Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistry Internal Assessment
Uploaded by
Ravindra Narayan AherOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemistry Internal Assessment
Uploaded by
Ravindra Narayan AherCopyright:
Available Formats
Internal Assessment
The Internal Assessment (IA) is a collection of work completed by the student during the course of the year. Each candidate must keep a portfolio (lab notebook), which is a compilation of all investigations carried out, and summarized on IBO form 4/PSOW (Group 4 - Experimental Science, Practical Scheme of Work). HL students in each science are required to demonstrate 60 hours of laboratory/field investigations in their portfolios, SL students in each science are required to demonstrate 40 hours of laboratory/field investigations in their portfolios. The portfolio must include: A copy of the candidate's form 4/PSOW A contents page Instruction sheets and/or summaries of verbal instructions relating to each investigation Evidence of the candidate's involvement in the Group 4 Project Observations/drawings/diagrams Tables, graphs and 'partial' write-ups 'Full' write-ups of 3-6 investigations
The Portfolio is also likely to include: Data analysis made in the field/laboratory Outcomes of data manipulation exercises Results of computer simulations
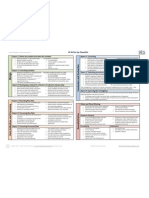
There are eight assessment criteria which are used to assess the work of higher level candidates: o o o o o o o o
planning (a)P (a) planning (b)P (b) data collectionD(c) data analysisD(a) conclusion and evaluationCE manipulative skillsMS personal skills (a)PS (a) personal skills (b)PS (b)
Each of the assessment criteria can be separated into two or three aspects as shown below. Descriptions are provided to indicate what is expected in order to meet the requirements of a given aspect completely (c) and partially (p). A description is also given for circumstances in which the requirements are not satisfied, not at all (n).
Planning (a) ASPECTS LEVELS Defining the problem Formulating a hypothesis Selecting or research question Complete Identifies problem question. a or or prediction variables the
focused Relates the hypothesis or Selects research prediction directly to the relevant research question and independent
and
explains it, quantitatively controlled where appropriate. Partial variable(s). some
States the problem or States the hypothesis or Selects
research question, but prediction but does not relevant variables. it is unclear or explain it.
incomplete. Not at all Does not or state the Does not state a Does not select any variables. relevant
problem
research hypothesis or prediction.
question or repeats the general aim provided by the teacher. Planning (b) ASPECTS LEVELS Selecting appropriate apparatus materials* Complete
Designing a method Designing a method for for the control of the collection of
or variables
sufficient relevant data
Selects appropriate Describes a method Describes a method that apparatus materials. or that allows of for the allows for the collection the of sufficient relevant
control variables.
data.
Partial
Selects appropriate apparatus materials.
some Describes a method Describes a method that that makes some allows for the collection
or attempt to control the of insufficient relevant variables. data.
Not at all
Does
not
select Describes a method Describes a method that not allow data to any be
any apparatus or that does not allow for does materials. the control of
the relevant collected.
variables.
* suitable diagrams are acceptable
Data Collection ASPECTS LEVELS Collecting and recording raw data Organizing and presenting raw data Complete Records (qualitative appropriate and/or raw data Presents raw data clearly, for easy
quantitative), allowing
including units and uncertainties where interpretation. necessary. Partial Records some appropriate raw data. Presents raw data but does not allow for easy
interpretation. Not at all Does not record any appropriate raw Does not present raw data data. or presents it
incomprehensibly.
Data Processing and Presentation ASPECTS LEVELS Complete Processing raw data Presenting processed data
Processes the raw data Presents processed data appropriately, correctly. helping interpretation and, where
relevant, takes into account errors and uncertainties. Partial Some raw data is Presents processed data appropriately but with some errors and/or omissions.
processed correctly. Not at all
No processing of raw data Presents processed data inappropriately is carried out or major or incomprehensibly. errors are made in
processing. Conclusion and Evaluation ASPECTS LEVELS Drawing conclusions Evaluating procedure(s) results Complete Gives a valid Evaluates procedure(s) the results limitations, Identifies weaknesses and and states realistic to the Improving and investigation the
conclusion, based correct on
including suggestions improve
interpretation of weaknesses or errors. investigation. the results, with an and, explanation where
appropriate, compares results with values. Partial States conclusion has validity. a Evaluates that procedure(s) some results some but Suggests and simplistic misses improvements. obvious only literature
limitations or errors. Not at all Draws conclusion a The evaluation is Suggests unrealistic
that superficial
or improvements.
misinterprets the irrelevant.
results. Manipulative Skills ASPECTS LEVELS Carrying out techniques safely Following instructions* Complete Is competent and methodical in Follows the use of the technique(s) and the accurately, the adapting instructions to new a variety of
equipment, and pays attention to circumstances safety issues. Partial
(seeking
assistance when required). the instructions but
Requires assistance in the use of Follows
a routine technique. Works in a requires assistance. safe manner with occasional
prompting. Not at all Does not carry or out the Does not follow the instructions the or requires constant supervision.
technique(s)
misuses
equipment, showing no regard for safety.
* Instructions may be given in a variety of forms: oral, written worksheets, diagrams, photographs, videos, flowcharts, audiotapes, models, computer programs etc.
Personal Skills (a) ASPECTS LEVELS Working within Recognizing a team* Complete Collaborates with the Exchanging integrating ideas and
contributions of others
Expects, actively seeks Exchanges ideas with integrating
others, and acknowledges the others, views of others.
recognizing their needs, in order complete task. to the
them into the task.
Partial
Requires guidance collaborate with others.
Acknowledges to views.
some Exchanges ideas with others but requires
guidance in integrating them into the task. views of Does not contribute.
Not at all
Is unsuccessful Disregards when working others.
with others.
* A team is defined as two or more people.
Personal Skills (b) ASPECTS LEVELS Approaching scientific Working in an Paying attention
investigations with self- ethical manner motivation perseverance Complete Approaches the Pays and
to environmental impact
considerable Pays to the considerable to the
investigation with self- attention
motivation and follows it authenticity of the attention through to completion. data
and environmental of the
information, and the impact approach
to investigation.
materials (living or non-living). Partial Approaches the Pays some attention Pays some the
investigation with self- to the authenticity of attention to motivation or follows it the through to completion. data and environmental of
information, and the impact approach
the
to investigation.
materials (living or non-living). Not at all Lacks perseverance and Pays little attention Pays motivation. to the authenticity of attention to the data and environmental little the
information, and the impact approach
of
the
to investigation
materials (living or non-living).
For a particular criterion, a piece of work is judged to see whether the requirements of each aspect have been fulfilled completely, partially or not at all. This can then be translated into an achievement level 0, 1, 2 or 3 using the achievement level matrixes below. The lowest level of achievement is represented by 0, and 3 represents the highest level of achievement. Planning (a), Planning (b), Conclusion and Evaluation, Personal Skills (a), Personal Skills (b) The matrix below refers to planning (a), planning (b), conclusion and evaluation, personal skills (a) and personal skills (b), where each criterion has three aspects.
Level Completely Partially Not at all
Aspects Level Completely Partially Not at all Aspects 1
Aspects 1
Aspects 1
Aspects 0
Aspects 0
Aspects
Aspects
Aspects
Aspects
Data Collection, Data Processing and Presentation, Manipulative Skills The matrix below applies to data collection, data processing and presentation, and manipulative skills, where each criterion has two aspects.
Level Completely
Partially Not at all Aspects Aspects Aspects Aspects Aspects Aspects
Assessment in the Diploma Program
Assessment is by means of examination and practical for both higher and standard level chemistry courses. Examination weighting Practical work weighting - 76% - 24%
Examination (higher level)
There are three papers: Paper 1 Paper 2 Paper 3 Multiple choice Structured questions Options questions Total - 20% - 36% - 20% - 76%
Paper 1 (high): 1 hour consists of 40 multiple choice questions. Calculators are not allowed. A periodic table is provided Paper 2 (high): 2 hours 15 minutes consists of five structured questions and a choice of two from four longer answer questions. Calculators are allowed and a data booklet is provided Paper 3 (high): 1 hour 15 minutes consists of three questions form each of two selected options. The paper presents eight option choices. Calculators are allowed and data booklets are provided. Exam timing
Examination (standard level)
There are three papers: Paper 1 Paper 2 Paper 3 Multiple choice Structured questions Options questions Total - 20% - 32% - 24% - 76%
Paper 1 (standard): 45 minutes consists of 30 multiple choice questions. Calculators are not allowed. A periodic table is provided Paper 2 (standard): 1 hours 15 minutes consists of some structured questions and a choice of one from three longer answer questions. Calculators are allowed and a data booklet is provided Paper 3 (standard): 1 hour consists of two questions from each of two selected options. The paper presents eight option choices. Calculators are allowed and data booklets are provided. Exam timing
Examination action verbs
As with all examinations, it is important to know what the examiners require. The IBO releases a list of key words and what they mean when referring to exam questions. For example the word "Draw" is taken to mean "represent by a series of pencil lines and labels (unless specifically told not to do so)" This leaves the students clear as to the actual requirements of the questions. A full list of these so-called action verbs can be found here
Practical (Internal) Assessment 2008 exams
This is assessed by means of a practical course consisting of a series of experiments which the students carry out and write reports on in a separate laboratory exercise book. The reports are assessed according to eight criteria. These are: Criterion planning (a) planning (b) data collection data analysis evaluation personal skills (a) personal skills (b) manipulation handling and using apparatus and instrumentation Description aim, hypothesis, variable control apparatus selection and method measuring and recording data manipulating and processing data concluding and evaluating experimentation level 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3
maximum total = 24
The criteria are mostly formative in that the students develop skills during the course of their studies and are given a final level for each criterion*. The assessment is carried out by the teacher(s) in charge and samples sent away for external moderation. Further details on the assessment criteria can be seen here. *Note: A student is not expected to begin the course with highly developed skills in these areas and low levels are normal at first.
Practical (Internal) Assessment 2009 exams
Criterion marks available marks 12 marks 12 marks 12 marks
Design
two grades out of 6 are to be presented
Data collection and processing
two grades out of 6 are to be presented
Conclusions and Evaluation
two grades out of 6 are to be presented
Manipulative skills Personal skills
1 grade out of 6 will be presented 1 grade out of 6 will be presented
6 marks 6 marks 48 marks
Total =
Final grades
The final grade awarded for an IB subject is from 1-7. The schools receive a breakdown of the grade achieved in each part of the exam.
ACTION VERBS These action verbs indicate the depth of treatment required for a given assessment statement. These verbs will be used in examination questions and so it is important that students are familiar with the following definitions. Objective 1 Define give the precise meaning of a word or phrase as concisely as possible represent by means of pencil lines (add labels unless told not to do so) give a sequence of names or other brief answers with no elaboration, each one clearly separated from the others find a value for a quantity give a specific name, value or other brief answer (no supporting argument or calculation is necessary)
Draw
List
Measure State
Objective 2 Annotate Apply Calculate add brief notes to a diagram, drawing or graph use an idea, equation, principle, theory or law in a new situation find an answer using mathematical methods (show the working unless instructed not to do so) give an account of similarities and differences between two (or more) items, referring to both (all) of them throughout (comparisons can be given using a table)
Compare
Describe Distinguish Estimate
give a detailed account, including all the relevant information give the differences between two or more different items find an approximate value for an unknown quantity, based on the information provided and scientific knowledge find an answer from a number of possibilities give a brief account or summary (include essential information only)
Identify Outline Objective 3 Analyse Construct Deduce Derive Design Determine Discuss
interpret data to reach conclusions represent or develop in graphical form reach a conclusion from the information given manipulate a mathematical equation to give a new equation or result produce a plan, object, simulation or model find the only possible answer give an account including, where possible, a range of arguments, assessments of the relative importance of various factors or comparisons of alternative hypotheses assess the implications and limitations give a clear account including causes, reasons or mechanisms give an expected result obtain an answer using algebraic and/or numerical methods propose a hypothesis or other possible answer
Evaluate Explain Predict Solve Suggest
You might also like
- IB Chemistry IA RubricDocument2 pagesIB Chemistry IA RubricMelissa Chan100% (1)
- HL Chemistry IA Checklist Updated Dec 2011Document6 pagesHL Chemistry IA Checklist Updated Dec 2011Karl Naumann100% (1)
- Assessment IB Chemistry PracticalsDocument7 pagesAssessment IB Chemistry Practicalsنور هدايو احمدNo ratings yet
- IA MarksheetDocument8 pagesIA Marksheettemar1215No ratings yet
- IB Chemistry IA Guidance and HintsDocument4 pagesIB Chemistry IA Guidance and HintsGinevraPiccioniNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Internal AssessmentDocument11 pagesChemistry Internal AssessmentTinesh GovindarajooNo ratings yet
- Chem IA Bonding LabDocument7 pagesChem IA Bonding LabJason YuanNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry Internal Assessment 2Document18 pagesIB Chemistry Internal Assessment 2beslisevvalNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry Internal Assessment 1Document13 pagesIB Chemistry Internal Assessment 1beslisevval100% (1)
- Chemistry IA 3Document10 pagesChemistry IA 3Vanessa TumanggorNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry IA: KineticsDocument12 pagesIB Chemistry IA: KineticsMomina Amjad81% (32)
- Ib Chem IaDocument9 pagesIb Chem IaFrank Lala0% (1)
- Chem IA Redox Titration of IronDocument9 pagesChem IA Redox Titration of IronWalter Chung Yin Leung89% (9)
- IB Chemistry IA ChecklistDocument7 pagesIB Chemistry IA ChecklistOGswaggerNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Sample IADocument11 pagesChemistry Sample IAJulianna Alysha100% (1)
- IB Chemistry - Uncertainty & ErrorsDocument25 pagesIB Chemistry - Uncertainty & ErrorsBindu M PillaiNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry IA Hess's LawDocument4 pagesIB Chemistry IA Hess's LawJason J. Ln75% (4)
- Introduction To IB ChemistryDocument46 pagesIntroduction To IB ChemistryAnnika FeignNo ratings yet
- Chemistry HL IADocument12 pagesChemistry HL IALeena SaikumarNo ratings yet
- How Cooking Temp Affects Kailan CalciumDocument12 pagesHow Cooking Temp Affects Kailan CalciumRona100% (1)
- IB Chemistry IADocument12 pagesIB Chemistry IAEmily Sun100% (1)
- Internal Assessment Chemistry (HL) - Comparing the Activation Energy and Enthalpy of Neutralization to Find Total Bond Strengths of Product in Two Different Neutralization Reactions that Produce Sodium ChlorideDocument16 pagesInternal Assessment Chemistry (HL) - Comparing the Activation Energy and Enthalpy of Neutralization to Find Total Bond Strengths of Product in Two Different Neutralization Reactions that Produce Sodium ChlorideSadhaSatyaLotan100% (2)
- Chemistry Internal AssessmentDocument10 pagesChemistry Internal AssessmentFery FekriNo ratings yet
- Chemistry IADocument6 pagesChemistry IAuday agrawal100% (1)
- Determination of KC For An Esterification Reaction ReportDocument5 pagesDetermination of KC For An Esterification Reaction ReportTuo Hundou Lee100% (3)
- IA Write-Up Checklist: Essential Biology: Internal AssessmentDocument1 pageIA Write-Up Checklist: Essential Biology: Internal AssessmentSiddhant Kobe KothariNo ratings yet
- DP Chemistry AssessmentsDocument7 pagesDP Chemistry AssessmentsMegan ElliottNo ratings yet
- IB DP Chemistry HL IA: Free-range Eggs Have Higher Calcium CarbonateDocument8 pagesIB DP Chemistry HL IA: Free-range Eggs Have Higher Calcium CarbonateWalter Chung Yin LeungNo ratings yet
- Possible Chemistry Internal Assessment 2015Document4 pagesPossible Chemistry Internal Assessment 2015BijoyNo ratings yet
- IB CHEMISTRY Toothpaste Experiment IADocument14 pagesIB CHEMISTRY Toothpaste Experiment IASri Vishnu Prabhakar33% (3)
- IB HL Chemistry Assessment Statements Topic 5Document4 pagesIB HL Chemistry Assessment Statements Topic 5AndrewNo ratings yet
- Ib Chemistry SL BookletDocument8 pagesIb Chemistry SL BookletBoshra NouriNo ratings yet
- How Solubility of Luminol in Bases Affects ChemiluminescenceDocument28 pagesHow Solubility of Luminol in Bases Affects ChemiluminescenceDarren Tan50% (2)
- Chemistry IA Example 2Document12 pagesChemistry IA Example 2Vanessa Tumanggor100% (1)
- Chemistry Topic One QuestionsDocument30 pagesChemistry Topic One QuestionsAruba Dhaduk100% (1)
- Internal Assessment - IB ChemistryDocument16 pagesInternal Assessment - IB ChemistryrosemKate522967% (3)
- CHem IA Oxalyic AcidDocument5 pagesCHem IA Oxalyic AcidKennard ChiaNo ratings yet
- IB Acids and BasesDocument45 pagesIB Acids and BasesAhmad Hajj AliNo ratings yet
- Chemistry IA TopicsDocument1 pageChemistry IA TopicspootisNo ratings yet
- I A Extended Essay Ideas For Ib ChemistryDocument3 pagesI A Extended Essay Ideas For Ib ChemistryAaliyaNo ratings yet
- DP Chem Unit 8 Acids and BasesDocument6 pagesDP Chem Unit 8 Acids and BasesPatrick AbidraNo ratings yet
- Ib Chemistry Syllabus 2016-2017Document5 pagesIb Chemistry Syllabus 2016-2017api-325581554No ratings yet
- Ib Unit Plan ChemistryDocument6 pagesIb Unit Plan ChemistryTarique MasoodNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry IA: EnergeticsDocument10 pagesIB Chemistry IA: EnergeticsMomina Amjad89% (55)
- IB Chemistry IA GuideDocument12 pagesIB Chemistry IA Guideanon_234967605No ratings yet
- IB HL Chemistry Assessment Statements Topic 7Document3 pagesIB HL Chemistry Assessment Statements Topic 7AndrewNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry Student HandbookDocument28 pagesIB Chemistry Student Handbookmgupta72100% (1)
- Chemistry IA 2019Document23 pagesChemistry IA 2019Taher PNo ratings yet
- Possible Chemistry Internal Assessment 2015Document3 pagesPossible Chemistry Internal Assessment 2015Ananya Sanagavaram (yr. 18-20)No ratings yet
- HL Biology IA 20/24Document14 pagesHL Biology IA 20/24dev0% (1)
- IB Chemistry Objectives - KineticsDocument1 pageIB Chemistry Objectives - KineticslizarrdoNo ratings yet
- IB Stiochiometry QuestionDocument10 pagesIB Stiochiometry QuestionPakorn Winayanuwattikun0% (1)
- Chem IA TopicsDocument2 pagesChem IA TopicsMichelle57% (7)
- O Level Chemistry Structured Practice Papers 9From EverandO Level Chemistry Structured Practice Papers 9Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Stress Amongst Healthcare Professionals and Migrant Workers During Covid-19 PandemicDocument6 pagesStress Amongst Healthcare Professionals and Migrant Workers During Covid-19 PandemicIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Eco Schools Action PlanDocument1 pageEco Schools Action PlanJohnty GreentoesNo ratings yet
- Ropes and Wires: Malaysian Maritime Academy/Seamanship/May2003 1 of 6Document6 pagesRopes and Wires: Malaysian Maritime Academy/Seamanship/May2003 1 of 6Rohit SinghNo ratings yet
- mf8240 160824142620 PDFDocument698 pagesmf8240 160824142620 PDFArgopartsNo ratings yet
- Qc-Sop-0 - Drilling of PoleDocument7 pagesQc-Sop-0 - Drilling of PoleAmeerHamzaWarraichNo ratings yet
- Adjustment: - Electronic Modulated Air SuspensionDocument2 pagesAdjustment: - Electronic Modulated Air SuspensionThar KyiNo ratings yet
- Legal Opinion WritingDocument53 pagesLegal Opinion WritingBenedict AnicetNo ratings yet
- Jda Connects The Dots at Its 209821Document5 pagesJda Connects The Dots at Its 209821Gerardo LujanNo ratings yet
- OSRAM LEDriving XENARC Headlamp Brochure For Audi A4 B7Document8 pagesOSRAM LEDriving XENARC Headlamp Brochure For Audi A4 B7Fourtitude.comNo ratings yet
- Sick GM31Document54 pagesSick GM31Magdy SalehNo ratings yet
- ZF 4hp14 - 2Document9 pagesZF 4hp14 - 2Miguel BentoNo ratings yet
- Anthony Robbins With Harvard Business SchoolDocument3 pagesAnthony Robbins With Harvard Business SchoolluffylovemangaNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument5 pagesProjectMahi MalikNo ratings yet
- Sae Technical Paper Series 2015-36-0353: Static and Dynamic Analysis of A Chassis of A Prototype CarDocument12 pagesSae Technical Paper Series 2015-36-0353: Static and Dynamic Analysis of A Chassis of A Prototype CarGanesh KCNo ratings yet
- 5 Overview PsasDocument19 pages5 Overview Psasعلي صالحNo ratings yet
- Ternary Phase Diagram Guided Question 1 PDFDocument1 pageTernary Phase Diagram Guided Question 1 PDFLuci FernNo ratings yet
- Design Prof BlankoDocument11 pagesDesign Prof BlankoAousten AAtenNo ratings yet
- ISO 9000 Audit Checklist for Quality Management SystemsDocument28 pagesISO 9000 Audit Checklist for Quality Management SystemsphilipalexjonesNo ratings yet
- Directory of Importers Associations Worldwide 2009Document57 pagesDirectory of Importers Associations Worldwide 2009Thanh Tam75% (12)
- False CeilingDocument70 pagesFalse CeilingBharti Sikri93% (15)
- Worksheet Chapter 50 Introduction To Ecology The Scope of EcologyDocument2 pagesWorksheet Chapter 50 Introduction To Ecology The Scope of EcologyFernando CastilloNo ratings yet
- English 10 - WHLP - Q1 - Module 3Document3 pagesEnglish 10 - WHLP - Q1 - Module 3Mar Florence SebastianNo ratings yet
- High Level Cyber Security Assessment - Detailed ReportDocument57 pagesHigh Level Cyber Security Assessment - Detailed Reportdobie_e_martinNo ratings yet
- Local Materials Used in Creating Art and TechniquesDocument29 pagesLocal Materials Used in Creating Art and TechniquesAnne Carmel PinoNo ratings yet
- CASE ANALYSIS: DMX Manufacturing: Property of STIDocument3 pagesCASE ANALYSIS: DMX Manufacturing: Property of STICarmela CaloNo ratings yet
- Rosalind FranklinDocument1 pageRosalind FranklinMichael SmithNo ratings yet
- Gr07 S DanceDocument17 pagesGr07 S DanceMaliNo ratings yet
- Energy Conservation Opportunities Sugar Industry IDocument8 pagesEnergy Conservation Opportunities Sugar Industry INikhil MohiteNo ratings yet
- PowerFlex 4M LabDocument22 pagesPowerFlex 4M Labmaria laura delgado morenoNo ratings yet
- Slit LampDocument20 pagesSlit LampTricia Gladys SoRiano80% (5)