Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Specific Energy Diagram
Uploaded by
Ktk ZadOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Specific Energy Diagram
Uploaded by
Ktk ZadCopyright:
Available Formats
Chap.
2 Chaudhry - Specific Energy Energy of open channel flow with respect to the channel bottom
specific energy : E = y + v2/2g
depth of flow - y Fr < 1 critical conditions: Fr = 1 y1 Fr > 1 450 v12/2g y2
water depth specific energy equation: E = y + specific flow and depth v
2
y=E
note: for all E values except critical conditions there are 2 sets of y and v which will satisfy the specific energy equation v22/2g
y2 y1 Specific Energy - E
ONLY AT CRITICAL FLOW IS THERE A SINGLE UNIQUE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN DEPTH AND VELOCITY FOR A GIVEN FLOW
SPECIFIC ENERGY DIAGRAMS FOR SPECIFIC FLOWS y := .05 ft , .06 ft .. 3 ft
2g
however v =
q y
so we can write the S.E. equation in terms of
E ( y , q) := y +
2 2
2 g y
specific_energy_diagram_and_discussion.m E:\public_html\specific_energy_diagram_an cd d_discussion.mcd
1 of 3
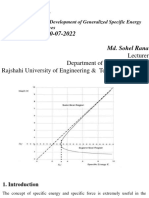
1.01 0.91 y FLOW DEPTH (FT) ft y ft y ft 0.81 0.71 0.61 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 0 0.3 0.6
SPECIFIC ENERGY DIAGRAMS
0.9
1.2
1.5
1.8
2.1
2.4
2.7
gal gal gal E y , 10 E y , 5 E y , 2.5 sec ft sec ft sec ft , , ft ft ft SPECIFIC ENERGY (FT)
q = 10 gal/sec*ft channel width q = 5 gal/sec*ft channel width q = 2.5 gal/sec*ft channel width
Specific energy diagrams are explored more fully below
What a specific energy diagram says : 1. A given flow can have a large number of specific energy values depending on the flow depth and velocity. There is one minimum value of specific energy is called the critical specific energy. It is defined by the red dot on the specific energy curve 2. For any given flow rate there are 2 different sets of depth and velocity which have the same specific energy. a. One of the flow depths (Fr < 1) has most of its energy tied up in depth of flow, see point 2 above b. the other flow depth (Fr > 1) has most of its energy tied up as velocity head, see point 1 above 3. If the flow depth is changed in a channel the specific energy of that flow will change
specific_energy_diagram_and_discussion.m E:\public_html\specific_energy_diagram_an cd d_discussion.mcd
2 of 3
4. For any flow there is a combination of depth and velocity that results in a minimum specific energy. Any channel feature which causes the specific energy to drop below this value will necessitate a change in the flow depth and velocity upstream of said feature in order to provide the minimum specific energy at the feature. Such a feature is referred to as a "choke". A practical example of a choke might be a culvert under a roadway or a bridge crossing a stream. The significance of a choke is that it may raise the upstream water surface causing flooding of surrounding land.
specific_energy_diagram_and_discussion.m E:\public_html\specific_energy_diagram_an cd d_discussion.mcd
3 of 3
You might also like
- Wave Forces on Small Diameter Structural MembersDocument25 pagesWave Forces on Small Diameter Structural Members금동민No ratings yet
- HydrogenDocument45 pagesHydrogenangusyoung1No ratings yet
- Computational HydraulicsDocument404 pagesComputational HydraulicsAbhishek Master100% (1)
- NASA SP290 Turbine DesignDocument392 pagesNASA SP290 Turbine Designcramerps2084100% (1)
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsFrom EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Introduction to Hydraulics Open ChannelsDocument63 pagesIntroduction to Hydraulics Open ChannelsAchal I100% (2)
- Principle of Open Channel FlowDocument39 pagesPrinciple of Open Channel FlowEugene Acuin Jaraplasan100% (2)
- The Pressure's On Innovations in Gas Lift, Maharon Bin JadidDocument10 pagesThe Pressure's On Innovations in Gas Lift, Maharon Bin JadidjoreliNo ratings yet
- To Investigate Relationship Between Specific Energy and Depth of FlowDocument9 pagesTo Investigate Relationship Between Specific Energy and Depth of FlowFaisal Sardar100% (12)
- Part I Fundamentals of Fluid DynamicsDocument42 pagesPart I Fundamentals of Fluid Dynamicsmike100% (1)
- Deflection of BeamsDocument41 pagesDeflection of BeamsMubaaracq Meerasahib100% (3)
- Detailed Open Channel HydraulicsDocument404 pagesDetailed Open Channel Hydraulicspcguru.oregon5759100% (3)
- Development of A Bellmouth Airflow Measurement Technique For Turbine Engine Ground Test FacilitiesDocument21 pagesDevelopment of A Bellmouth Airflow Measurement Technique For Turbine Engine Ground Test FacilitiesNicolas DuboisNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Critical FlowDocument5 pagesCharacteristics of Critical FlowJerrydawangNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Brief Review of TensorsDocument15 pagesBrief Review of TensorsG Hernán Chávez LandázuriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Design of Steel Frames by Second-Order Analysis Fulifilling Code RequirementsDocument54 pagesChapter 3 - Design of Steel Frames by Second-Order Analysis Fulifilling Code RequirementsIvan KlyuchkaNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamics 2 SummaryDocument44 pagesAerodynamics 2 SummaryKrishna MyakalaNo ratings yet
- Compressible FlowDocument75 pagesCompressible FlowAkshatRaizada100% (2)
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Critical VelocityDocument35 pagesCritical Velocitykalimullah_kmNo ratings yet
- Non-Uniform Flow Analysis in Open ChannelsDocument117 pagesNon-Uniform Flow Analysis in Open ChannelsTing Wee Kiet100% (2)
- Calculating Average Gas Release RatesDocument5 pagesCalculating Average Gas Release RatesakashawalkerNo ratings yet
- Ansi Isa-75.01.01-2012 (60534-2-1 Mod)Document70 pagesAnsi Isa-75.01.01-2012 (60534-2-1 Mod)Abdelaadim FadlallahNo ratings yet
- Pressurisation and Depressurization ResultsDocument8 pagesPressurisation and Depressurization ResultsQayyum KhanNo ratings yet
- ISO 10790 Standard497 1pdfDocument12 pagesISO 10790 Standard497 1pdfSUPERGOICONo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa Institute of Technology Energy-Depth RelationsDocument27 pagesAddis Ababa Institute of Technology Energy-Depth RelationsBIRUK ABATENo ratings yet
- OCH - Part1-Energy-Critica DepthDocument33 pagesOCH - Part1-Energy-Critica Depthtewodros getuNo ratings yet
- SWTC022 Assignment 2Document5 pagesSWTC022 Assignment 2MokgadiNo ratings yet
- Experiment#02Document7 pagesExperiment#02sheikhali9180No ratings yet
- Chapter Two Student-Fluid MechanicsDocument15 pagesChapter Two Student-Fluid MechanicsMathiTwadCNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Part 2 HHMDocument21 pagesUnit 1 Part 2 HHMSwati ChaudharyNo ratings yet
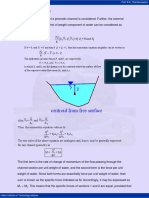
- Centroid From Free Surface: 9.1 Specific ForceDocument7 pagesCentroid From Free Surface: 9.1 Specific ForceVal LuisNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Review of Hydraulic FluidsDocument31 pages1.2 Review of Hydraulic FluidsHailemariam WeldegebralNo ratings yet
- Energy Depth RelationshipsDocument87 pagesEnergy Depth RelationshipsChris AdaminovicNo ratings yet
- Lecturenote - 1253970270open Channel Hydraulics Chapter TwoDocument20 pagesLecturenote - 1253970270open Channel Hydraulics Chapter TwoAlfatah muhumedNo ratings yet
- To Investigate The Relationship Between Specific Energy (E) and Depth of Flow (Y) in A Rectangular ChannelDocument4 pagesTo Investigate The Relationship Between Specific Energy (E) and Depth of Flow (Y) in A Rectangular ChannelAfzal Waseem67% (3)
- Centroid From Free Surface: 9.1 Specific ForceDocument7 pagesCentroid From Free Surface: 9.1 Specific ForceSahil BhardwajNo ratings yet
- 7) Generalized Specific Energy and Specific Force Curves-1Document25 pages7) Generalized Specific Energy and Specific Force Curves-1Md Sajedul Islam SetuNo ratings yet
- Date: 09-09-2014 Tuesday Time: 12:30-14:30 HrsDocument2 pagesDate: 09-09-2014 Tuesday Time: 12:30-14:30 HrsRahat UsmanNo ratings yet
- Assignment Ovi SirDocument7 pagesAssignment Ovi Sir232449045No ratings yet
- Assignment Ovi SirDocument7 pagesAssignment Ovi Sir232449045No ratings yet
- Chapter 7: Energy and Momentum Principle in Open Channel: 1 V /2g Water Surface Energy Line HDocument19 pagesChapter 7: Energy and Momentum Principle in Open Channel: 1 V /2g Water Surface Energy Line HAsmita Aryal100% (1)
- Topic 3.4 - SEPT 2018Document19 pagesTopic 3.4 - SEPT 2018Andrew SebastianNo ratings yet
- Floodplain HydraulicsDocument25 pagesFloodplain HydraulicsIanChristopherRiveraNasolNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Jumps R1Document26 pagesHydraulic Jumps R1Abdirazak Sama WadeNo ratings yet
- Open Channel Flow: 1 Revised: 2013 EditionDocument11 pagesOpen Channel Flow: 1 Revised: 2013 EditionAli AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 OPCHDocument13 pagesChapter 3 OPCHgemadogelgaluNo ratings yet
- Critical Flow: Department of Civil EngineeringDocument12 pagesCritical Flow: Department of Civil EngineeringBIRUK ABATENo ratings yet
- Equations in OCFDocument46 pagesEquations in OCFTheeva RajNo ratings yet
- Linear Graph Modeling: Two-Port Energy Transducing Elements 1Document26 pagesLinear Graph Modeling: Two-Port Energy Transducing Elements 1Khamees Marwan MuhiesenNo ratings yet
- Automatic Generation ControlDocument12 pagesAutomatic Generation Controlrois tazNo ratings yet
- 1582524392expt 2 Development of SP Energy and SP Force CurveDocument6 pages1582524392expt 2 Development of SP Energy and SP Force Curvesnigdha sadarlaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lecture 4 - Chapter - 4Document17 pagesFluid Mechanics Lecture 4 - Chapter - 4Benjamin BageyaNo ratings yet
- CEE-6281 Lab Report on Open Channel Hydraulics FlowDocument12 pagesCEE-6281 Lab Report on Open Channel Hydraulics FlowMuhammadAhmadNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics for Civil Engineers Volume 1Document13 pagesHydraulics for Civil Engineers Volume 1Jeisther Timothy GalanoNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics 1-2-3Document4 pagesHydraulics 1-2-3veeveegarcia_0% (1)
- Specific Energy PDFDocument39 pagesSpecific Energy PDFwacotc2163No ratings yet
- Notes Ce 503 Fluid Mechanics 2 Unit 2Document18 pagesNotes Ce 503 Fluid Mechanics 2 Unit 2HyperHimansh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Computational HydraulicsDocument404 pagesComputational HydraulicsTesfaye NegasaNo ratings yet
- Sliding Mode Control Design of Current Fed Full Bridge DC To DC Converter For Fuel Cell ApplicationsDocument4 pagesSliding Mode Control Design of Current Fed Full Bridge DC To DC Converter For Fuel Cell ApplicationsJyothiPunemNo ratings yet
- Hydro ch2Document15 pagesHydro ch2neway mamushetNo ratings yet
- Non-Uniform Flow AnalysisDocument113 pagesNon-Uniform Flow AnalysisEncik ComotNo ratings yet
- A Resonant Dual Full-Bridge Class-E BidirectionalDocument11 pagesA Resonant Dual Full-Bridge Class-E Bidirectionallinh quangNo ratings yet
- Part I A Fundamentals of Fluid DynamicsDocument38 pagesPart I A Fundamentals of Fluid Dynamicsdritz tevesNo ratings yet
- 11.2.1 Adding A Momentum Source To A Duct FlowDocument4 pages11.2.1 Adding A Momentum Source To A Duct FlowDiego Regaladi MtzNo ratings yet
- Therefore, The Specific Energy Is The Sum of The Water-Depth (Y) and The Velocity Head, If The Streamlines Are Straight and ParallelDocument40 pagesTherefore, The Specific Energy Is The Sum of The Water-Depth (Y) and The Velocity Head, If The Streamlines Are Straight and ParallelDawit TesfayeNo ratings yet
- CRITICAL FLOW ANALYSISDocument31 pagesCRITICAL FLOW ANALYSISRobert BuiNo ratings yet
- Influence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesFrom EverandInfluence of System Parameters Using Fuse Protection of Regenerative DC DrivesNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsFrom EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNo ratings yet
- Quaternions TranfromationDocument29 pagesQuaternions TranfromationKtk ZadNo ratings yet
- Design of Ocean EnvniornmentDocument17 pagesDesign of Ocean EnvniornmentKtk ZadNo ratings yet
- Column Magnification FactorDocument3 pagesColumn Magnification FactorKtk ZadNo ratings yet
- Herimite Shape Function For BeamDocument29 pagesHerimite Shape Function For BeamPisey KeoNo ratings yet
- Wave SpectrumDocument21 pagesWave SpectrumlsatchithananthanNo ratings yet
- Ansys FaqDocument3 pagesAnsys FaqKhushpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- BeamsDocument21 pagesBeamsSrinivas TanarapuNo ratings yet
- SolidsDocument1 pageSolidsAnindya Dian AsriNo ratings yet
- Beam DeflectionDocument5 pagesBeam DeflectionChinna ValleNo ratings yet
- BeamDocument13 pagesBeamShahryar MunawarNo ratings yet
- Morison EquationDocument8 pagesMorison Equationmailnewaz96770% (1)
- Steady State HeatDocument5 pagesSteady State HeatKtk ZadNo ratings yet
- HermiteDocument6 pagesHermiteKtk ZadNo ratings yet
- Torsional PropertiesDocument19 pagesTorsional PropertiesAndrés Felipe HernándezNo ratings yet
- TensorsDocument116 pagesTensorsUmair IsmailNo ratings yet
- JacobiDocument8 pagesJacobiSyed H ShahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Indical NotationDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Indical NotationKtk ZadNo ratings yet
- Numerical Analysis in Coastal EngDocument11 pagesNumerical Analysis in Coastal EngKtk ZadNo ratings yet
- A Simple Displacement Control Technique For Pushover AnalysisDocument16 pagesA Simple Displacement Control Technique For Pushover AnalysisKtk Zad100% (1)
- SolidsDocument1 pageSolidsAnindya Dian AsriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Finite Difference Methods: Math6911 S08, HM ZhuDocument90 pagesChapter 5 Finite Difference Methods: Math6911 S08, HM ZhuGinanjar DikaNo ratings yet
- Design of Beam-ColumnsDocument37 pagesDesign of Beam-Columnssalahaddinsharif100% (1)
- Calculus of VariationsDocument61 pagesCalculus of VariationsPedro Palacios AvilaNo ratings yet
- Seismic Data Processing and InterpretationDocument15 pagesSeismic Data Processing and InterpretationmustafaNo ratings yet
- ACV-12 Adjustable Choke Valves: For Wide Applications in Oil, Gas, and Water ServiceDocument2 pagesACV-12 Adjustable Choke Valves: For Wide Applications in Oil, Gas, and Water ServiceDeyokeNo ratings yet
- Fluid Flow Basics OF Throttling ValvesDocument43 pagesFluid Flow Basics OF Throttling ValvesSandro AraújoNo ratings yet
- Criteria For Operation Stability of Gas-Lift WellsDocument27 pagesCriteria For Operation Stability of Gas-Lift WellsAhmed MamdouhNo ratings yet
- Anemometer: ME Laboratory 2 Report Number 4 Anenometer and Air Velocity Measurement ReportersDocument8 pagesAnemometer: ME Laboratory 2 Report Number 4 Anenometer and Air Velocity Measurement ReportersLorenz BanadaNo ratings yet
- GDJP Question BankDocument56 pagesGDJP Question BankRavindiran ChinnasamyNo ratings yet
- Equipment UnitDocument7 pagesEquipment UnitAhmed MahdiNo ratings yet
- Modelling and Simulating Ballast Tank Blowing and Venting Operations in Manned SubmarinesDocument6 pagesModelling and Simulating Ballast Tank Blowing and Venting Operations in Manned SubmarinesOm Parkash Sharma100% (1)
- H 07121 Choke ManifoldDocument2 pagesH 07121 Choke ManifoldmonokoeNo ratings yet
- Gas Dynamics Book (Dr. El-Sayed M. Marzouk)Document173 pagesGas Dynamics Book (Dr. El-Sayed M. Marzouk)Karim SalesNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Introductory Concept To Compressible FlowDocument10 pagesChapter Two Introductory Concept To Compressible FlowAli SabahNo ratings yet
- Q H V W H V: Chapter 16: Thermodynamics of High-Speed Gas Flow Stagnation PropertiesDocument42 pagesQ H V W H V: Chapter 16: Thermodynamics of High-Speed Gas Flow Stagnation PropertiesDono SusilNo ratings yet
- Aerodynamics Question BankDocument8 pagesAerodynamics Question BankmaniNo ratings yet
- Convergent & Convergent-Divergent Nozzle Performance Lab ReportDocument25 pagesConvergent & Convergent-Divergent Nozzle Performance Lab ReportAkmal Aiman100% (1)
- Note 1455804851Document27 pagesNote 1455804851Ajith KumarNo ratings yet
- ME6604-Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion PDFDocument12 pagesME6604-Gas Dynamics and Jet Propulsion PDFNANCY JUDITHNo ratings yet
- CH 04 Turbojet Cycle PDFDocument54 pagesCH 04 Turbojet Cycle PDFAshrafNo ratings yet
- IITD Study of Compressible Flow and Cooling Pack PerformanceDocument6 pagesIITD Study of Compressible Flow and Cooling Pack PerformanceramsastryNo ratings yet
- Assignment6 SolutionsDocument5 pagesAssignment6 SolutionsVishal NadiyaNo ratings yet
- Richard Nakka's Experimental Rocketry Web Site: Solid Rocket Motor Theory - IntroductionDocument66 pagesRichard Nakka's Experimental Rocketry Web Site: Solid Rocket Motor Theory - Introductionhr290952No ratings yet
- Ae2255 Propulsion-1 Question Bank UNIT-1Document5 pagesAe2255 Propulsion-1 Question Bank UNIT-1kanscse100% (1)