Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anti Hypertensive Drugs
Uploaded by
bananita_20065339Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anti Hypertensive Drugs
Uploaded by
bananita_20065339Copyright:
Available Formats
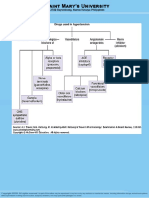
Antihypertensive drugs Drug Sympatholytics Reserpine Guanethidine Mechanism of action Depletes nerve terminal of norepinephrine.
Depletes nerve terminal of norepinephrine. Side effects Sedation, depression, suicidal tendencies, sexual dysfunction. Orthostatic and exercise hypotension, sexual dysfunction. Other
Methyldopa
MNE is an agonist of 2 receptors which leads to a decrease of sympathetic discharges from CNS. 2 receptor agonist in CNS, same mechanism as methyldopa 1 receptors antagonist
Clonidine
Prazosin Diuretics Thiazides
Bradycardia, dry mouth, hypertensive rebound. Positive Coombs test due to haemolytic anemia. Severe hypertensive rebound, never discontinue abruptly. Mental depression. Dizziness, lipothymia (nearsyncope) Hypokalemia, hyperuricemia, hypomagnesemia, hyperlipidemia. Hypokalemia generates cardiac arrhythmias. Hypokalemia, hyponatremia
Abrupt removal could cause a hypertensive crisis because of upregulation of 1 receptors in vessels. Safe during hypertension associated with pregnancy.
Important in heroine withdrawal.
Reduce sodium in vessel wall by blocking Na+/Cl- cotransporter on distal convoluted tubule. Acts on the Na+/K+/2Clcotransporter to inhibit Na+ and Cl- reabsorption blockade, blockade in kidney (1 and renin). Lobetalol and Carvedilol also blocks receptors
Loop diuretics
Essential for treatment of hypertension. To prevent hypokalemia choose Spirolactone or Amiloride Necessary when hypertension is severe or other drugs retain sodium. Less effective in blacks. Avoid in patients with asthma or COPD, and peripheral artery disease.
blockers Metoprolol, Nadolol, Lobetalol, Caevedilol Vasodilators
Impotence, asthma, bradycardia, CHF, AV block, sedation, sleep alterations
Hydralazine
Increases formation of NO
Minoxidil
Open K+ channels, hyperpolarization that causes smooth muscle relaxation. Dilates only arterioles. Inhibit conversion of ANG I to ANG II, reduce or prevent release of aldosterone by ANG II and prevents vasoconstriction by ANG II Causes vasodilation and prevent vascular and cardiac remodeling. Block voltage-dependant L-type calcium channels of cardiac (Verapamil, DIltiazem) and vascular smooth muscle (Nifepidine, Nicardipine) thereby reduce muscle contractility. Increases cGMP via direct release of NO Dopamine D1 receptor agonist. Relaxes renal vascular smooth muscle. Causes peripheral vasodilation and natriuresis. K+ channel opener, hyperpolarizes and relaxes vascular smooth muscle.
Arthalgia, myalgia, lupus like syndrome, tachycardia, headaches, angina, perineuritis Hirsutism, arrhythmias
Fast and slow acetylators, fast shorter effect
ACE inhibitors Enalapril ,Captopril, Lisinopril
Cough, angioedema, small hyperkalemia, hypotension
Avoid in patients with bilateral renal stenosis, contraindicated in pregnant women.
AT1 receptor blockers (Losartan) Ca2+ channel blockers Verapamil, Diltiazem, Nifepidine, Nicardipine
Similar to ACE inhibitors, except cough. Excessive decrease in heart contractility, bradycardia, AV block.
Contraindicated in pregnant women. Contraindicated in heart failure. Interacts with digitalis and blockers at cardiac level.
Hypertensive crisis treatment Sodium Nitroprusside Fenoldopam
Cyanide toxicity (arrhythmias and metabolic acidosis) Ventricular tachycardia, increase intraocular pressure.
Sodium thiosulfate to prevent cyanide accumulation.
Diazoxide
Severe hypotension, MI, angina, tachycardia.
Contraindicated in patients with angina.
You might also like
- Medicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtFrom EverandMedicine in Brief: Name the Disease in Haiku, Tanka and ArtRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- PCOL - Chapter 11 - Anti Hypertensive AgentsDocument3 pagesPCOL - Chapter 11 - Anti Hypertensive AgentsCharles BayogNo ratings yet
- Training Manual: 49197 Wixom Tech DriveDocument70 pagesTraining Manual: 49197 Wixom Tech DriveMore - Dan Consumer Goods TradingNo ratings yet
- Antianginal DrugsDocument19 pagesAntianginal DrugsAnusha ZubairNo ratings yet
- Anti HypertensivesDocument23 pagesAnti HypertensivesLeena AlateeqNo ratings yet
- Anoosha Roll#21Document19 pagesAnoosha Roll#21Anusha ZubairNo ratings yet
- Lec 22 ANTIHYPERTENSIVE - 2Document22 pagesLec 22 ANTIHYPERTENSIVE - 2Abdul MananNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive DrugsDocument7 pagesAntihypertensive Drugshamadadodo7No ratings yet
- Antihypertensive AgentsDocument41 pagesAntihypertensive AgentsRwapembe StephenNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument44 pagesHypertensionMushabeNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic System: e CarbamatesDocument26 pagesCholinergic System: e CarbamatesAcai BoncaiNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Drugs.Document35 pagesAntihypertensive Drugs.Abdul WahabNo ratings yet
- CVS DiseasesDocument15 pagesCVS DiseasesNaavaNo ratings yet
- Antinanginal DrugsDocument43 pagesAntinanginal DrugsHUZAIFA YAMAANNo ratings yet
- 1 Antihypertensive DrugsDocument14 pages1 Antihypertensive DrugsReda SoNo ratings yet
- Easy Learning 2016Document6 pagesEasy Learning 2016Jhon Jade PalagtiwNo ratings yet
- CVPR Prototype Drugs TableDocument27 pagesCVPR Prototype Drugs TablethommyvaNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument3 pagesDrugsMarion Liana DayritNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Drugs: HypertensionDocument8 pagesAntihypertensive Drugs: Hypertensionalmastar officeNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensives WMDocument16 pagesAntihypertensives WMALNAKINo ratings yet
- SYMPATHOLOGICSDocument14 pagesSYMPATHOLOGICSLuiza Mae CastroNo ratings yet
- CardiotonicsDocument21 pagesCardiotonicsmohsen mirdamadiNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive & Antianginal DrugsDocument5 pagesAntihypertensive & Antianginal Drugsdomememe1No ratings yet
- Anti Hypertensive 20191211Document35 pagesAnti Hypertensive 20191211helloitsmenadNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive Drugs ٠١١٦٥٨Document10 pagesAntihypertensive Drugs ٠١١٦٥٨mohnad806mNo ratings yet
- Obat Gagal Jantung N Anti AnginaDocument42 pagesObat Gagal Jantung N Anti AnginaAyu Devi YantiNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument54 pagesHypertensionBadri KarkiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Assignment No.02: Submitted By: Submitted To: Nandraj Ma'am Areeba Shafiq Roll No. 1817007Document23 pagesPharmacology Assignment No.02: Submitted By: Submitted To: Nandraj Ma'am Areeba Shafiq Roll No. 1817007Nandraj123100% (1)
- Vasodilators by Hiren PatelDocument28 pagesVasodilators by Hiren PatelHiren_Patel_2427No ratings yet
- Calcium Channel MedicationsDocument17 pagesCalcium Channel MedicationsMarriette Bayaya AntiquinaNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument43 pagesHypertensionAbin PNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive DrugsDocument5 pagesAntihypertensive DrugsAiman TymerNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology SummaryDocument16 pagesPharmacology Summaryshenric16No ratings yet
- MedicationsDocument30 pagesMedicationsvamshidhNo ratings yet
- CVS PharmacologyDocument60 pagesCVS PharmacologyGølà Sèèñàà–baale irraaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Drugs (Veterinary Pharmacology)Document44 pagesCardiovascular Drugs (Veterinary Pharmacology)DR Muhammad Abdul BasitNo ratings yet
- HYPERTENSIONDocument5 pagesHYPERTENSIONRajesh RamanNo ratings yet
- Cardiology Review: HTN: Julia Akaah M.DDocument40 pagesCardiology Review: HTN: Julia Akaah M.DJose LunaNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects GN: Dopamine BN: Classification: AdrenergicDocument14 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects GN: Dopamine BN: Classification: AdrenergicSteffi MurielNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic SystemDocument6 pagesAdrenergic SystemdocsNo ratings yet
- 0 - Presentation Pharma Samra ShoukatDocument18 pages0 - Presentation Pharma Samra ShoukatMohib Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Hypertension: Dr. R. PilvinieneDocument33 pagesDrugs Used in Hypertension: Dr. R. PilvinieneNewteNo ratings yet
- Drenergic AND Anti Adrenergic Drugs: Shabib AkhtarDocument21 pagesDrenergic AND Anti Adrenergic Drugs: Shabib AkhtarDeepa ShaiekhNo ratings yet
- 11A Drugs Acting On The Cardiovascular SystemDocument85 pages11A Drugs Acting On The Cardiovascular SystemJaps De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used To Treat Cardiovascular Diseases: HypertensionDocument35 pagesDrugs Used To Treat Cardiovascular Diseases: HypertensionAyro Business CenterNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive Emergencies: BY: Dr. Imtiyaz Hashim (PGR) Dr. Khalida Baloch (Ho)Document31 pagesHypertensive Emergencies: BY: Dr. Imtiyaz Hashim (PGR) Dr. Khalida Baloch (Ho)امتیاز ہاشم بزنجوNo ratings yet
- 9 Drugs Affecting Angina PectorisDocument3 pages9 Drugs Affecting Angina PectoristiaraNo ratings yet
- 03 AntihypertensiveDocument89 pages03 Antihypertensive2nnfpjy5yvNo ratings yet
- Drug Profiling PHARMACOLOGYDocument71 pagesDrug Profiling PHARMACOLOGYJay MagsaysayNo ratings yet
- Antihypertensive AgentsDocument52 pagesAntihypertensive Agentssameena ramzanNo ratings yet
- Drug ClassDocument13 pagesDrug ClassEdfren Salazar Colon100% (1)
- Heart Failure and Its Drug ClassificationDocument37 pagesHeart Failure and Its Drug ClassificationMaham AzmatNo ratings yet
- Vasodilators 1233318450814478 3Document29 pagesVasodilators 1233318450814478 3Nehal AmjadNo ratings yet
- 10-11 Treatment of HypertensionDocument11 pages10-11 Treatment of HypertensionHanif GandohNo ratings yet
- Hypertension An OverviewDocument214 pagesHypertension An OverviewdkhandkeNo ratings yet
- Atrial Fibrillation A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesFrom EverandAtrial Fibrillation A Simple Guide to The Condition, Treatment And Related DiseasesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Platinum Formulary 2016Document61 pagesPlatinum Formulary 2016jNo ratings yet
- 4 Reconstitution of Powdered Drugs1 PDFDocument6 pages4 Reconstitution of Powdered Drugs1 PDFJB ReyesNo ratings yet
- Fentanyl SublimazeDocument2 pagesFentanyl SublimazeENo ratings yet
- Frank Shann - 040315153700Document63 pagesFrank Shann - 040315153700juwitapratiwiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyNicole GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Benzodiazepines 2022 Drug Fact Sheet - 1Document1 pageBenzodiazepines 2022 Drug Fact Sheet - 1Sharique KhanNo ratings yet
- D.Pharm. Syllabus PDFDocument21 pagesD.Pharm. Syllabus PDFBhowanisankar Charati Ias HunterNo ratings yet
- Rekapitulasi Laporan Narkotika: NO Nama Satuan Stok Awal Pemasukan PBFDocument10 pagesRekapitulasi Laporan Narkotika: NO Nama Satuan Stok Awal Pemasukan PBFAnonymous idPPyERfBnNo ratings yet
- Copy NoDocument40 pagesCopy Noromulo pacupacNo ratings yet
- 3.02.19 Verbal Orders and Critical Values2Document2 pages3.02.19 Verbal Orders and Critical Values2Robert TucayNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Research in Pharmacy and ScienceDocument10 pagesInternational Journal of Research in Pharmacy and ScienceAat Prayoga MuhtarNo ratings yet
- Surat Permintaan Obat Dinkes BaruDocument21 pagesSurat Permintaan Obat Dinkes BaruHafizh JhunkoNo ratings yet
- Complications of Intravenous TherapyDocument29 pagesComplications of Intravenous TherapyKrizia BonillaNo ratings yet
- DUI Handbook 2011Document33 pagesDUI Handbook 2011ajafogelNo ratings yet
- Side Effects: FentanylDocument2 pagesSide Effects: FentanylArianda Nurbani WidyaputriNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Potassium ChlorideDocument6 pagesDrug Study - Potassium ChlorideBalloonsRus PHNo ratings yet
- Quia Timet InjunctionDocument7 pagesQuia Timet InjunctiondivyashekarNo ratings yet
- Call Grand Master +27734818506 HOW TO JOIN 666 ILLUMINATI SECRET SOCIETY FOR MONEY IN USA, UK, Canada, Spain, Italy, China, Hong Kong FreestateDocument176 pagesCall Grand Master +27734818506 HOW TO JOIN 666 ILLUMINATI SECRET SOCIETY FOR MONEY IN USA, UK, Canada, Spain, Italy, China, Hong Kong FreestateJohn RichNo ratings yet
- Practice Test Questions Downloaded From FILIPINO NURSES CENTRALDocument8 pagesPractice Test Questions Downloaded From FILIPINO NURSES CENTRALFilipino Nurses Central100% (4)
- Cefazolin Sodium AncefDocument1 pageCefazolin Sodium AncefKristi WrayNo ratings yet
- Transdermal Opioid Patches: Quick Reference Guide: Important InformationDocument2 pagesTransdermal Opioid Patches: Quick Reference Guide: Important Informationemilia_sweetyNo ratings yet
- Brain PaperDocument3 pagesBrain PaperDanielle PediniNo ratings yet
- Semisolid Dosage FormDocument9 pagesSemisolid Dosage Formsayid saidNo ratings yet
- Online Pharmacy Dec 1: Contextual Spelling Grammar Punctuation Sentence Structure StyleDocument15 pagesOnline Pharmacy Dec 1: Contextual Spelling Grammar Punctuation Sentence Structure StyleRome Empe BalNo ratings yet
- ASHP Statement On UDDDocument1 pageASHP Statement On UDDZamrotul IzzahNo ratings yet
- Lipiget Tab Leaflet Export GADocument2 pagesLipiget Tab Leaflet Export GAsakhawat rehmanNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Typhoid Fever Using Antibiotics: Class SummaryDocument8 pagesTreatment of Typhoid Fever Using Antibiotics: Class SummaryRani Henty NovitaNo ratings yet
- Op-Ed (Final Draft)Document3 pagesOp-Ed (Final Draft)api-283808039No ratings yet
- MaxolonDocument2 pagesMaxolonTan Chew SiaNo ratings yet