Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sizing Steam Pipes & Steam Velocities
Uploaded by
Macarthur B. MonsantoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sizing Steam Pipes & Steam Velocities
Uploaded by
Macarthur B. MonsantoCopyright:
Available Formats
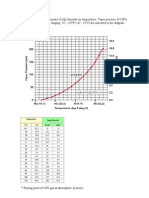
Sizing Steam Pipes (lb/h)
Steam is a compressible gas where the capacity of the pipe line depends on the
size of the pipes and the steam pressure. This table can be used for fast
sizing of steam pipes dimensions
This table can be used for fast calculation of steam pipes. 80 ft/sec is in general a recommended steam velocity.
Capacity (lb/hour)
Steam
Pressure
Velocity
(psi)
(ft/sec)
10
20
30
40
60
Pipe Size (inch)
1/2"
3/4"
1"
1 1/4" 1 1/2"
2"
2 1/2"
3"
4"
5"
6"
8"
10"
12"
50
12
26
45
70
100
190
280
410
760
1250
1770
3100
5000
7100
80
19
45
75
115
170
300
490
710
1250
1800
2700
5200
7600
11000
120
29
60
110
175
245
460
700
1000
1800
2900
4000
7500
12000
16500
50
15
35
55
88
130
240
365
550
950
1500
2200
3770
6160
8500
80
24
52
95
150
210
380
600
900
1500
2400
3300
5900
9700
13000
120
35
72
135
210
330
590
850
1250
2200
3400
4800
9000
14400
20500
50
21
47
82
123
185
210
520
740
1340
1980
2900
5300
8000
11500
80
32
70
120
190
260
520
810
1100
1900
3100
4500
8400
13200
18300
120
50
105
190
300
440
840
1250
1720
3100
4850
6750
1300
19800
28000
50
26
56
100
160
230
420
650
950
1650
2600
3650
6500
10500
14500
80
42
94
155
250
360
655
950
1460
2700
3900
5600 10700 16500
23500
120
62
130
240
370
570
990
1550
2100
3950
6100
8700 16000 25000
35000
50
32
75
120
190
260
505
790
1100
1900
3100
4200
12800
18000
80
51
110
195
300
445
840
1250
1800
3120
4900
6800 13400 20300
28300
120
75
160
290
460
660
1100
1900
2700
4700
7500 11000 19400 30500
42500
50
43
95
160
250
360
650
1000
1470
2700
3900
24000
8200
5700 10700 16500
80
100
120
150
200
80
65
140
250
400
600
1000
1650
2400
4400
6500
9400 17500 27200
38500
120
102
240
410
610
950
1660
2600
3800
6500 10300 14700 26400 41000
58000
50
53
120
215
315
460
870
1300
1900
3200
5200
7000 13700 21200
29500
80
83
190
320
500
730
1300
2100
3000
5000
8400 12200 21000 33800
47500
120
130
290
500
750
1100
1900
3000
4200
7800 12000 17500 30600 51600
71700
50
63
130
240
360
570
980
1550
2100
4000
8800 16300 26500
35500
80
102
240
400
610
950
1660
2550
3700
6400 10200 14600 26000 41000
57300
120
150
350
600
900
1370
2400
3700
5000
9100 15000 21600 38000 61500
86300
50
74
160
290
440
660
1100
1850
2600
4600
7000 10500 18600 29200
41000
80
120
270
450
710
1030
1800
2800
4150
7200 11600 16500 29200 48000
73800
120
175
400
680
1060
1520
2850
4300
6500 10700 17500 26000 44300 70200
97700
50
90
208
340
550
820
1380
2230
3220
5500
8800 12900 22000 35600
50000
80
145
320
570
900
1250
2200
3400
4900
8500 14000 20000 35500 57500
79800
120
215
450
850
1280
1890
3400
5300
7500 13400 20600 30000 55500 85500 120000
50
110
265
450
680
1020
1780
2800
4120
80
180
410
700
1100
1560
2910
4400
6600 11000 18000 26600 46000 72300 100000
120
250
600
1100
1630
2400
4350
6800
9400 16900 25900 37000 70600 109000 152000
6100
7100 11500 16300 28500 45300
64000
Pipe Sizing - Sizing steam and condensate pipes - pressure loss, recommended
velocity, capacity and more
Steam and Condensate - Steam & condensate properties - capacities, pipe sizing,
systems configuration and more
Pressure Drop in Steam Pipes - Steam pipes and pressure drop diagrams - imperial and
metric units
Recommended Velocities in Steam Systems - The steam velocity in a steam distribution
system should be within certain limits to avoid excessive wear and tear
Sizing Steam Pipes (kg/h) - Steam is a compressible gas where the mass flow capacity
of the pipe lines depends on the steam pressure. This table, where pressure is in bar,
velocity in m/s and capacity in kg/h, is suitable for sizing steam pipes
Steam Heating Processes - Load Calculating - Calculating the amount of steam in nonflow batch and continuous flow heating processes
Steam Pipe Pressure drop Calculator - Calculate pressure drop in steam distribution
pipe lines
Steam Trap Selection Guide - A steam trap selection guide - Float & Thermostatic,
Inverted Bucket, Bimetal Thermostatic, Impulse and Thermodynamic Disc steam traps
Steam and Condensate Loads in Heating Systems - Calculating steam and condensate
loads in steam heated systems
STEAM VELOCITIES FOR PIPING DISTRIBUTION
The steam velocities or speeds below are commonly recommended as acceptable for steam distribution
systems:
Velocity
Steam System
(m/s)
(ft/s)
Saturated Steam medium and low
pressure
25 - 40
82 - 131
Saturated Steam - high pressure
30-40
99 - 131
Saturated Steam at peak load
< 50
< 164
Steam and Water mix
< 25
< 82
Superheated Steam
35 - 100
100 - 300
Saturated steam - low pressure - is common for heating services and secondary process
pipes.
Saturated steam - high pressure - is common in powerhouse, boiler and main process
lines.
Superheated steam is common in power generation and turbine plants.
You might also like
- Pipe Sizing for Optimal Steam FlowDocument6 pagesPipe Sizing for Optimal Steam Flowferdie14No ratings yet
- Once Through BoilerDocument9 pagesOnce Through Boilerbhuvi_patu12No ratings yet
- Construction Parts of BoilerDocument5 pagesConstruction Parts of BoilerMdParbhezNo ratings yet
- LPG Energy IntegrationDocument6 pagesLPG Energy IntegrationBandaru KiranNo ratings yet
- TurboDocument8 pagesTurboKorichiKarimNo ratings yet
- Toolbox4Planning - Basic Concept of Civil - Structure Engineering Work Flow For Schedule DevelopmentDocument1 pageToolbox4Planning - Basic Concept of Civil - Structure Engineering Work Flow For Schedule DevelopmentMuslimNo ratings yet
- PETRONAS' Malaysia RAPID Steam Craker Complex - TOYODocument3 pagesPETRONAS' Malaysia RAPID Steam Craker Complex - TOYOKitty JoyceNo ratings yet
- King Hussein Airport Expansion Project Quality Control LogDocument3 pagesKing Hussein Airport Expansion Project Quality Control LogAmran MohammedNo ratings yet
- CJ Project Activity ScheduleDocument3 pagesCJ Project Activity ScheduleWisnu Setiawan100% (1)
- Energies 10 00205Document19 pagesEnergies 10 00205radanpetricaNo ratings yet
- What Is Carry Over and Carry Under at The Boiler DrumDocument12 pagesWhat Is Carry Over and Carry Under at The Boiler Drumabdulyunus_amirNo ratings yet
- Design Review of AbsorbersDocument46 pagesDesign Review of AbsorbersAngelik MoralesNo ratings yet
- Definition & Types of Reboilers - A. Thermosiphon - : Reboiler CircuitsDocument2 pagesDefinition & Types of Reboilers - A. Thermosiphon - : Reboiler CircuitsWade ColemanNo ratings yet
- Functional Test: FT-Packaged Boiler and Boiler System Including HW Pumps 1 & 2Document7 pagesFunctional Test: FT-Packaged Boiler and Boiler System Including HW Pumps 1 & 2vin ssNo ratings yet
- Teg ContactorDocument4 pagesTeg ContactorrepentinezNo ratings yet
- Korf BrochureDocument1 pageKorf Brochurelhphong021191No ratings yet
- FlareDocument39 pagesFlareMuhammad Tahir RazaNo ratings yet
- At M/S Jindal Steel &power Limited: For More ProjectsDocument26 pagesAt M/S Jindal Steel &power Limited: For More ProjectsvasqueznvNo ratings yet
- Ethylene Plant Planning StudyDocument8 pagesEthylene Plant Planning StudyAngelica Rosario Flores LecoñaNo ratings yet
- Integrated Amine Degreasing Schedule 30mar2018Document1 pageIntegrated Amine Degreasing Schedule 30mar2018KhairulNo ratings yet
- ITR B StatusDocument8 pagesITR B StatusPazhamalai RajanNo ratings yet
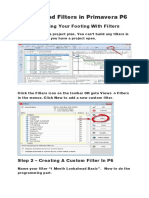
- Primavera P6 Lookahead Filters in 40 StepsDocument8 pagesPrimavera P6 Lookahead Filters in 40 StepshichemokokNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Production Flow Diagram. 2Document1 pageHydrogen Production Flow Diagram. 2DumarTorresNo ratings yet
- JERP Brief ProcessDocument14 pagesJERP Brief Processbikas_sahaNo ratings yet
- 13 - Oxygen Removal From Boiler WaterDocument12 pages13 - Oxygen Removal From Boiler Waterarunkumar23101100% (1)
- Gas Sweetening Processes and ApplicationsDocument6 pagesGas Sweetening Processes and ApplicationsEdwin AguilarNo ratings yet
- SMR Hydrogen Generators-Technologies and Producers 2009Document28 pagesSMR Hydrogen Generators-Technologies and Producers 2009Zoran JuricNo ratings yet
- Improved Level Control of A Feed Water ValveDocument7 pagesImproved Level Control of A Feed Water ValveAli Bari100% (1)
- What Are The Types of HRSGDocument2 pagesWhat Are The Types of HRSGThiruvengadamNo ratings yet
- FGP WPMP OverviewDocument15 pagesFGP WPMP OverviewyazardNo ratings yet
- Oil Facility: Main ProcessDocument1 pageOil Facility: Main ProcessRaghavan VenkatramanNo ratings yet
- 3800-210-710-01-q Rev 1 Chemical Cleaning and Steam Blowing SRQDocument28 pages3800-210-710-01-q Rev 1 Chemical Cleaning and Steam Blowing SRQEslam ShiblNo ratings yet
- O&Msec2 Heat & Material BalanceDocument8 pagesO&Msec2 Heat & Material Balanceugun87No ratings yet
- 2016 - Thermal Performance Calculation and Analysis of Heat Transfer Tube in Super Open Rack VaporizerDocument10 pages2016 - Thermal Performance Calculation and Analysis of Heat Transfer Tube in Super Open Rack VaporizerLong Nguyễn HoàngNo ratings yet
- Alkali Boil Out Procedure - Rev-1Document10 pagesAlkali Boil Out Procedure - Rev-1vahab shaikNo ratings yet
- Boiler Operation Made Easy - Procedure For Starting and Stopping A Boiler PDFDocument13 pagesBoiler Operation Made Easy - Procedure For Starting and Stopping A Boiler PDFDavid WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Irri Kwale Gas PipelineDocument7 pagesIrri Kwale Gas PipelineEfosaUwaifoNo ratings yet
- Yanbu Refinery Tank Farm Process DescriptionDocument9 pagesYanbu Refinery Tank Farm Process DescriptionJanakiraman MalligaNo ratings yet
- Boiler Chemical Cleaning ProcedureDocument20 pagesBoiler Chemical Cleaning ProcedureHandoko AurelNo ratings yet
- Flash Skim Vessel Descr.Document5 pagesFlash Skim Vessel Descr.vanashley1No ratings yet
- Document Submission Status: FOR APPROVAL: Vung Ang 1 Thermal Power Plant 2 X 600Mw Lot M4A Cooling Water System (Bop)Document10 pagesDocument Submission Status: FOR APPROVAL: Vung Ang 1 Thermal Power Plant 2 X 600Mw Lot M4A Cooling Water System (Bop)khang10182No ratings yet
- Typical EfW Plant Commissioning Plan Feb 2010Document176 pagesTypical EfW Plant Commissioning Plan Feb 2010mbetts6304No ratings yet
- 50 MMSCFD Low BTU Gas Combined Cycle Power PlantDocument42 pages50 MMSCFD Low BTU Gas Combined Cycle Power PlantShaikh BilalNo ratings yet
- Level 3 - Project Schedule - Gambat South EWT ProjectDocument8 pagesLevel 3 - Project Schedule - Gambat South EWT ProjectAli Mohsin100% (1)
- HRSG Water Chemistry and Inspection OverviewDocument5 pagesHRSG Water Chemistry and Inspection OverviewRahul ChoubeyNo ratings yet
- Air Coolers Versus Shell-And-tube Water CoolersDocument8 pagesAir Coolers Versus Shell-And-tube Water CoolersDefenceDog67% (3)
- Boilers Basic Components (Att. VIII)Document28 pagesBoilers Basic Components (Att. VIII)Vijay RajNo ratings yet
- ENGINEERING DESIGN GUIDELINES Boiler Systems Rev1.3web PDFDocument29 pagesENGINEERING DESIGN GUIDELINES Boiler Systems Rev1.3web PDFMohsen KadivarNo ratings yet
- Estimate Subsonic Flare Tip Pressure Drop With Graph Derived CorrelationDocument3 pagesEstimate Subsonic Flare Tip Pressure Drop With Graph Derived CorrelationbtjajadiNo ratings yet
- Penjelasan TLEsDocument28 pagesPenjelasan TLEsFauzi IhsanNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineer CVDocument3 pagesMechanical Engineer CVRaj AryanNo ratings yet
- Korf Hydraulic ReportDocument10 pagesKorf Hydraulic ReportMuthuKumar ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- SAMSUNG SEM-9471E - Process Design Manual - Health and Design Safety Specification Rev0 2004Document7 pagesSAMSUNG SEM-9471E - Process Design Manual - Health and Design Safety Specification Rev0 2004d_mazieroNo ratings yet
- Installing Conda PackageDocument4 pagesInstalling Conda Packagepolaris44No ratings yet
- Globe Valve Bs 1873 and Api 602: ASME B16.10Document7 pagesGlobe Valve Bs 1873 and Api 602: ASME B16.10swapnil PATILNo ratings yet
- Velocity of Water in PipeDocument4 pagesVelocity of Water in Pipeabidch143100% (1)
- As A Rule of Thumb The Following Velocities Can Be Used in Design of Piping and Pumping Systems For WaterDocument2 pagesAs A Rule of Thumb The Following Velocities Can Be Used in Design of Piping and Pumping Systems For WaterbhupsjangirNo ratings yet
- Fluid Pipping - 21-30Document10 pagesFluid Pipping - 21-30andytuorNo ratings yet
- Steam Distribution System Design GuideDocument70 pagesSteam Distribution System Design GuideMohamed RiyaazNo ratings yet
- Propane Gas and Liquefied GasDocument10 pagesPropane Gas and Liquefied GasJ.SIVIRANo ratings yet
- Dow Chemicals. Review of AminesDocument48 pagesDow Chemicals. Review of AminesEloy SanzNo ratings yet
- Electrolytic Flow CellDocument0 pagesElectrolytic Flow CellMacarthur B. MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Dow Chemicals. Review of AminesDocument48 pagesDow Chemicals. Review of AminesEloy SanzNo ratings yet
- Cyanogenic Glycosides in Bitter Apricot KernelsDocument8 pagesCyanogenic Glycosides in Bitter Apricot KernelsMacarthur B. MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Cyanogenic Glycosides in Bitter Apricot KernelsDocument8 pagesCyanogenic Glycosides in Bitter Apricot KernelsMacarthur B. MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Alkaline Acid Food ChartDocument16 pagesAlkaline Acid Food ChartRyan Livingston67% (3)
- Cyanogenic Glycosides in Bitter Apricot KernelsDocument8 pagesCyanogenic Glycosides in Bitter Apricot KernelsMacarthur B. MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Ultra Fine Grinding - A Practical Alternative To OxidativeDocument21 pagesUltra Fine Grinding - A Practical Alternative To OxidativeSarah PerezNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Simulation of Gold Recovery ProcessesDocument13 pagesDynamic Simulation of Gold Recovery ProcessesMacarthur B. MonsantoNo ratings yet
- ANTI-FRICTION - Test Report of 4 Ball Test From Chinese Academy SciencesDocument3 pagesANTI-FRICTION - Test Report of 4 Ball Test From Chinese Academy SciencesMacarthur B. MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Black UreaDocument20 pagesBlack UreaMacarthur B. Monsanto0% (1)
- Dynamic Simulation of Gold Recovery ProcessesDocument13 pagesDynamic Simulation of Gold Recovery ProcessesMacarthur B. MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Effect of Additive On The Viscosity Index of LubeoilDocument6 pagesEffect of Additive On The Viscosity Index of LubeoilMacarthur B. MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Bucket Elevator Owners ManualDocument87 pagesBucket Elevator Owners ManualMacarthur B. Monsanto100% (1)
- Advanced Wastewater Treatment Technology - Mech Vapor RecompressionDocument42 pagesAdvanced Wastewater Treatment Technology - Mech Vapor RecompressionMacarthur B. Monsanto100% (1)
- CWSF Combustion Testing For Oil-Fired BoilerDocument15 pagesCWSF Combustion Testing For Oil-Fired BoilerMacarthur B. MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution Control Systems For BoilerDocument122 pagesAir Pollution Control Systems For BoilerMacarthur B. MonsantoNo ratings yet
- SO2 ControlDocument5 pagesSO2 ControlMacarthur B. MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Process For Recovering Lube Oil Base Stocks From Used Motor Oil FormulationsDocument19 pagesProcess For Recovering Lube Oil Base Stocks From Used Motor Oil FormulationsMacarthur B. MonsantoNo ratings yet
- SO2 ControlDocument5 pagesSO2 ControlMacarthur B. MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Parabolic Trough Solar PlantsDocument16 pagesParabolic Trough Solar PlantsMacarthur B. Monsanto100% (1)
- Active Freeze DryingDocument3 pagesActive Freeze DryingMacarthur B. MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Method of Re Refining Used Lubricating Oil & Salt Bath RefiningDocument35 pagesMethod of Re Refining Used Lubricating Oil & Salt Bath RefiningMacarthur B. MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Engineering - Handbook of Steam Power PlantDocument302 pagesEngineering - Handbook of Steam Power PlantShailendra Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Thermal Power Plant PresentationDocument46 pagesThermal Power Plant PresentationMacarthur B. MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Cable NomenclatureDocument5 pagesCable NomenclatureSushantGore100% (1)
- CTD 05-2008 enDocument303 pagesCTD 05-2008 enRodger LeonNo ratings yet
- Boiler ParameterDocument2 pagesBoiler ParameterFieNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4: Chemical Equilibrium: Lab ReportDocument2 pagesExperiment 4: Chemical Equilibrium: Lab ReportNhật Tân Võ VươngNo ratings yet
- Alcor Atf Super - enDocument2 pagesAlcor Atf Super - enronaldNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 SimpleDistillationDocument52 pagesTopic 2 SimpleDistillationJA NableNo ratings yet
- MPI Architectural Painting Manual: Guide Specification Revision - September 2012 Section 09900 Painting Page 1 of 28Document28 pagesMPI Architectural Painting Manual: Guide Specification Revision - September 2012 Section 09900 Painting Page 1 of 28Alsayed DiabNo ratings yet
- 05.09.21 OSR - CO-SC Jee Adv 2020 P1 GTA-28 (P-I) QPDocument17 pages05.09.21 OSR - CO-SC Jee Adv 2020 P1 GTA-28 (P-I) QPRahul RanjanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16Document55 pagesChapter 16Khalil AlluhaybiNo ratings yet
- MS 1539 PT3 2003 Portable Fire Extinguisher PDFDocument31 pagesMS 1539 PT3 2003 Portable Fire Extinguisher PDFLee GP100% (3)
- General Chemistry II Module on Intermolecular ForcesDocument5 pagesGeneral Chemistry II Module on Intermolecular ForcesJerry De Leon TaayNo ratings yet
- Global Warming and Climate ChangeDocument101 pagesGlobal Warming and Climate Changes selva prakashNo ratings yet
- CARBOXYLIC ACID Derivatives - Salts and ReactionsDocument6 pagesCARBOXYLIC ACID Derivatives - Salts and ReactionsmarcelompassosNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Bravais LatticesDocument17 pagesIntroduction and Bravais LatticesBilal BarutNo ratings yet
- Bulletin Nov 08 Conformal Coating Failure MechanismsDocument2 pagesBulletin Nov 08 Conformal Coating Failure MechanismsLee Hitchens100% (2)
- BS en 10136-2019Document16 pagesBS en 10136-2019Martijn GrootNo ratings yet
- Tabla de Colores Winsor & NewtonDocument8 pagesTabla de Colores Winsor & NewtonArq Copy ChorrillosNo ratings yet
- Code All Item RohanDocument127 pagesCode All Item RohanKapooNo ratings yet
- Samuela Lahai - WSJ-DemandDocument3 pagesSamuela Lahai - WSJ-DemandSamuela LahaiNo ratings yet
- The Solid State Class 12 MCQs Questions With AnswersDocument19 pagesThe Solid State Class 12 MCQs Questions With AnswersRohit Chavariya100% (1)
- Catalog: PrefaceDocument155 pagesCatalog: PrefaceTalita Yasmin TalitaNo ratings yet
- Fresh Cut FruitsDocument25 pagesFresh Cut FruitsMuhammad FaisalNo ratings yet
- G 21 - 96 R02 - RzixDocument5 pagesG 21 - 96 R02 - RzixjayakumarNo ratings yet
- Compost Tea Manual PDFDocument38 pagesCompost Tea Manual PDFbaspipsNo ratings yet
- Minfm54307 Astm A131 Grade ADocument6 pagesMinfm54307 Astm A131 Grade AEmerson IpialesNo ratings yet
- MS-26 Vii: Asphalt - FM - Indd 7 7/9/11 2:57 PMDocument5 pagesMS-26 Vii: Asphalt - FM - Indd 7 7/9/11 2:57 PMChristineNyambeNo ratings yet
- VMP Manual PDFDocument106 pagesVMP Manual PDFkikiNo ratings yet
- Biological Safety CabinetsDocument5 pagesBiological Safety CabinetsAhmed Ali AssafNo ratings yet
- QO390-SS200025 Technical Sheet (Actuated On Off Valve & RESDVForel Bronang)Document2 pagesQO390-SS200025 Technical Sheet (Actuated On Off Valve & RESDVForel Bronang)Iqbal MatondangNo ratings yet
- Gis 18-013Document22 pagesGis 18-013Dinesh NadarNo ratings yet