Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Formula Sheet
Uploaded by
jainswapnilOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Formula Sheet
Uploaded by
jainswapnilCopyright:
Available Formats
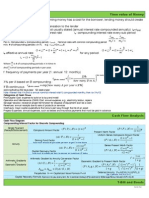
1.
FV = PV (1+i)
n
..Compounded Annually
2. FV = PV + PVin ..Simple interest
n
3. P
0
= C
t
/(1 + r
f
)
t
+ P
n
/
(1 + r
f
)
n
t=1
where P
0
= present value
C
t
= interest payment (Coupon payment) at time t
Pn= face value (principal repayment) at maturity
n= number of periods to maturity
rf= risk-free interest rate (yield)
4. Annuity Due:
PV = C + (C/i) * [1 1/(1+i)
n-1
]
Where: PV = present value
C= cash flow per period
i = interest rate per period
n = number of cash flows
5. Normal/Ordinary Annuity:
PV = C/i * [1 1/(1+i)
n
]
6. Deferred Annuity:
P = 1/(1+i)
k-1
* C/i * [1 1/(1+i)
n
]
where: k= number of time periods deferred until the first cash flow
n= number of cash flows
7. The average rate (geometric rate) :
Total Return = (1 + percent return) * (1 + percent return) *.(number of periods)
Geometric average = ((total return)
(1/number of years)
) - 1
8. FVIF(in) = future value interest factor for t periods at interest rate i.
= (1+i)
n
9. PVIF(in) = present value interest factor for t periods at interest rate i. = (1+i)
-n
10. FVIFA(in) = future value interest factor for annuity of n periods (payments) at interest rate i.
= [(1+i)
n
-1]/i .. [text uses S (n,i) ]
11. PVIFA(in) = present value interest factor for annuity of n periods at interest rate i.
= [1- (1+i)
-n
]/i .. [text uses A (n,i) ]
12. Calculate effective annual rate
i = (1 + j/m )
m
- 1
Where, i = effective annual rate
j = nominal interest rate
m = frequency of compounding
13. Effective monthly rate = Nominal interest rate/ 12
14. Nominal monthly rate = Nominal interest rate/ 12
15. Perpetuity
P
0
= D/k
e
Where
Po = price time zero (now)
D = constant dividend
ke = cost of equity
16. Constant Growth Model: P
0
= D
1
/ (k - g) => P
0
= D
0
(1 + g) / (k g)
D
1
= D
0
(1 + g)
D
2
= D
1
(1 + g) or D
2
= D
0
(1 + g)
2
..and so on
If there are two growth rate then
P
x
= D
x
/(k
e
-g
2
)
17. Standard Model
18. Interest = Opening balance * Interest rate
19. Fisher equation: (1+N) = (1+R)(1+EI) (1+nominal) = (1+real) x (1+ expected inflation)
20. Expected Return of the Portfolio: E(R
p
) = a x E(R
a
) + b x E(R
b
)
21. Variance of the Portfolio:
22. CAPM : Capital Asset Pricing Model
23. | | )
~
( )
~
(
f m i f i
R R E R R E + = |
Required Return = Risk Free Rate + Number of Units of Risk X Risk Premium per Unit of
Risk
R
f
is the risk free rate (about 6% - govt bond rate)
E(R
m
) is the return on the market (about 12%)
Risk/return relationship for all assets, investments and portfolios (efficient or inefficient)
R
i
- R
f
is the risk premium on asset i
R
m
- R
f
premium on the market portfolio, (about 6%)
=
+
+
+
=
n
t
n
e
n
t
e
t
o
k
P
k
D
P
1
) 1 ( ) 1 (
2 2 2 2 2
2 2 2 2 2
2
2
p a b ab
p a b ab a b
a b ab
a b ab
o o o o
o o o o o
= + +
= + +
2
) (
) (
m
im
m
m i
R Var
R R Cov
Beta
o
o
| = = =
Riskfree rate has beta of zero
Market return has beta of one
24. Using the CAPM, Risk Adjust discount rate (RADR)
R
i
(RADR) = R
f
+ Beta(R
m
- R
f
)
You might also like
- Mathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandMathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- MGT201 Financial Management Formulas Lect 1 To 22Document13 pagesMGT201 Financial Management Formulas Lect 1 To 22Farhan UL HaqNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandCorporate Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
- Financial Management FormulasDocument9 pagesFinancial Management FormulasTannao100% (1)
- FM (Actuary Exam) FormulasDocument15 pagesFM (Actuary Exam) Formulasmuffinslayers100% (1)
- CPA Review Notes 2019 - BEC (Business Environment Concepts)From EverandCPA Review Notes 2019 - BEC (Business Environment Concepts)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- Important FormulasDocument5 pagesImportant FormulasKhalil AkramNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Compound InterestDocument14 pagesLesson 6 Compound InterestDaniela CaguioaNo ratings yet
- Accounting and Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandAccounting and Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
- FNCE Cheat Sheet Midterm 1Document1 pageFNCE Cheat Sheet Midterm 1carmenng1990No ratings yet
- Inverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandInverse Trigonometric Functions (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- MGT201 Formulas From Chapter 1 To 22 (Document11 pagesMGT201 Formulas From Chapter 1 To 22 (Ali IbrahimNo ratings yet
- FM FormulasDocument10 pagesFM Formulasyesha-parikh-4523No ratings yet
- Corporate Finance Formula SheetDocument4 pagesCorporate Finance Formula Sheetogsunny100% (3)
- Formulas - All Chapters - Corporate Finance Formulas - All Chapters - Corporate FinanceDocument6 pagesFormulas - All Chapters - Corporate Finance Formulas - All Chapters - Corporate FinanceNaeemNo ratings yet
- Financial Management: (Formulas From Chapter 1-22)Document12 pagesFinancial Management: (Formulas From Chapter 1-22)Li Hui FooNo ratings yet
- Formule Blad CME: C (N K) +W + +W +W + +W I 1 M MDocument3 pagesFormule Blad CME: C (N K) +W + +W +W + +W I 1 M MLente ChristanNo ratings yet
- Formulae SheetDocument4 pagesFormulae SheetSameer SharmaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics of Investment FormulaDocument23 pagesMathematics of Investment FormulaFatima Ira ArcillaNo ratings yet
- Finance 3000 Midterm2 Formula Sheet: October 28, 2015Document2 pagesFinance 3000 Midterm2 Formula Sheet: October 28, 2015Jack JacintoNo ratings yet
- R M R M R M R M: Time Value of MoneyDocument8 pagesR M R M R M R M: Time Value of MoneyHenry JiangNo ratings yet
- Fin All Formula - Docx 1Document9 pagesFin All Formula - Docx 1Marcus HollowayNo ratings yet
- EM302 Formula Sheet 2013Document4 pagesEM302 Formula Sheet 2013Jeff JabeNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam Formula Sheet: R C G R CDocument2 pagesMidterm Exam Formula Sheet: R C G R Cleafsfan85No ratings yet
- Pvif 1 - (1+i) - N (1 - (1+i) - N) /i I FVIF (1+i) N - 1 (1+i) (N) - 1) /i IDocument12 pagesPvif 1 - (1+i) - N (1 - (1+i) - N) /i I FVIF (1+i) N - 1 (1+i) (N) - 1) /i ISyed Abdul Mussaver ShahNo ratings yet
- Annuities - A Series of Equal Payments Occurring at Equal Periods of TimeDocument5 pagesAnnuities - A Series of Equal Payments Occurring at Equal Periods of TimeMarcial MilitanteNo ratings yet
- CFA Level I Formula SheetDocument27 pagesCFA Level I Formula SheetAnonymous P1xUTHstHT100% (4)
- Corporate FinanceDocument96 pagesCorporate FinanceRohit Kumar80% (5)
- E ENGINEERING ECONOMICS ReviewDocument16 pagesE ENGINEERING ECONOMICS ReviewJM CopinoNo ratings yet
- AnnuityDocument29 pagesAnnuityChristed aljo barroga100% (1)
- Chapter 2Document28 pagesChapter 2SHIRISH KNo ratings yet
- Test EdiDocument2 pagesTest EdiHeba AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Time Value of Money Formulas SheetDocument1 pageTime Value of Money Formulas SheetBilal HussainNo ratings yet
- Pvif 1 - (1+i) - N (1 - (1+i) - N) /i I FVIF (1+i) N - 1 (1+i) (N) - 1) /i IDocument15 pagesPvif 1 - (1+i) - N (1 - (1+i) - N) /i I FVIF (1+i) N - 1 (1+i) (N) - 1) /i INadir AhmedNo ratings yet
- FM Formula Sheet 01Document2 pagesFM Formula Sheet 01Aninda DuttaNo ratings yet
- Finance NoteDocument19 pagesFinance NoteHui YiNo ratings yet
- Financial Mathematics: 1 The Measurement of InterestDocument10 pagesFinancial Mathematics: 1 The Measurement of InterestJoeKnittelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Risk and ReturnDocument25 pagesChapter 4 Risk and Returnsharktale2828No ratings yet
- FM II Midterm Formula SheetDocument1 pageFM II Midterm Formula SheetSalman J. SyedNo ratings yet
- FIN 401 - Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesFIN 401 - Cheat SheetStephanie NaamaniNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Cash Flows, Interest & Time Value For MoneyDocument7 pages2.1 Cash Flows, Interest & Time Value For MoneyDiana RebeccaNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance - FormulasDocument3 pagesCorporate Finance - FormulasAbhijit Pandit100% (1)
- HM321Lec02 F23Document18 pagesHM321Lec02 F23muhammad afzzalNo ratings yet
- Mathimatics For Finance CH 4Document9 pagesMathimatics For Finance CH 4Yeabtsega FekaduNo ratings yet
- R) (1 CF ...... R) (1 CF R) (1 CF CF NPV: Invesment Initial NPV 1 Invesments Initial Flows Cash Future of PVDocument9 pagesR) (1 CF ...... R) (1 CF R) (1 CF CF NPV: Invesment Initial NPV 1 Invesments Initial Flows Cash Future of PVAgnes LoNo ratings yet
- CFA Formula Cheat SheetDocument9 pagesCFA Formula Cheat SheetChingWa ChanNo ratings yet
- 2017 Level I Formula SheetDocument28 pages2017 Level I Formula SheetVishal GoriNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument5 pagesNotesfiseco4756No ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Time Value of MoneyDocument41 pagesChapter 4: Time Value of MoneyAnkush SharmaNo ratings yet
- 2018 Level I Formula Sheet 1 PDFDocument27 pages2018 Level I Formula Sheet 1 PDFShamima YesminNo ratings yet
- Investing & EconomicsDocument18 pagesInvesting & EconomicsiamdarshandNo ratings yet
- Wealth Management: (Page 1 of 2) (Printed Only On One Side)Document2 pagesWealth Management: (Page 1 of 2) (Printed Only On One Side)mohakbhutaNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems in Engineering Economy 2016 - CompressDocument61 pagesSolved Problems in Engineering Economy 2016 - CompressCol. Jerome Carlo Magmanlac, ACP100% (1)
- ECON 211 Notes 10 19 23Document4 pagesECON 211 Notes 10 19 23Christine Joy RemegioNo ratings yet
- Session One FormulasDocument1 pageSession One FormulasSalarAliMemonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - How Time and Interest Affect MoneyDocument50 pagesLecture 2 - How Time and Interest Affect MoneyDanar AdityaNo ratings yet
- Exam FM Formula Summary: A Few NotesDocument9 pagesExam FM Formula Summary: A Few NotesFemibarinNo ratings yet
- What Are The Safest Strategies (Iron Condors, Verticals) For Selling OptionsDocument3 pagesWhat Are The Safest Strategies (Iron Condors, Verticals) For Selling OptionscoccoNo ratings yet
- Elliott Wave TheoryDocument18 pagesElliott Wave TheoryQTP TrainerNo ratings yet
- FM - Bond & Stock ValuationDocument10 pagesFM - Bond & Stock ValuationSeneca GonzalesNo ratings yet
- AF Tugas 8 - RifqahDocument8 pagesAF Tugas 8 - RifqahFadhi LullahNo ratings yet
- Assess Hutchison WhampoaDocument4 pagesAssess Hutchison WhampoaAyesha KhalidNo ratings yet
- Smart Money Entry TypesDocument15 pagesSmart Money Entry TypesEyad Qarqash95% (41)
- Fact Sheet: Kingsgate Consolidated Limited: Board of DirectorsDocument1 pageFact Sheet: Kingsgate Consolidated Limited: Board of Directorsreine1987No ratings yet
- Titman PPT Ch07Document59 pagesTitman PPT Ch07Benny TanNo ratings yet
- Free Cash Flow Estimate (In INR CRS)Document2 pagesFree Cash Flow Estimate (In INR CRS)SaiVamsiNo ratings yet
- Risk Parity Is About BalanceDocument4 pagesRisk Parity Is About Balancejrf230100% (1)
- BFC5935 - Tutorial 9 SolutionsDocument6 pagesBFC5935 - Tutorial 9 SolutionsXue XuNo ratings yet
- Debit: Cash / Bank Account Credit: Share Capital AccountDocument2 pagesDebit: Cash / Bank Account Credit: Share Capital AccountAkram HussainNo ratings yet
- Finance Word LibDocument45 pagesFinance Word LibTor 2No ratings yet
- MC Complex AnsDocument4 pagesMC Complex AnsJustine Mae AgapitoNo ratings yet
- Pre-Course Assignment Questions & SolutionsDocument3 pagesPre-Course Assignment Questions & SolutionsKenny HoNo ratings yet
- List of Authorised and Recognised Financial Market Infrastructures (Including Trading Venues) and Foreign ParticipantsDocument6 pagesList of Authorised and Recognised Financial Market Infrastructures (Including Trading Venues) and Foreign ParticipantsPedroNo ratings yet
- 13.5 AS 11 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange RatesDocument7 pages13.5 AS 11 The Effects of Changes in Foreign Exchange RatesAakshi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Karvy Stock Broking LTD.: Summer Training Report ONDocument47 pagesKarvy Stock Broking LTD.: Summer Training Report ONAkshay SinghalNo ratings yet
- Kelompok 17 Stocks and SharesDocument6 pagesKelompok 17 Stocks and SharesishmidaNo ratings yet
- Capital Markets & InvestmentsDocument4 pagesCapital Markets & InvestmentsHarshit BaranwalNo ratings yet
- Beyond Cash Dividends: Buybacks, Spin Offs and DivestituresDocument49 pagesBeyond Cash Dividends: Buybacks, Spin Offs and DivestituresayzlimNo ratings yet
- Amazon Whole FoodsDocument15 pagesAmazon Whole Foodsbingcheng HuNo ratings yet
- Risk of Bond InvestmentDocument30 pagesRisk of Bond InvestmentJIROJBLOGNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Bond ValuationDocument28 pagesChapter 11 Bond ValuationGracia Tiffany Septiana100% (1)
- Dynamic ReplicationDocument20 pagesDynamic ReplicationAtiahNo ratings yet
- Gyertyák5 - Doji Long Legged - Candlestick Pattern DictionarDocument5 pagesGyertyák5 - Doji Long Legged - Candlestick Pattern DictionarTSXfx01No ratings yet
- AKUZAWA NewApproachVolatilitySkewDocument38 pagesAKUZAWA NewApproachVolatilitySkewfloqfloNo ratings yet
- A Project Report SynopsisDocument6 pagesA Project Report SynopsisTrisha SohalNo ratings yet
- EXERCISE 5-5 (30-35 Minutes) Uhura Company Balance Sheet ...Document4 pagesEXERCISE 5-5 (30-35 Minutes) Uhura Company Balance Sheet ...Thùy Dương ĐồngNo ratings yet
- Stocks: Finance: The Management of MoneyDocument29 pagesStocks: Finance: The Management of MoneyMike GruzwaldNo ratings yet
- Summary of The Black Swan: by Nassim Nicholas Taleb | Includes AnalysisFrom EverandSummary of The Black Swan: by Nassim Nicholas Taleb | Includes AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- 2019 Business Credit with no Personal Guarantee: Get over 200K in Business Credit without using your SSNFrom Everand2019 Business Credit with no Personal Guarantee: Get over 200K in Business Credit without using your SSNRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- The Six Secrets of Raising Capital: An Insider's Guide for EntrepreneursFrom EverandThe Six Secrets of Raising Capital: An Insider's Guide for EntrepreneursRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- The Masters of Private Equity and Venture Capital: Management Lessons from the Pioneers of Private InvestingFrom EverandThe Masters of Private Equity and Venture Capital: Management Lessons from the Pioneers of Private InvestingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (17)
- Finance Basics (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)From EverandFinance Basics (HBR 20-Minute Manager Series)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (32)
- These are the Plunderers: How Private Equity Runs—and Wrecks—AmericaFrom EverandThese are the Plunderers: How Private Equity Runs—and Wrecks—AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- The Caesars Palace Coup: How a Billionaire Brawl Over the Famous Casino Exposed the Power and Greed of Wall StreetFrom EverandThe Caesars Palace Coup: How a Billionaire Brawl Over the Famous Casino Exposed the Power and Greed of Wall StreetRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- 7 Financial Models for Analysts, Investors and Finance Professionals: Theory and practical tools to help investors analyse businesses using ExcelFrom Everand7 Financial Models for Analysts, Investors and Finance Professionals: Theory and practical tools to help investors analyse businesses using ExcelNo ratings yet
- Ready, Set, Growth hack:: A beginners guide to growth hacking successFrom EverandReady, Set, Growth hack:: A beginners guide to growth hacking successRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- Burn the Boats: Toss Plan B Overboard and Unleash Your Full PotentialFrom EverandBurn the Boats: Toss Plan B Overboard and Unleash Your Full PotentialRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (32)
- The 17 Indisputable Laws of Teamwork Workbook: Embrace Them and Empower Your TeamFrom EverandThe 17 Indisputable Laws of Teamwork Workbook: Embrace Them and Empower Your TeamNo ratings yet
- Financial Intelligence: A Manager's Guide to Knowing What the Numbers Really MeanFrom EverandFinancial Intelligence: A Manager's Guide to Knowing What the Numbers Really MeanRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (79)
- Financial Risk Management: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandFinancial Risk Management: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Venture Deals: Be Smarter Than Your Lawyer and Venture CapitalistFrom EverandVenture Deals: Be Smarter Than Your Lawyer and Venture CapitalistRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (32)
- Startup CEO: A Field Guide to Scaling Up Your Business (Techstars)From EverandStartup CEO: A Field Guide to Scaling Up Your Business (Techstars)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Venture Deals, 4th Edition: Be Smarter than Your Lawyer and Venture CapitalistFrom EverandVenture Deals, 4th Edition: Be Smarter than Your Lawyer and Venture CapitalistRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (73)
- Private Equity and Venture Capital in Europe: Markets, Techniques, and DealsFrom EverandPrivate Equity and Venture Capital in Europe: Markets, Techniques, and DealsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Joy of Agility: How to Solve Problems and Succeed SoonerFrom EverandJoy of Agility: How to Solve Problems and Succeed SoonerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Value: The Four Cornerstones of Corporate FinanceFrom EverandValue: The Four Cornerstones of Corporate FinanceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Investment Valuation: Tools and Techniques for Determining the Value of any Asset, University EditionFrom EverandInvestment Valuation: Tools and Techniques for Determining the Value of any Asset, University EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Creating Shareholder Value: A Guide For Managers And InvestorsFrom EverandCreating Shareholder Value: A Guide For Managers And InvestorsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- How to Measure Anything: Finding the Value of Intangibles in BusinessFrom EverandHow to Measure Anything: Finding the Value of Intangibles in BusinessRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- The Six Secrets of Raising Capital: An Insider's Guide for EntrepreneursFrom EverandThe Six Secrets of Raising Capital: An Insider's Guide for EntrepreneursRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (34)
- Financial Modeling and Valuation: A Practical Guide to Investment Banking and Private EquityFrom EverandFinancial Modeling and Valuation: A Practical Guide to Investment Banking and Private EquityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Other People's Money: The Real Business of FinanceFrom EverandOther People's Money: The Real Business of FinanceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (34)