Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pregnancy Risk Category B DIN RD Trimester
Uploaded by
Lheajane SocratesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pregnancy Risk Category B DIN RD Trimester
Uploaded by
Lheajane SocratesCopyright:
Available Formats
Bagona Lhea Jane BSN 309 Group 33
DRUG
DOSAGE
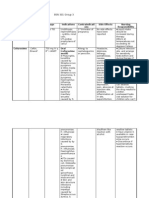
Generic Name: Diclofenac potassium Brand name: Cataflam Classification: NSAID Therapeutic classification: antiarthritic; antiinflammatory
PREGNANCY RISK CATEGORY B; D IN 3RD TRIMESTER
Available Forms Tablets: 50 mg
Doctors Order: 50mg TID
THERAPEUTI C ACTIONS May inhibit prostaglandin synthesis, to produce antiinflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic effects.
INDICATIONS Ankylosing spondylitis Adults: 25 mg delayedrelease diclofenac sodium P.O. q.i.d.; may add another 25mg dose at bedtime. Osteoarthrit is Adults: 50 mg P.O. b.i.d. or t.i.d., or 75 mg P.O. b.i.d. diclofenac potassium or delayedrelease diclofenac
CONTRAINDI CATION Contraindic ated in patients hypersensiti ve to drug and in those with hepatic porphyria or history of asthma, urticaria, or other allergic reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs. Avoid using during late pregnancy or breastfeeding. Use cautiously
ADVERSE EFFECTS
NURSING CONSIDERATI ONS CNS Administratio aseptic n meningitis P.O. anxiety Give drug depression with milk, dizziness meals, or drowsiness antacids. headache Don't crush insomnia or break irritability enteric-coated CV tablets. heart failure Clinical edema Consideration fluid retention s hypertension Because EENT NSAIDs impair laryngeal the synthesis of edema renal blurred vision prostaglandins, epistaxis they can eye pain decrease renal night blindness blood flow and reversible lead to hearing loss reversible renal swelling of the impairment, lips and tongue especially in
sodium only. Or, 100 mg P.O. daily or b.i.d. extendedrelease diclofenac sodium only. Rheumatoid arthritis Adults: 50 mg P.O. t.i.d. or q.i.d., or 75 mg P.O. b.i.d. diclofenac potassium or delayedrelease diclofenac sodium only. Or, 100 mg P.O. daily or b.i.d. extendedrelease diclofenac sodium only, or 50
in patients with history of peptic ulcer disease, hepatic dysfunction, cardiac disease, hypertensio n, fluid retention, or impaired renal function.
tinnitus GI abdominal distention abdominal pain or cramps bleeding constipation diarrhea flatulence indigestion melena nausea peptic ulceration taste disorder bloody diarrhea appetite change colitis GU nephrotic syndrome acute renal failure fluid retention interstitial nephritis oliguria papillary necrosis proteinuria
patients with renal or heart failure or liver dysfunction, in elderly patients, and in those taking diuretics. Monitor these patients closely. Liver function test values may increase during therapy. Monitor transaminase, especially ALT, levels periodically in patients undergoing long-term therapy. Make first transaminase measurement no later than 8 weeks after therapy begins. Because of their antipyretic and anti-
to 100 mg diclofenac sodium P.R. at bedtime as substitute for last P.O. dose of the day. Don't exceed 150 mg daily. Analgesia, primary dysmenorrh ea Adults: 50 mg diclofenac potassium P.O. t.i.d. For some patients, the first dose on the 1st day may be 100 mg, followed by 50 mg for the second and third doses; maximum dose for 1st
Hepatic jaundice hepatitis hepatotoxicity Metabolic hypoglycemia hyperglycemia Musculoskele tal back leg or joint pain Respiratory asthma Skin StevensJohnson syndrome allergic purpura alopecia bullous eruption dermatitis eczema photosensitivity reactions pruritus rash urticaria Other anaphylactoid reactions anaphylaxis
inflammatory actions, NSAIDs may mask the signs and symptoms of infection. Alert: NSAI Ds may increase the risk of potentially fatal cardiovascular thrombotic events, MI, and stroke. Serious GI toxicity, including peptic ulcers and bleeding, can occur in patient taking NSAIDs, despite lack of symptoms. Look alikesound alike: Don't confuse diclofenac with Diflucan. Patient Teaching Tell patient
day is 200 mg. Don't exceed 150 mg daily after the 1st day.
angioedema
to take drug with milk, meals, or antacids to minimize GI distress. Instruct patient not to crush, break, or chew entericcoated tablets. Advise patient not to take this drug with any other diclofenaccontaining products (such as Arthrotec). Teach patient signs and symptoms of GI bleeding, including blood in vomit, urine, or stool; coffeeground vomit; and black, tarry stool. Tell him to notify prescriber immediately if any of these
occurs. Teach patient the signs and symptoms of damage to the liver, including nausea, fatigue, lethargy, itching, yellowed skin or eyes, right upper quadrant tenderness, and flulike symptoms. Tell patient to contact prescriber immediately if these symptoms occur. Advise patient to avoid drinking alcohol or taking aspirin during drug therapy. Tell patient to wear sunscreen or
protective clothing because drug may cause sensitivity to sunlight. Warn patient to avoid hazardous activities that require alertness until it is known whether the drug causes CNS symptoms. Tell pregnant woman to avoid use of drug during last trimester. Advise patient that use of OTC NSAIDs and diclofenac may increase the risk of GI toxicity.
You might also like
- Timolol MaleateDocument3 pagesTimolol MaleateAP TOROBXNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument3 pagesDrug AnalysisAnn Aquino100% (1)
- Drug Study Stugeron and Kalium DuruleDocument1 pageDrug Study Stugeron and Kalium DuruleawesomedawnNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAbigail BascoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CefuroximeDocument2 pagesDrug Study CefuroximeDave Michael GeliNo ratings yet
- Drug Studies (DMII) (Humulin, NACh03, Losartan, Vessel Due F)Document5 pagesDrug Studies (DMII) (Humulin, NACh03, Losartan, Vessel Due F)Alvin OrizaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - OB WardDocument8 pagesDrug Study - OB WardCheska YsabelleNo ratings yet
- ClindamycinDocument2 pagesClindamycinDino V EscalonaNo ratings yet
- Drug Classificati ON Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindications Side Effects/ Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument3 pagesDrug Classificati ON Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindications Side Effects/ Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationsFranz Earl Niño AlbesaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Cushing's SyndromeDocument5 pagesDrug Study Cushing's SyndromeSelena MarieNo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument3 pagesDrug AnalysisAbby BorabienNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: (Celecoxib)Document11 pagesDrug Study: (Celecoxib)Princess Brigitte R. PATE�ANo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Acetaminophen)Document1 pageDrug Study (Acetaminophen)Kian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyMa R DyNo ratings yet
- NeoblocDocument2 pagesNeoblocianecunar100% (2)
- Drug Action Indication/Contraindicatio N Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument6 pagesDrug Action Indication/Contraindicatio N Nursing ResponsibilitiesBryan BosqueNo ratings yet
- Drug Study LevofloxacinDocument2 pagesDrug Study LevofloxacinDannah BulliandayNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of Ceftriaxone & RowatinexDocument5 pagesDrug Study of Ceftriaxone & RowatinexLorina Lynne ApelacioNo ratings yet
- Senokot-S (Senna Concentrate 8.6mg + Docusate Sodium 50mg)Document2 pagesSenokot-S (Senna Concentrate 8.6mg + Docusate Sodium 50mg)E100% (1)
- DS (Calcium + Vit. D)Document6 pagesDS (Calcium + Vit. D)Mary April MendezNo ratings yet
- Tramadol Drug StudyDocument2 pagesTramadol Drug StudyTipey Segismundo0% (1)
- Subcutaneous Injection: Humalog U-100 or U-200: More CommonDocument2 pagesSubcutaneous Injection: Humalog U-100 or U-200: More Commonahmad ryanNo ratings yet
- Amoxicillin Tri Hydrate Table FormatDocument3 pagesAmoxicillin Tri Hydrate Table FormatNico DonatoNo ratings yet
- Losartan Drug StudyDocument2 pagesLosartan Drug StudyXerxes DejitoNo ratings yet
- AldazideDocument2 pagesAldazideianecunarNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Brand Name: Pletal: Pharmacologic Class: Pharmacokinetics General Indications Contraindications BeforeDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: Brand Name: Pletal: Pharmacologic Class: Pharmacokinetics General Indications Contraindications Beforeart_mutantNo ratings yet
- Drug Study LosartanDocument2 pagesDrug Study LosartanIris BalinoNo ratings yet
- IsosorbideDocument2 pagesIsosorbideSNo ratings yet
- F. Case Study Thesis-Drug Study (Revised)Document5 pagesF. Case Study Thesis-Drug Study (Revised)Lopirts NiganiNo ratings yet
- DRUG PantoprazoleDocument1 pageDRUG PantoprazoleEngelbert CruzNo ratings yet
- Med 3 Drug StudyDocument12 pagesMed 3 Drug StudyJinky Nacar DomingoNo ratings yet
- DS - ColchicineDocument2 pagesDS - ColchicineMarie Kelsey Acena MacaraigNo ratings yet
- EtoricoxibDocument7 pagesEtoricoxibsatwika28100% (1)
- Drug Study Ferrous Sulfate + FADocument3 pagesDrug Study Ferrous Sulfate + FAKristine ChampnessNo ratings yet
- Sulfa Sal AzineDocument2 pagesSulfa Sal Azineikke alma alukaNo ratings yet
- Amlodipine CPDocument2 pagesAmlodipine CPRose EchevarriaNo ratings yet
- PrednisoneDocument22 pagesPrednisoneAlthea AlicandoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument1 pageDrug StudycliffordbuenoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Table 3Document5 pagesDrug Study Table 3Juliet De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Mu CostaDocument7 pagesMu Costayvoniemaebruno0% (1)
- NafarinDocument2 pagesNafarinianecunar100% (2)
- Fluvastatin - Drug StudyDocument1 pageFluvastatin - Drug StudyKevin H. MilanesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyJenny YenNo ratings yet
- ChlorpromazineDocument2 pagesChlorpromazineFay Dominguez100% (1)
- Drug SDocument2 pagesDrug SJane CasiquinNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ferrous SulfateDocument2 pagesDrug Study Ferrous SulfatePauline AnesNo ratings yet
- Drug CarbocisteineDocument1 pageDrug CarbocisteineDhan LopezNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug Studyjanelle123 toribioNo ratings yet
- Impaired Tissue Perfusion Related To The Weakening / Decreased Blood Flow To The Area of Gangrene Due To Obstruction of Blood VesselsDocument3 pagesImpaired Tissue Perfusion Related To The Weakening / Decreased Blood Flow To The Area of Gangrene Due To Obstruction of Blood VesselsKat AlaNo ratings yet
- IrbesartanDocument3 pagesIrbesartanapi-3797941No ratings yet
- 66 Drug AnaDocument3 pages66 Drug AnaAlexa RoqueNo ratings yet
- Drug StuyJJASGHDocument7 pagesDrug StuyJJASGHJan Pierre RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyOdarp PradzNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyanon_11638632No ratings yet
- Drug Study DiclofenacDocument2 pagesDrug Study Diclofenackezia_reyes100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyFranco ObedozaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyCamilley De Vera100% (1)
- Drug Study For ITPDocument25 pagesDrug Study For ITPMary Ann QuinonesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (FINAL)Document31 pagesDrug Study (FINAL)iamjenivicNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Drug Class Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibility Treatment of Urinary Tract InfectionDocument5 pagesDrug Name Drug Class Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibility Treatment of Urinary Tract InfectionOamaga NajlaNo ratings yet
- Drotaverine: Solution For Injection - 40 MG / 2 MLDocument1 pageDrotaverine: Solution For Injection - 40 MG / 2 MLZarbakht AliNo ratings yet
- SddaDocument2 pagesSddaJeny Alva RojasNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Pengaruh Musik Mozart Terhadap Perubahan Perilaku Hiperaktif Anak Adhd Usia 7-12 TahunDocument16 pagesJurnal Pengaruh Musik Mozart Terhadap Perubahan Perilaku Hiperaktif Anak Adhd Usia 7-12 TahunroryputrisartikaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Understanding Evidence-Based PracticeDocument29 pagesChapter 5 - Understanding Evidence-Based PracticeIgnacio TroianoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Usefulness of Propofol As An Anesthetic Induction Agent in Dogs and CatsDocument3 pagesClinical Usefulness of Propofol As An Anesthetic Induction Agent in Dogs and CatsSatria Adi MarhendraNo ratings yet
- Hepatic Encephalopathy in Adults - Treatment - UpToDateDocument8 pagesHepatic Encephalopathy in Adults - Treatment - UpToDatenaka_thanatosNo ratings yet
- Polyphenols, and Physical PerformanceDocument7 pagesPolyphenols, and Physical PerformancezoliteamlavylitesNo ratings yet
- Treatment Plan Form John Doe - Coun755Document3 pagesTreatment Plan Form John Doe - Coun755api-310813184No ratings yet
- Invos System Improving Patient Outcomes Cerebral Somatic Oximetry BrochureDocument6 pagesInvos System Improving Patient Outcomes Cerebral Somatic Oximetry Brochuremihalcea alinNo ratings yet
- FibromyalgiaDocument36 pagesFibromyalgiaSyed Tameem Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- Report - SIDDHANT CHOUDHARY (231013056)Document17 pagesReport - SIDDHANT CHOUDHARY (231013056)Siddhant choudharyNo ratings yet
- Service Annotated BibliographyDocument6 pagesService Annotated Bibliographyapi-355966257No ratings yet
- Articles by Dr. Nata ParnesDocument19 pagesArticles by Dr. Nata ParnesWatertown Daily TimesNo ratings yet
- Vasopressor Use in Adult Patients: Nadia Ferguson-Myrthil, PharmdDocument6 pagesVasopressor Use in Adult Patients: Nadia Ferguson-Myrthil, PharmdWILLIAM RICARDO CASTAÑEDA VARGASNo ratings yet
- Third-Line Antiretroviral Therapy in Africa: Effectiveness in A Southern African Retrospective Cohort StudyDocument7 pagesThird-Line Antiretroviral Therapy in Africa: Effectiveness in A Southern African Retrospective Cohort StudyPetros TemboNo ratings yet
- Government College of Nursing JodhpurDocument7 pagesGovernment College of Nursing JodhpurNaresh JeengarNo ratings yet
- K-02 (Imunologi Dasar)Document40 pagesK-02 (Imunologi Dasar)amiksalamahNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Dysreflexia-Part OneDocument3 pagesAutonomic Dysreflexia-Part OneManuel BucurNo ratings yet
- D G Model Making Sense of Clinical Examination of The Adult Patient Hands-On GuideDocument313 pagesD G Model Making Sense of Clinical Examination of The Adult Patient Hands-On GuidevaidyamNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Postpartum ComplicationsDocument24 pagesPresentation On Postpartum ComplicationsBeulah DasariNo ratings yet
- Thyroid Gland (Mam Suba)Document2 pagesThyroid Gland (Mam Suba)Mark Vincent SahagunNo ratings yet
- Bosniak 2F Cysts - GuidelinesDocument9 pagesBosniak 2F Cysts - Guidelinesfelixsafar3243No ratings yet
- Recalls 3Document26 pagesRecalls 3Charisse CaydanNo ratings yet
- Drug Education in The PhilippinesDocument32 pagesDrug Education in The PhilippinesTrixie Ann MenesesNo ratings yet
- CV DR Ari Sami Hussain NadhimDocument5 pagesCV DR Ari Sami Hussain NadhimAri SamiNo ratings yet
- MANIFESTASI KLINIK Penyakit Jantung KoronerDocument4 pagesMANIFESTASI KLINIK Penyakit Jantung KoronerDwitya NoviariNo ratings yet
- Medgears: We Have Been Pioneers at Manufacturing, Exporting and Wholesaling A Wide Assortment of High-QualityDocument24 pagesMedgears: We Have Been Pioneers at Manufacturing, Exporting and Wholesaling A Wide Assortment of High-QualitySubhasis MallikNo ratings yet
- Stok Opname Nopember 2015-RevisiDocument146 pagesStok Opname Nopember 2015-RevisinooNo ratings yet
- Utility of Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Lymph Nodes: Dr. Ripunjaya Mohanty, Dr. Anne WilkinsonDocument6 pagesUtility of Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Lymph Nodes: Dr. Ripunjaya Mohanty, Dr. Anne WilkinsonAmanda AlmaNo ratings yet
- Checklist For Enrollment of ProvidersDocument7 pagesChecklist For Enrollment of ProvidersMaria Crayton HaliburtonNo ratings yet