Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrical - Maintenance
Uploaded by
Channa BasavaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrical - Maintenance
Uploaded by
Channa BasavaCopyright:
Available Formats
NSTec Presentation Title
MAINTENANCE PROGRAMS Where are you?
Vision Service Partnership
Page 1
NSTec Presentation Title
WHERE ARE YOU?
MAINTENANCE PROGRAMS:
Panic Maintenance: Maintenance performed only after a machine fails or experiences problems. PM (Preventative Maintenance) Actions performed on a time- or machine-run-based schedule that detect, preclude, or mitigate degradation of a component or system with the aim of sustaining or extending its useful life and reduce the need for major repairs. PdM (Predictive Maintenance) Attempts to evaluate the condition of equipment by performing periodic or continuous (online) equipment condition monitoring. Basically, predictive maintenance differs from preventive maintenance by basing maintenance need on the actual condition of the machine rather than on some preset schedule. Proactive Maintenance Concentrates on the monitoring and correction of root causes to equipment failures. RCM (part of which is root-cause-analysis), Laser Alignment, Precision Balancing are all part of proactive maintenance initiatives initiatives.
Vision Service Partnership
Page 2
NSTec Presentation Title
Panic Maintenance P i M i t
Crisis M i t C i i Maintenance / Reactive Maintenance / RTF R ti M i t Unplanned downtime g p p High parts and labor costs due to unplanned downtime and equipment damage Inefficient use of staff resources Maintenance and repair is controlled/set by machine failure Vague equipment status and reliability Cannot predict equipment reliability
Vision Service Partnership
Page 3
NSTec Presentation Title
Preventative Maintenance P v t tiv M i t
Histories of each machine type are analyzed and periodic overhauls are scheduled before statically expected problems occur. Potential for incidental damage to components in conducting unneeded maintenance. Catastrophic failures still likely to occur. Typically creates unwanted corrective maintenance (in some companies over 50% of total CMs) Includes performance of unneeded maintenance. Expensive (Inefficient use of resources for most equipment) Not taken seriously by most craft
Vision Service Partnership
Page 4
NSTec Presentation Title
Preventive Maintenance Risk P v tiv M i t
Preventive maintenance does involve risk. The risk here refers to the potential for creating defects of various types while performing the PM t ti l f ti d f t f i t hil f i th task. In other words, human errors committed during the PM task and infant mortality of newly installed components eventually lead to additional failures of the equipment on which the PM was performed. Frequently, these failures occur very soon after the PM is performed. F tl th f il ft th i f d Typical examples of human errors are shown on the following page. Especially disturbing about these types of errors is the fact that they go unnoticed - until they cause an unplanned shutdown. There is some published data that illustrates this point. It comes from the fossil-fuel power industry. A review of the data from fossil-fueled power plants that examined the frequency and duration of forced outages after a planned or forced g p maintenance outage reinforces this concept. That data showed that of 3146 maintenance outages, 1772 of them occurred in less than one week after a maintenance outage. Clearly, this is pretty strong evidence that suggests that in 56% of the cases, unplanned maintenance outages were caused by errors committed during a recent maintenance outage.
Vision Service Partnership
Page 5
NSTec Presentation Title
SELF INDUCED FAILURES
70-80 70 80 % of equipment f il f i t failures are SELF INDUCED SELF-INDUCED Putting hydraulic fluid into a reservoir without filtering it g q p g gp p y Welding on equipment without grounding properly Running equipment to failure when it is not part of your maintenance strategy Aligning couplings without using a laser Improperly lubricating electric motors
Vision Service Partnership
Page 6
NSTec Presentation Title
Predictive Maintenance P di tiv M i t
Based on machine condition while it is running B d hi diti hil i i Dependent on components providing early warning g( y y Non-destructive testing (PdM tools: vibration analysis, oil analysis, IR, Ultrasound, Motor Analyzer Tester. Etc.) Allows management to control machinery and maintenance Allows for preemptive corrective actions Increases plant readiness Greater mainline reliability Reduces expenditure on spare parts and labor R d di dl b Reduces the likelihood of catastrophic failure Improvement in worker safety p y
Vision Service Partnership
Page 7
NSTec Presentation Title
Key T h ologi s for K Technologies fo PdM P og Programs s
Predictive M i t P di ti Maintenance tools: t l Infra-Red Thermography Ultrasound Vibration Analysis Motor/Transformer Tester Analyzer Oil Lubricant and Wear Particle Analysis Oil, Proactive Maintenance tools: RCM Root Cause Analysis Laser Alignment Precision Balancing
Vision Service Partnership
Page 8
NSTec Presentation Title
Infra-Red Thermography I f R d Th og ph
Thermography is the measurement of surface temperature through remote means to indicate equipment health and assigning a color based on the temperature. Uses include: Equipment startup acceptance and commissioning Temperature survey of low voltage, 600 volts and less nominal, electrical Temperature survey of medium voltage, 600 to 47kV, electrical distribution di t ib ti Temperature survey of high voltage, greater than 47kV, electrical transmission and distribution Electro-Mechanical equipment condition monitoring (HVAC (HVAC, Pumps, Motors, Bearings, Gearboxes, Belt-Drives, etc.) Building envelope inspection Heat loss and gain evaluation g Cooling loss and gain evaluation Roofing inspection for wet insulation Inspection of insulation characteristics
Vision Service Partnership
Page 9
NSTec Presentation Title
Infra-Red Thermography I f R d Th og ph
Vision Service Partnership
Page 10
NSTec Presentation Title
Ultrasound Ult so d
Equipment startup acceptance and commissioning E i t t t t d i i i Pressure and vacuum leaks detection Bearing inspection and monitoring High speed gearbox defect detection Steam trap leakage inspection Check valve functional verification Pump cavitation Electrical arcing y g Electrical system corona discharge Heat exchanger and condenser tube and tube sheet leakage Boiler monitoring Boiler tube leakage Tank and pressure vessel leakage Enclosure leakage inspection
Vision Service Partnership
Page 11
NSTec Presentation Title
Ultrasound Ult so d
Vision Service Partnership
Page 12
NSTec Presentation Title
Vibration Analysis Vib tio A l sis
E i Equipment startup acceptance and commissioning t t t t d i i i Rotating equipment analysis on HVAC, Pumps, Motors, Bearings, Gearboxes, Belt-Drives, etc. High speed, >600 RPM component vibration analysis speed RPM, ibration anal sis Low speed, <600 RPM, component vibration analysis Shock pulse analysis (bearing lubrication issues) Structural analysis Looseness of transformer coils Misalignment Belt tension and alignment Unbalance condition Lubrication issues Bad bearings Mechanical looseness Worn gears Electrical problems (rotor & stator issues)
Vision Service Partnership
Page 13
NSTec Presentation Title
Vibration Analyzer Vib tio A l
Vision Service Partnership
Page 14
NSTec Presentation Title
Off-Line Moto /T Off Li Motor/Transformer Tester A sfo T st Analyzer l
Detects any type of motor electrical fault: Turn-to-turn, coil-to-coil, and phase-to-phase faults Shorted windings Open phases Burned or contamination windings Insulation breakdown Poor connections Ground faults Phase unbalances Cable faults Cab e au ts All types of rotor faults. Example: Broken/cracked rotor bars and rotor casting voids & Rotor eccentricity Good for testing spare motors to confirm their status and insures against installing a faulty motor i t i t lli f lt t NOTE: It tests virtually any size or type of motor, generator or transformer, transformer even from a remote locations locations.
Vision Service Partnership
Page 15
NSTec Presentation Title
On-Line Moto /T O Li Motor/Transformer Tester A sfo T st Analyzer l
Motor Current Si M t C t Signature A l i Evaluate, Detect, and Monitor: t Analysis E l t D t t d M it Stator electrical and mechanical health Rotor bar health Air gap/eccentricity issues Mechanical component health including bearings, balance and alignment, alignment and driven equipment Adaptors for external equipment plug in
Vision Service Partnership
Page 16
NSTec Presentation Title
All Test Pro Off Line Motor/Transformer Tester Off-Line Analyzer
Vision Service Partnership
Page 17
NSTec Presentation Title
Oil, L b i Oil Lubricant and W t d Wear P ti l A Particle Analysis l sis
Choose the tests that are appropriate for your piece of equipment and pp p y p q p oil type! Example of Various Transformer Oil Tests: Dissolved gas analysis (DGA or TOGA) (ASTM D 3612) Water Content (D 1533) Acid Number (TAN-E) (D 664) Interfacial Tension (D 971) y Myers Index = IFT/TAN Color (D 1500) Dielectric Breakdown (D 1816) Polychlorinated Biphenyls (D 4059) Furanic Compounds (D 5837)
Vision Service Partnership
Page 18
NSTec Presentation Title
Oil, L b i Oil Lubricant and W t d Wear P ti l A Particle Analysis l sis
Trace Elements (D5185) T El t Particle Counts (ASTM draft method) y (RBOT) ( 2112) ) (D ) Oxidation Stability ( Oxidation Inhibitor Content (D 2668) Power Factor (D 924) Specific Gravity (D 1298) Viscosity (D 445) Static Charge Density Halogens (D5384 and D808) Flash Point (D 92)
Vision Service Partnership
Page 19
NSTec Presentation Title
Proactive Maintenance P o tiv M i t
What i Wh t is proactive maintenance? While preventive and predictive ti i t ? Whil ti d di ti maintenance seek to catch and prevent symptoms before they result in breakdowns, proactive programs seek to lessen or eliminate the root causes. Proactive maintenance is a maintenance strategy for causes stabilizing the reliability of machines or equipment. Its central theme involves directing corrective actions aimed at failure root causes, not active failure symptoms, faults, or machine wear conditions. A typical proactive maintenance regiment involves three steps: (1) setting a quantifiable target or standard relating to a root cause of concern (e.g., a target fluid cleanliness level for a lubricant), (2) implementing a maintenance program to control the root cause property to within the target level (e.g., routine exclusion or removal of contaminants), and (3) routine monitoring of the root cause property using a measurement technique (e.g., particle counting) to verify the current level is within the target.
Vision Service Partnership
Page 20
NSTec Presentation Title
Proactive Maintenance P o tiv M i t
According to major industries throughout the world, its time to A di j i d i h h h ld i i throw out your old ideas on machine maintenance. The costsaving trend is toward a maintenance program that targets the root causes of machine wear and failure. Preventive methods are out: proactive maintenance are in. Why? Because proactive maintenance methods are currently saving industries of all y g sizes thousands, even millions, of dollars on machine maintenance every year. According to DuPont, maintenance is the largest single controllable expenditure in a plant. In many plant companies it often exceeds annual net profit. The problem of costly maintenance has truly reached a serious level, but as some companies have found out, and more come to realize out every day, their maintenance costs can be cut drastically by establishing a proactive line of defense.
Vision Service Partnership
Page 21
NSTec Presentation Title
Proactive Maintenance P o tiv M i t
Proactive maintenance uses the following basic techniques to P i i h f ll i b i h i extend machinery life:
Proper installation and precision rebuild Failed-parts analysis Root-cause f il R t failure analysis l i Reliability engineering Rebuild certification/verification Age exploration Recurrence control Continuous monitoring of things such as lubricants, hydraulic lubricants fluids and coolants Developing strict contamination control program for: lubrication fluids, fluids hydraulic fluids, gear oils, and transmission fluids fluids oils
Vision Service Partnership
Page 22
NSTec Presentation Title
RCM
Reliability-Centered M i R li bili C d Maintenance, often known as RCM i an f k RCM, is industrial improvement approach focused on identifying and establishing the operational, maintenance, and capital improvement policies that will manage the risks of equipment failure most effectively. Reliability Centered Maintenance can be used to create a cost-effective maintenance strategy to address dominant causes gy of equipment failure. It is a systematic approach to defining a routine maintenance program composed of cost-effective tasks that preserve important functions It is defined by the technical standard functions. SAE JA1011.
Vision Service Partnership
Page 23
NSTec Presentation Title
The Th RCM P o ss Process
Phase 1 consists of identifying the functions of the equipment, Ph i t f id tif i th f ti f th i t identifying the functional failures, identify the different failure modes, identify the effects of the failure modes (at the plant level), identify the consequences conseq ences to the facility as a result of the failure effects This is facilit res lt fail re effects. the COFA (Consequence of failure analysis) evaluation analysis process. Phase 2 consist of specifying the appropriate maintenance task (PM, PdM, Proactive, or simply RTF) for the equipment identified in Phase 1. These tasks must be both applicable and effective. This phase also Th k b b h li bl d ff i Thi h l includes a very prescriptive method for identifying default actions if an applicable and effective preventive task cannot be found. Phase 3 consists of properly executing the tasks specified in phase 2 and includes the sustainment process.
Vision Service Partnership
Page 24
NSTec Presentation Title
Conclusion Co l sio
A proactive maintenance program is the capstone of an RCM ti i t i th t f philosophy. From the RCM program you can develop the appropriate maintenance philosophy to use for a particular piece of equipment whether it is run-to-fail, pre entati e predicti e or proacti e hether is: r n to fail preventative, predictive, proactive.
Vision Service Partnership
Page 25
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Lesson 3 - Materials That Undergo DecayDocument14 pagesLesson 3 - Materials That Undergo DecayFUMIKO SOPHIA67% (6)
- VSP-12Way - Is Rev.03Document55 pagesVSP-12Way - Is Rev.03Marcelo AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- Managing operations service problemsDocument2 pagesManaging operations service problemsJoel Christian Mascariña0% (1)
- WASTE HEAT RECOVERY (HRSG) PerformanceDocument17 pagesWASTE HEAT RECOVERY (HRSG) PerformanceEjaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Auxiliary Systems Guide SBU 130MW PlantDocument13 pagesAuxiliary Systems Guide SBU 130MW PlantChanna BasavaNo ratings yet
- 2 X 115 TPH CFBC Boiler: Ultratech Cement Limited - Apcw TadipatriDocument51 pages2 X 115 TPH CFBC Boiler: Ultratech Cement Limited - Apcw TadipatriChanna BasavaNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat Recovery Power Plant Load Trials ReportDocument22 pagesWaste Heat Recovery Power Plant Load Trials ReportChanna BasavaNo ratings yet
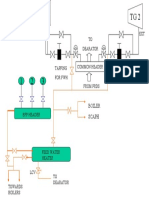
- TG1 TG2: TO Dearator Tapping For FWH Tapping For FWH EXT EXTDocument1 pageTG1 TG2: TO Dearator Tapping For FWH Tapping For FWH EXT EXTChanna BasavaNo ratings yet
- 2X70 Power Plant Technical SpecificationDocument53 pages2X70 Power Plant Technical SpecificationChanna BasavaNo ratings yet
- APCW TadipatriDocument25 pagesAPCW TadipatriChanna BasavaNo ratings yet
- 4 MW Waste Heat Recovery Power Plant Performance ReportDocument24 pages4 MW Waste Heat Recovery Power Plant Performance ReportChanna BasavaNo ratings yet
- Turbine: Dumping Control ValveDocument2 pagesTurbine: Dumping Control ValveChanna BasavaNo ratings yet
- 9 (1) .Power Plant CyclesDocument20 pages9 (1) .Power Plant CyclesChanna BasavaNo ratings yet
- DrivesDocument17 pagesDrivesanjes1No ratings yet
- Electrical InstrumentationDocument1 pageElectrical InstrumentationChanna BasavaNo ratings yet
- Drum Level CompensationDocument8 pagesDrum Level CompensationSmriti PrasadNo ratings yet
- Quotatioon 243 SWMLDocument2 pagesQuotatioon 243 SWMLChanna BasavaNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Inspection Standards for Wrought MetalsDocument44 pagesUltrasonic Inspection Standards for Wrought Metalsdomsoneng100% (1)
- Harry Styles: The Rise of a Pop StarDocument9 pagesHarry Styles: The Rise of a Pop StarBilqis LaudyaNo ratings yet
- A Research About The Canteen SatisfactioDocument50 pagesA Research About The Canteen SatisfactioJakeny Pearl Sibugan VaronaNo ratings yet
- Jodi Ridgeway vs. Horry County Police DepartmentDocument17 pagesJodi Ridgeway vs. Horry County Police DepartmentWMBF NewsNo ratings yet
- GSM Multi-Mode Feature DescriptionDocument39 pagesGSM Multi-Mode Feature DescriptionDiyas KazhiyevNo ratings yet
- Maths Lit 2014 ExamplarDocument17 pagesMaths Lit 2014 ExamplarAnymore Ndlovu0% (1)
- Safety of High-Rise BuildingsDocument14 pagesSafety of High-Rise BuildingsHananeel Sandhi100% (2)
- Ethical Leadership Karen May P. UrlandaDocument8 pagesEthical Leadership Karen May P. UrlandaKaren May UrlandaNo ratings yet
- Brightline Guiding PrinciplesDocument16 pagesBrightline Guiding PrinciplesdjozinNo ratings yet
- 1 N 2Document327 pages1 N 2Muhammad MunifNo ratings yet
- DAP FullTextIntroductionByStuartLichtman PDFDocument21 pagesDAP FullTextIntroductionByStuartLichtman PDFAlejandro CordobaNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship and EconomicDocument2 pagesEntrepreneurship and EconomicSukruti BajajNo ratings yet
- Research Design Elements for ScenariosDocument25 pagesResearch Design Elements for Scenariosrohizal ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Company's Profile Presentation (Mauritius Commercial Bank)Document23 pagesCompany's Profile Presentation (Mauritius Commercial Bank)ashairways100% (2)
- Norms and specifications for distribution transformer, DG set, street light poles, LED lights and high mast lightDocument4 pagesNorms and specifications for distribution transformer, DG set, street light poles, LED lights and high mast lightKumar AvinashNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management NotesDocument115 pagesMarketing Management NotesKajwangs DanNo ratings yet
- LNGC Q-Flex Al Rekayyat - Imo 9397339 - Machinery Operating ManualDocument581 pagesLNGC Q-Flex Al Rekayyat - Imo 9397339 - Machinery Operating Manualseawolf50No ratings yet
- fr1177e-MOTOR CUMMINS 195HPDocument2 pagesfr1177e-MOTOR CUMMINS 195HPwilfredo rodriguezNo ratings yet
- United States Court of Appeals, Third CircuitDocument3 pagesUnited States Court of Appeals, Third CircuitScribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- A Dream Takes FlightDocument3 pagesA Dream Takes FlightHafiq AmsyarNo ratings yet
- Article. 415 - 422Document142 pagesArticle. 415 - 422Anisah AquilaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - Mech 3rd YearDocument130 pagesSyllabus - Mech 3rd YearAbhishek AmarNo ratings yet
- Axtraxng™: Networked Access Control Management Software V27.XDocument2 pagesAxtraxng™: Networked Access Control Management Software V27.XChiluvuri VarmaNo ratings yet
- ECED Lab ReportDocument18 pagesECED Lab ReportAvni GuptaNo ratings yet
- Books 2738 0Document12 pagesBooks 2738 0vinoohmNo ratings yet
- Huawei 9000aDocument27 pagesHuawei 9000aAristideKonanNo ratings yet
- User-Centered Website Development: A Human-Computer Interaction ApproachDocument24 pagesUser-Centered Website Development: A Human-Computer Interaction ApproachKulis KreuznachNo ratings yet