Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Current of Electricity Tutorial 2011 Solution
Uploaded by
bandagecookieOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Current of Electricity Tutorial 2011 Solution
Uploaded by
bandagecookieCopyright:
Available Formats
9646 H2 PHYSICS Tutorial
Nanyang Junior College 1
Chapter 11
CURRENT OF ELECTRICITY
Conceptual Questions
1 What do you understand by the internal resistance an e.m.f source? What physical
evidence of internal resistance can you observe when using a dry cell?
Internal resistance is electrical resistance within an e.m.f source. It stays with the e.m.f
source. An e.m.f source with internal resistance can be replaced by an ideal source in
series with a resistor r.
When dry cell is being used for a while, it becomes hot. The heat dissipation from the cell is
a physical evidence that there is resistance inside the cell. It gives rise to power loss within
the cell.
2. Explain why it is difficult to precisely state a value for the resistance of a filament lamp.
Filament lamp does not have a fixed value for resistance. It depends on its temperature.
The higher the temperature, the higher its resistance.
3. Explain why the potential difference across the terminals of a battery is normally lower than
the batterys e.m.f. Under what conditions is the potential difference across a batterys
terminals equal to its e.m.f.?
The potential difference across the terminals of a battery is normally lower than the
batterys e.m.f because there is potential drop across the internal resistance.
Only when there is no current flow (open circuit), and when the e.m.f source is ideal (no
internal resistance), the terminal p.d will be the same as e.m.f value.
4. A customer of an electricity company argues that the company should not charge him for
electricity usage after all, any electron that enters the wires in his home leaves again
some time later and returns to the power station. Do you agree with him? Explain.
What the electricity company provides to our home are electrons with electrical potential
energy. After passing these electrons through our appliances, this energy is being used up
and it returns to the power station. What we are paying for is the electrical energy and not
the electrons. The electrons are just the energy carriers.
Application questions
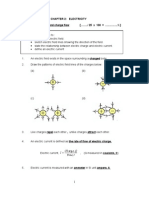
5. In a gas, conduction occurs as a result of negative particles flowing one way and positive
particles flowing in the opposite direction.
As shown above, the copper conductors of the gas carry a current of 0.28 mA. The number
of negative particles passing any point in the gas per unit time is 1.56 x 10
15
s
-l
and the
charge on each negative particle is -1.6 x 10
-19
C. Calculate
(i) the negative charge flowing past any point in the gas per second, [2.5 x 10
-4
C]
9646 H2 PHYSICS Tutorial
Nanyang Junior College 2
15 19
4
(1.56 10 )(1.6 10 )
1
2.50 10
0.25
Q
I
t
Ne
t
A
mA
=
| |
=
|
\ .
=
=
=
(ii) the positive charge flowing past any point in the gas per second, [3.0 x 10
-5
C]
Both the positive charge and negative charge carriers are responsible for the total
current in the conductor
I = I
+
+ I
-
I
+
= I I
-
= (0.280)-(0.250)
= 0.030 mA
(iii) the number of positively charged particles passing any point in the gas per second,
given that the charge on each positive particle is +3.2 x 10
-19
C. [9.4 x 10
13
]
3
13 1
19
(0.030 10 )(1.0)
9.4 10
3.20 10
Q
I
t
Q I t
N q I t
I t
N s
q
+
+
+ +
+ +
+
+
=
=
=
= = =
6. A torch bulb is rated as 2.5 V, 30 mA.
a) How much charge flows through the bulb in 1 minute when it is operating at its rated
current? [1.8 C]
3
30 10 60 1.8 Q It C
= = =
b) At what rate is electrical energy dissipated in the lamp when it is operating at its rated
voltage and current? [0.075 W]
Rate of electrical energy dissipation = P = VI = 2.5 x 30 x 10
-3
= 0.075 W
7. A car headlamp is marked 12 V, 72 W. It is switched on for a 20 minute journey. Calculate
a) the current in the lamp [6.0 A]
72
6.0
12
P
I A
V
= = =
9646 H2 PHYSICS Tutorial
Nanyang Junior College 3
b) the charge which passes through the lamp during the journey [7.2 x 10
3
C]
Q = I t = 6.0 x 20 x 60 = 7.2 x 10
3
C
c) the energy supplied to the lamp during the journey [8.6 x 10
4
J]
Energy = P x t = 72 x 20 x 60 = 8.6 x 10
4
J
d) the working resistance of the lamp [2.0 ]
12
2.0
6.0
V
R
I
= = = O
8. Jump leads may be used for starting the engine of one car using the battery of another car.
One such set of leads is 4.0 m long, and consists of copper cables with a cross-sectional
area of 13.6 mm
2
a) What is the voltage drop along the length of one of these cables when it is carrying a
current of 100 A? (Take the resistivity of copper as 1.7 x 10
-8
m) [0.50 V]
8
3
3 2
1.7 x 10 4.0
5.0 10
13.6 (10 )
l
R
A
= = = O
V = R I =
3
(5.0 10 ) 100 0.50V
=
b) In practice, such cables are made of many strands of thin copper wires twisted
together rather than a single strand of thicker wire. What is the advantage of this?
The advantage of twisting together many wires rather than a single strand of thicker
wire is that it allows the cable to be bent and it is better for storage purpose.
9. A thin film resistor in solid state circuit has a thickness of 1.0 m and is made of nichrome of
resistivity 1.0 x 10
-6
O m.
Calculate the resistance available between opposite edges of a 1.0 mm
2
area of film
(a) if it is square shaped [1.0 O]
The resistance between edges P and Q is
6 3)
6 3
10 (1.0 10
(1.0 10 1.0 10 )
1.0
R
A
=
=
= O
l
9646 H2 PHYSICS Tutorial
Nanyang Junior College 4
(b) if it is rectangular 100 times as long as it is wide. [100 O]
10. A generator supplies a fixed power to an electrical installation by power lines of resistance R.
a) Show that the power lost as heat in the cables is proportional to
2
1
V
, where V is the
potential difference at the generator output.
P
generated
= V I => (1)
generated
P
I
V
=
P
loss in cable =
2 2 2
1
( ) [( ) ]
generated
generated
P
I R R P R
V V
= =
Where Power generated and R is a constant. power lost as heat in the cables is
proportional to
2
1
V
b) This result suggests that power losses can be reduced indefinitely by stepping up the
transmission voltage to a very high value (eg.100 GV). Discuss briefly whether this is
practicable.
It is not practical because if the potential difference between the transmission cable
and the ground is too large (>3 x 10
6
V m
-1
). Air which is an excellent electrical insulator
normally will experience electrical breakdown and conduct electricity.
An example of air that conducts electricity is during lightning, it happens when the
potential difference between the cloud and the ground is too large.
11. An electric kettle is rated at 2.0 kW when operating on a 240 V supply. What power will the
kettle absorb if the supply is reduced to 220 V? [1.7 x 10
2
W]
2
2
2
3
(240)
28.8
2.0 10
V
P
R
V
R
P
=
=
= = O
The resistance of the kettle remains constant though the supply is reduced.
2
2
'
'
(220)
1680 1.68 1.7
28.8
V
P
R
W kW kW
=
= = = ~
100 x
The resistance between the edges
P and Q is
6
6
10 (100 )
(1.0 10 )
100
R
A
x
x
= O
l
9646 H2 PHYSICS Tutorial
Nanyang Junior College 5
12. Give three examples of electrical components in which the current is not directly
proportional to applied potential difference. For each component, sketch graph showing the
I-V relationship and explain the physical meaning relating to the shape of the graph.
Refer to page 8 and 9 of lecture notes. State the three components: the semiconductor
diode, the filament lamp and the thermistor.
13. A light bulb of unknown resistance is connected across a 12 V cell with internal resistance
5.0 O. The current in the circuit is 0.62 A. Find
(i) the resistance of the light bulb, [14 ]
V
R
= E - Ir
= 12 (5.0)(0.62) = 8.9 V
R =
8.9
14.4 14
0.62
R
V
I
= = O ~ O
(ii) the power output from the bulb, and [5.5 W]
P
bulb
= I
2
R = (0.62)
2
(14.4) = 5.5 W
(iii) the power delivered by the cell. [7.4 W]
P
cell
= VI = (12)(0.62) = 7.4 W
14. A battery is known to have an e.m.f. of 5.00 V but when a certain voltmeter is connected to
it, the reading is 4.90 V. Given that the battery delivers a current of 0.400 A when
connected to a resistor of 12.0 O. What is the resistance of the voltmeter? [24.5 ]
circuit 1 circuit 2
From circuit 1, E Ir = V
voltmeter
= 4.9 ---------------(1)
From circuit 2, E Ir = V
R
= IR
Ir = E IR
r =
E IR
I
=
E
R
I
=
5.0
12
0.40
V= 4.9V
I
9646 H2 PHYSICS Tutorial
Nanyang Junior College 6
= 0.50 O
Substitute r = 0.50 O into equation (1)
E I(0.50) = 4.9
I =
4.9 5.0 4.9
0.20
0.50 0.50
E
A
= =
since IR
voltmeter
= 4.9 R
voltmeter
=
4.9
24.5
0.20
= O
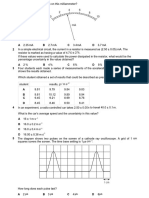
15. The graph below shows the I-V characteristic of a resistive load R.
a) Find the resistance of R when it is connected to a supply of (i) 1.5 V (ii) 3.5 V.
According to graph, R
1.5V
=
1.5
0.3
= 5.0
According to graph, R
3.5V
=
3.5
0.6
= 5.8
b) Find the power dissipation in R when it is connected to a 5.0 V cell.
P
R
= V I = (5.0)(0.7) = 3.5 W
R is connected to a steady supply for 10 minutes, during which a total charge of 300 C
passes through R. Find the voltage of the supply and the energy dissipated during that
period. [2.5 V, 7.5 x 10
2
J]
I =
Q
t
=
300
(10 60)
= 0.50 A
According to graph V = 2.5 V when I = 0.50 A
E = VIt = (2.5)(0.50)(10 x 60) = 7.5 x 10
2
J
9646 H2 PHYSICS Tutorial
Nanyang Junior College 7
c) R dissipates 2.0 W of power when connected to steady supply. Suggest how you
would find the voltage of the supply and estimate its value.
Voltage can be found using the graph. P = VI = 2.0 W
According to the graph, VI = 2.0 W when V = 3.4 V and I = 0.59 A
9646 H2 PHYSICS Assignment
Nanyang Junior College 1
Chapter 11
CURRENT OF ELECTRICITY
Name: ___________________________ CT: __________
1. A car battery of e.m.f. 12 V and internal resistance 0.014 delivers a current of 110 A
when first connected to the starter motor. Calculate
a) the resistance of the starter motor [2]
E = I (R+r)
12 = 110 (R+0.014) R = 0.0951 ~0.095
b) power delivered to the motor [2]
P
R
= I
2
R = (110)
2
(0.0951) = 1150 W ~1200 W
c) power generated by the battery [2]
P
batt
= E I = 12 x 110 = 1320 W ~1300 W
d) the fraction of the total power which is dissipated in the battery [2]
1320 1150
0.13
1320
r
batt
P
P
= =
2. Two wires A and B, each of the same length and the same material, are connected in
parallel to a battery. The diameter of A is twice that of B. What fraction of the total current
passes through A? [3]
2 2
2
2 2
2
(1), (2)
( ) ( )
2 2
( )
1
2
( ) ( )
2
( )
2
4
A B
A B
B
A B
A
B A
A B
l l
R R
d d
d
R d l
d
R l d
R R
= =
= = =
=
Current flowing through B will be 4 times of A since the potential different between both A
and B is the same and the resistance of A is 4 times of B, therefore
1 1
4 1 5
A
I
I
= =
+
25
9646 H2 PHYSICS Assignment
Nanyang Junior College 2
3. A light bulb of unknown resistance is connected across a 12 V cell with internal resistance
5.0 O. The current in the circuit is 0.62 A. Find
(i) the resistance of the light bulb, [4]
V
R
= E Ir
= 12 (0.62)(5.0)
= 8.9 V
R
V
R
I
8.90
0.62
14.4 14
=
=
= O ~ O
(ii) the power output from the bulb, and [2]
P
output
= I V
R
= (0.62)(8.90)
= 5.5 W
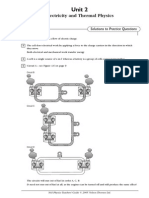
4. Fig 4.1 and 4.2 shows two circuits X and Y that are used by a student to test a battery of
three identical cells. In circuit X there is no load resistor. In circuit Y a load resistor is
connected. You can assume that the meters in the circuits are ideal. Their readings are
shown on each figure.
(i) In both circuits, the voltmeter is connected across the cells to measure its terminal
potential differences. Explain the difference between the voltmeter readings recorded
in the two circuits. [2]
Voltmeter in circuit X measures the e.m.f. of the battery since there is no current flow in
the circuit while voltmeter in circuit Y measures the p.d. across the load resistor.
(ii) Calculate the internal resistance of one cell. [2]
For circuit Y, E = V
R
+ Ir
4.5 = 3.1 + 0.39 r
r = 3.6
Hence, internal resistance for each cell =
3.6
3
= 1.2
Fig. 4.1 Fig. 4.2
=12 V
= 5.0
= 0.62 A
R
9646 H2 PHYSICS Assignment
Nanyang Junior College 3
(iii) One of the cells in the battery is reversed for both circuits. Determine the new reading
1. on the voltmeter in circuit X, [1]
Reading on voltmeter in X = 1.5 + 1.5 1.5 = 1.5 V
2. on the ammeter in circuit Y. [2]
Resistance in circuit Y = 8.0 + 3.6 = 11.6
Hence new current =
1.5
11.6
= 0.13 A
(iv) The load resistor in circuit Y is replaced by an unknown device. The student finds that
the voltmeter reading decreases as the temperature of the device increases. Suggest
what is the unknown device. [1]
Thermistor
You might also like
- As and A Level Physics Core Practical 3 Emf and Internal Resistance StudentDocument5 pagesAs and A Level Physics Core Practical 3 Emf and Internal Resistance StudentAmeerHamzaa100% (1)
- Preboard Sept 2013 Set B SolutionDocument20 pagesPreboard Sept 2013 Set B Solutionmark ian100% (4)
- SEO-OPTIMIZED TITLEDocument19 pagesSEO-OPTIMIZED TITLERohit NairNo ratings yet
- Phy 12 (Ncert)Document10 pagesPhy 12 (Ncert)Aravind BhomboreNo ratings yet
- Physics: Senior Secondary School: ThirdDocument32 pagesPhysics: Senior Secondary School: ThirdAdio Babatunde Abiodun CabaxNo ratings yet
- 10 Physics ch12 Electricity Ncert SolutioDocument19 pages10 Physics ch12 Electricity Ncert SolutiothemidnightismNo ratings yet
- Electricity In-text and Book Exercise AnswersDocument16 pagesElectricity In-text and Book Exercise AnswersLorith Plays SMPNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11_electricity_mabborang, Mary Kristelle uDocument4 pagesChapter 11_electricity_mabborang, Mary Kristelle uyram LetsirkNo ratings yet
- Q ElectricityDocument29 pagesQ Electricityvidhan tiwariNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science ELECTRICITYDocument12 pagesClass 10 Science ELECTRICITYDebsuvro RoyNo ratings yet
- Electricity Numerical Text BookDocument21 pagesElectricity Numerical Text BookShriya SNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument11 pagesElectricityskluckyskashifNo ratings yet
- 2.3 and 2.4 ElectricityDocument17 pages2.3 and 2.4 ElectricityAziz BakarNo ratings yet
- Unit 4: Electromagnetic Induction & Alternating Current: Question BankDocument8 pagesUnit 4: Electromagnetic Induction & Alternating Current: Question BankNathanianNo ratings yet
- Unit 10 Regents Physics Test (Circuits Review)Document7 pagesUnit 10 Regents Physics Test (Circuits Review)aznblehtnNo ratings yet
- Electricity Class 10 NotesDocument10 pagesElectricity Class 10 NotesKota SrinadhNo ratings yet
- L-5 Chapter-14 Physics-10 Mushtaq Ahmed M.Sc. PhysicsDocument29 pagesL-5 Chapter-14 Physics-10 Mushtaq Ahmed M.Sc. PhysicsMushtaq AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Electricity (Students Copy)Document28 pagesChapter 7 - Electricity (Students Copy)Faizah Nur ZaNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS 4th QuarterDocument86 pagesPHYSICS 4th QuarterJ i nNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Physics Chapter 2 - Teacher'sDocument15 pagesForm 5 Physics Chapter 2 - Teacher'sPavithiran100% (4)
- 3RD Term S1 PhysicsDocument14 pages3RD Term S1 PhysicsMARYQUEEN AMARACHUKWUNo ratings yet
- Segment 2 QB - AnswersDocument14 pagesSegment 2 QB - Answersavp sNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Topic 4: Lokman Awad 2013/2014Document107 pagesUnit 2 Topic 4: Lokman Awad 2013/2014MrApexNo ratings yet
- EEE SyllabusDocument11 pagesEEE Syllabussamarpit_anandNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Test1Document10 pagesCurrent Electricity Test1Harsh RuhalNo ratings yet
- Question 543500 3Document8 pagesQuestion 543500 3Nabaratna BiswalNo ratings yet
- Electric Revision on Charge, Current, Voltage & Resistance CalculationsDocument1 pageElectric Revision on Charge, Current, Voltage & Resistance CalculationsLim JingNo ratings yet
- (Theory) VCBE/PO1/A/12: Sample Paper - 2012 Class - XII Subject - PhysicsDocument6 pages(Theory) VCBE/PO1/A/12: Sample Paper - 2012 Class - XII Subject - PhysicsNithin BalanNo ratings yet
- p1 - 1Document79 pagesp1 - 1Aya MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Nelson Thornes Electrcity and Thermal Physics Prac2Document26 pagesNelson Thornes Electrcity and Thermal Physics Prac2Mitul KaziNo ratings yet
- Angel Education Half Yearly Exam Physics 2017-2018Document3 pagesAngel Education Half Yearly Exam Physics 2017-2018Atul Verma0% (1)
- HW7 B SolutionsDocument4 pagesHW7 B Solutionsmmsingh91100% (2)
- ELECTRICITY NUMERICAL WORKSHEETDocument3 pagesELECTRICITY NUMERICAL WORKSHEETayerjayaram59No ratings yet
- NCERT ExamplerDocument18 pagesNCERT ExamplerGeetha.H.R 9th G.H.S.HonsigereNo ratings yet
- Tutorial-2 EE AC, 1-Phase PartDocument3 pagesTutorial-2 EE AC, 1-Phase PartDebendra Bahadur RautNo ratings yet
- ECV211Document103 pagesECV211Daniel KariukiNo ratings yet
- Exam MEP1553 Apr2010Document7 pagesExam MEP1553 Apr2010Abid JamaliNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Electricity QuestionsDocument18 pagesNCERT Exemplar Class 10 Electricity QuestionsPriyanshu BhardwajNo ratings yet
- 2015 h1 DC Circuit Satt QNDocument11 pages2015 h1 DC Circuit Satt QNEndi FendiNo ratings yet
- Resistor Color Codes, Ohm Law: Principle of Electrical EngineeringDocument36 pagesResistor Color Codes, Ohm Law: Principle of Electrical EngineeringMugheera MalikNo ratings yet
- MODULE 3 - (ELECTROSTATIC MAGNETISM) - Lecture Only (3)Document27 pagesMODULE 3 - (ELECTROSTATIC MAGNETISM) - Lecture Only (3)ARBOLEDA, LADY CHRSTINE C.No ratings yet
- Physics 12 Hot PhysicsDocument50 pagesPhysics 12 Hot PhysicsdhirendrasisodiaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Technology Topic 1 Sem 1 PoliteknikDocument118 pagesElectrical Technology Topic 1 Sem 1 Politeknikinjung89% (9)
- Worksheet (2) On Current ElectricityDocument7 pagesWorksheet (2) On Current ElectricitySrijit SahaNo ratings yet
- Intro Electrical Engineering ExercisesDocument19 pagesIntro Electrical Engineering Exerciseshatem aliNo ratings yet
- BetDocument16 pagesBetShivendra SangwanNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 12 ElectricityDocument29 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 10 Science Chapter 12 ElectricityManwinder Singh GillNo ratings yet
- Exam1a SolutionsDocument4 pagesExam1a SolutionsBambang Trenggono MuhammadNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument18 pagesElectricityrahulsenNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7 FinalDocument11 pagesExperiment 7 Finalernie5000No ratings yet
- CA08 AlfonsoMJADocument12 pagesCA08 AlfonsoMJAMJA.AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Short Answer Questions - I (PYQ)Document31 pagesShort Answer Questions - I (PYQ)Gorima GoonNo ratings yet
- 3rd Term PhysicsDocument14 pages3rd Term Physicssaidu musaNo ratings yet
- ch_3Document24 pagesch_3nirmaladevisolairaj1977No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document117 pagesChapter 1badrilaminNo ratings yet
- Physics II Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNo ratings yet
- Electricity Numerical WorksheetDocument3 pagesElectricity Numerical WorksheetVijayKumar LokanadamNo ratings yet
- August 2014Document17 pagesAugust 2014MIRA JHON MICHAEL100% (1)
- CBSE Board-XII Physics - Paper - SolutionDocument15 pagesCBSE Board-XII Physics - Paper - SolutionMichelle DennisNo ratings yet
- Modern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsFrom EverandModern Electrical Installation for Craft StudentsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- $ba/b6916 4@@B05.@/.? @:) 5:.7i?c6$?.c..?.:.6 /B6916 4Document5 pages$ba/b6916 4@@B05.@/.? @:) 5:.7i?c6$?.c..?.:.6 /B6916 4bandagecookieNo ratings yet
- 233 ?aa 0 ::B 60 A2Document2 pages233 ?aa 0 ::B 60 A2bandagecookieNo ratings yet
- Pohjois-Karjalan Arkkitehtuuria, Osa 1 - Compressed - Fi.enDocument67 pagesPohjois-Karjalan Arkkitehtuuria, Osa 1 - Compressed - Fi.enbandagecookieNo ratings yet
- MathDocument1 pageMathbandagecookieNo ratings yet
- Cancellation Form 2016Document1 pageCancellation Form 2016bandagecookieNo ratings yet
- Prudential Business ReplyDocument1 pagePrudential Business ReplybandagecookieNo ratings yet
- 01#90 8F Layout v2014Document1 page01#90 8F Layout v2014bandagecookieNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1-3 Answers (Last Updated On 5th Aug 2010)Document4 pagesTutorial 1-3 Answers (Last Updated On 5th Aug 2010)bandagecookieNo ratings yet
- 2002 A - Level Paper 1 General PaperDocument1 page2002 A - Level Paper 1 General PaperbandagecookieNo ratings yet
- ECP 11-0008 LV Cable Testing ProcedureDocument9 pagesECP 11-0008 LV Cable Testing Procedurerobertovm2002No ratings yet
- EECE370 Q2 F11 Key PostDocument7 pagesEECE370 Q2 F11 Key PosttelNo ratings yet
- Measuring Instruments Practice QuestionsDocument6 pagesMeasuring Instruments Practice QuestionsAsif Ayaz100% (2)
- ATRA 2003 Seminar ManualDocument311 pagesATRA 2003 Seminar Manualdboo100% (9)
- Escom-Practica 3 CircuitosDocument13 pagesEscom-Practica 3 CircuitosVico LopezNo ratings yet
- MCQ, S Current ElectricityDocument4 pagesMCQ, S Current Electricitybilal5202050No ratings yet
- GABISAN - Experiment No. 1Document9 pagesGABISAN - Experiment No. 1Mary Judy GabisanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Questions in AC Systems: N Order To Tune A Parallel Resonant Circuit To A Lower Frequency, The Capacitance MustDocument4 pagesReviewer Questions in AC Systems: N Order To Tune A Parallel Resonant Circuit To A Lower Frequency, The Capacitance MustRonald James DiazNo ratings yet
- Gen PhysicsDocument14 pagesGen Physicsmerry annNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document35 pagesChapter 03david jenil nabuaNo ratings yet
- HV XLPE Cable Commissioning FormDocument3 pagesHV XLPE Cable Commissioning FormMustafa MohamedNo ratings yet
- CoilsDocument20 pagesCoilsAnup Kumar Gupta0% (1)
- Maximum Permissible Voltage DropDocument1 pageMaximum Permissible Voltage DropBaoLCNo ratings yet
- Pinza Prova 5601Document2 pagesPinza Prova 5601Sublimec San RafaelNo ratings yet
- PSIM HelpDocument8 pagesPSIM HelpFayyaz KashifNo ratings yet
- Whirlpool Service Manual Dishwasher ADP9521WHMDocument28 pagesWhirlpool Service Manual Dishwasher ADP9521WHMcarlammartins100% (1)
- Frank ElectricalMeasurementAnalysis TextDocument457 pagesFrank ElectricalMeasurementAnalysis TextPrasanth Kumar100% (1)
- IGCSE Physics Formula SheetDocument5 pagesIGCSE Physics Formula SheetBrandly NyamapnziNo ratings yet
- KUS Electric Liquid Level Sending UnitDocument2 pagesKUS Electric Liquid Level Sending UnitPablo BurgosNo ratings yet
- RAYCHEM DS H60448 Elexant4020i ENDocument6 pagesRAYCHEM DS H60448 Elexant4020i ENsunny kumarNo ratings yet
- 11 000 Measuring Equipment SummaryDocument38 pages11 000 Measuring Equipment SummaryAdrian GarciaNo ratings yet
- Yocan Catalog-2022.10 ElisaDocument8 pagesYocan Catalog-2022.10 ElisaNelson chau QuevedNo ratings yet
- A-140 F & Block: Construction FeaturesDocument2 pagesA-140 F & Block: Construction FeaturesCarlos Eduardo Flores TorresNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Number 06 Kirchofs Cicuit KCL and KVL Ohm LawDocument6 pagesLab Report Number 06 Kirchofs Cicuit KCL and KVL Ohm LawMuhAmmad AqiB ShAykhNo ratings yet
- 544-560-18 - Duct TemperatureDocument2 pages544-560-18 - Duct TemperatureMinh nhut LưuNo ratings yet
- KCET Mock Test Paper 6Document55 pagesKCET Mock Test Paper 6indigohghNo ratings yet
- M01 Moto0256 00 Se L01 PDFDocument50 pagesM01 Moto0256 00 Se L01 PDFlartsim115No ratings yet
- Electronics Fundamentals: Circuits, Devices, and ApplicationsDocument36 pagesElectronics Fundamentals: Circuits, Devices, and Applicationsmugammad wasimNo ratings yet
- Ultra-Slim Signal Conditioners with Dual Isolated OutputsDocument3 pagesUltra-Slim Signal Conditioners with Dual Isolated OutputsErick de la FuenteNo ratings yet