Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Customs in India Nature & Types
Uploaded by
Saagar HingoraniOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Customs in India Nature & Types
Uploaded by
Saagar HingoraniCopyright:
Available Formats
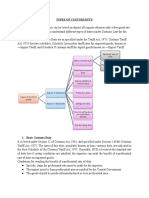
1. The Customs Act, 1962: The Customs Act.
1962 is the basic Act for levy and collection of customs duty in India. It contains various provisions relating to imports and exports of goods and merchandize as well as baggage of persons arriving in India. The main purpose of Customs Act, 1962 is the prevention of illegal imports and exports of goods. 2. The Customs Tariff Act, 1975: The Customs Duty is levied on goods imported or exported from India at the rates specified under the Customs Tariff Act, 1975.The Act contains two schedules - Schedule 1 gives classification and rate of duties for imports, while schedule 2 gives classification and rates of duties for exports Nature of Custom Duty: The levy of duty on imports and exports is subject matter of Union and the parliament derives power to make laws related to the duties of customs. The Customs Act, 1962 was enacted by the Parliament. Duties of customs shall be levied at such rates as may be specified Under the Customs Tariff Act, 1975 or any other law for the time being in force, on goods imported into or exported from India. Goods become liable to duty if there is import into and export from India. Type of customs duties: 1. Basic Customs Duty All goods imported into India are chargeable to a duty under Customs Act, 1962 .The rates of this duty, popularly known as basic customs duty. 2. Additional (Countervailing) Duty of Customs This countervailing duty is leviable as additional duty on goods imported into the country and the rate structure of this duty is equal to the excise duty on like articles produced in India. 3. Cesses Cesses are leviable on some specified articles of exports like coffee, coir, lac, mica, tobacco (unmanufactured), marine products cashew kernels, black pepper, cardamom, iron ore, oil cakes and meals, animal feed and turmeric. These cesses are collected as parts of Customs Duties. 4. Special Additional Duty of Customs 5. Anti Dumping Duty Often, large manufacturer from abroad may export goods at very low prices compared to prices in his domestic market. Such dumping may be with intention to cripple domestic industry or to dispose of their excess stock. This is called dumping'. In order to avoid such dumping, Anti Dumping Duty was levied. 6. Protective Duties This duty may be levied if Tariff Commission is of the opinion that the import of certain goods is causing injury to the interest of the Indian industry. 7. Export Duties
Goods exported from India are chargeable to export duty and the rate at which the duty is levied are given in the customs tariff act,1975 8. Duty on Bounty fed Article The Central Government may impose additional import duty in case a foreign country subsidizes its exporters for exporting goods to India. It would be equal to the amount of such subsidy or bounty.
You might also like
- Executive SummaryDocument1 pageExecutive SummaryJoseph Hernandez-Ramirez Bañados-Alinsod100% (1)
- Import and Export Markets in IndiaDocument21 pagesImport and Export Markets in IndiaAnant Bajaj50% (2)
- Exempted Income Under Section 10Document21 pagesExempted Income Under Section 10Vaishali SharmaNo ratings yet
- Tariff and Non-Tariff BarriersDocument41 pagesTariff and Non-Tariff Barriersjagdish91100% (1)
- CS Executive Notes For Factories Act 1948Document41 pagesCS Executive Notes For Factories Act 1948Cma SankaraiahNo ratings yet
- Income TaxDocument60 pagesIncome TaxAnshu LalitNo ratings yet
- Customs ActDocument24 pagesCustoms ActSoujanya NagarajaNo ratings yet
- What Is The Meaning of Customs Duty in India and Its TypesDocument35 pagesWhat Is The Meaning of Customs Duty in India and Its Typesrohit singh100% (3)
- A Study of Five Heads of Income Tax - MaheshDocument46 pagesA Study of Five Heads of Income Tax - MaheshNikita Salve100% (3)
- Taxation Project Sem VDocument21 pagesTaxation Project Sem VSara Parveen50% (2)
- Types of Custom DutyDocument3 pagesTypes of Custom DutyKarina ManafNo ratings yet
- A Synopsis On Impact and Challenges of GST in IndiaDocument8 pagesA Synopsis On Impact and Challenges of GST in IndiaPrince RamananNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On Direct TaxDocument52 pagesA Project Report On Direct Taxrani26oct72% (18)
- The Sick Unit & Case Study NICCO BATTERIESDocument18 pagesThe Sick Unit & Case Study NICCO BATTERIESabhinav75% (4)
- Advance TaxDocument11 pagesAdvance TaxAdv Aastha MakkarNo ratings yet
- BoDocument22 pagesBomonik50% (2)
- Economic Project On Banking Regulation Act 1949Document45 pagesEconomic Project On Banking Regulation Act 1949ezekielNo ratings yet
- Advance Payment of TaxDocument4 pagesAdvance Payment of Taxparag03No ratings yet
- Income Tax ProjectDocument17 pagesIncome Tax ProjectRajeev RajNo ratings yet
- Social Security of WorkmenDocument10 pagesSocial Security of WorkmenPalak JoshiNo ratings yet
- Entry and Regulation of Foreign Banks in IndiaDocument26 pagesEntry and Regulation of Foreign Banks in IndiaSuvedhya ReddyNo ratings yet
- Income Tax ProjectDocument22 pagesIncome Tax ProjectGeetanjali KashyapNo ratings yet
- Impact of GST On Indian Economy PDFDocument9 pagesImpact of GST On Indian Economy PDFBinod Kumar PadhiNo ratings yet
- TAX PROJECT - ADITYA PRATAP SINGH - Concept of Charge in Income Tax ACTDocument15 pagesTAX PROJECT - ADITYA PRATAP SINGH - Concept of Charge in Income Tax ACTMayank KumarNo ratings yet
- Income From SalaryDocument66 pagesIncome From SalaryShamika LloydNo ratings yet
- A Dissertation Report Titled "A Study On Examining Impact of GST On Various Sectors "Document64 pagesA Dissertation Report Titled "A Study On Examining Impact of GST On Various Sectors "shiv mehraNo ratings yet
- Banking Systems in IndiaDocument25 pagesBanking Systems in IndiaMandira PriyaNo ratings yet
- Rights and Obligations of Banker and CustomerDocument12 pagesRights and Obligations of Banker and Customerbeena antu100% (1)
- Summer Internship ReportDocument47 pagesSummer Internship ReportBijal Mehta43% (7)
- GST PPT TaxguruDocument30 pagesGST PPT Taxguru50raj506019No ratings yet
- Tax Capital Gain Mcom Project of 31 OagesDocument33 pagesTax Capital Gain Mcom Project of 31 Oageskarthika kounder50% (6)
- Various Types of Companies Under Companies Act, 1956-11Document54 pagesVarious Types of Companies Under Companies Act, 1956-11Upneet Sethi67% (3)
- Basic Concepts: 1.1 What Is A Tax?Document31 pagesBasic Concepts: 1.1 What Is A Tax?sourav kumar rayNo ratings yet
- Nidhi STR NewDocument72 pagesNidhi STR NewSamuel DavisNo ratings yet
- Tax Planning MergerDocument4 pagesTax Planning MergerAks SinhaNo ratings yet
- 00 Income Tax Basic ConceptsDocument13 pages00 Income Tax Basic Conceptsapi-286872716No ratings yet
- Classification of Taxable Income Under Various Heads and Computation of Taxable IncomeDocument4 pagesClassification of Taxable Income Under Various Heads and Computation of Taxable IncomeAnkit Kr MishraNo ratings yet
- FdI in Banking Sector in IndiaDocument38 pagesFdI in Banking Sector in IndiaSumedhAmaneNo ratings yet
- LPGDocument11 pagesLPGRobinvarshneyNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On Taxation in IndiaDocument59 pagesA Project Report On Taxation in IndiaYash Bhagat100% (1)
- Labour Law 1Document16 pagesLabour Law 1Ritesh KumaiNo ratings yet
- Customs Notes (Introduction and Types of Duty PDFDocument16 pagesCustoms Notes (Introduction and Types of Duty PDFJayshree ShettiNo ratings yet
- Double Tax Avoidance AgreementDocument13 pagesDouble Tax Avoidance AgreementRavi SinghNo ratings yet
- Consequences of Winding Up of CompaniesDocument4 pagesConsequences of Winding Up of CompaniesKeshav MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Taxation - Business and ProfessionDocument45 pagesTaxation - Business and ProfessionSanah Bijlani67% (3)
- A Study On Impact of GST On RetailersDocument9 pagesA Study On Impact of GST On RetailersKrishna Nandhini Viji100% (1)
- Income From Other SourcesDocument7 pagesIncome From Other Sourcesshankarinadar100% (1)
- Funding of Mergers & TakeoversDocument31 pagesFunding of Mergers & TakeoversMohit MohanNo ratings yet
- Naresh Chandra Committe, PresentationDocument14 pagesNaresh Chandra Committe, Presentationrjruchirocks100% (9)
- A STUDY OF PERCEPTION OF TAXPAYERS TOWARDS NewDocument41 pagesA STUDY OF PERCEPTION OF TAXPAYERS TOWARDS NewsiddhantNo ratings yet
- Rbi Impact On Indian EconomyDocument15 pagesRbi Impact On Indian EconomyJP MusicNo ratings yet
- Doctrine of Indoor ManagementDocument14 pagesDoctrine of Indoor ManagementSudhanshu MehtaNo ratings yet
- Project Assignment: Role of Banking Instituitons in IndiaDocument31 pagesProject Assignment: Role of Banking Instituitons in IndiaYash HoraNo ratings yet
- Classification of Contract-Vikash KR Basant PPT-2Document17 pagesClassification of Contract-Vikash KR Basant PPT-2Sameer SapaligaNo ratings yet
- Article On Financial PlanningDocument16 pagesArticle On Financial PlanningShyam KumarNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION To NPADocument3 pagesINTRODUCTION To NPApradeeppinku50% (4)
- Income From Other SourcesDocument5 pagesIncome From Other SourcesGovarthanan NarasimhanNo ratings yet
- Residential Status: Project Report OnDocument6 pagesResidential Status: Project Report OnTarun Inder KaurNo ratings yet
- Depository ServicesDocument7 pagesDepository ServicesakhilNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Indian Banking SystemDocument23 pagesProject Report On Indian Banking Systemsaif aliNo ratings yet
- Final Project On Social Security and Labour Welfare in IndiaDocument42 pagesFinal Project On Social Security and Labour Welfare in IndiaswapnabharathiNo ratings yet
- Customs DutyDocument8 pagesCustoms DutyBhavana GadagNo ratings yet
- Custom Duty M.P. Stamp DutyDocument30 pagesCustom Duty M.P. Stamp Dutynousheen riyaNo ratings yet
- Custom DutyDocument2 pagesCustom DutyNawab SahabNo ratings yet
- Sales Force Management in Rural MarketingDocument5 pagesSales Force Management in Rural MarketingSaagar HingoraniNo ratings yet
- Consumer Protection ACT FinalDocument12 pagesConsumer Protection ACT FinalSaagar HingoraniNo ratings yet
- Prof. Samruddhi R. DhoteDocument20 pagesProf. Samruddhi R. DhoteSaagar HingoraniNo ratings yet
- Manual IIIDocument2 pagesManual IIISaagar HingoraniNo ratings yet
- Absenteeism 97 03Document1 pageAbsenteeism 97 03Saagar HingoraniNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Ppt-Word Introduction To ManagementDocument5 pagesUnit 1 Ppt-Word Introduction To ManagementSaagar HingoraniNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4 - PlanningDocument3 pagesUNIT 4 - PlanningSaagar HingoraniNo ratings yet
- Job AnalysisDocument17 pagesJob Analysischirjotkaurz92% (24)
- Amity MBA 4th Sem International Business AssignmentDocument3 pagesAmity MBA 4th Sem International Business AssignmentluckyNo ratings yet
- China's Teapot Refineries Face Regulatory Challenges: 26 October 2012Document3 pagesChina's Teapot Refineries Face Regulatory Challenges: 26 October 2012Bhagoo HatheyNo ratings yet
- API IDN DS2 en Excel v2 562039Document440 pagesAPI IDN DS2 en Excel v2 562039Ardilla Noor Paramashanti WirahadikusumaNo ratings yet
- MQ10 13 BDocument16 pagesMQ10 13 BCresca Cuello CastroNo ratings yet
- World: Iron Oxides and Hydroxides - Market Report. Analysis and Forecast To 2020Document8 pagesWorld: Iron Oxides and Hydroxides - Market Report. Analysis and Forecast To 2020IndexBox MarketingNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 BBB Test Review - Shared AnswersDocument8 pagesUnit 1 BBB Test Review - Shared AnswersSunya SyedNo ratings yet
- Duty Entitlement Passbook SchemeDocument13 pagesDuty Entitlement Passbook SchemeParamu NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Export Promotion and Import Substitution StrategyDocument19 pagesExport Promotion and Import Substitution StrategyTaiyaba100% (3)
- IB - Import ExportDocument12 pagesIB - Import ExportimanandNo ratings yet
- Junior Worldmark Encyclopedia of The Nations Vol 1Document296 pagesJunior Worldmark Encyclopedia of The Nations Vol 1feritNo ratings yet
- Import Policy Order English-2015-18 - 24 Oct 2016Document127 pagesImport Policy Order English-2015-18 - 24 Oct 2016Raquibul HassanNo ratings yet
- MCR 21 Jan 22Document37 pagesMCR 21 Jan 22Ivan FirmandaNo ratings yet
- The Benefits of Free TradeDocument30 pagesThe Benefits of Free TradeBiway RegalaNo ratings yet
- Bhagwati & Panagariya (1996)Document66 pagesBhagwati & Panagariya (1996)JuliánNo ratings yet
- Wine China TaxesDocument59 pagesWine China TaxesMarceloInversorNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh Final SurveyDocument103 pagesBangladesh Final Surveyjony_nsu022No ratings yet
- Prohibition On Export and ImportDocument2 pagesProhibition On Export and ImportImport Export ConsultancyNo ratings yet
- The Apparel Market Overview 2009-2014Document15 pagesThe Apparel Market Overview 2009-2014Rommel AouadNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Restrictions On Trade: Revised Version of Paper Presented at TheDocument13 pagesQuantitative Restrictions On Trade: Revised Version of Paper Presented at TheasifanisNo ratings yet
- DSE Past Paper S6 CH 24 Trade BarriersDocument3 pagesDSE Past Paper S6 CH 24 Trade BarriersSunny HuangNo ratings yet
- Importing Commercial Goods Into Canada - B3Document48 pagesImporting Commercial Goods Into Canada - B3api-522706100% (3)
- Balance of PaymentDocument4 pagesBalance of PaymentAMALA ANo ratings yet
- Unit 1: International TradeDocument5 pagesUnit 1: International Tradehh hhhNo ratings yet
- Durand - Indicators of International Competitiveness - Conceptual Aspects and EvaluationDocument51 pagesDurand - Indicators of International Competitiveness - Conceptual Aspects and EvaluationelvinsetanNo ratings yet
- International Business WORD NotesDocument11 pagesInternational Business WORD NotesShivam MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- International Business: The New Realities: Fifth EditionDocument49 pagesInternational Business: The New Realities: Fifth EditionEswari PerisamyNo ratings yet