Device - EE HelpDocument21 pagesSony Xperia Z - Assemble Your Device - EE HelpsugambordoloiNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Policing Social Media Isn't A Smart Policy - BL - 17aug10Document2 pagesPolicing Social Media Isn't A Smart Policy - BL - 17aug10sugambordoloiNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Konkan Railway Corporation LTD - KRCL Goes All Out To Encourage Transporters To Use RoRo Services - Times of IndiaDocument5 pagesKonkan Railway Corporation LTD - KRCL Goes All Out To Encourage Transporters To Use RoRo Services - Times of IndiasugambordoloiNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Paint Industry PDFDocument9 pagesPaint Industry PDFsugambordoloiNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Story of Toughest Konkan Railways Project India by Its Project Director E ShreedharanDocument17 pagesThe Story of Toughest Konkan Railways Project India by Its Project Director E ShreedharanSreeranjini Ranjith KumarNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- New Doc 19 PDFDocument1 pageNew Doc 19 PDFsugambordoloiNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Sony Xperia Z - Assemble Your Device - EE HelpDocument2 pagesSony Xperia Z - Assemble Your Device - EE HelpsugambordoloiNo ratings yet
- New Doc 18Document1 pageNew Doc 18sugambordoloiNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Request Details: Plant Visit Permission FormatDocument1 pageRequest Details: Plant Visit Permission FormatsugambordoloiNo ratings yet
- VTU Mba SyllabusDocument164 pagesVTU Mba Syllabusanushata100% (1)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Madura Garments Co-InfoDocument14 pagesMadura Garments Co-InfosugambordoloiNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Nature of Finanacial ManagementDocument19 pagesNature of Finanacial ManagementsugambordoloiNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Company PhilosophyDocument1 pageCompany PhilosophysugambordoloiNo ratings yet
- Cover PageDocument1 pageCover PagesugambordoloiNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- DLF Group StrategyDocument15 pagesDLF Group Strategyblackberry7100g100% (1)
- Factors Affecting International PricingDocument5 pagesFactors Affecting International Pricingविशाल गुप्ता100% (1)
- Bus 110-Introduction To MarketingDocument45 pagesBus 110-Introduction To MarketingEligius NyikaNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Moore MedicalDocument16 pagesMoore MedicalNiyati GargNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Market PositioningDocument17 pagesMarket PositioningJackie CasadoNo ratings yet
- PA-1 Adjusments and Worksheet (Problems)Document5 pagesPA-1 Adjusments and Worksheet (Problems)Safira ChairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Pestel and PorterDocument4 pagesPestel and PorterJonarissa BeltranNo ratings yet
- FSA Appendix 2Document267 pagesFSA Appendix 2MRVNo ratings yet
- The Fundamentals of Managerial EconomicsDocument58 pagesThe Fundamentals of Managerial EconomicshussainNo ratings yet
- I'm An Actress Who Has Performed in Various Stage Plays and Musicals. I Also Do Makeup, Stage Design, Production Design, and Costume Design.Document1 pageI'm An Actress Who Has Performed in Various Stage Plays and Musicals. I Also Do Makeup, Stage Design, Production Design, and Costume Design.Video rajaNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Sum of The Reach Number of Specific Media Vehicles in A Given Media Plan Gives The Message Weight Is Expressed in Terms of Gross Impressions or Gross Rating Points (GRP)Document10 pagesThe Sum of The Reach Number of Specific Media Vehicles in A Given Media Plan Gives The Message Weight Is Expressed in Terms of Gross Impressions or Gross Rating Points (GRP)keen writerNo ratings yet
- Relationship Marketing and Customer Relationship Management (CRM)Document17 pagesRelationship Marketing and Customer Relationship Management (CRM)Shilpi PrasadNo ratings yet
- Accounting 1 Review QuizDocument6 pagesAccounting 1 Review QuizAikalyn MangubatNo ratings yet
- Biskfarm Case StudyDocument1 pageBiskfarm Case StudyArpann AratdarNo ratings yet
- Jaguar Racing LimitedDocument24 pagesJaguar Racing LimitedVarun DubeyNo ratings yet
- Marketing NotesDocument76 pagesMarketing NotesVenessa YongNo ratings yet
- Task 2 Model AnswerDocument8 pagesTask 2 Model Answerthulli06No ratings yet
- Walmart Case StudyDocument3 pagesWalmart Case StudyMeareg MebratuNo ratings yet
- RETATIL MANAGEMENT - MasterDocument38 pagesRETATIL MANAGEMENT - MasterPravish KhareNo ratings yet
- Transcript of Conference Call With Investors/Analysts (Company Update)Document20 pagesTranscript of Conference Call With Investors/Analysts (Company Update)Shyam SunderNo ratings yet
- Red Hot Selling - Paul GoldnerDocument238 pagesRed Hot Selling - Paul GoldnerBibleNut777No ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- MBA Semester-I: Work Allotment Schedule Subject Code Subject Instructor 18MBA11 18MBA12 18MBA13 18MBA14 18MBA15 18MBA16Document1 pageMBA Semester-I: Work Allotment Schedule Subject Code Subject Instructor 18MBA11 18MBA12 18MBA13 18MBA14 18MBA15 18MBA16Mrudhula RaniNo ratings yet
- Marketing Chapter 3Document98 pagesMarketing Chapter 3JimmyLozadaNo ratings yet
- Gini N JonyDocument5 pagesGini N JonyHarshada Sambare50% (2)
- 01 Wegagen Bank Ar 2009-10Document52 pages01 Wegagen Bank Ar 2009-10Ajmel Azad Elias100% (8)
- Business Plan BarbershopDocument13 pagesBusiness Plan Barbershopsunlightshines germono13No ratings yet
- Slides of Engro FoodsDocument60 pagesSlides of Engro FoodsTalha KhanNo ratings yet
- PT Mega Perintis TBK Dan Entitas AnakDocument90 pagesPT Mega Perintis TBK Dan Entitas AnakGesti saputra SaputraNo ratings yet
- Oshi Sharma PDFDocument1 pageOshi Sharma PDFrads_1405No ratings yet
- Sales Forecast Excel Template With ChartsDocument28 pagesSales Forecast Excel Template With ChartsCKhae SumaitNo ratings yet