Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CHEM Chapter 1
Uploaded by
Shu SinOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CHEM Chapter 1
Uploaded by
Shu SinCopyright:
Available Formats
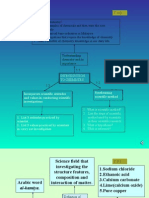
Chapter 1 1. Chemistry---al-kimiya (Arabic word for alchemy) 2.
Scientist: Antoine Lavoiser combustion and composition of water : Robert Boyle separated chemistry for alchemy 3. Study of : Composition of matter : Structure of matter : Properties of matter : Interaction of matter 4. Importance ~sodium chloride (salt)-preserving food ~oxygen-for respiration ~calcium carbonate-making marble ~copper-made into wires 5. Related carrier ~medical doctors & biochemists- understand the chemical process in human body ~pharmacists- expert in medicinal drugs- interaction between each other or with the body ~Forensic scientist- helps police to solve crime by analyzing evidence ~pathologists- determine the cause of death by an autopsy ~food technologists- develop ways of processing and preserve food ~farmers- need chemistry to understand the proper usage of fertilizers and pesticide 6. Chemical based industry ~palm-oil industry ~paint industry ~petroleum industry ~rubber industry ~agrochemical industry ~pharmaceutical industry ~healthcare industry ~cosmetic industry ~inorganic industry *benefits= they contribute to our economy, support other industries in the country and provide job opportunities to our people. 7. Scientific method Steps involved in a scientific method: 1) Making Observations - using our five senses (sight, hearing, smell, taste and touch) 2) Making Inference - a smart guess made based on our observation 3) Identifying problem - written in a form of a question (?) based on the inference made 4) Making hypothesis - a general statement based on the relationship between a manipulated variable and a responding variable. 5) Identifying variables - manipulated, responding and constant (fixed) variables to test the hypothesis made 6) Controlling variables - deciding on how to manipulate the chosen variable, what to measure and how to keep a fixed variable constant 7) Planning an experiment - deciding what materials & apparatus to use; procedure of an experiment; method of collecting data and ways to analyze and interpret the data 8) Collecting data - making observations and measurements. Record them in a form of a table. - Do ensure that all measured values are recorded with the correct number of signicant gures. - Do include the units of the physical quantities listed in the header of the table. 9) Interpreting data - organizing and analyzing a data (graph, charts) 10) Making conclusion - making a statement about the outcome of the experiment and whether the hypothesis is accepted/rejected. 11) Writing a report - When writing experiment reports, write in present tense, passive voice.
You might also like
- Purification of Laboratory Chemicals: Part 2 Inorganic Chemicals, Catalysts, Biochemicals, Physiologically Active Chemicals, NanomaterialsFrom EverandPurification of Laboratory Chemicals: Part 2 Inorganic Chemicals, Catalysts, Biochemicals, Physiologically Active Chemicals, NanomaterialsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document3 pagesChapter 1Zainudin Abdul RazakNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Biology Chapter OverviewDocument21 pagesForm 4 Biology Chapter OverviewKar KuanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document23 pagesChapter 1wienna1987No ratings yet
- Somaville University Semester: I Lecture: Chemistry Topic: AssignmentDocument3 pagesSomaville University Semester: I Lecture: Chemistry Topic: AssignmentnuurNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemistry"Document41 pagesIntroduction To Chemistry"Judy Ann CastorNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiologyDocument3 pagesIntroduction To BiologyRozaini OthmanNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Study GuideDocument24 pagesBiotechnology Study GuideÖzlem ErdemNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY (4551) : Paper 1 (50 Objectives) - 50 MDocument24 pagesBIOLOGY (4551) : Paper 1 (50 Objectives) - 50 Mwienna1987No ratings yet
- Chem Note SS1 1st TermDocument32 pagesChem Note SS1 1st TermVictor Okosun94% (16)
- Chapter 1 Scientific InvestigationDocument25 pagesChapter 1 Scientific InvestigationanamarietuvNo ratings yet
- Gen ChemDocument226 pagesGen ChemKemal PujabNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Summer Pack - 2022.2023Document169 pagesYear 10 Summer Pack - 2022.2023Zeyad MohamedNo ratings yet
- Research 10 Q4 W1Document7 pagesResearch 10 Q4 W1Trexia SingsonNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Experiments and Project ReportsDocument3 pagesInvestigatory Experiments and Project ReportsAmiyo SarkarNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology SBA GuidelinesDocument4 pagesCSEC Biology SBA GuidelinesMichelle Benskin100% (2)
- Investigatory ProjectDocument3 pagesInvestigatory ProjectKushagra TripathiNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry: Fundamentals ofDocument33 pagesAnalytical Chemistry: Fundamentals ofJhon dave SurbanoNo ratings yet
- Holiday Assignment/Project Investigatory Project For Class Xii BiologyDocument2 pagesHoliday Assignment/Project Investigatory Project For Class Xii BiologyJagatha RaasmiNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Study of BiologyDocument17 pagesUnderstanding The Study of BiologyachikgaiNo ratings yet
- Investigatory Experiments and Project ReportsDocument2 pagesInvestigatory Experiments and Project ReportsAnonymous XJocHPNo ratings yet
- Weeks: Science Form 1 Learning Objectives Suggested Learning Activities Learning Outcomes Notes VocabularyDocument23 pagesWeeks: Science Form 1 Learning Objectives Suggested Learning Activities Learning Outcomes Notes VocabularyAsmanura YahyaNo ratings yet
- (Introduction To Chemistry) : General Engineering DepartmentDocument5 pages(Introduction To Chemistry) : General Engineering DepartmentDanny Riel BarachinaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry: Chapter 1A WEEK 2 - October 12-16, 2020 Learning ObjectivesDocument11 pagesGeneral Chemistry: Chapter 1A WEEK 2 - October 12-16, 2020 Learning ObjectivesReygemae Quitoras-ObsidNo ratings yet
- High School Research Made EasyDocument46 pagesHigh School Research Made EasyG19 Domino, MarionNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Scientific InvestigationDocument25 pagesChapter 1 Scientific InvestigationFazza Rudy100% (8)
- Chemistry NotesDocument2 pagesChemistry NotesAngelo Kyle AdrianoNo ratings yet
- Science F4 Chapter 1Document3 pagesScience F4 Chapter 1Keen WayNo ratings yet
- LHT in Research Q3W1Document6 pagesLHT in Research Q3W1Chiara PaulinNo ratings yet
- Sodium Chloride: Chapter 1: Introduction To ChemistryDocument3 pagesSodium Chloride: Chapter 1: Introduction To ChemistryWei ChingNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Science 7 CompendiumDocument105 pages1st Quarter Science 7 CompendiumJohn Cedrick Coronel RafananNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarter Science 7 CompendiumDocument105 pages1st Quarter Science 7 CompendiumJohn Cedrick Coronel RafananNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chem Course OverviewDocument13 pagesAnalytical Chem Course OverviewKarl Patrick SiegaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1st Secondary 2018 With URLDocument168 pagesChemistry 1st Secondary 2018 With URLMina RafatNo ratings yet
- 1.1 & 1.2 - Chemistry and Its Importance & Scientific MethodDocument24 pages1.1 & 1.2 - Chemistry and Its Importance & Scientific MethodsivagurusasNo ratings yet
- MC Chem2-Analytical ChemistryDocument5 pagesMC Chem2-Analytical ChemistryMonica OlorosoNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Year Note - 2023Document119 pagesGrade 10 Year Note - 2023maqhawentsakoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 TahsiliDocument7 pagesUnit 1 Tahsilieducationpurpuses111No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document2 pagesChapter 1Nurul SalehahNo ratings yet
- 1ST Year SyllabusDocument6 pages1ST Year SyllabusSelvakumardxbNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Ss11sttermDocument80 pagesChemistry Ss11sttermDidimako GodstimeNo ratings yet
- DMLT (10) 3RD SemDocument6 pagesDMLT (10) 3RD Semnavaziskhan363No ratings yet
- Bio Eoc Review PacketDocument29 pagesBio Eoc Review Packetapi-267855902No ratings yet
- Lectures 1ST 4THDocument78 pagesLectures 1ST 4THNorie Castillo Santos AmadorNo ratings yet
- STK1211 Practical Analytical ChemistryDocument39 pagesSTK1211 Practical Analytical Chemistrylox agencyNo ratings yet
- Intro to Chem Chapter 1 NotesDocument15 pagesIntro to Chem Chapter 1 NotesMehak KhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Analytical ChemistryDocument28 pagesIntroduction To Analytical ChemistryPeter ParkerNo ratings yet
- Practice of Natural Product Chemistry - Q2 - Arabidopsides - 2023 (16) - CopieDocument5 pagesPractice of Natural Product Chemistry - Q2 - Arabidopsides - 2023 (16) - CopieJérôme HuretNo ratings yet
- 1.2 The Scientific InvestigationDocument16 pages1.2 The Scientific InvestigationIMELDA100% (3)
- Branches of BiologyDocument3 pagesBranches of BiologyDith JarillaNo ratings yet
- M.Sc. Foods and Nutrition: Semester I Max. MarksDocument21 pagesM.Sc. Foods and Nutrition: Semester I Max. MarksMalaika ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Chemical Biology II Analytical Methods in Biology Lecture Reviewer Lesson 1Document9 pagesChemical Biology II Analytical Methods in Biology Lecture Reviewer Lesson 1Ajuy VenturaNo ratings yet
- Y8 Autumn Assessment Booklet 201718Document12 pagesY8 Autumn Assessment Booklet 201718Tamara Martínez LiriaNo ratings yet
- Scientific Method: - A Systematic Method Used To Solve Problems in ScienceDocument13 pagesScientific Method: - A Systematic Method Used To Solve Problems in ScienceFid AwanNo ratings yet
- Major Research Designs (Calcmorin) : When To Use Historical Research?Document4 pagesMajor Research Designs (Calcmorin) : When To Use Historical Research?Habin PermantanNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory Experiments and Project ReportsDocument5 pagesBiology Investigatory Experiments and Project ReportsJasim AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Quarter 1 Common LabDocument4 pagesChemistry Quarter 1 Common LabLynsey WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Notice Comments Guidelines Sampling Microbiology 14-10-2021Document38 pagesNotice Comments Guidelines Sampling Microbiology 14-10-2021sheela bethapudiNo ratings yet
- Author Guidelines, Journal Style and List of Journals - IDOSI (7-2021)Document9 pagesAuthor Guidelines, Journal Style and List of Journals - IDOSI (7-2021)KenesaNo ratings yet
- How To Instill Patriotism Among MalaysianDocument2 pagesHow To Instill Patriotism Among MalaysianShu SinNo ratings yet
- CHEM Chapter 1Document1 pageCHEM Chapter 1Shu SinNo ratings yet
- CHEM Chapter 1Document1 pageCHEM Chapter 1Shu SinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 BioDocument2 pagesChapter 2 BioShu SinNo ratings yet
- Stabilization of Expansive Soil Using Bagasse Ash & LimeDocument6 pagesStabilization of Expansive Soil Using Bagasse Ash & LimeRajveer SaeNo ratings yet
- The Role of Chemistry in Energy and IndustryDocument15 pagesThe Role of Chemistry in Energy and IndustryDayu AgungNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document6 pagesChapter 8Jerico LlovidoNo ratings yet
- A Presentation On: Presented byDocument67 pagesA Presentation On: Presented byOlufemi KolawoleNo ratings yet
- Mineralogi Part.2 3Document10 pagesMineralogi Part.2 3Roges tomara mahesa100% (2)
- Coal Fired Power Plant Termopaipa Iv: Compañía Eléctrica de Sochagota S.A. E.S.PDocument16 pagesCoal Fired Power Plant Termopaipa Iv: Compañía Eléctrica de Sochagota S.A. E.S.PControl Office and Technical Department CESNo ratings yet
- Me 8301 EtdDocument3 pagesMe 8301 Etdsrinithims78No ratings yet
- Contractor Quality Control Plan For Welding WorkDocument3 pagesContractor Quality Control Plan For Welding WorkCak Nhass50% (2)
- Types of Oil Seed Used in Oil Processing AreDocument27 pagesTypes of Oil Seed Used in Oil Processing AredagimNo ratings yet
- Enzymes CoWinDocument3 pagesEnzymes CoWinabinradhNo ratings yet
- TZM LAB Equipment-原件Document15 pagesTZM LAB Equipment-原件Emily AiNo ratings yet
- Dissolvine DZ P PDLDocument2 pagesDissolvine DZ P PDLizzybjNo ratings yet
- ExperimentalDocument5 pagesExperimentalbabuNo ratings yet
- A Review On Grease Lubrication in Rolling BearingsDocument12 pagesA Review On Grease Lubrication in Rolling BearingsRepositorio MantenimientoNo ratings yet
- Environmental EngineeringDocument5 pagesEnvironmental EngineeringOktrian SinathryaNo ratings yet
- Laminar and Turbulent FlowDocument16 pagesLaminar and Turbulent FlowMariya ZolotarNo ratings yet
- Study of Process Parameters in High Pressure Die CastingDocument9 pagesStudy of Process Parameters in High Pressure Die Castingruben6286No ratings yet
- Effectively Remove DropletsDocument1 pageEffectively Remove Dropletsfawmer61No ratings yet
- Pour Point TestingDocument10 pagesPour Point TestingAAKASHNo ratings yet
- Thermo Acoustic RefrigerationDocument23 pagesThermo Acoustic RefrigerationSujitNo ratings yet
- Sand MouldingDocument33 pagesSand MouldingSuman DeyNo ratings yet
- Hytrel Extrusion Manual PDFDocument28 pagesHytrel Extrusion Manual PDFashkansoheylNo ratings yet
- HP BITUMEN HANDBOOKDocument53 pagesHP BITUMEN HANDBOOKAnuj Mathur100% (1)
- Mole Concept ActivitiesDocument9 pagesMole Concept Activitiesjoan marie PeliasNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1: Reactions of Aliphatic HydrocarbonsDocument8 pagesExperiment 1: Reactions of Aliphatic HydrocarbonsTHASVIN OFFICIAL NETWORKNo ratings yet
- Membrane - FunctionDocument4 pagesMembrane - Functionphuong anhNo ratings yet
- DPF System PDFDocument15 pagesDPF System PDFKevine KhaledNo ratings yet
- Carbon Filter Garbage Incinerator Reduces Waste Volume /TITLEDocument23 pagesCarbon Filter Garbage Incinerator Reduces Waste Volume /TITLEAlnor Latabat AlontoNo ratings yet
- Superabsorbent PolymerDocument21 pagesSuperabsorbent PolymerIsha MeshramNo ratings yet
- A Method To Test The Detectability of GC PFPD ForDocument8 pagesA Method To Test The Detectability of GC PFPD ForMarian Si Teofana HasnaNo ratings yet