Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Antepartum Fetal Assessment Chapter10
Uploaded by
cahuber602Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Antepartum Fetal Assessment Chapter10
Uploaded by
cahuber602Copyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 10: Antepartum Fetal Assessment SUMMARY CONCEPTS Ultrasound is widely used during pregnancy to determine a variety of fetal
l and placental conditions and aid in the performance of other tests such as amniocentesis. It is also used in gynecology and infertility care as well as medical and surgical conditions. Color Doppler ultrasound is a variation that allows estimation and direction of blood flow and vascular resistance in fetal structures. Alpha-fetoprotein assessment is performed on maternal serum or amniotic fluid with the primary goal of detecting open body wall defects such as neural tube defects. Additional tests are required if alpha-fetoprotein levels are abnormal. Other markershCG, estriol and possibly inhibin Amay be assessed with maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein in a triple or quad screen for chromosomal anomalies such as trisomy 21. Chorionic villus sampling is performed at 10-12 weeks gestation to provide parents with information about chromosomal and other congenital defects in the first trimester of pregnancy. Chorionic villus sampling does NOT provide a sample of amniotic fluid or alpha-fetoprotein testing. Amniocentesis is usually performed in the second trimester to identify fetal genetic defects or open defects such as neural tube defects. It may be used during third trimester to evaluate fetal maturity or Rh incompatibility problems. Standard amniocentesis is performed at 15-20 weeks gestation. Early amniocentesis (11-14 weeks) allows earlier diagnosis of genetic problems. Percutaneous umbilical blood sampling involves aspiration of blood from umbilical vessels to detect blood disorders, acid-base balance or fetal disease. Therapeutic medications and blood products can also be injected by the same route. Fetal bradycardia is the most common complication. The nonstress test determines whether the fetal heart rate accelerates when the fetus moves. Accelerations of the heart rate, regardless of fetal movement, are a reassuring sign because they are associated with adequate fetal oxygenation and an intact neural pathway from the fetal brain to the heart. The healthy fetus younger than 32 weeks gestation may not have accelerations that meet the criteria for a reactive nonstress test in the older fetus. Contraction stress tests evaluate response of the fetal heart to recurrent short interruptions in placental blood flow and oxygen supply that occur with uterine contractions. Maternal assessment of fetal movement (kick counts) is a noninvasive method of evaluating the fetus; another advantage of this test is that it has no cost. The poorly oxygenated fetus usually moves less than the welloxygenated fetus. The woman may be advised to follow any of several protocols because no standard protocol exists. All perinatal nurses must be prepared to offer clear explanations of diagnostic procedures and any problems the woman should report. Support for the family requiring fetal diagnostic tests can reduce their anxiety. CHECK YOUR READING 1. What are the major indications for ultrasonography during the first trimester? During the second and third trimesters? Major indications for ultrasonography during the first trimester include confirmation of pregnancy, verify the location of pregnancy, detect multifetal gestation, determine gestational age with measurements, confirm number and viability of fetuses, identify markers and to determine the locations of the uterus, cervix, and placenta for procedures such as CVS. In the second and third trimesters ultrasonography is used to confirm fetal viability, evaluate fetal anatomy, determine gestational age, assess serial fetal growth, compare growth of fetuses in multifetal gestations, evaluate four of five markers in a BPP, locate the placenta in placenta previa, determine fetal presentation, and guide needle placement for amniocentesis or PUBS. 2. How does the procedure for first-trimester ultrasonography differ from that performed during the second trimester?
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
The procedure for the first trimester ultrasonography differs from the second trimester procedure because in the second trimester a full bladder may be needed to displace the gas-filled intestines and elevate the uterus for better image quality. What are major advantages and disadvantages of ultrasonography? Major disadvantages of ultrasonography include the cost and it cannot identify all defects of fetal structures and/or fetal functions. Major advantages of ultrasonography include the ability to clearly visualize the fetus and surrounding structures, it is safe, noninvasive and relatively comfortable with immediate results. Why is MSAFP considered a screening test? MSAFP is considered a screening test because it has several limitations and factors that can affect the results. This include timing, inaccurate estimation of gestation age resulting in apparently abnormal levels in a healthy fetus, and closed defects (such as neural tube defects) do not produce elevated levels of AFP and normal levels of AFP do not guarantee the baby is free of structural defects. What are possible causes for elevated levels of AFP? Possible causes for elevated levels of AFP include open neural tube defects, esophageal obstruction, abdominal wall defects, increased amount leaked by fetal kidney, threatened abortion, fetal demise, inaccurate gestational age (underestimated age), incorrect maternal weight (lower than true weight), type 1 diabetes and multifetal gestation. What are possible causes of low levels of AFP? Possible causes of low levels of AFP include chromosomal trisomies, gestational trophoblastic disease, and overestimation of gestational age with a normal fetus or increased maternal weight (higher than true weight). What is a multiple-marker screening? Why is it performed? A multiple marker screening includes testing for trisomy 21, hCG, unconjugated estriol, and inhibin. This test is performed to identify chromosome abnormalities noninvasively for both younger and older pregnant women. What is the major advantage of CVS compared with amniocentesis? The major advantage of CVS compared with amniocentesis is that CVS is performed between 10-12 weeks gestation providing earlier results. What major risks are associated with CVS? Major risks associated with CVS include rate of pregnancy loss (similar to amniocentesis) and limb reduction defects. What factors make a pregnant woman a candidate for amniocentesis? Factors that make a pregnant woman a candidate for amniocentesis include maternal age greater than 35 yrs old, chromosomal abnormality in a close family member, gender determination for maternal carrier of X-lined disorder, birth of previous infant with chromosomal abnormalities or an open neural tube or body wall defect, pregnancy after three or more spontaneous abortions, elevated levels of maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein or multiple marker screen that remain unexplained, maternal Rh sensitization of maternal Rh-negative blood to fetal Rh-positive blood. How is fetal lung maturity confirmed? Fetal lung maturity is confirmed by the lecithin/sphingomyelin (L/S) ratio test. Lecithin is a phospholipid component of fetal lung fluid and surfactant and sphingomyelin is a general amniotic membrane lipid. Levels are equal until 30 weeks gestation, levels then become a ratio of 2:1 (L/S) and are indicative of adequate surfactant and mature fetal lungs. Why is bilirubin in amniotic fluid evaluated?
Bilirubin in amniotic fluid is evaluated to test if the mother is Rh-negative and was sensitized after being exposed to Rh-positive blood. Antibodies of the sensitized woman can destroy Rh-positive blood of the fetus leaving the fetus vulnerable to erythroblastosis fetalis and hydrops fetalis. 13. Why is early amniocentesis sometimes chosen over standard amniocentesis for prenatal diagnosis of genetic disorders? What possible problems make the early procedure less desirable? Early amniocentesis is sometimes chosen over standard amniocentesis for prenatal diagnosis of genetic disorders to provide the woman time for decisions about additional tests or whether to terminate her pregnancy before 20 weeks. Problems with the early procedure include failure to obtain adequate amniotic fluid for sampling and an increased risk of pregnancy loss rate of 2-5% is also noted. 14. What is a nonstress test and why is it so named? A nonstress test is a fetal surveillance test that identifies whether an increase in the FHR occurs when the fetus moves, indicating adequate oxygenation, a healthy neural pathway from the fetal central nervous system to the fetal heart and the ability of the fetal heart to respond to stimuli. It is called a nonstress test because it does not require the mother or the fetus to be stressed for the procedure. 15. What is vibroacoustic stimulation and what is its expected result during the last trimester of pregnancy? Vibroacoustic stimulation is used to confirm nonreactive NST findings and shorten the time required to obtain high-quality NST data. A vibroacoustic stimulator is applied to the maternal abdomen over the area of the fetal head and stimulation with vibration sound is given for up to 3 seconds and can be repeated at 1 minute intervals for up to three times. During the last trimester of pregnancy, brain responses to auditory stimulation have developed and fetuses near term show increase in the number of gross body movementsthis suggest maturational change in response to vibroacoustic stimulation. 16. Why is initiating contractions usually necessary in a CST? Under what circumstances would the nurse NOT initiate contractions? Initiating contractions is usually necessary in a CST because the mother is not having natural contractions which are necessary to determine if the fetus has adequate oxygen reserves to tolerate the recurrent mild hypoxia of uterine contractions. Contraindications include preterm labor or women who have a high risk for preterm labor, preterm membrane rupture, history of extensive uterine surgery or classical uterine incision for cesarean birth, and placenta previa. 17. In a CST, what do late decelerations of FHR indicate? Late decelerations of FHR indicate the fetus has inadequate reserves and substantial hypoxia has led to anaerobic metabolism and fetal acidosis results. 18. What is the relationship between loss of fetal tone and hypoxia? Fetal CNS centers that control each individual parameter of the BPP react differently to hypoxemia. Centers that develop later require higher oxygenation levels than those developed earlier. Fetal tone is the last area affected the absence of fetal tone indicates advanced asphyxia and acidosis. 19. Why is amniotic fluid volume an important parameter in the BPP? Amniotic fluid is an important parameter in the BPP because it provides information about chronic hypoxia if loss of fluid is not the result of premature membrane rupture. During periods of hypoxemia the fetus shunts blood from noncritical areas (kidneys and lungs) and to vital organs (heart, brain, placenta). If hypoxemia is prolonged, blood flow to the kidneys and lungs, which produce much of the amniotic fluid, may virtually cease. Indications for Fetal Diagnostic Tests Medical Conditions
Preexisting diabetes mellitus or gestational diabetes Hypertension (chronic of preeclampsia) Acute or nonacute infections Sexually transmitted diseases Severe anemia Parents carry or express a genetic disorder Demographic Factors Maternal age >16 or >35 Poverty Nonwhite (greater risk for prematurity or neonatal or infant death) Inadequate prenatal care (initial visit after 20 weeks of gestation or fewer than five prenatal visits to physician or nurse midwife) Obstetric Factors History of low-birth weight or preterm Multifetal pregnancy Malpresentation (breech, shoulder) Previous fetal loss or birth of infant with congenital anomaly Previous infant >4000g at birth Hydramnios Oligohydramnios Decrease in or absence of fetal movements Uncertainty about gestational age Suspected intrauterine growth restriction Discordant (unequal)fetal growth of twins Postmatuirty (>42 weeks) Preterm labor Grand multiparity Concurrent Maternal Factors Prepregnancy BMI less than 18.5 Prepregnancy BMI 25 or higher Inadequate weight gain or poor pattern of weight gain Excessive weight gain Use of unprescribed or illegal drugs, alcohol, tobacco
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Micromine TutorialDocument5 pagesMicromine TutorialFerdinand Siahaan100% (1)
- Automatic Access Control System Using Student Identification Card Based On Rfid TechnologyDocument100 pagesAutomatic Access Control System Using Student Identification Card Based On Rfid TechnologythgnguyenNo ratings yet
- PQS Catalogue 4 2Document143 pagesPQS Catalogue 4 2sagarNo ratings yet
- Centiloquium of PtolemyDocument37 pagesCentiloquium of PtolemyNatasa Karalic Koprivica100% (9)
- Quiz Application in Visual BasicDocument20 pagesQuiz Application in Visual BasicShivangi SahaNo ratings yet
- Light Design by Anil ValiaDocument10 pagesLight Design by Anil ValiaMili Jain0% (1)
- 33kV BS7835 LSZH 3core Armoured Power CableDocument2 pages33kV BS7835 LSZH 3core Armoured Power Cablelafarge lafargeNo ratings yet
- Philippines and Singapore Trade Relations and Agreements: 1. What Leads To Said Agreement?Document11 pagesPhilippines and Singapore Trade Relations and Agreements: 1. What Leads To Said Agreement?Ayrah Erica JaimeNo ratings yet
- Year 10 English Unit Plan AdvertisingDocument5 pagesYear 10 English Unit Plan Advertisingapi-333849174No ratings yet
- Plato, Timaeus, Section 17aDocument2 pagesPlato, Timaeus, Section 17aguitar_theoryNo ratings yet
- 2400 8560 PR 8010 - A1 HSE Management PlanDocument34 pages2400 8560 PR 8010 - A1 HSE Management PlanMohd Musa HashimNo ratings yet
- National Article Writing Competition 2020: Centre For Competition and Investment Laws and PolicyDocument8 pagesNational Article Writing Competition 2020: Centre For Competition and Investment Laws and PolicyNisha PasariNo ratings yet
- 1600 Cal Meal Planning GuideDocument6 pages1600 Cal Meal Planning GuideAlyssa Jennings100% (2)
- Reading in MCJ 216Document4 pagesReading in MCJ 216Shela Lapeña EscalonaNo ratings yet
- #5-The Specialities in The Krithis of Muthuswamy DikshitharDocument5 pages#5-The Specialities in The Krithis of Muthuswamy DikshitharAnuradha MaheshNo ratings yet
- Letter For LACDocument7 pagesLetter For LACDahlia G. MaglasangNo ratings yet
- Calculations: M 0 M 1 c1 c1 0 c2 c2 1 2Document6 pagesCalculations: M 0 M 1 c1 c1 0 c2 c2 1 2shadab521100% (1)
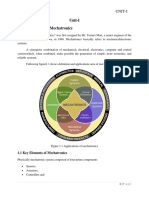
- Mechatronics MaterialDocument86 pagesMechatronics MaterialKota Tarun ReddyNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension Lesson Plan FinalDocument9 pagesReading Comprehension Lesson Plan Finalapi-254917183No ratings yet
- PMP Exam Questions and Answers PDFDocument12 pagesPMP Exam Questions and Answers PDFAshwin Raghav SankarNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 23-Feb-2024Document4 pagesAdobe Scan 23-Feb-2024muzwalimub4104No ratings yet
- Cosmology Questions and Answers - SanfoundryDocument9 pagesCosmology Questions and Answers - SanfoundryGopinathan MNo ratings yet
- Diploma Thesis-P AdamecDocument82 pagesDiploma Thesis-P AdamecKristine Guia CastilloNo ratings yet
- 0 - Danica Joy v. RallecaDocument2 pages0 - Danica Joy v. RallecaRandy Jake Calizo BaluscangNo ratings yet
- Part-II Poem Article and Report For College Magazine-2015-16 Dr.M.Q. KhanDocument4 pagesPart-II Poem Article and Report For College Magazine-2015-16 Dr.M.Q. KhanTechi Son taraNo ratings yet
- Theories of GrowthDocument33 pagesTheories of Growthdr parveen bathlaNo ratings yet
- Comparison of The EC-GMP Guide Part I With The SFDA-GMP Guideline For Chinese CompaniesDocument7 pagesComparison of The EC-GMP Guide Part I With The SFDA-GMP Guideline For Chinese Companiesrambabukomati472No ratings yet
- DIFFERENCE BETWEEN Intrior Design and DecorationDocument13 pagesDIFFERENCE BETWEEN Intrior Design and DecorationSadaf khanNo ratings yet
- Cics 400 Administration and Operations GuideDocument343 pagesCics 400 Administration and Operations GuidedafraumNo ratings yet
- Class XI-Writing-Job ApplicationDocument13 pagesClass XI-Writing-Job Applicationisnprincipal2020No ratings yet