Professional Documents
Culture Documents
5 Kaizen Supplementary Material
Uploaded by
Amer RahmahOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
5 Kaizen Supplementary Material
Uploaded by
Amer RahmahCopyright:
Available Formats
KAIZEN Management
KAIZEN Management
(Supplementary materials)
Graduate School of Asia-Pacific Studies Waseda University, Tokyo Professor Dr. Seiichi FUJITA
fujitas@waseda.jp http://www.wiaps.waseda.ac.jp/user/fujita/
Copyright S. Fujita
KAIZEN Management
Industrial 1
Industrial 2
What are these?
Industrial Collection
The Japan HR Association
Bolt Nut Washer
The Japan HR Association
The Japan HR Association
Industrial 3
Industrial 4
Washer (Before KAIZEN)
It is difficult to pick up a washer placed on a table.
Washer (After KAIZEN 1)
Curved table
Thin sponge
The Japan HR Association The Japan HR Association
Industrial 5
Industrial 6
Washer (After KAIZEN 2)
Drawer (Before KAIZEN)
Workers had to bend to read the label of the tool drawer. Well
Wrench
10 cm thick sponge
Label
The Japan HR Association
The Japan HR Association
Copyright S. Fujita
KAIZEN Management
Industrial 7
Industrial 8
Drawer (After KAIZEN 1)
The tool drawers were lifted up, but another problem occurred.
Easy to look.
Difficult to pick up
Drawer (After KAIZEN 2)
Names of tools were listed in a table. It was posted on a wall.
Heres a wrench
The Japan HR Association
The Japan HR Association
Industrial 9
Industrial 10
Flag Pulley (Before KAIZEN)
The metal pulley located at the top of the pole made noise.
Sque ak !
Oil is needed. Noisy
Picture of Flag Pole
The Japan HR Association
The Japan HR Association
Industrial 11
Industrial 12
Flag Pulley (After KAIZEN)
A vinyl bag in which oil was contained was tied with rope. The bag would break at the pulley.
Oil
Vinyl bag
Time Table (Before KAIZEN)
When a fluorescent lamp burn out, it had to be replaced by two workers.
Hey! Are you done?
Wait a second.
The Japan HR Association The Japan HR Association
Copyright S. Fujita
KAIZEN Management
Industrial 13
Industrial 14
Time Table (After KAIZEN 1)
The worker who supported the cover was replaced by a pole.
Time Table (After KAIZEN 2)
A handy tool with a sharp edge was made.
Simple Handy Safe
Ah!
A flexible vise Sharp edge
Rubber coating
The Japan HR Association
The Japan HR Association
Industrial 15
Industrial 16
Tank (Before KAIZEN)
When drawing out the water, the hose stuck to the bottom of the tank frequently.
Tank (After KAIZEN)
A T-shaped joint was attached to the tip of the hose.
The Japan HR Association
The Japan HR Association
Industrial 17
Industrial 18
Bumper Car (Before KAIZEN)
A worker found a nut on the floor. Which bumper car lost it?
Bumper Car (After KAIZEN)
Each car, as well as the nut, was painted with a same color.
Same color
The Japan HR Association
The Japan HR Association
Copyright S. Fujita
KAIZEN Management
Industrial 19
Industrial 20
Bulb (Before KAIZEN)
The hand was too big to reach the burnt out bulb.
Uh m !
Bulb (After KAIZEN)
Push a rubber hose to replace the bulb. Rubber Easy
hose
installation and removal
The Japan HR Association
The Japan HR Association
Industrial 21
Industrial 22
Bulb (Application)
A hose is used to pick up a cap of the tire at Japanese gas stations. This way
It was difficult to move the bulb cap.
Oyster (Before KAIZEN)
In winter, workers requested a pair of gloves to keep hands warm. However, a use of rubber gloves made the work more difficult.
never loses the cap.
The Japan HR Association
The Japan HR Association
Industrial 23
Industrial 24
Oyster (After KAIZEN)
Tips of thumb and forefinger of the rubber gloves were cut off.
Bucket (Before KAIZEN)
At the company dormitory, buckets with water were placed at several locations for fire prevention. Many people were stumbling over the buckets and the floor was flooded.
The Japan HR Association
The Japan HR Association
Copyright S. Fujita
KAIZEN Management
Industrial 25
Bucket (After KAIZEN)
The water was packed with a transparent vinyl plastic bag, and it was placed in the bucket. This could prevent the water from flooding and could be usable in case of a fire.
The Japan HR Association
Copyright S. Fujita
KAIZEN Management
World 1
World 2
Egypt
World Collection
FUJITA
Egypt Pyramids
World 3
World 4
Highway (Before KAIZEN)
Difficult to take a left turn.
by El-Kashef Osman
(Egypt)
World 5
World 6
Highway (After KAIZEN)
U-turn zone makes left turns easy.
U-turn zone
Sink (Before KAIZEN)
Product Shape
90 Side View
by El-Kashef Osman
(Egypt)
by Sayed Ibrahim (Egypt)
Copyright S. Fujita
KAIZEN Management
World 7
World 8
Sink (After KAIZEN) Mongolia
by Sayed Ibrahim (Egypt)
Mongolia Green
World 9
Mongolia Summer (June 96)
World 10
Mongolia Winter (November 98)
World 11
World 12
Sheep (Before KAIZEN)
One must stay to push the sheeps head into the water.
by Dorjsursn (Mongolia)
Copyright S. Fujita
KAIZEN Management
World 13
World 14
Sheep (After KAIZEN)
By making a ditch at the bottom of the pool, the sheeps head goes underwater by itself.
Knitting (Before KAIZEN)
Yarn balls are rolling and mixed up.
by Dorjsursn (Mongolia)
by Munkhtsetseg
(Mongolia)
World 15
World 16
Knitting (Before KAIZEN)
Yarn balls are placed in a container.
Ghana
by Munkhtsetseg (Mongolia)
Picture Ghana 1
World 17
Picture Ghana 2
World 18
Copyright S. Fujita
KAIZEN Management
World 19
World 20
Carry Water (Before
KAIZEN)
Ghana Pic.
by Harun (Ghana)
World 21
World 22
Carry Water (After KAIZEN)
He fetches water directly into bucket on his head.
Goat (Before KAIZEN)
When an owner calls them back home, a goat will head home, but a sheep will not.
by Harun (Ghana)
by Asare Bedman
(Ghana)
World 23
World 24
Goat (After KAIZEN)
By tying both animals, they both came back home together.
Sri Lanka
by Asare Bedman
(Ghana)
Copyright S. Fujita
10
KAIZEN Management
World 25
World 26
Sri Lanka Fruits 1
Sri Lanka Fruits 2
What is this fruit ?
Kandy, Sri Lanka
World 27
World 28
Problem (India) What is written on the red signal?
1. STOP 2. WAIT 3. RELAX
India
4. DONT DRIVE 5. DONT WALK
World 29
World 30
Answer 1 (India)
Answer 2 (India)
1. STOP 2. WAIT 3. RELAX 4. DONT DRIVE 5. DONT WALK
1. STOP 2. WAIT 3. RELAX 4. DONT DRIVE 5. DONT WALK
Copyright S. Fujita
11
KAIZEN Management
World 31
Qatar What is this?
Picture Qatar 1
World 32
The Japan HR Association
World 33
World 34
Picture Qatar 2
What can you buy from this vending machine?
The Japan HR Association
Japan
World 35
World 36
Answer: EGGS
China
(Taiwan)
Copyright S. Fujita
12
KAIZEN Management
World 37
World 38
Expel Fly (Before KAIZEN)
Expel Fly (After KAIZEN)
Water balloon magnifies the flys image to frighten the fly.
by Liao Chien-Hung
(R.O.C.)
by Liao Chien-Hung (R.O.C.)
Copyright S. Fujita
13
KAIZEN Management
Reference books
Many reference books are available. You may search Amazon.com by putting one of the following keywords: KAIZEN, 5S, JIT or Toyota. Some reference books which are recommended to have a deep understanding for KAIZEN Management are listed as follows: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Tozawa Bunji, Norman Bodok The Idea Generator: Quick and Easy Kaizen PCS Press 2001 Imai Masaaki Kaizen (Kyzen): the key to Japans competitive success McGraw Pub. 1986 Japan Human Relations Association The improvement engine: creativity & innovation through employee involvement: The Kaizen Teian system Productivity Press, 1995 Osada Takashi The 5Ss: five keys to a total quality environment Asian Productivity Organization, 1995 Hirano Hiroyuki Putting 5S to work: a practical step-by-step approach PHP Institute, 1993 Shingo Shigeo A revolution in manufacturing: the SMED system Productivity Press, 1985 Shingo Shigeo A study of the Toyota production system from an industrial engineering viewpoint Productivity Press, 1989 Christensen Clayton The innovators Dilemma Harper Collins, 2003 Utterback James Mastering the Dynamics of Innovation: How companies can seize opportunities inn the face of technological change Harvard Business School Press, 1994
10. Sugiyama Tomoo 5S approach to improvement PHP Institute, 1998 11. Ohno Taiichi Toyota production system: Beyond large-scale production Productivity Press, 1988 12. Shingo Shigeo Non-stock production: The Shingo System for Continuous Improvement Productivity Press, 1995 13. Liker Jeffrey The Toyota Way: 14 Management Principles from the Worlds Greatest Manufacturer, McGraw-Hill 2004 14. Robinson, Alan (Editor) The continuous improvement in Operations: A systematic Approach to Waste Reduction Productivity Press, 1991 15. Japan HR Association KAIZEN Teian I: Development systems for Continuous Improvement through Employee Suggestions Productivity Press 1992 16. Japan HR Association KAIZEN Teian II: Guiding Continuous Improvement through Employee Suggestions Productivity Press, 1992 17. Japan HR Association The Idea Book: Improvement through TEI (Total Employee Involvement) Productivity Press 18. Hirano, H. JIT Factory Revolution: A Pictorial Guide to Factory Design of the Future Productivity Press. ISBN 0-915299-44-5 19. Majima, I. The shift to JIT: How people make the difference Productivity Press. ISBN0-9915299-93-3 20. Monden, Y. Toyota Production Systems Institute of Industrial Engineers. 1983
Copyright S. Fujita
14
KAIZEN Management
KAIZEN awareness check 1
1. A driving force to KAIZEN activities is a. Monetary award b. Problem consciousness c. Workers' motivation d. Management skill "Innovation" (in contrast to KAIZEN) is a. A short cut approach b. A new fashion c. A good management d. A big change KAIZEN is defined as a. An accumulation of small changes b. A quick way of changing your work c. A method to increase productivity d. A good manner KAIZEN steps are defined as a. Change - Eliminate - Reduce b. Reduce - Change - Eliminate c. Eliminate - Reduce - Change d. Simplify - Combine - Remove Approximately what percent of Japanese companies seems to adopt KAIZEN suggestion system? a. 40% b. 70% c. 90% d. 100% Japanese production managers believe that the most important issue/concept for production management in 1990's is a. Reduction of production lead-time b. Integration of production and sales c. Improvement of customer service d. Marketing research
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7. An original idea of JIT came from a. Drive-in theater b. Fast food restaurant c. Supermarket d. Gas station 8. KANBAN which is used in JIT production systems is a. A tool to supply products to customers b. A tool to fill up parts which are used. c. A sign for alarm d. A billboard
Copyright S. Fujita
15
9.
"Poka-Yoke (Fool proof) devices" are a. Protection devices from earthquake and typhoons b. Devices which increase production volume c. Devices which motivates production workers d. Devices which eliminate operator's careless mistakes A purpose of minimum inventory (stockless production) is a. To find out (or visualize) problems to be improved. b. To enhance management capability for the risk. c. To make inventory control easy. d. To save inventory cost. The 5S stands for a. Five times more satisfaction b. Five keys for success c. Five Japanese words with an initial S d. Five factors for a work improvement The average time allowed to fetch (search, find and bring back) a hammer is a. 10 seconds b. 30 seconds c. 60 seconds d. 90 seconds For a facility investment, approximately how much is used for cleanliness? a. 80% of the investment cost b. 60% of the investment cost c. 30% of the investment cost d. 10% of the investment cost The essence of "Seiso (cleaning)" is a. An inspection b. Picking up a garbage c. A search d. A standardization
KAIZEN Management
10.
11.
12.
13.
14.
15. The essence of " Shitsuke (self-discipline) " is a. To set up a rule b. To let people greet to each other c. A communication d. A habit formation
Copyright S. Fujita
16
KAIZEN Management
KAIZEN awareness check 2
[KAIZEN] 1. A driving force to KAIZEN activities is a. Monetary award b. Problem consciousness c. Workers' motivation d. Management skill "Innovation" (in contrast to KAIZEN) is a. A short cut approach b. A new fashion c. A good management d. A big change KAIZEN is defined as a. An accumulation of small changes b. A quick way of changing your work c. A method to increase productivity d. A good manner What does KAIZEN change? a. Change - Eliminate - Reduce b. Reduce - Change - Eliminate c. Eliminate - Reduce - Change d. Simplify - Combine Remove KAIZEN steps are defined as a. Change - Eliminate - Reduce b. Reduce - Change - Eliminate c. Eliminate - Reduce - Change d. Simplify - Combine - Remove For KAIZEN suggestion system, what type of ideas must be submitted? a. Ideas to change company policy b. Ideas to change your own work c. Ideas to improve profit d. Ideas to improve management style Approximately what percent of Japanese companies seems to adopt KAIZEN suggestion system? a. 40% b. 70% c. 90% d. 100%
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Copyright S. Fujita
17
[JIT] 1.
KAIZEN Management
Japanese production managers believe that the most important issue/concept for production management in 1990's is a. Reduction of production lead-time b. Integration of production and sales c. Improvement of customer service d. Marketing research
2. An original idea of JIT came from a. Drive-in theater b. Fast food restaurant c. Supermarket d. Gas station 3. A factor which makes your production schedule difficult is a. A demand fluctuation b. A marketing strategy c. An employee involvement d. A bonus incentives KANBAN which is used in JIT production systems is e. A tool to supply products to customers f. A tool to fill up parts which are used. g. A sign for alarm h. A billboard An aim of one-piece flow is a. A high productivity b. A high flexibility c. A low defective rate d. A low cost "Poka-Yoke (Fool proof) devices" are a. Protection devices from earthquake and typhoons b. Devices which increase production volume c. Devices which motivates production workers d. Devices which eliminate operator's careless mistakes A purpose of minimum inventory (stockless production) is a. To find out (or visualize) problems to be improved. b. To enhance management capability for the risk. c. To make inventory control easy. d. To save inventory cost.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Copyright S. Fujita
18
[5S] 1.
KAIZEN Management
The 5S stands for a. Five times more satisfaction b. Five keys for success c. Five Japanese words with an initial S d. Five factors for a work improvement The purpose of theRed Tag Movement is a. To distinguish the necessary things and unnecessary things b. To clean up a workplace c. To decorate products d. To find the shortest way of achieving an objective The average time allowed to fetch (search, find and bring back) a hammer is a. 10 seconds b. 30 seconds c. 60 seconds d. 90 seconds For a facility investment, approximately how much is used for cleanliness? a. 80% of the investment cost b. 60% of the investment cost c. 30% of the investment cost d. 10% of the investment cost The essence of "Seiso (cleaning)" is a. An inspection b. Picking up a garbage c. A search d. A standardization A problemis defined as a. Homework assignment b. Objects which you must attack c. A gap between ideal state and current state d. Something which you can buy at supermarket The essence of " Shitsuke (self-discipline) " is a. To set up a rule b. To let people greet to each other c. A communication d. A habit formation The value offixed-position photographic approach is a. Employees involvement b. Customer satisfaction c. Job rotation d. Quality improvement
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Copyright S. Fujita
19
KAIZEN Management
Instructions:
Copyright S. Fujita
Draw sketches of Before KAIZEN and After KAIZEN Use a DARK black pen or a THICK pencil
20
You might also like
- Overview of TGA's Involvement in The International Regulatory EnvironmentDocument30 pagesOverview of TGA's Involvement in The International Regulatory EnvironmentAmer RahmahNo ratings yet
- IntdDocument13 pagesIntdAmer RahmahNo ratings yet
- Pics Guide For GMP and Data Integrity Relating To Microbiological Quality 181220050451Document20 pagesPics Guide For GMP and Data Integrity Relating To Microbiological Quality 181220050451Amer RahmahNo ratings yet
- Sop-Gen 013 Business Continuity PlanDocument4 pagesSop-Gen 013 Business Continuity PlanAmer RahmahNo ratings yet
- Boarding PassDocument1 pageBoarding PassAmer RahmahNo ratings yet
- Exercise: Group 1Document5 pagesExercise: Group 1Amer RahmahNo ratings yet
- 9001 Audit Checklist - Quality Planning and DesignDocument14 pages9001 Audit Checklist - Quality Planning and DesignAmer RahmahNo ratings yet
- 9001 Planning Checklist - Production ProcessDocument14 pages9001 Planning Checklist - Production ProcessAmer RahmahNo ratings yet
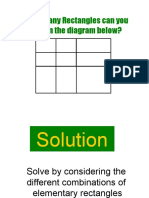
- How Many Rectangles Can You See in The Diagram Below?Document10 pagesHow Many Rectangles Can You See in The Diagram Below?Amer RahmahNo ratings yet
- David L Chesney Parexel International UsaDocument34 pagesDavid L Chesney Parexel International UsaAmer RahmahNo ratings yet
- Balance Scorecard NoqDocument57 pagesBalance Scorecard NoqAmer Rahmah100% (1)
- Handout 4 - Audit PlanningDocument1 pageHandout 4 - Audit PlanningAmer RahmahNo ratings yet
- Quotation: Date: Mr. Attention Test Drive ProjectDocument2 pagesQuotation: Date: Mr. Attention Test Drive ProjectAmer RahmahNo ratings yet
- Corporate Values Organization Practices Success Habits TaboosDocument4 pagesCorporate Values Organization Practices Success Habits TaboosAmer RahmahNo ratings yet
- Decision and GamesDocument527 pagesDecision and GamesAmer RahmahNo ratings yet
- Teaching Risk Management Using Jenga GameDocument1 pageTeaching Risk Management Using Jenga GameAmer RahmahNo ratings yet
- Hazards Risk Management - Final SyllabusDocument7 pagesHazards Risk Management - Final SyllabusAmer RahmahNo ratings yet
- Audit One-Liner Form: One Line Description of The Nonconformity/opportunity For ImprovementDocument1 pageAudit One-Liner Form: One Line Description of The Nonconformity/opportunity For ImprovementAmer RahmahNo ratings yet
- Audit Program Survey: of The Audit Team?Document3 pagesAudit Program Survey: of The Audit Team?Amer RahmahNo ratings yet
- QMS Audit Checklist 1 - Area Manager-Owner InterviewDocument1 pageQMS Audit Checklist 1 - Area Manager-Owner InterviewAmer RahmahNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Gitau - The Effect of Inventory Management Practices On Operational Performance of Warehousing Firms in Mombasa CountyDocument60 pagesGitau - The Effect of Inventory Management Practices On Operational Performance of Warehousing Firms in Mombasa CountyJamieNo ratings yet
- MIS Report On Pantaloon RetailDocument11 pagesMIS Report On Pantaloon RetailRohit GoyalNo ratings yet
- Inventory Control TechniquesDocument15 pagesInventory Control TechniquesNikhil ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Preparation Auditing II: Condition Yang Terjadi Dan Mempengaruhi Akun-Akun Sebelum TanggalDocument5 pagesFinal Exam Preparation Auditing II: Condition Yang Terjadi Dan Mempengaruhi Akun-Akun Sebelum TanggalAlvira FajriNo ratings yet
- Fall 2006 Chemco Case Study Page 1 of 5Document5 pagesFall 2006 Chemco Case Study Page 1 of 5Byron Galáctico RodríguezNo ratings yet
- MRP, Jit, ErpDocument26 pagesMRP, Jit, ErpRupendra TripathiNo ratings yet
- Pom - Inventory ManagementDocument5 pagesPom - Inventory ManagementMURALI KRISHNA VELAVETI Dr.No ratings yet
- Management Information Question Bank 2019Document336 pagesManagement Information Question Bank 2019k20b.lehoangvu100% (1)
- Erp Implementation in SmeDocument5 pagesErp Implementation in SmeArpit SaxenaNo ratings yet
- This Job?Document6 pagesThis Job?JO SH UANo ratings yet
- Idea Cellular StrategyDocument45 pagesIdea Cellular Strategybrmehta06No ratings yet
- Current Theory and Management PracticeDocument9 pagesCurrent Theory and Management PracticeJesa CamilanNo ratings yet
- Masquerade (Regional Eliminations)Document5 pagesMasquerade (Regional Eliminations)Ayvee BlanchNo ratings yet
- Epicor ERP Inventory Transactions Technical Reference GuideDocument88 pagesEpicor ERP Inventory Transactions Technical Reference GuideVMRO100% (1)
- National Human Right Organisation: Mannual BookDocument27 pagesNational Human Right Organisation: Mannual BookPawan KumarNo ratings yet
- Notes Management AccountingDocument23 pagesNotes Management AccountingAbidNo ratings yet
- Periodic Review Inventory Model WithDocument18 pagesPeriodic Review Inventory Model WithDr-Mohammed FaridNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM 1: Materials Added at The of The ProcessDocument5 pagesPROBLEM 1: Materials Added at The of The ProcessEarl Hyannis ElauriaNo ratings yet
- Pom CH1Document64 pagesPom CH1Syed Zain AhmadNo ratings yet
- Accounting Ratios - NotesDocument7 pagesAccounting Ratios - NotesgiloralaboraNo ratings yet
- Master Production ScheduleDocument21 pagesMaster Production ScheduleLogeshkumar JNo ratings yet
- Charaf Hamdouni Resume21Document7 pagesCharaf Hamdouni Resume21CharafNo ratings yet
- Audit Project-A514: Provided byDocument22 pagesAudit Project-A514: Provided bySaad MajeedNo ratings yet
- Revenue: MaicsaDocument13 pagesRevenue: MaicsaJamilah EdwardNo ratings yet
- Category Management and Assortment Planning PresentationDocument29 pagesCategory Management and Assortment Planning Presentationpavankks50% (2)
- Vendor Identification Selection and EvaluationDocument13 pagesVendor Identification Selection and Evaluationaravind rxNo ratings yet
- Revenue (Ifrs 15)Document43 pagesRevenue (Ifrs 15)Sherlock HomlesNo ratings yet
- SEC MC FVB Enablement - SD v1Document66 pagesSEC MC FVB Enablement - SD v1kodyNo ratings yet
- Health Economics Paper FinalDocument29 pagesHealth Economics Paper FinalVonrey Tiana73% (11)
- Manual On The Financial Management of BarangaysDocument30 pagesManual On The Financial Management of BarangaysKathleenNo ratings yet