Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cellular Resp
Uploaded by
truckerrr1Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cellular Resp
Uploaded by
truckerrr1Copyright:
Available Formats
Anthony Tucker Period 2 12/7/11
Video on Cellular Respiration
The first law of thermodynamics states that energy cannot be created nor can it be destroyed. It can only be released or stored. Cellular respiration is the process that releases the stored energy from food. In order for growth in living things, proteins, carbohydrates, fats, and nucleic acids must be made. The energy for the construction of these complex macromolecules is needed by an outside source. The cellular energy required is stored in food which originally derived its energy from the sun.
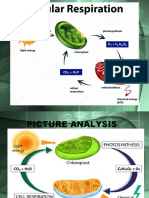
Respiration is often confused with breathing. Breathing is only a step in respiration. Cellular respiration consists of three stages. The first is the external stage: breathing movements that exchange gases between air sacs in the lungs and the bloodstream. The second is the internal stage: the exchange of gases between blood and cells. The last stage is the cellular stage which is the combination of food and oxygen to release energy. Breathing is a physical process that allows us to come into contact with gases in the air such as oxygen.
Through diffusion, food cells and oxygen travel in the blood to all the cells in the body. Cells contain organelles which help carry out the work of the cell. The mitochondria supply most of the energy needs of the cell. In nature the combination of oxygen with a substance is referred to as oxidation. A very rapid oxidation reaction causes combustion which mostly releases heat and less energy. Cellular respiration releases energy slowly so that cells can
be as efficient as possible. Cells can extract about 40% of the energy in a glucose molecule. An analogy often used is that of a car extracting energy from gasoline slowly and not in one huge explosive reaction. Even with the slow extraction of energy from gasoline, the energy release efficiency from glucose by cellular respiration supersedes it.
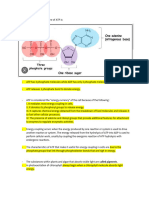
Usable energy is derived from cellular respiration in the form of a molecule called ATP. Adenosine tri phosphate powers ALL living things. The products from cellular respiration are 6 carbon dioxide molecules, 6 water molecules, and 36 ATP molecules. The number of ATP molecules sometimes varies depending on the needs of the cell. Each step in cellular respiration is controlled by enzymes. ATP provides energy by donating one phosphate group out of the three that it has to special receptors throughout the cell. It then becomes ADP which is replenished to ATP by cellular respiration.
Most living things on Earth require oxygen. Before Earth was an oxygen plenty biosphere however, organisms produced their energy from anaerobic respiration which is the release of energy in living things without oxygen. Today organisms still use anaerobic respiration in the initial stages of the respiration process. This process begins with the molecule glucose which is a product of photosynthesis. Animals can digest glucose in the form of starch, a long chain of glucose molecules. Glycolysis (another word for anaerobic respiration) splits glucose and goes through many enzymes to produce pyruvate and 2 net ATP molecules. Two ATPs are initially used and 4 ATPs are the output. More than 90% of the energy in glucose is not released in glycolysis. Most of the energy in food is released
by aerobic respiration which occurs in the mitochondria. It is much more efficient and it consists of the Citric Acid cycle and Oxidative Phosphorylation.
You might also like
- Cellular RespirationDocument10 pagesCellular RespirationXavier LecarosNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Metabolic Toxins On The Process of Cellular RespirationDocument9 pagesThe Effects of Metabolic Toxins On The Process of Cellular RespirationMar RiahNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument10 pagesRespirationapi-237593339No ratings yet
- Cellular1 2Document16 pagesCellular1 2Kaeshamaureen DresNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Activity in Chapter 4. Cellular MetabolismDocument4 pagesAssessment and Activity in Chapter 4. Cellular MetabolismArmie Rose FaldasNo ratings yet
- Pp19 Cellular RespirationDocument71 pagesPp19 Cellular Respirationu22811495No ratings yet
- Cellular - Respiration Lecture KoDocument60 pagesCellular - Respiration Lecture KoEvangelene Esquillo SanaNo ratings yet
- Eals 11abma1 MangosingDocument34 pagesEals 11abma1 MangosingAndrea Mae V. MangosingNo ratings yet
- Biology FolioDocument2 pagesBiology Folio黃將賓No ratings yet
- RespirationDocument3 pagesRespirationKhadijah HabeebahNo ratings yet
- Slide 1Document1 pageSlide 1NickTheTurtleNo ratings yet
- General Biology 101Document7 pagesGeneral Biology 101Czarina AsisNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis NcellularrespirationDocument18 pagesPhotosynthesis NcellularrespirationBobby Arguilles PaboresNo ratings yet
- Biology Class 7Document4 pagesBiology Class 7Jon Williams100% (4)
- CHBH13 - Laboratory Manual 6Document17 pagesCHBH13 - Laboratory Manual 6Ysa DienteNo ratings yet
- BIOENERGETICSDocument3 pagesBIOENERGETICSJaemsNo ratings yet
- Energy and Metabolism Energy and MetabolismDocument17 pagesEnergy and Metabolism Energy and MetabolismSebastian RodriguezNo ratings yet
- The Energy of LifeDocument22 pagesThe Energy of LifeAminul Islam Arafat 2132536642No ratings yet
- Lec 11,12 Energy of Life RMDocument9 pagesLec 11,12 Energy of Life RMEnmuskNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and CRDocument5 pagesPhotosynthesis and CRKhyla Grace DijenoNo ratings yet
- Q2 Module 5Document6 pagesQ2 Module 5joseantoniolcastro408No ratings yet
- Reviewer-In-Gen Bio 1 - Q2Document5 pagesReviewer-In-Gen Bio 1 - Q2alamagelyzaNo ratings yet
- Week 18 ModuleDocument3 pagesWeek 18 Modulerose maryNo ratings yet
- Teaching Science in Elementary GradesDocument2 pagesTeaching Science in Elementary GradesJenniferChantengcoCatacutan50% (2)
- BioDocument18 pagesBiomarcneil773No ratings yet
- Gen Bio1 ReviewerDocument4 pagesGen Bio1 ReviewerRhea SuarezNo ratings yet
- ReflectionsDocument1 pageReflectionsJovy LobarbioNo ratings yet
- Effects of Disease On AgricultureDocument6 pagesEffects of Disease On Agriculturecool joesNo ratings yet
- Measure Oxygen Uptake by RespirometerDocument17 pagesMeasure Oxygen Uptake by RespirometerTootsie100% (12)
- 3 7 Cell RespirationDocument3 pages3 7 Cell Respirationapi-296446683No ratings yet
- Lecture I - Respiration and Photosynthesis Version 1Document14 pagesLecture I - Respiration and Photosynthesis Version 1Andre NesbethNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument13 pagesCellular Respirationapi-329164492No ratings yet
- Module 12 PDFDocument13 pagesModule 12 PDFJohn Bernard VeloriaNo ratings yet
- ECOSYSTEMDocument39 pagesECOSYSTEMJessica Manawes NavorNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration NotesDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration Notescsujithan100% (1)
- Differences Between Mitochondria and ChloroplastDocument10 pagesDifferences Between Mitochondria and ChloroplastAsma Adawiyah Idris100% (1)
- Exchange Gases, Cellular RespirationDocument4 pagesExchange Gases, Cellular RespirationGISRemoteSensingNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Respiratory Process in Energy ProductionDocument13 pages7.1 Respiratory Process in Energy ProductionNor Rafidah Che YusofNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: How We Obtain Chemical Energy From FoodDocument28 pagesCellular Respiration: How We Obtain Chemical Energy From FoodJanet LarideNo ratings yet
- ATP To ADP - Energy Release: ATP Stands For Adenosine Tri-Phosphate, and Is The Energy Used by An Organism inDocument3 pagesATP To ADP - Energy Release: ATP Stands For Adenosine Tri-Phosphate, and Is The Energy Used by An Organism inlakasNo ratings yet
- Metabolic ProcessesDocument6 pagesMetabolic ProcessesMark Andrian PontanalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To RespirationDocument14 pagesIntroduction To RespirationAzneezal Ar-RashidNo ratings yet
- GCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- GN 3.3 - Cell RespirationDocument7 pagesGN 3.3 - Cell RespirationJuan CastellanosNo ratings yet
- 2.8-Cell Respiration:: Cell Respiration Is The Controlled Release of Energy From Organic Compounds To Produce ATPDocument4 pages2.8-Cell Respiration:: Cell Respiration Is The Controlled Release of Energy From Organic Compounds To Produce ATPTanvir KauraNo ratings yet
- Revision Handout 1 For Grade 12Document10 pagesRevision Handout 1 For Grade 12babaNo ratings yet
- Ange EeeeeDocument4 pagesAnge EeeeeHazel BandayNo ratings yet
- DAT Bootcamp Bio Academy: Chapter 3: Cellular EnergyDocument33 pagesDAT Bootcamp Bio Academy: Chapter 3: Cellular EnergyEmilyNo ratings yet
- Samantha Sealy 10/3/15 5 PeriodDocument2 pagesSamantha Sealy 10/3/15 5 PeriodsamanthasameNo ratings yet
- 2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103Document46 pages2.8 Cell Respiration SL: Chapter 2 Molecular Biology p.98-103PaolaNo ratings yet
- Topic I: Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeDocument70 pagesTopic I: Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeJai CataluñaNo ratings yet
- Biodas 8 (Aeman Hakim)Document19 pagesBiodas 8 (Aeman Hakim)aekimNo ratings yet
- Place Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideDocument52 pagesPlace Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideADR GARDIOLANo ratings yet
- Biology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandBiology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Year 8 Science Summary Notes For ReferenceDocument15 pagesYear 8 Science Summary Notes For ReferenceNurulAinMatAron71% (7)
- 9 1 PWPTPDFDocument19 pages9 1 PWPTPDFapi-262378640No ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration ExplanationDocument2 pagesCellular Respiration Explanationvestermail50% (2)
- EaSc 001 - Learning Check 2.2 - ABMDocument2 pagesEaSc 001 - Learning Check 2.2 - ABMColein FranleighNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisDocument33 pagesCellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisJoshua MeraNo ratings yet
- Worship Aid - May Crowning 2020Document5 pagesWorship Aid - May Crowning 2020Kevin RyanNo ratings yet
- Linic - by SlidesgoDocument84 pagesLinic - by SlidesgoKhansa MutiaraHasnaNo ratings yet
- January 2014 QP - Paper 1 Edexcel (B) Maths IGCSEDocument24 pagesJanuary 2014 QP - Paper 1 Edexcel (B) Maths IGCSEStevenstrange001 CattyNo ratings yet
- Rabbit Book PDFDocument20 pagesRabbit Book PDFMatumelo Rebecca DaemaneNo ratings yet
- Cics 400 Administration and Operations GuideDocument343 pagesCics 400 Administration and Operations GuidedafraumNo ratings yet
- JamPlay 30 Minute Guitar Pratice TemplateDocument23 pagesJamPlay 30 Minute Guitar Pratice TemplateSunkilr Sönny100% (4)
- 2400 8560 PR 8010 - A1 HSE Management PlanDocument34 pages2400 8560 PR 8010 - A1 HSE Management PlanMohd Musa HashimNo ratings yet
- Plasterboard FyrchekDocument4 pagesPlasterboard FyrchekAlex ZecevicNo ratings yet
- Play Tennis Manual PDFDocument52 pagesPlay Tennis Manual PDFAnonymous GJuRvp9A5T100% (2)
- I. Errors, Mistakes, Accuracy and Precision of Data Surveyed. A. ErrorsDocument53 pagesI. Errors, Mistakes, Accuracy and Precision of Data Surveyed. A. ErrorsJETT WAPNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument196 pagesElectricityjingcong liuNo ratings yet
- Prince Ryan B. Camarino Introduction To Philosophy of The Human PersonDocument2 pagesPrince Ryan B. Camarino Introduction To Philosophy of The Human PersonKyle Aureo Andagan RamisoNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Noc: NIC: Fluid ManagementDocument10 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Noc: NIC: Fluid ManagementSkyla FiestaNo ratings yet
- Eps 400 New Notes Dec 15-1Document47 pagesEps 400 New Notes Dec 15-1BRIAN MWANGINo ratings yet
- An1914 PDFDocument56 pagesAn1914 PDFUpama Das100% (1)
- 1600 Cal Meal Planning GuideDocument6 pages1600 Cal Meal Planning GuideAlyssa Jennings100% (2)
- Syntax Ps4Document6 pagesSyntax Ps4blue_child86% (7)
- Joy BoosterDocument2 pagesJoy BoosterAlexsandro TorezinNo ratings yet
- Technical RequirementsDocument14 pagesTechnical RequirementsLucas GuadaNo ratings yet
- Youth and Moral ValuesDocument6 pagesYouth and Moral ValuesAlka SinghNo ratings yet
- Rubber Stamp BusinessDocument4 pagesRubber Stamp BusinessvasantsunerkarNo ratings yet
- Vivekananda'S Conception of Normative Ethics and Resolution Ethical Problems in BusinessDocument8 pagesVivekananda'S Conception of Normative Ethics and Resolution Ethical Problems in BusinessYajat BhargavNo ratings yet
- Practical Econometrics Data Collection Analysis and Application 1st Edition Hilmer Test BankDocument27 pagesPractical Econometrics Data Collection Analysis and Application 1st Edition Hilmer Test Bankdavidhallwopkseimgc100% (28)
- Syllabus EM1Document2 pagesSyllabus EM1Tyler AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Computer Forensics ReportDocument7 pagesComputer Forensics ReportMatias IacobuzioNo ratings yet
- Linguistic LandscapeDocument11 pagesLinguistic LandscapeZara NurNo ratings yet
- Comparison of The EC-GMP Guide Part I With The SFDA-GMP Guideline For Chinese CompaniesDocument7 pagesComparison of The EC-GMP Guide Part I With The SFDA-GMP Guideline For Chinese Companiesrambabukomati472No ratings yet
- Rawtani 2019Document9 pagesRawtani 2019CutPutriAuliaNo ratings yet
- Calgary Project Consultants, DubaiDocument18 pagesCalgary Project Consultants, DubaiManish GuptaNo ratings yet
- Mooka Panchsati Arya SatakamDocument18 pagesMooka Panchsati Arya SatakamPrasad Raviprolu100% (1)