Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fiber Optic Paper
Uploaded by
Eduardo EspinosaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fiber Optic Paper
Uploaded by
Eduardo EspinosaCopyright:
Available Formats
Project Engineer Name: Eduardo Espinosa Project Name: Fiber-Optic Paper Project Manager: K.
Daraie Date: February 25, 2012 Grade:
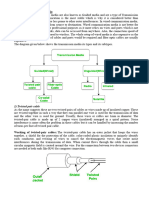
Fiber-optic are long, thin strands of pure glass that are about the diameter of a human hair. They are arranged in bundles called optical cables and are used to transmit light signals over long distances. The fiber-optic cables are made of three parts which are the core, cladding, and the buffer coating. The core is a thin glass center of the fiber where light travels. The cladding is the outer optical material that surrounds the core that reflects the light back into the core. The buffer coating is a plastic coating that protects the fiber from damage and moisture. The hundreds or thousands of optical fibers are arranged in optical cables. The bundles are protected by the cables outer covering called the jacket. There are two types of fiber: Singlemode fibers and Multi-mode fibers. Single-mode fibers have small cores that are about 9 microns in diameter. One micron is one-millionth of a meter. The single-mode fibers transmit infrared laser light at 1,300 to 1550 nanometers per wavelength. The multi-mode fibers have larger cores which are 62.5 microns in diameter. The multi-mode fibers transmit infrared light at 850 to 1300 nanometers from light-emitting diodes also known as LED. Fiber-optics has many benefits compared to copper wire cable. Fiber-optic cable are less expensive, thinner, higher carrying capacity, less signal degradation, light signals, low power, digital signals, non-flammable, lightweight, and are flexible. They are less expensive because it can go several miles and can be made cheaper than the lengths of copper wire. This can save you money. This cable also costs much less to maintain than copper as well as it provides a greater resistance to electromagnetic noise such as radios, motors or another nearby cables. Signals can be transmitted further without needing to be refreshed or strengthen like other cables. Fiber-optics can be drawn to small diameters than copper wire. It can also have more fibers bundled into a given-diameter cable than in copper wire because of how thin the optical fibers are compared to the copper wires. The cables being so small, it allows more phone lines to go over the same cable or more channels to come through the cable into the cable TV box. The signal loss in fiber-optics is less than in copper wire. The light signals of the fibers from the fiber-optics do not interfere with those of other fibers in the same cable unlike the electrical signals in copper wires. The signal in fiberoptics degrades less which will mean that lower-powered transmitters can be used instead of the high-voltage electrical transmitters needed for copper wires. Fiber-optics is best suited for carrying digital information which can be extremely useful in computer networks. They are suited for carrying digital information also because fiber-optics operates at high speeds, up into the gigabits range. It is also non-flammable because there is no electricity that is passed through the optical fibers, which means no fire hazard. The optical fiber weighs less than copper wire cable. Fiber-optic cables take up less space in the ground than copper wire. Fiber-optics is so flexible that they can transmit and receive light that are used in many flexible digital cameras. A few good examples of this include medical imaging, mechanical imaging, and plumbing.
You might also like
- Assignment On Fiber Obtic CommunicationDocument8 pagesAssignment On Fiber Obtic Communicationmd.jewel rana100% (2)
- THE BASICS OF FIBER OPTIC CABLE A TutorialDocument4 pagesTHE BASICS OF FIBER OPTIC CABLE A TutorialSiddharth Bastia100% (1)
- Metrocluster Ip: Solution Architecture and DesignDocument36 pagesMetrocluster Ip: Solution Architecture and DesignpedirstuffNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics (Optical Fiber)Document4 pagesFiber Optics (Optical Fiber)LaLa BanksNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics: Principle of OperationDocument4 pagesFiber Optics: Principle of OperationThura Htet AungNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Fiber Optic CableDocument8 pagesThe Basics of Fiber Optic Cableveeramaniks408100% (1)
- Optical FiberDocument13 pagesOptical FiberPawan Meena100% (1)
- Optical Fiber: Jawad Abdul Qayyum 07-0282Document14 pagesOptical Fiber: Jawad Abdul Qayyum 07-0282Jawad Abdul QayyumNo ratings yet
- Fiber OpticsDocument10 pagesFiber OpticstanmyNo ratings yet
- Optic Fiber ReportDocument25 pagesOptic Fiber Reportronalyn ablesNo ratings yet
- Optics FiberDocument8 pagesOptics Fiberahmed alquhaliNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics TutorialDocument15 pagesFiber Optics TutorialdioumbNo ratings yet
- Cables PDFDocument6 pagesCables PDFAaaNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument10 pagesSeminar ReportPatphytu Accordclubthailand100% (1)
- Fiber Optics ReloadedDocument116 pagesFiber Optics ReloadedNwachukwu Evan IzunnaNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optic Cable Core-How Much Do You Know About It?Document16 pagesFiber Optic Cable Core-How Much Do You Know About It?UmairNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkingDocument3 pagesComputer NetworkingRanNa ArhamNo ratings yet
- Fibre OpticsDocument15 pagesFibre OpticsPrakash RajNo ratings yet
- Fibre OpticsDocument15 pagesFibre OpticsNeeraj PatilNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Optical FiberDocument9 pagesAdvantages of Optical Fibersai saiNo ratings yet
- Communication: Optical Fiber Working and Its ApplicationsDocument4 pagesCommunication: Optical Fiber Working and Its ApplicationssmeenaNo ratings yet
- Fiber OpticsDocument22 pagesFiber OpticsRayaldi MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optic Cable Single-Mode Multi-Mode TutorialDocument12 pagesFiber Optic Cable Single-Mode Multi-Mode TutorialfnasimiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 CCNDocument5 pagesAssignment 2 CCNsajjadNo ratings yet
- Exposé AnglaisDocument8 pagesExposé AnglaisAnichatou BELEMNo ratings yet
- OpticalDocument3 pagesOpticalAshok Pradhan100% (1)
- Fiber OpticsDocument9 pagesFiber Opticsapi-3745830No ratings yet
- Handout Activity: HA710: Fiber OpticsDocument1 pageHandout Activity: HA710: Fiber OpticsDGGNo ratings yet
- Title of The Work: Network Infrastructures A.A. 2008-2009Document5 pagesTitle of The Work: Network Infrastructures A.A. 2008-2009Abel Martín MarínNo ratings yet
- Practical 2Document7 pagesPractical 2umair riazNo ratings yet
- Fiber OpticDocument3 pagesFiber OpticNazmul HasanNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber: Rushit Patel B.E.ElectricalDocument29 pagesOptical Fiber: Rushit Patel B.E.ElectricalDr-AmrArafaNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optics: Jacques Babinet in Paris in The Early 1840sDocument22 pagesFiber Optics: Jacques Babinet in Paris in The Early 1840sMartin John RamirezNo ratings yet
- Communication Skills of Group DiscussionDocument5 pagesCommunication Skills of Group DiscussionShambhavi BiradarNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optic Power PointDocument105 pagesFiber Optic Power PointKevinAngeloMaNo ratings yet
- 1.5 Wired MediaDocument5 pages1.5 Wired Mediayabocew846No ratings yet
- Fibre Optcs BasicDocument23 pagesFibre Optcs BasicAshmieu SesayNo ratings yet
- FiberDocument1 pageFiberManura BhashithaNo ratings yet
- Optical FiberDocument55 pagesOptical FiberSameer Raj100% (3)
- Optical FiberDocument42 pagesOptical FiberDon D DadaNo ratings yet
- Optical FiberDocument3 pagesOptical FiberPaul Jazz LopezNo ratings yet
- Fiber OpticsDocument10 pagesFiber OpticsVishal Kumar ShawNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediumDocument5 pagesTransmission MediumQUSI E. ABDNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument5 pagesEarth and Life Scienceits mauiNo ratings yet
- Network CableDocument14 pagesNetwork Cablesyukz0% (1)
- NSDCDocument73 pagesNSDChimanshuchawla654No ratings yet
- Network MediaDocument11 pagesNetwork MediaSajal GhoshNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Optical Fiber CommunicationDocument7 pagesAdvantages of Optical Fiber Communicationmohammadanas7686No ratings yet
- Optic FiberDocument29 pagesOptic FiberJohn MathewNo ratings yet
- CH1 IntroductionDocument28 pagesCH1 IntroductionNazar AzizNo ratings yet
- The Most Common Uses of Fiber Optic Cables: Data Communications تﻻﺎﺼﺗاDocument7 pagesThe Most Common Uses of Fiber Optic Cables: Data Communications تﻻﺎﺼﺗاljjbNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 and 9Document15 pagesChapter 8 and 9Nandhini PNo ratings yet
- Networks and Communications: BSCS-2Document5 pagesNetworks and Communications: BSCS-2JAYROLD LLAVANNo ratings yet
- Common Network CableDocument18 pagesCommon Network CableRey Lacdan GlendroNo ratings yet
- Optical CommunicationDocument29 pagesOptical Communication9921005047No ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project!Document25 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project!noobnamo dynamoNo ratings yet
- Optical Fibers-NotesDocument7 pagesOptical Fibers-NotesGurram GiridharNo ratings yet
- Transmission Media (Communication Media)Document22 pagesTransmission Media (Communication Media)HarishNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optic Basic Training 2Document51 pagesFiber Optic Basic Training 2Bhegz Escalona100% (1)
- Optical FiberDocument5 pagesOptical FiberMohit MrinalNo ratings yet
- CISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)From EverandCISA Exam - Testing Concept-Network Physical Media (Fiber Optic/ UTP/STP/Co-axial) (Domain-4)No ratings yet
- Netscout Tap Connect Guide 733-0604 PDFDocument76 pagesNetscout Tap Connect Guide 733-0604 PDFFabricio VindasNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Communication TESTDocument3 pagesOptical Fiber Communication TESTarpana0709No ratings yet
- Lecture 6. Transmission Characteristics of Optical Fibers - Fiber PDFDocument92 pagesLecture 6. Transmission Characteristics of Optical Fibers - Fiber PDFVijay JanyaniNo ratings yet
- Tia 568 B.1 3Document10 pagesTia 568 B.1 3k1gabitzu9789No ratings yet
- Network Communications, Options and Specifications: Fire Alarm Network ReferenceDocument4 pagesNetwork Communications, Options and Specifications: Fire Alarm Network ReferenceMarco Antonio RubinaNo ratings yet
- An Experimental Investigation On Light Emitting Concrete - Translucent ConcreteDocument11 pagesAn Experimental Investigation On Light Emitting Concrete - Translucent ConcreteTECH MACNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Communication Unit 3 NotesDocument33 pagesOptical Fiber Communication Unit 3 NotesEr SarbeshNo ratings yet
- Transiton Networks E-100BTX-FX-05 User GuideDocument7 pagesTransiton Networks E-100BTX-FX-05 User GuidegabegallNo ratings yet
- PCS 978sDocument8 pagesPCS 978sSattawat PuntaNo ratings yet
- CRTelecommunications Standards Jan 2002Document137 pagesCRTelecommunications Standards Jan 2002hashemowidaNo ratings yet
- Ls s5352c Ei DatasheetDocument5 pagesLs s5352c Ei DatasheetDio ArdiansyahNo ratings yet
- Glosario FTTHDocument34 pagesGlosario FTTHJOSE DANNY SIESQUEN CHAMBERGONo ratings yet
- Softing IT Networks WireXpert 4500 Datasheet EN PDFDocument8 pagesSofting IT Networks WireXpert 4500 Datasheet EN PDFAndrés Felipe Fandiño MNo ratings yet
- AAU5339w Hardware Description (01) (PDF) - ENDocument20 pagesAAU5339w Hardware Description (01) (PDF) - ENlorenzoNo ratings yet
- BTS Training DWDM and Routing TodayDocument3 pagesBTS Training DWDM and Routing TodayOnésimo ManuelNo ratings yet
- 1um (2+1) x1 Multimode Pump and Signal CombinerDocument3 pages1um (2+1) x1 Multimode Pump and Signal CombinerDK PhotonicsNo ratings yet
- New OM5 Fiber. Multimode Fiber, WBMMF Will Bring Color Into NetworkDocument4 pagesNew OM5 Fiber. Multimode Fiber, WBMMF Will Bring Color Into NetworksrsantosNo ratings yet
- Solved MCQsDocument4 pagesSolved MCQsAli AhmedNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Communications, 3e - Gerd KeiserDocument289 pagesOptical Fiber Communications, 3e - Gerd Keiserअमित सचान100% (5)
- CN Unit-IIIDocument14 pagesCN Unit-IIIAb VNo ratings yet
- Signal Degradiation in Optical Fibers - LmsDocument112 pagesSignal Degradiation in Optical Fibers - Lmsdr.suchita varadeNo ratings yet
- MPPTDraftDocument2 pagesMPPTDraftosadeamos8684No ratings yet
- 18-TIA606 Admin StandardDocument44 pages18-TIA606 Admin StandarddexiNo ratings yet
- DMRC Project Report FileDocument47 pagesDMRC Project Report FileSRISHTI BHARDWAJNo ratings yet
- 2.3-Data-Communication Ver2Document46 pages2.3-Data-Communication Ver2Llal SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Comunications FundamentalsDocument271 pagesComunications FundamentalsDiego100% (1)
- Optical FibresDocument21 pagesOptical FibresSanjeev Kumar80% (5)
- Industry Standards Activity OverviewDocument7 pagesIndustry Standards Activity OverviewHugo Soruco SolizNo ratings yet
- Multi-Mode Optical Fiber: Navigation Search Merged DiscussDocument43 pagesMulti-Mode Optical Fiber: Navigation Search Merged DiscussdsenpenNo ratings yet