Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Impaired Breathing Pattern
Uploaded by
Hanya Bint PotawanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Impaired Breathing Pattern
Uploaded by
Hanya Bint PotawanCopyright:
Available Formats
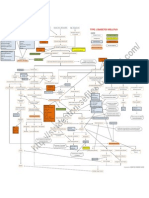
Problem Identified: Impaired breathing pattern Nursing Diagnoses: Impaired Breathing Pattern related to imbalance between oxygen supply
and demand secondary to Chronic Bronchitis Cause Analysis: Chronic Bronchitis causes depletion of oxygen delivery due to the presence of increase mucus production made by chronic inflammation thus making the oxygen demand and oxygen supply imbalance. This imbalance causes our brain to increase respiration to compensate the decrease oxygen supply. (Pathophysiology by Bullock p.551)
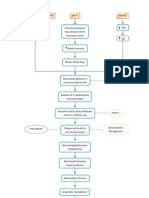
Cues Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Subjective: Paspas akong ginhawa as verbalized by the patient
STO: Within 8 hours of nursing intervention the patients will be able to identify comfortable position to ease work of breathing.
Independent: Assessed respiratory rate and depth. Note use of accessory muscles, pursed lips breathing and inability to speak or converse. Useful in evaluating the degree of respiratory distress and chronicity of the disease process
STO: After 8 hours of providing nursing interventions, the patient was able to practice techniques on how to ease the work of his breathing.
Objective: O2 sat-92% BP-140/70 LTO: RR-26 After 3 days of proving nursing PR-89 -presence of crackles all over upon auscultation - productive cough with white sputum -O2 inhalation @2L/min via nasal cannula -minimal pleural thickening ,left lower chest intervention in collaboration with administration of oxygen and patient respiratory rate will be on acceptable range from 26 cpm 18cpm.
Auscultated breath sounds, noting areas of decreased airflow and adventitious sounds.
Presence of wheezes may indicate bronchospasm or retained secretions.
LTO: After 3 days of providing nursing interventions,
Elevated head of bed and assist client to assume position to ease work of breathing.
Oxygen delivery may be improved by upright position and breathing exercises to decrease airway collapse, dyspnea, and work of breathing.
the patient became less tachypneic as evidenced by a respiratory rate of 22bpm and non-use of accessory muscles.
Provided quiet and cool environment to encouraged rest and sleep.
Rest and sleep decreases oxygen demand.
Assisted patient in doing ADL.
Decreases oxygen demand.
Collaborative: Administered O2 inhalation @2L/min via nasal cannula as indicated. Administer Pulmodual 5-6drops q 6 hours RTC. For bronchodilation to enhance oxygen delivery. To increase oxygen availability.
Reference: Pathophysiology by Bullock, Nursing Care Plan by Doenges 6th Edition
You might also like
- Nursing ManagementDocument16 pagesNursing ManagementNica Marie LumbaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care Planapi-309251523No ratings yet
- NCP BronchopneumoniaDocument8 pagesNCP BronchopneumoniaCrisantaCasliNo ratings yet
- Wk2 NCP Edited2012Document6 pagesWk2 NCP Edited2012Jessely Caling SalasNo ratings yet
- NCP PTBDocument2 pagesNCP PTBMack Jhed AnarconNo ratings yet
- NCP 1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesNCP 1 Ineffective Airway ClearanceDivine Jane PurciaNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjennelyn losantaNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance Nursing Care Planrois romaNo ratings yet
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceEmirose Fatima TagabNo ratings yet
- Tuberculous Meningitis Nursing AssessmentDocument1 pageTuberculous Meningitis Nursing AssessmentMark Adrian D. DizorNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument1 pageIneffective Airway ClearanceChristineAlaNo ratings yet
- Assessing and Treating Pneumonia Through Respiratory Monitoring and InterventionsDocument3 pagesAssessing and Treating Pneumonia Through Respiratory Monitoring and InterventionsDyanne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Acute PainDocument3 pagesAcute PainJayr ChinNo ratings yet
- ANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesANOLIN, Marc Edriann T. Nursing Care Plan Assessmen T Diagnosis Rationale Planning Interventio N Rationale EvaluationEdrianne Tui100% (2)
- HTP of AsthmaDocument1 pageHTP of AsthmaMarland Faith Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Angel Therisse B. Ramelb BSN Ii-C Nursing DiagnosisDocument2 pagesAngel Therisse B. Ramelb BSN Ii-C Nursing DiagnosisSalvaje CaballeroNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance CareplanDocument6 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance CareplanderreshaNo ratings yet
- Asthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressDocument2 pagesAsthma Nursing Care Plan NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance CompressMargarette GeresNo ratings yet
- NCP BMDocument1 pageNCP BMSourabh MehraNo ratings yet
- Difficulty Breathing Intervention and EvaluationDocument1 pageDifficulty Breathing Intervention and EvaluationJamaica Leslie NovenoNo ratings yet
- NCP Acitivity IntoleranceDocument3 pagesNCP Acitivity IntolerancegizelleNo ratings yet
- NCP TBDocument7 pagesNCP TBLorraine CilloNo ratings yet
- Breathing Pattern Assessment and InterventionDocument3 pagesBreathing Pattern Assessment and InterventionAziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Assessing and Managing Risk of AspirationDocument6 pagesAssessing and Managing Risk of AspirationaianrNo ratings yet
- Problem: Viii. Planning (Nursing Cre Plan)Document10 pagesProblem: Viii. Planning (Nursing Cre Plan)Raidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- NCP HemothoraxDocument3 pagesNCP Hemothoraxroseonabreeze0% (2)
- NCP PTBDocument6 pagesNCP PTBJay Dela VegaNo ratings yet
- Far Eastern University Nursing Care Plan Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageFar Eastern University Nursing Care Plan Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationSarah CarreteroNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearancejancel_bollaNo ratings yet
- NCP PainDocument4 pagesNCP PainMark Allison BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Scribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kDocument2 pagesScribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kKellie DNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternjuanmarcostaglishNo ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPneumoniaPia MedinaNo ratings yet
- NCP Mandibular)Document5 pagesNCP Mandibular)yellarfNo ratings yet
- NCP Copd4Document15 pagesNCP Copd4Alessa Marie Crisostomo Salazar100% (1)
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument5 pagesDecreased Cardiac Outputshuang81No ratings yet
- Elena Ocyo (Pedia - NCP)Document3 pagesElena Ocyo (Pedia - NCP)elle leliNo ratings yet
- Pain NCP BillrothDocument2 pagesPain NCP BillrotharjayNo ratings yet
- NCP #2Document4 pagesNCP #2Nutz TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Student NurseDocument2 pagesStudent NurseTAYABAN, KENNETH JAKE, Q.No ratings yet
- ASTHMADocument9 pagesASTHMAmildred alidonNo ratings yet
- REQUIREMENT IN NCP 312: IMPAIRED GAS EXCHANGEDocument4 pagesREQUIREMENT IN NCP 312: IMPAIRED GAS EXCHANGEFremelen Rose CadalinNo ratings yet
- Pleural Effusion FdarDocument1 pagePleural Effusion FdarvanessabdeveraNo ratings yet
- Applying a Tourniquet for Bleeding EmergenciesDocument3 pagesApplying a Tourniquet for Bleeding EmergenciesTom-tom LunaNo ratings yet
- Ineffectuve Breathign PatternDocument2 pagesIneffectuve Breathign PatternDiana Marie Magango FranciaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanMarielle SorianoNo ratings yet
- St. Anthony's Nursing Care Plan for Acute Chest PainDocument1 pageSt. Anthony's Nursing Care Plan for Acute Chest PainjoegeNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument5 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceEmm Estipona HaoNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance - PTBDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance - PTBIrish Eunice FelixNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument4 pagesNCP Ineffective Breathing PatternSeika SouiNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternEna Katherine CanonoNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsDocument3 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsSarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanNo ratings yet
- 4 NCP's FinalDocument9 pages4 NCP's FinalZenel Yap100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for Billy Admitted with Ear and Throat InfectionsDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan for Billy Admitted with Ear and Throat InfectionsNatukunda Dianah100% (1)
- NCP IcuDocument2 pagesNCP Icujennelyn losantaNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesImpaired Gas ExchangeHanya Bint PotawanNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway ClearanceHanya Bint PotawanNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument3 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternTrixie Anne Gamotin100% (3)
- NCP For PneumoniaDocument3 pagesNCP For PneumoniaKahMallari100% (10)
- Activity Intolerance NCPDocument6 pagesActivity Intolerance NCPDoo NahNo ratings yet
- Impaired Verbal and or Written CommunicationDocument2 pagesImpaired Verbal and or Written CommunicationHanya Bint Potawan100% (1)
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocument2 pagesImpaired Physical MobilityHanya Bint PotawanNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionDocument3 pagesIneffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionHanya Bint Potawan88% (25)
- Rhu Day 1 RequirementsDocument4 pagesRhu Day 1 RequirementsHanya Bint PotawanNo ratings yet
- Psychotropic DrugsDocument49 pagesPsychotropic DrugsHanya Bint PotawanNo ratings yet
- BSN - 4C: PresentorsDocument52 pagesBSN - 4C: PresentorsHanya Bint Potawan100% (1)
- Herbal MedicinesDocument6 pagesHerbal MedicinesHanya Bint PotawanNo ratings yet
- Rhu Day 1 RequirementsDocument4 pagesRhu Day 1 RequirementsHanya Bint PotawanNo ratings yet
- Herbal MedicinesDocument6 pagesHerbal MedicinesHanya Bint PotawanNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia UndifferentiatedDocument88 pagesSchizophrenia UndifferentiatedHanya Bint Potawan75% (4)
- Rhu Day 1 RequirementsDocument4 pagesRhu Day 1 RequirementsHanya Bint PotawanNo ratings yet
- MSHC Ordr PRC FormatDocument4 pagesMSHC Ordr PRC FormatHanya Bint PotawanNo ratings yet
- Akiya - DiphtheriaDocument52 pagesAkiya - DiphtheriaHanya Bint PotawanNo ratings yet
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument1 pageImpaired Skin IntegrityHanya Bint PotawanNo ratings yet
- Hanieyah Guro OR DR PRC FormatDocument4 pagesHanieyah Guro OR DR PRC FormatHanya Bint PotawanNo ratings yet
- Jose Rizal: 'Those Who Cannot See Where They Came From Will Never Get To Where They Are Going.'Document55 pagesJose Rizal: 'Those Who Cannot See Where They Came From Will Never Get To Where They Are Going.'Anne Ginez BilledoNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology - Type 1 Diabetes (Hanieyah Guro)Document1 pagePa Tho Physiology - Type 1 Diabetes (Hanieyah Guro)Hanya Bint PotawanNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway ClearanceHanya Bint PotawanNo ratings yet
- Dopamine HydrochlorideDocument1 pageDopamine HydrochlorideJoannes SanchezNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 pagesImpaired Gas ExchangeHanya Bint PotawanNo ratings yet
- DOH Officials Directory Execom MembersDocument2 pagesDOH Officials Directory Execom MembersHanya Bint PotawanNo ratings yet
- Angina PectorisDocument2 pagesAngina PectorisHanya Bint PotawanNo ratings yet
- Mr. Bean's diagnostic blood test resultsDocument2 pagesMr. Bean's diagnostic blood test resultsHanya Bint PotawanNo ratings yet
- IDA and AsthmaDocument5 pagesIDA and AsthmacatherineNo ratings yet
- Patterns of Unexpected In-Hospital Deaths: A Root Cause AnalysisDocument25 pagesPatterns of Unexpected In-Hospital Deaths: A Root Cause AnalysisAmira DayoubNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet for Liquid ChlorineDocument5 pagesSafety Data Sheet for Liquid ChlorineAlma PustaNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment ReviewerDocument5 pagesHealth Assessment ReviewerCUARTERO, SHERYL ANNENo ratings yet
- Resp Cheat SheetDocument4 pagesResp Cheat SheetHassaid33No ratings yet
- Lung Volumes and CapacitiesDocument16 pagesLung Volumes and CapacitiesMoses DumbuyaNo ratings yet
- Addis Ababa University Faculty of Medicine Difficult Airway ManagementDocument54 pagesAddis Ababa University Faculty of Medicine Difficult Airway ManagementagatakassaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for ELBW Baby with RDSDocument21 pagesNursing Care Plan for ELBW Baby with RDSMeena KoushalNo ratings yet
- Disturbances in OxygenationDocument10 pagesDisturbances in OxygenationjenrylNo ratings yet
- Instrucciones Uso Drager Autorrescatador 25Document28 pagesInstrucciones Uso Drager Autorrescatador 25julio_92No ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument19 pagesRespiratory SystemayuNo ratings yet
- 2019-11-09 PPT PpokDocument26 pages2019-11-09 PPT PpokAmha ViethreeNo ratings yet
- 07.03.09 Chest PhysiotherapyDocument10 pages07.03.09 Chest PhysiotherapyMuhammad Fuad MahfudNo ratings yet
- Brochure GE Versamed Ivent 201 VentilatorDocument2 pagesBrochure GE Versamed Ivent 201 Ventilatoreslam MansourNo ratings yet
- English Homework 2Document2 pagesEnglish Homework 2Teodora TanaseNo ratings yet
- Clinical Manifestations and Assessment of Respiratory Disease 5th Edition Jardins Test BankDocument36 pagesClinical Manifestations and Assessment of Respiratory Disease 5th Edition Jardins Test Bankgeincupola.06zi100% (22)
- Altitude Diving PhysiologyDocument12 pagesAltitude Diving PhysiologyKarin Gandeswari100% (1)
- Zoology Finals ReviewerDocument18 pagesZoology Finals ReviewerZian Lei MienNo ratings yet
- Care of Patient With Chest-Tube DrainageDocument60 pagesCare of Patient With Chest-Tube Drainageu0907593No ratings yet
- Characteristics of Animal Organ SystemsDocument9 pagesCharacteristics of Animal Organ SystemsMaycee ʚĭɞNo ratings yet
- Final NCP (Jannel)Document6 pagesFinal NCP (Jannel)Zed P. EstalillaNo ratings yet
- A&P Target ScoresDocument72 pagesA&P Target ScoresMercurie8592% (12)
- Chest PhysiotherapyDocument29 pagesChest PhysiotherapyHari25885No ratings yet
- Yogam Is Most Important ServiceDocument15 pagesYogam Is Most Important ServiceUdaya KumarNo ratings yet
- Managing Asthma Allergies in DC SchoolsDocument228 pagesManaging Asthma Allergies in DC SchoolsDC Asthma PartnershipNo ratings yet
- DR Firhat Esfandiari, SpPD. Diagnosis Nosokomial PneumoniaDocument41 pagesDR Firhat Esfandiari, SpPD. Diagnosis Nosokomial PneumoniaCindy TiaraNo ratings yet
- Makalah B. Inggris SputumDocument8 pagesMakalah B. Inggris SputumDian FaqihNo ratings yet
- MC031.00 Ventrain Borchure ENDocument2 pagesMC031.00 Ventrain Borchure ENBiancaPancuNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Pathophysiology - The Essentials (PULMONARY PATHOPHYSIOLOGY (WEST) ), 8th Edition (2012)Document193 pagesPulmonary Pathophysiology - The Essentials (PULMONARY PATHOPHYSIOLOGY (WEST) ), 8th Edition (2012)Mircea Vleoanga100% (1)
- Oxygen Therapy: Faisal Malmstrom, Critical Care Department SKMCDocument27 pagesOxygen Therapy: Faisal Malmstrom, Critical Care Department SKMCLingga GumelarNo ratings yet