Professional Documents
Culture Documents
M&E Assignment 3
Uploaded by
han0701Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
M&E Assignment 3
Uploaded by
han0701Copyright:
Available Formats
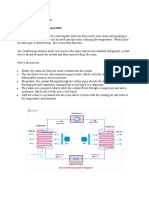
Assignment3: Recirculating Air Conditioning Unit
1.0
INTRODUCTION
1.1
Air Conditioning
Air Conditioning, which may be described as the control of the atmosphere so that a desired temperature, humidity, distribution and movement are achieved, is a rapidly expanding activity throughout the world. Obvious applications for air conditioning are homes, hospitals, public meeting places, mines, shops, offices, factories, land, air and sea transport, but there are numerous other applications in which human comfort is not the prime consideration. These include textile and printing industries, computers, laboratories, photographic and pharmaceutical industries, manufacture, inspection and storage of sensitive equipment, horticulture, animal husbandry, food storage and many others.
1.2
Recirculating Air Conditioning
The Recirculating Air Conditioning Trainer unit is related to the Air Conditioning Laboratory Unit and enables even more experimentation as it features recirculation of the air stream. This unit provides for the study of a self-contained air conditioning system, as you would find within a typical building. Air flow may be introduced from outside or it may be recirculated for recycling within the system. Thus it is able to simulate open loop or closed loop systems. The student may simulate different types of environments and conditions within a circuit or a room type situation.
1.3
Types of Air Conditioning
1.3.1
Portable Air Conditioning If youve ever lived in a small house or an apartment building, youve
probably used a PTAC portable terminal air conditioner. Portable air conditioners are typically noisier and less efficient than central air conditioners and cool a much smaller area than central air conditioners. That said, if you have limited space or a limited budget, you wont do much better than a portable air conditioner.
Assignment3: Recirculating Air Conditioning Unit
1.3.2 Wall/Window Air Conditioning
A wall/window model is usually installed in a window or external wall, and can cool rooms and open-plan areas of up to 50 square meters. While smaller units can be plugged into a normal power point, larger ones may require additional wiring.
1.3.3
Central Air Conditioners Central air conditioners can be broken down into two different types split
system and packaged air conditioners.
1.3.3.1
Split System Air Conditioners
The more common of the two types of central air conditioners, split system air conditioners have the compressor / condenser housed in a unit outdoors and the evaporator indoors. The primary benefit of split system air conditioners is that they keep the noisy part outside! Split system air conditioners connect into your existing ductwork, cooling your home evenly and quietly. 1.3.3.2 Packaged Central Air Conditioners
less common in homes than split system air conditioners, packaged air conditioners, as the name suggests, package the two components in a single unit, usually mounted on the roof or, occasionally, on a wall. If youve ever seen an air conditioning unit on the top of a building, youve seen a packaged central air conditioner. 1.3.4 Ductless Air Conditioners
Air conditioners that you can hook up throughout your home without installing ductwork. Ductless air conditioners can be thought of as a combination of split system central air conditioners and portable air conditioners basically you have an outdoor unit that connects to multiple small indoor units connected via smaller conduits instead of ducts.
Assignment3: Recirculating Air Conditioning Unit
1.3.5 Evaporation Coolers
Also called swamp coolers, evaporation coolers pull hot air through damp pads, evaporating the water in the pads. Theyre primarily used in places like Arizona where the dry heat is almost unbearable. Once the air is pulled through the pad and cooled, it is circulated through the house by means of a large blower fan. It might not seem like it, but swamp coolers can bring the temperature of a house down by as much as 30 F. 1.3.6 Inverter Technology
With conventional air conditioners, the compressor is either on (working to 100% capacity) or off. Inverters can vary the compressor speed and maintain the set temperature within a narrow range. Manufacturers claim inverter models are more efficient and reduce running costs. 1.3.7 Cooling-only/Reverse Cycle
Reverse-cycle models only cost a bit more than cooling-only models, but you can also use them for heating in winter. While the purchase and installation costs can be high, reverse-cycle air conditioners are among the cheapest forms of heating to run. They cause less carbon dioxide to be produced in power plants burning fossil fuel than other kinds of electric heater
Assignment3: Recirculating Air Conditioning Unit
2.0 OBJECTIVES Familiarization with an air conditioning system and its components Investigating the prime factors that can be controlled in a typical air conditioning system. 3. To provide data for which a psychometric chart be plotted, heat transfer be explored, recirculation and adiabatic mixing be investigated, condensate be measured and the effects of cooling and heating loads be observed. 4. To study the process of humidification, pre-heating, and cooling and dehumidification. 5. To investigate and calculate the energy and discrepancy of heat transfer in the preheater process.
1. 2.
Assignment3: Recirculating Air Conditioning Unit
3.0 APPARATUS/EQUIPMENT
1. A771 Recirculating Air Conditioning Unit 2. Compressor 3. Condenser 4. Expansion Valve 5. Evaporator
Assignment3: Recirculating Air Conditioning Unit
4.0 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
Condenser
A condenser is a device or unit used to condense a substance from gas to liquid. They are basically heat exchangers which have various designs and come in many sizes ranging from rather small (hand-held) to very large industrial-scale units used in plant processes. A condenser unit used in central air conditioning systems typically has a heat exchanger section to cool down and condense incoming refrigerant vapor into liquid, a compressor to raise the pressure of the refrigerant and move it along, and a fan for blowing outside air through the heat exchanger section to cool the refrigerant inside. A typical configuration of such a condenser unit is as follows: The heat exchanger section wraps around the sides of the unit with the compressor inside. In this heat exchanger section, the refrigerant goes through multiple tube passes, which are surrounded by heat transfer fins through which cooling air can move from outside to inside the unit. There is a motorized fan inside the condenser unit near the top, which is covered by some grating to keep any objects from accidentally falling inside on the fan. The fan is used to blow the outside cooling air in through the heat exchange section at the sides and out the top through the grating. These condenser units are located on the outside of the building they are trying to cool, with tubing between the unit and building, one for vapor refrigerant entering and another for liquid refrigerant leaving the unit. Of course, an electric power supply is needed for the compressor and fan inside the unit.
Assignment3: Recirculating Air Conditioning Unit
Compressor
Air conditioner compressors are the heart of the system because they pump the refrigerant through the system in a closed cycle in much the same way as the heart pumps blood through the bodys system. The other main function of the air conditioner compressor is to compress low pressure refrigerant gas from the evaporator converting it to a hot, high pressure gas. In doing this the compressor also removes vapor from the evaporator to help it maintain a constant temperature. Generally,refrigerant enters an air conditioner compressor as a low-pressure gas and decreases in size so the fluid molecules will compact and increase in energy and temperature. The refrigerant then leaves the compressor and enters the condenser, which cools it and changes it to a high-pressure liquid to cool the air that enters your home or car. The compressor is needed to pumping refrigerant. There are pistons inside a compressor motor, which move up and down. Refrigerant is drawn into the compressor on the down strokes and compresses on the up strokes.
Besides that, compressor also needed to adjust temperature. Compressing a gas causes its temperature to rise. The refrigerant enters an air conditioner compressor at a low temperature and moves to the exiting side of the compressor at a higher temperature before it enters the condenser. A compressor removes vapor from the evaporator, which will draw the humidity out of the air before it blows.
Assignment3: Recirculating Air Conditioning Unit
Expansion valve
The expansion device is one of major component in air conditioner units. It is also known as meter devices. Air conditioner expansion valve is the divided point between the low side and the high side of the air conditioner units. The meter device is located indoor (air handler) units with the evaporator coils. Its small and hard to see, unless you open the evaporator compartment. The function of expansion valve to removes pressure from the liquid refrigerant to allow expansion or change of state from a liquid to a vapor in the evaporator. The high-pressure liquid refrigerant entering the expansion valve is quite warm. This may be verified by feeling the liquid line at its connection to the expansion valve. The liquid refrigerant leaving the expansion valve is quite cold. The orifice within the valve does not remove heat, but only reduces pressure. Heat molecules contained in the liquid refrigerant are thus allowed to spread as the refrigerant moves out of the orifice. Under a greatly reduced pressure the liquid refrigerant is at its coldest as it leaves the expansion valve and enters the evaporator. Pressures at the inlet and outlet of the expansion valve will closely approximate gauge pressures at the inlet and outlet of the compressor in most systems. The similarity of pressures is caused by the closeness of the components to each other. The slight variation in pressure readings of a very few pounds is due to resistance, causing a pressure drop in the lines and coils of the evaporator and condenser.
Assignment3: Recirculating Air Conditioning Unit
Evaporator
Air conditioning evaporator works by absorb heat from the area (medium) that need to be cooled. It does that by maintaining the evaporator coil at low temperature and pressure than the surrounding air. Since, the AC evaporator coil contains refrigerant that absorbs heat from the surrounding air, the refrigerant temperature must be lower than the air. The expansion device provides a pressure reduces between the high side and the low side of the system, the saturation temperature of the refrigerant entering the air conditioning evaporator is lower than the medium to be cooled. One of the characteristic of a ac refrigerant is that as the pressure is reduced the boiling point is also reduced. Therefore, as the pressure is reduced through the expansion device so is the point at which it will boil and become a vapor. As the warm air from the space passes over the evaporator coil, it gives up its heat to the lower temperature liquid/vapor mixture passing through the evaporator. As the liquid refrigerant absorbs this heat it boils changing from the liquid state to the vapor state. The amount of heat the air conditioner evaporator absorbs must equal the amount of heat it lost For instance, if the air conditioning evaporator gives up 100 Btus of heat to the surrounding hot air, then the refrigerant within the air conditioning evaporator coil must gain 100 Btus of heat. The amount of liquid entering the evaporator must be enough, so by the time it reaches the end of the evaporator. It will be completely boiled to the vapor state.There must be enough air flows across the AC evaporator coil to provides heat to the refrigerant in the evaporator coil. This is just a safety way to ensure the air conditioner compressor doesnt have the liquid refrigerant entering it.
Assignment3: Recirculating Air Conditioning Unit
5.0
CONCLUSION
As a conclusion, the Recirculating Air conditioning unit may used to demonstrate and evaluate most of the processes found in practical air conditioning plant, such as heating, cooling, humidification, dehumidification air stream. Sometime two or more of these process are needed to bring air to desired temperature and humidity level. Various air conditioning processes appear as horizontal line on this chart since moisture content of the air remains constant during this processes. Air is commonly heated and humidified in winter and cooled and dehumidified in summer. . 6.0 REFERENCES
1. Hilton
P.A,
(1994),
Experimental
operating
and
maintenance
manual
(Reciculating air conditioning unit A771), P.A Hilton limited Hampshire, England. 2. SOLDEQ, Air Conditioning Laboratory Unit, Equipment For Engineering Education & Research Solution Engineering Holdings Berhad,Puchong. Selangor Darul Ehsan. 3. http://oee.nrcan.gc.ca/equipment/cooling-ventilation/5503 4. http://www.brighthub.com/engineering/mechanical/articles/897.aspx 5. http://www.aelag.com.au/air-conditioning-types 6. http://www.michaelbonsbyhvac.com/blog/types-of-air-conditioners/
10
Assignment3: Recirculating Air Conditioning Unit
7.0
APPENDIXS
Figure1
Figure2
Figure3
Figure4
11
Assignment3: Recirculating Air Conditioning Unit
Figure5
Figure6
12
You might also like
- Building Services - Iii: 3 Year BS - Semester 1Document32 pagesBuilding Services - Iii: 3 Year BS - Semester 1TaanayaNo ratings yet
- OJT Outputs: Raphael Justine D. Hismana Bsme 5Document27 pagesOJT Outputs: Raphael Justine D. Hismana Bsme 5Khaster NavarraNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument10 pagesAbstractabushasolomon75% (4)
- Air Conditioning SystemDocument12 pagesAir Conditioning SystemShahanajshanu100% (1)
- Airconditioning and Ventilation SystemsDocument6 pagesAirconditioning and Ventilation SystemsJohn Kenneth Santiago PaulinoNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Report.Document15 pagesAir Conditioning Report.Ethan XavierNo ratings yet
- Mapua Institute of Technolog1Document15 pagesMapua Institute of Technolog1Ian KasaiNo ratings yet
- UNIT I - Air ConditionDocument62 pagesUNIT I - Air ConditionNeha JojanNo ratings yet
- Types of Air Conditioning UnitsDocument10 pagesTypes of Air Conditioning Unitssnowgalvez44No ratings yet
- HVAC Equipment Guide for Heating and Cooling SystemsDocument16 pagesHVAC Equipment Guide for Heating and Cooling SystemsRahul Prajapati100% (1)
- Aircon System and Fire Protection SystemDocument31 pagesAircon System and Fire Protection SystemReijen Canary S TierraNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning SystemDocument7 pagesAir Conditioning SystemT SRNo ratings yet
- Script:-.Air Condition ScriptDocument11 pagesScript:-.Air Condition Scriptaimri_cochinNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Basics: Air-Source, Split SystemsDocument4 pagesAir Conditioning Basics: Air-Source, Split SystemsAhmad MujahidNo ratings yet
- 141 Lecture 66Document14 pages141 Lecture 66kimNo ratings yet
- Types of Air Conditioning: Qus 3206 / MDM Nurul AiniDocument56 pagesTypes of Air Conditioning: Qus 3206 / MDM Nurul AiniMalik MussaNo ratings yet
- Airconditioning ProcessDocument5 pagesAirconditioning ProcessMark Anthony SibayanNo ratings yet
- Split Air Conditioner Learning SimulationDocument19 pagesSplit Air Conditioner Learning SimulationkablasNo ratings yet
- Architectural Building Services: Vedita Bhat Roll No-03Document8 pagesArchitectural Building Services: Vedita Bhat Roll No-03Vedita Bhat100% (1)
- Air Conditioning SystemDocument15 pagesAir Conditioning SystemSamer Zebare100% (1)
- ECM216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 2.2 Air ConditioningDocument8 pagesECM216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 2.2 Air ConditioningAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZI100% (3)
- Air Conditioning SystemDocument7 pagesAir Conditioning SystemPapri MahataNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning PDFDocument133 pagesAir Conditioning PDFعبدالله عمر67% (3)
- Hvac DesignDocument84 pagesHvac DesignShine Kumar100% (4)
- Rac Lab ReportDocument5 pagesRac Lab ReportEliyas AdamuNo ratings yet
- Carrier Split SystemDocument12 pagesCarrier Split SystemabuMalakNo ratings yet
- Split AC Guide: How They Work & System ComponentsDocument8 pagesSplit AC Guide: How They Work & System ComponentssadNo ratings yet
- Air-Conditioning SystemDocument54 pagesAir-Conditioning Systemhasrul_nizam100% (6)
- Screw Type of CompressorDocument9 pagesScrew Type of CompressorAnish KumarNo ratings yet
- R&AC Lab ManualDocument29 pagesR&AC Lab ManualPARAMESHNo ratings yet
- Study On Air-Conditioning and Its ProcessDocument5 pagesStudy On Air-Conditioning and Its Processsdeep1990No ratings yet
- Selection Tips For HVAC SystemsDocument41 pagesSelection Tips For HVAC SystemsImtiaz Ahmed100% (1)
- Air ConditionerDocument5 pagesAir ConditionerArun Pravin APNo ratings yet
- Parts of Air ConditionerDocument6 pagesParts of Air ConditionerAntonio Lara MuñozNo ratings yet
- Principle of VRFDocument5 pagesPrinciple of VRFghazanfarhayat456No ratings yet
- Window Air Conditioner Literature ReviewDocument27 pagesWindow Air Conditioner Literature ReviewMohd SalmanNo ratings yet
- Heat Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC)Document46 pagesHeat Ventilation and Air Conditioning (HVAC)Sagar GoyalNo ratings yet
- Hvac Notes: Vapor-Compression Absorption Refrigeration Cycle Heat ExchangerDocument36 pagesHvac Notes: Vapor-Compression Absorption Refrigeration Cycle Heat ExchangerMohd Tarique AnwarNo ratings yet
- On Air ConditioningDocument26 pagesOn Air ConditioningTej KalyanNo ratings yet
- Air - ConditioningDocument4 pagesAir - ConditioningDinesh ChahalNo ratings yet
- An Air Conditioner Has 5 Main Parts:: 1. RefrigerantDocument11 pagesAn Air Conditioner Has 5 Main Parts:: 1. RefrigerantRitu SinghNo ratings yet
- UCA - BST.F.2019.18 (Assingment 01)Document11 pagesUCA - BST.F.2019.18 (Assingment 01)shehan harshithaNo ratings yet
- Basics of HVAC SystemDocument9 pagesBasics of HVAC SystemDevarya ChhibberNo ratings yet
- Air ConditioningDocument57 pagesAir Conditioningnim_gourav1997No ratings yet
- Central Air Conditioning PlantsDocument8 pagesCentral Air Conditioning PlantsNilesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Central Air ConditioningDocument14 pagesCentral Air ConditioningHashim MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Experiment 11-Hvac For Small HouseDocument9 pagesExperiment 11-Hvac For Small Houseengrjayasis20No ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Types and Working PrincipleDocument9 pagesAir Conditioning Types and Working PrincipleAshikur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning System NoteDocument4 pagesAir Conditioning System NoteSourav KumarNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocument7 pagesRefrigeration and Air ConditioningManjunatha EikilaNo ratings yet
- Types of Air Conditioning SystemDocument5 pagesTypes of Air Conditioning SystemLArry Vasquez100% (2)
- Building Service PDFDocument35 pagesBuilding Service PDFamirahNo ratings yet
- Investigatory ProjectDocument17 pagesInvestigatory ProjectIan Villavicencio83% (6)
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning 2Document33 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioning 2Christina OhNo ratings yet
- Working of Split ACDocument2 pagesWorking of Split ACNamrta KapseNo ratings yet
- Architectural Science (HVAC) Lecture 6 & 7Document32 pagesArchitectural Science (HVAC) Lecture 6 & 7ezakbelachewNo ratings yet
- TypesDocument9 pagesTypesKarlo MalenicaNo ratings yet
- HVAC System: Prepared by Amanuel Teshome Bruktawit Gebru Elshaday Getahun Emran Bahredin Ephrem HailuDocument57 pagesHVAC System: Prepared by Amanuel Teshome Bruktawit Gebru Elshaday Getahun Emran Bahredin Ephrem HailuEphrem HailuNo ratings yet
- Oral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseFrom EverandOral and Practical Review: Reflections on the Part 147 CourseNo ratings yet
- Temperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemFrom EverandTemperature and Humidity Independent Control (THIC) of Air-conditioning SystemNo ratings yet
- HVACPow Den 08 ADocument64 pagesHVACPow Den 08 AEric MagnayeNo ratings yet
- LOAD CALCULATION FORM BLAST FREEZERDocument4 pagesLOAD CALCULATION FORM BLAST FREEZERKarthik HegdeNo ratings yet
- TestDocument1 pageTestPhilip ArpiaNo ratings yet
- RESUME For Mechanical Engineer MSC PMP CSEDocument3 pagesRESUME For Mechanical Engineer MSC PMP CSEmakahlehNo ratings yet
- Wall Mounted Air Conditioners with Long-Reach Airflow and Powerful CoolingDocument7 pagesWall Mounted Air Conditioners with Long-Reach Airflow and Powerful CoolingYaser ShabasyNo ratings yet
- HVAC Brochure PDFDocument16 pagesHVAC Brochure PDFCarlos Benavides AlvarezNo ratings yet
- M007 Rak MHV DWG Ucst010 CL 00100Document1 pageM007 Rak MHV DWG Ucst010 CL 00100Adnan Attish0% (1)
- VRMP Projects - #973 Hgu Reformer Insulation Monthly Completion Plan Project: Reformer Works - HGU-EPCC 6, HPCL, VIZAGDocument1 pageVRMP Projects - #973 Hgu Reformer Insulation Monthly Completion Plan Project: Reformer Works - HGU-EPCC 6, HPCL, VIZAGsusantaNo ratings yet
- Smacna Hvac Duct Construction Standards ScribdDocument2 pagesSmacna Hvac Duct Construction Standards ScribdMuhamad Richard Menarizki0% (2)
- Appendix 1 Section 3 AS1668.2 2002Document5 pagesAppendix 1 Section 3 AS1668.2 2002bobNo ratings yet
- Humidity ControlDocument22 pagesHumidity ControlkkkhattabbbNo ratings yet
- Calculate payback period for water vs air cooled screw chillersDocument1 pageCalculate payback period for water vs air cooled screw chillersAVINo ratings yet
- Data Sheet Unit ENEGERNCE Info LCH 20-25-30 Tons ENGDocument80 pagesData Sheet Unit ENEGERNCE Info LCH 20-25-30 Tons ENGAnonymous qg0hpB2xNUNo ratings yet
- Gambar Instalasi HeatpumpDocument1 pageGambar Instalasi HeatpumpFajarnurjamanNo ratings yet
- Joule ThomsonDocument10 pagesJoule Thomsonanoopkmr18120% (1)
- Pinch Technology: by S. RajagopalDocument28 pagesPinch Technology: by S. RajagopalTieu KakaNo ratings yet
- Cassette AC Catalogue - 1517298783 PDFDocument39 pagesCassette AC Catalogue - 1517298783 PDFArun Kumar PNo ratings yet
- ASHRAE RTS MethodDocument49 pagesASHRAE RTS MethodCameron Braun67% (3)
- SIMATIC For Industrial HVACDocument8 pagesSIMATIC For Industrial HVACaudithanNo ratings yet
- LG ThermaV Fault Codes UKDocument20 pagesLG ThermaV Fault Codes UKSesko123100% (1)
- ASHRAE Chart PDFDocument2 pagesASHRAE Chart PDFpatricio-1703No ratings yet
- Absorption Chiller GuidelineDocument97 pagesAbsorption Chiller Guidelineeng_badawy20044942100% (3)
- Exp. 2 Heat Transfer Study On Shell and Tube Heat ExchangerDocument5 pagesExp. 2 Heat Transfer Study On Shell and Tube Heat ExchangerElaine PuiNo ratings yet
- VCRS RacDocument15 pagesVCRS RacmonilNo ratings yet
- PsDocument5 pagesPsjaneeka_rNo ratings yet
- 2015 Volvo S60 2.0L Eng VIN 26 T5Document106 pages2015 Volvo S60 2.0L Eng VIN 26 T5Data TécnicaNo ratings yet
- Ariston Thermo Company Profile 2015 ENGDocument38 pagesAriston Thermo Company Profile 2015 ENGrealll0% (1)
- What Is Hermetically Sealed CompressorDocument2 pagesWhat Is Hermetically Sealed CompressorKaustubh PotnisNo ratings yet
- TES Calculation 1Document19 pagesTES Calculation 1AnamolNo ratings yet
- Discussion: The Flow Meter That Were Used in The Refrigeration Cycle Was Not Functioning When We WereDocument2 pagesDiscussion: The Flow Meter That Were Used in The Refrigeration Cycle Was Not Functioning When We WereSuhan SuharezNo ratings yet