Professional Documents
Culture Documents
UHS Entry Test Syllabus 2012
Uploaded by
Nauman AhmadOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
UHS Entry Test Syllabus 2012
Uploaded by
Nauman AhmadCopyright:
Available Formats
SYLLABUS
FOR
ENTRANCE TEST
2012
UNI VERSI TY OF HEALTH SCI ENCES
LAHORE, PAKI STAN
STRUCTURE OF ENTRANCE TEST PAPER 2012
Sr. # Subj ect No. of
Quest ions
1.
PHYSI CS
44
2.
CHEMI STRY
58
3.
ENGLI SH
30
4.
BI OLOGY
88
TOTAL
220
CONTENTS PAGE#
PHYSI CS
Syllabus 1- 5
TOS 6
Self Test Quest ions 7- 9
CHEMI STRY
Syllabus 10- 21
TOS 22
Self Test Quest ions 23- 28
ENGLI SH
Syllabus
29- 34
Self Test Quest ions 35- 36
BI OLOGY
Syllabus 37- 44
TOS 45
Self Test Quest ions 46- 51
1
PHYSI CS
STRUCTURE OF THE SYLLABUS ( 2012)
F.Sc. and Non- F.Sc.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. Physi cal Quant it i es and Unit s
2. Forces
3. Fl ui d Dynami cs
4. Li ght
5. Waves
6. Deformat i on of Soli ds
7. I deal Gases
8. Heat and Thermodynamics
9. El ect roni cs
10. Current Elect ri cit y
11. Magnet i sm and El ect romagnet i sm
12. Modern Physi cs
13. Nucl ear Physi cs
2
1. PHYSI CAL QUANTI TI ES AND UNI TS:
Learning Out comes
a) Underst and what is physics.
b) Underst and t hat all physical quant it ies consist of a numerical magnit ude and a unit .
c) Recall t he following base quant it ies and t heir unit s; mass ( kg) , lengt h ( m) , t ime ( s) ,
current (A) , t emperat ure ( K) , luminous int ensit y ( cd) and amount of subst ance (mol)
d) Describe and use base unit s and derived unit s.
e) Dimensional unit s of physical quant it ies.
2. FORCES:
Learning Out comes
a) Show an underst anding t he concept of weight .
b) Show an underst anding t hat t he weight of a body may be t aken as act ing at a single
point known as it s cent re of gravit y.
c) Weight lessness in an elevat or.
d) Define and apply t he moment of force.
3. FLUI D DYNAMI CS:
Learning Out comes
a) Concept of viscosit y.
b) Underst and t he t erms st eady ( Laminar, st reamline) flow, incompressible flow, non-
viscous flow as applied t o t he mot ion of an ideal fluid.
c) Appreciat e t he equat ion of cont inuit y.
2 2 1 1
V A V A = for t he flow of an ideal and incompressible fluid.
d) Underst and Bernoullis equat ion
= + + gh v P
2
2
1
Const ant
e) Underst and t hat t he pressure difference can arise from different rat es of flow of a fluid
( Blood flow) .
3
4. LI GHT:
Learning Out comes
a) Underst and int erference of light .
b) Underst and diffract ion of light .
c) Describe t he phenomenon of diffract ion of X- rays by cryst als and it s use.
d) Underst and polarizat ion of light .
e) Concept s of least dist ance of dist inct vision.
- Short sight edness, long sight edness.
f) Underst and t he t erms magnifying power and resolving power
( = R
min
1
, = R
A
) of opt ical inst rument s.
g) Derive expressions for magnifying power of simple microscope and compound
microscope.
h) Underst and t he principle of opt ical fibres, t ypes and it s applicat ion.
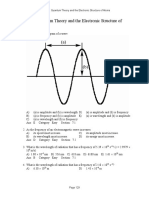
5. WAVES:
Learning Out comes
a) Underst and t he simple harmonic mot ion wit h examples.
b) Explain energy in simple harmonic mot ion.
c) Describe pract ical examples of free and forced oscillat ions.
d) Underst and t he resonance wit h it s applicat ions.
e) Underst and and describe Dopplers effect and it s causes. Recognize t he applicat ion of
Dopplers effect .
f) Underst and Ult rasound wit h it s uses in scanning.
g) Show an underst anding speed of sound in different media.
h) Audioable frequency range.
6. DEFORMATI ON OF SOLI DS:
Learning Out comes
a) Appreciat e deformat ion caused by a force and t hat is in one dimension.
b) Underst and t ensile or compressive deformat ion.
c) Underst and t he t erms st ress, st ain youngs modulus and Bulk modulus.
d) Energy st ored in deformed mat erial.
4
7. I DEAL GAS:
Learning Out comes
a) Recall and use equat ion of st at e of an ideal gas nRT PV = .
b) St at e t he basic assumpt ions of Kinet ic t heory of gases.
c) Derive gas laws on t he basis of kinet ic t heory of gases.
d) Underst and pressure of gas > < =
2
0
2
1
3
2
mv N P .
8. HEAT AND THERMODYNAMI CS:
Learning Out comes
a) Underst and t he t erm t hermal equilibrium.
b) Concept s of t emperat ure and t emperat ure scales.
c) Compare t he relat ive advant age and disadvant age of t hermocouple, t hermomet er
and mercury t hermomet er.
d) Underst and laws of t hermodynamics.
e) Show an underst anding t he t erm int ernal energy.
9. ELECTRONI CS:
Learning Out comes
a) Logic gat es:
- OR gat e, AND gat e, NOT Gat e, NOR gat e and NAND gat e.
b) Underst and t he basic principle of Cat hode Ray Oscilloscope and appreciat e it s use.
10. CURRENT ELECTRI CI TY:
Learning Out comes
a) St at e Ohms law and solve problems V= I R
b) Combinat ions of resist ors.
c) Show an underst anding of a capacit or.
d) Combinat ions of capacit ors.
5
11. MAGNETI SM AND ELECTROMAGNETI SM:
Learning Out comes
a) Magnet ic field due t o current in
i) St raight wire
ii) Solenoid
b) Underst and Magnet ic Resonance I maging ( MRI )
12. MODERN PHYSI CS:
Learning Out comes
a) Principle of product ion of X- rays by elect ron bombardment on met al t arget .
b) Describe main feat ures of X- ray t ube.
c) Use of X-rays in imaging int ernal body st ruct ures.
d) Show an underst anding of t he purpose of comput ed t omography or CT scanning.
e) Show an underst anding of t he principles of CT scanning.
f) Underst and laser principle and it s t ype (Helium Neon Laser) .
g) Describe t he applicat ion of laser in medicine and indust ry.
13. NUCLEAR PHYSI CS:
Learning Out comes
a) Underst and Radioact ivit y.
b) Underst and Radioact ive decay.
c) Radio I sot opes and t heir biological uses.
d) Nuclear radiat ion det ect ors
- GM t ube, Wilson cloud chamber.
e) Radiat ion hazards and biological effect of radiat ion.
6
Table of Specif icat ion ( PHYSI CS- 2012)
F.Sc. and Non- F.Sc.
Sr. No Topic MCQs
1. Physical Quant it ies and Unit s
02
2. Forces
02
3. Fluid Dynamics
03
4. Light
04
5. Waves
04
6. Deformat ion of Solids
02
7. I deal Gases
02
8. Heat and Thermodynamics
03
9. Elect ronics
02
10. Current Elect ricit y
03
11. Magnet ism and Elect romagnet ism
03
12. Modern Physics
07
13. Nuclear Physics
07
Tot al 44
7
SELF TEST QUESTI ONS ( PHYSI CS)
Choose single best opt ion
Q. 1 At t he pr esent t ime, how many front iers of f undament al science ar e t her e:
A) Two
B) Three
C) One
D) Four
Q. 2 The unit of pressure in base unit is:
A) Kg ms
- 2
B) Kg ms
2
C) Kg m
- 1
s
- 2
D) Kg m
- 1
s
- 1
Q. 3 The physical quant it y which produces angul ar acceler at ion in body is call ed:
A) Force
B) Moment um
C) Cent r ipet al force
D) Torque
Q. 4 A man in an elevat or ascending wit h an accelerat ion will conclude t hat his wei ght
has:
A) Decreased
B) I ncreased
C) Reduced t o zero
D) Remained const ant
Q. 5 The Law of conservat ion of mass gives us t he equat ion of:
A) St okes law
B) Cont inuit y
C) Bernoullis t heor em
D) Torricellis t heor em
Q. 6 1 t or r is equal t o :
A) 135. 3 Nm
- 2
B) 133. 3 Nm
- 2
C) 132. 3 Nm
- 2
D) 130. 3 Nm
- 2
Q. 7 Viscosit y of li qui ds wit h rise in t emper at ure:
A) I ncreases
B) Decreases
C) Remains t he same
D) Fir st decreases t hen increases
Q. 8 The phenomenon of pol arizat ion of li ght reveals t hat li ght waves are:
A) Ext remely short waves
B) Longit udinal waves
C) Transver se elect romagnet ic waves
D) Long wavelengt h waves
Q. 9 Diffr act ion of X- r ays by cryst al s show t hat :
A) X- rays are j ust like visible light
B) X- rays are elect romagnet ic waves
C) X- rays have very short wavelengt h
D) The int ensit y of X- rays is high
Q. 10 The image of an obj ect 7mm hi gh is only 1. 4 cm hi gh. The magnificat ion pr oduced by
lens is:
A) 0. 7
B) 1
C) 2
D) 0. 2
Q. 11 I nfr a- r ed si gnals t r avel t hrough opt ical fi bres of wavel engt h about :
A) 2 m
B) 1.3 m
C) 1. 5 m
D) 1.9 m
Q. 12 Tot al ener gy of a body execut i ng simple harmonic mot ion is dir ect ly pr opor t ional t o:
A) The amplit ude
B) Square root of amplit ude
C) Recipr ocal of amplit ude
D) Square of amplit ude
Q. 13 The wavelengt h of t he wave produced in a micr owave oven is:
A) 15 cm
B) 13 cm
C) 12 cm
D) 10 cm
Q. 14 The f requencies of ult rasonic waves ar e:
A) I n audible range
B) Great er t han 20 kHz
C) Lower t han 20 kHz
D) Great er t han 20 Hert z
Q. 15 A t rain is approaching a st at ion at 90 Kmh
- 1
sounding a whist l e of frequency 1000 Hz.
What will be t he apparent fr equency of t he whist l e as hear d by a list ener sit t i ng on
t he plat for m?
A) 1079. 4 Hz
B) 1179. 4 Hz
C) 1078. 5 Hz
D) 1178. 5 Hz
8
Q. 16 Mat hemat ical not at ion f or NAND gat e is:
A) B A X + =
B)
________
B . A = X
C)
__ __
. B A X =
D) B . A = X
Q. 17 Heat l eaves a syst em; it is t aken as:
A) Posit ive
B) Negat ive
C) Neit her posit ive nor negat ive
D) Zero
Q. 18 First Law of Thermodynamics is t he Law of :
A) Conservat ion of moment um
B) Conservat ion of Energy
C) Conservat ion of mass
D) Conservat ion of velocit y
Q. 19 I ncr ease in t emper at ure is due t o increase i n:
A) Translat ional K. E
B) Rot at ional K. E
C) Gravit at ional K. E
D) Vibrat ional K. E
Q. 20
P
N
V
3
2
= <
2
1
mv
2
> represent s:
A) Boyles law.
B) I deal gas
C) Charles law
D) Gas gener al equat ion
Q. 21 The dimension of st r ain is:
A) [ T ]
B) [ M ]
C) [ LT
- 1
]
D) None.
Q. 22 The rat i o of applied st ress t o vol umet ric st r ain is called:
A) Youngs modulus
B) Shear modulus
C) Bulk modulus
D) Modulus of elast icit y
Q. 23 Beam of elect ron can be call ed as:
A) Posit ive r ays
B) Cat hode rays
C) Cosmic rays
D) X- rays
Q. 24 Pressure of gas given by:
A)
3
2
= P N <
2
1
mv
2
>
B) P = Const ant K. E
C)
3
2
= P
V
N
<
2
1
mv
2
>
D)
3
1
= P No <
2
1
mv
2
>
Q. 25 OR and AND gat es have:
A) Two out put s
B) Single out put
C) Three out put
D) No out put
Q. 26 Shunt Resist ance is called:
A) Low resist ance
B) High resist ance
C) Bypass resist ance
D) Specif ic resist ance
Q. 27 One Coul omb per second is equal t o:
A) One volt
B) One ampere
C) One Walt
D) One ohm
Q. 28 Ohm is defi ned an:
A) VC
- 1
B) VA
- 1
C) CV
- 1
D) AV
- 1
Q. 29 A cur rent car rying conduct or is sur rounded by:
A) Magnet ic field
B) Elect ric field
C) Conservat ive f ield
D) Gravit at ional f ield
Q. 30 Force on a char ged part icl e having char ge q moving wit h velocit y v par all el t o
magnet ic fiel d of int ensit y B is given by:
A) F = q vb
B) F = vb/ q
C) F = q v/ B
D) F = 0
9
Q. 31 I n X- r ay t ube el ect rons ar e accel er at ed by appl ying a:
A) High current bet ween anode and
cat hode
B) High volt age bet ween anode and
cat hode
C) High st opping pot ent ial bet ween
anode and cat hode
D) High power bet ween anode and
cat hode
Q. 32 I n medical sci ence which r adi at i ons ar e used t o locat e f ract ur es or cr acks in bones or
t eet h:
A) I nfra- red radiat ions
B) Gamma r adiat ions
C) X- rays
D) Ult ra violet radiat ions
Q. 33 The mini mum wavel engt h of X- r ay produced if 10 kvp Pot ent ial difference is applied
across t he anode and cat hode of t he t ube is:
A) 1. 24 x 10
- 10
m
B) 12. 4 x 10
- 10
m
C) 124 x 10
- 10
m
D) 0. 124 x 10
- 10
m
Q. 34 Laser light is hi ghly:
A) Direct ional
B) Scat t ered
C) Unpolar ized
D) Non- direct ional
Q. 35 A li ght beam from a hi gh power l aser when focused by a lens can produce:
A) A high t emper at ure
B) A low t emperat ure
C) A moderat e t emper at ure
D) A very low t emperat ure
Q. 36 A laser beam can be employed safely t o wel d a det ached:
A) Bone of body
B) Finger of hand
C) Ret ina of eye
D) Toot h
Q. 37 CT scanning is t he abbreviat ed name of:
A) Comput ed Technology
B) Comput ed Tomography
C) Comput er ized Technique
D) Classical Technique
Q. 38 One curie is equal t o:
A) 3. 70 x 10
10
at oms decay in one
second
B) 3. 70 x 10
8
at oms decay in one
second
C) 3. 70 x 10
6
at oms decay in one
second
D) 3. 70 x 10
4
at oms decay in one
second
Q. 39 I n cloud chamber, each t r ack cor responds t o t he passage of:
A) One group of part icles
B) One
part icle
C) Two
part icles
D) Three
part icles
Q. 40 In par t icle emissi on it s mass of nucleus r emains pr act ically t he same while it s
char ge changes by:
A) One unit
B) Two unit
C) Three unit
D) Four unit
Q. 41 A nucli de
220
R8 4 decay t o a new nucli de S by two - emissions and two emissi ons;
t he nucli de S is:
A)
218
S84
B)
216
S84
C)
212
S82
D)
216
S82
Q. 42 Bet a par t icles ar e f ast moving part icl es, call ed:
A) Prot ons
B) Elect rons
C) Neut r ons
D) - Part icles
Q. 43 Cobal t - 60 is used t o:
A) Cure blood cancer
B) Cure bone cancer
C) Cure t hyr oid cancer
D) Cure t umor
Q. 44 I n r adioact ivit y, t he rat e of decay:
A) Can be increased by magnet ic f ield
B) Can be decreased by magnet ic f ield
C) Can be kept const ant by elect ric
field
D) I s not effect ed by elect r ic or
magnet ic f ield
10
CHEMI STRY
STRUCTURE OF THE SYLLABUS ( 2012)
F.Sc. and Non- F.Sc.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
A. Physical Chemist ry
1. Fundament al Concept s
2. St at es of Mat t er
3. At omic St r uct ur e
4. Chemical Bonding
5. Chemical Ener get ics
6. Solut ions
7. Elect r ochemist r y
8. Chemical Equilibr ium
9. React ion Kinet ics
B. I norganic Chemist ry
1. Per iods
2. Gr oups
3. Tr ansit ion element s
4. Element s of Biological I mpor t ance
C. Organic Chemist ry
1. Fundament al Pr inciples
2. Hydrocar bon
3. Alkyl Halides
4. Alcohols and Phenols
5. Aldehydes and Ket ones
6. Car boxylic Acid
7. Amino Acids
8. Macromolecules
9. Envir onment al Chemist r y
11
A. PHYSI CAL CHEMI STRY
1. FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS:
I n t his t opic, candidat e should be able t o:
a) Define relat ive at omic, isot opic, molecular and formula masses, based on t he
12
C
scale.
b) Explain mole in t erms of t he Avogadros const ant .
c) Apply mass spect romet ric t echnique in det ermining t he relat ive at omic mass of an
element using t he mass spect ral dat a provided.
d) Calculat e empirical and molecular formulae, using combust ion dat a.
e) Underst and st oichiomet ric calculat ions using mole concept involving.
i) React ing masses
ii) Volume of gases
2. STATES OF MATTER:
I n t his t opic, candidat e should be able t o:
a) Underst at e gaseous st at e wit h reference t o:
i) Post ulat es of kinet ic molecular t heory
ii) Deviat ion of real gases from ideal behavior
iii) Gas laws: Boyles law, Charles law, Avogadros law and gas equat ion ( PV= nRT)
and calculat ions involving gas laws.
iv) Deviat ion of real gases from ideal behaviour at low t emperat ure and high pressure
v) Causes of deviat ion from ideal behaviour
vi) Condit ions necessary for gasses t o approach ideal behaviour
b) Discuss liquid st at e wit h reference t o:
- Evaporat ion, vapour pressure, boiling and hydrogen bonding in wat er
c) Explain t he lat t ice st ruct ure of a cryst alline solid wit h special emphasis on:
i) Giant ionic st ruct ure, as in sodium chloride.
ii) Simple molecular, as in iodine
iii) Giant molecular, as in graphit e; diamond; silicon( I V) oxide
iv) Hydrogen- bonded, as in ice
v) Met allic as in Cu and Fe.
d) Out line t he import ance of hydrogen bonding t o t he physical propert ies of subst ances,
including NH
3
, H
2
O, C
2
H
5
OH and ice.
e) Suggest from quot ed physical dat a t he t ype of st ruct ure and bonding present in a
subst ance
12
3. ATOMI C STRUCTURE:
I n t his t opic, candidat e should be able t o:
a) I dent ify and describe t he prot on, neut ron and elect ron in t erms of t heir relat ive
charges and relat ive masses
b) Discuss t he behaviour of beams of prot ons, neut rons and elect rons in elect ric fields
c) Calculat e t he dist ribut ion of mass and charges wit hin an at om from t he given dat a
d) Deduce t he number of prot ons, neut rons and elect rons present in bot h at oms and
ions for a given prot on and nucleon numbers/ charge.
e)
i) Describe t he cont ribut ion of prot ons and neut rons t o at omic nuclei in t erms of
prot on number and nucleon number
ii) Dist inguish bet ween isot opes on t he basis of different numbers of neut rons
present
f) Describe t he number and relat ive energies of t he s, p and d orbit als for t he principal
quant um numbers 1, 2 and 3 and also t he 4s and 4p orbit als
g) Describe t he shapes of s and p orbit als
h) St at e t he elect ronic configurat ion of at oms and ions given t he prot on number/ charge
i) Explain:
i) I onizat ion energy
ii) The fact ors influencing t he ionizat ion energies of element s
iii) The t rends in ionizat ion energies across a Period and down a Group of t he Periodic
Table
4. CHEMI CAL BONDI NG:
I n t his t opic, candidat e should be able t o:
a) Charact erise elect rovalent ( ionic) bond as in sodium chloride and Calcium oxide.
b) Use t he dot - and- cross diagrams t o explain
i) Covalent bonding, as in hydrogen(H
2
) ; oxygen( O
2
) ; chlorine( Cl
2
) ; hydrogen
chloride; carbon dioxide; met hane and et hene
ii) Co- ordinat e ( dat ive covalent ) bonding, as in t he format ion of t he ammonium ion
and in H
3
N
+
-
BF
3
.
c) Describe t he shapes and bond angles in molecules by using t he qualit at ive model of
elect ron-pair repulsion t heory up t o 4 pairs of elect ron including bonded elect ron pair
and lone pair around cent ral at om.
d) Describe covalent bonding in terms of orbital overlap, giving and bonds
e) Explain t he shape of, and bond angles in et hane, et hene and benzene molecules in
terms of and bonds
13
f) Describe hydrogen bonding, using ammonia and wat er as simple examples of
molecules cont aining N-H and O- H groups
g) Explain t he t erms bond energy, bond lengt h and bond polarit y and use t hem t o
compare t he react ivit ies of covalent bonds
h) Describe int ermolecular forces ( Van der Waals forces) , based on permanent and
induced dipoles, as in CHCl
3,
Br
2
and in liquid noble gases
i) Describe met allic bonding in t erms of a lat t ice of posit ive ions surrounded by mobile
elect rons
j ) Describe, int erpret and/ or predict t he effect of different t ypes of bonding ( ionic
bonding; covalent bonding; hydrogen bonding; Van der Waals forces and met allic
bonding) on t he physical propert ies of subst ances
k) Deduce t he t ype of bonding present in a subst ance from t he given informat ion
5. CHEMI CAL ENERGETI CS:
I n t his t opic, candidat e should be able t o:
a) Underst and concept of energy changes during chemical react ions wit h examples of
exot hermic and endot hermic react ions.
b) Explain and use t he t erms:
i) Ent halpy change of react ion and st andard condit ions, wit h part icular reference t o:
Format ion; combust ion; hydrat ion; solut ion; neut ralizat ion and at omisat ion
ii) Bond energy (H positive, i.e. bond breaking)
iii) Lat t ice energy (H negat ive, i.e. gaseous ions t o solid lat t ice)
c) Find heat of react ions/ neut ralizat ion from experiment al result s using mat hemat ical
relat ionship.
H=mcT
d) Explain, in qualit at ive t erms, t he effect of ionic charge and of ionic radius on t he
numerical magnit ude of lat t ice energy
e) Apply Hesss Law t o const ruct simple energy cycles, and carry out calculat ions
involving such cycles and relevant energy t erms, wit h part icular reference t o:
i) Det ermining ent halpy changes t hat cannot be found by direct experiment , e.g. an
ent halpy change of format ion from ent halpy changes of combust ion
ii) Average bond energies
iii) Born-Haber cycles (including ionisat ion energy and elect ron affinit y)
14
6. SOLUTI ONS:
I n t his t opic, candidat e should be able t o:
a) Describe and explain following concent rat ion unit s of solut ions
i) Percent age composit ion
ii) Molarit y ( M)
iii) Molalit y ( m)
iv) Mole fract ion (X)
v) Part s of million ( ppm)
b) Underst and concept and applicat ions of colligat ive propert ies such as:
i) Elevat ion of boiling point
ii) Depression of freezing point
iii) Osmot ic pressure
7. ELECTROCHEMI STRY:
I n t his t opic, candidat e should be able t o:
a) Explain t he indust rial processes of t he elect rolysis of brine, using a diaphragm cell
b) Describe and explain redox processes in t erms of elect ron t ransfer and/ or of changes
in oxidat ion number
c) Define t he t erms:
- St andard elect rode ( redox) pot ent ial and St andard cell pot ent ial
d) Describe t he st andard hydrogen elect rode as reference elect rode
e) Describe met hods used t o measure t he st andard elect rode pot ent ials of met als or
non-met als in cont act wit h t heir ions in aqueous solut ion
f) Calculat e a st andard cell pot ent ial by combining t wo st andard elect rode pot ent ials
g) Use st andard cell pot ent ials t o:
i) Explain/ deduce t he direct ion of elect ron flow in t he ext ernal circuit .
ii) Predict t he feasibilit y of a react ion
h) Const ruct redox equat ions using t he relevant half- equat ions
i) St at e t he possible advant ages of developing t he H
2
/ O
2
fuel cell
j ) Predict and t o ident ify t he subst ance liberat ed during elect rolysis from t he st at e of
elect rolyt e (molt en or aqueous) , posit ion in t he redox series ( elect rode pot ent ial) and
concent rat ion
15
8. CHEMI CAL EQUI LI BRI UM:
I n t his t opic, candidat e should be able t o:
a) Explain, in t erms of rat es of t he forward and reverse react ions, what is meant by a
reversible react ion and dynamic equilibrium
b) St at e Le Chat eliers Principle and apply it t o deduce qualit at ively t he effect s of
changes in t emperat ure, concent rat ion or pressure, on a syst em at equilibrium
c) Deduce whet her changes in concent rat ion, pressure or t emperat ure or t he presence
of a cat alyst affect t he value of t he equilibrium const ant for a react ion
d) Deduce expressions for equilibrium const ant s in t erms of concent rat ions, Kc, and
part ial pressures, Kp
e) Calculat e t he values of equilibrium const ant s in t erms of concent rat ions or part ial
pressures from appropriat e dat a
f) Calculat e t he quant it ies present at equilibrium, given appropriat e dat a
g) Describe and explain t he condit ions used in t he Haber process.
h) Underst and and use t he Bronst ed- Lowry t heory of acids and bases
i) Explain qualit at ively t he differences in behaviour bet ween st rong and weak acids and
bases and t he pH values of t heir aqueous solut ions in t erms of t he ext ent of
dissociat ion
j ) Explain t he t erms pH; Ka; pKa; Kw and use t hem in calculat ions
k) Calculat e [ H
+
( aq) ] and pH values for st rong and weak acids and st rong bases
l) Explain how buffer solut ions cont rol pH
m) Calculat e t he pH of buffer solut ions from t he given appropriat e dat a
n) Show underst anding of, and use, t he concept of solubilit y product , Ksp
o) Calculat e Ksp from concent rat ions and vice versa
p) Show underst anding of t he common ion effect
16
9. REACTI ON KI NETI CS:
I n t his t opic, candidat e should be able t o:
a) Explain and use t he t erms: rat e of react ion; act ivat ion energy; cat alysis; rat e
equat ion; order of react ion; rat e const ant ; half- life of a react ion; rat e-det ermining
st ep
b) Explain qualit at ively, in t erms of collisions, t he effect of concent rat ion changes on t he
rat e of a react ion
c) Explain t hat , in t he presence of a cat alyst , a react ion has a different mechanism, i.e.
one of lower act ivat ion energy
d) Describe enzymes as biological cat alyst s ( prot eins) which may have specific act ivit y
e) Const ruct and use rat e equat ions of t he form
Rat e = k[ A]
m
[ B]
n
wit h special emphasis on:
i) Deducing t he order of a react ion by t he init ial rat es met hod
ii) Just ifying, for zero- and first - order react ions, t he order of react ion from
concent rat ion-t ime graphs
iii) Verifying t hat a suggest ed react ion mechanism is consist ent wit h t he observed
kinet ics
iv) Predict ing t he order t hat would result from a given react ion mechanism ( and vice
versa)
v) Calculat ing an init ial rat e using concent rat ion dat a
f) Show underst anding t hat t he half -life of a first -order react ion is independent of init ial
concent rat ion and use t he half-life t o calculat e order of react ion.
g) Calculat e t he rat e const ant from t he given dat a
h) Name a suit able met hod for st udying t he rat e of a react ion, from given informat ion
B. I NORGANI C CHEMI STRY
1. PERI ODS:
I n t his t opic, candidat e should be able t o:
Discuss t he variat ion in t he physical propert ies of element s belonging t o period 2 and 3
and t o describe and explain t he periodicit y in t he following physical propert ies of
element s.
a) At omic radius
b) I onic radius
c) Melt ing point
d) Boiling point
e) Elect rical conduct ivit y
f) I onizat ion energy
17
2. GROUPS:
I n t his t opic, candidat e should be able t o:
Describe and explain t he variat ion in t he propert ies of group I I , I V and VI I element s
from t op t o bot t om wit h special emphasis on:
a) React ions of group- I I element s wit h oxygen and wat er
b) Charact erist ics of oxides of carbon and silicon
c) Propert ies of halogens and uses of chlorine in wat er purificat ion and as bleaching
agent
d) Uses of Nobel gases ( group VI I I )
3. TRANSI TI ON ELEMENTS:
I n t his t opic, candidat e should be able t o:
Discuss t he chemist ry of t ransit ion element s of 3- d series wit h special emphasis on:
a) Elect ronic configurat ion
b) Variable oxidat ion st at es
c) Use as a cat alyst
d) Format ion of complexes
e) Colour of t ransit ion met al complexes
4. ELEMENTS OF BI OLOGI CAL I MPORTANCE:
I n t his t opic, candidat e should be able t o:
a) Describe t he inert ness of Nit rogen
b) Manufact ure of Ammonia by Haber process
c) Discuss t he preparat ion of Nit ric acid and nit rogenous fert ilizers
d) Describe t he presence of Suphur dioxide in t he at mosphere which causes acid rain
e) Describe t he manufact ure of Sulphuric acid by cont act met hod
18
C. ORGANI C CHEMI STRY
1. FUNDAMENTAL PRI NCI PLES:
I n t his t opic, candidat e should be able t o:
a) Classify t he organic compounds
b) Explain t he t ypes of bond fission, homolyt ic and het erolyt ic
c) Discuss t he t ypes of organic react ions; Polar and free radical
d) Discuss t he t ypes of reagent s; nucleophile, elect rophile and free radicals
e) Explain isomerism; st ruct ural and cis-t rans
f) Describe and explain condensed st ruct ural formula, displayed and skelet al formula
g) Discuss nomenclat ure of organic compounds wit h reference t o I UPAC names of
Alkanes, Alkenes, Alcohols and Acids
2. HYDROCARBON:
I n t his t opic, candidat e should be able t o:
Describe t he chemist ry of Alkanes wit h emphasis on
a) Combust ion
b) Free radical subst it ut ion including mechanism
Discuss t he chemist ry of Alkenes wit h emphasis on
a) Preparat ion of alkenes by eliminat ion react ions
i) Dehydrat ion of alcohols
ii) Dehydrohalogenat ion of Alkyl halide
b) React ion of Alkenes such as
i) Cat alyt ic hydrogenat ion
ii) Halogenat ion ( Br
2
addit ion t o be used as a t est of an alkene)
iii) Hydrat ion of alkenes
iv) React ion wit h HBr wit h special reference t o Markownikoffs rule
v) Oxidat ion of alkenes using Bayers reagent ( cold alkaline KMnO
4
) and using hot
concent rat ed acidic KMnO
4
for cleavage of double bond
vi) Polymerizat ion of et hene
Discuss chemist ry of Benzene wit h examples
a) Structure of benzene showing the delocalized - orbit al which causes st abilit y of
benzene
b) Elect rolphillic subst it ut ion react ions of benzene
i) Nit rat ion including mechanism
ii) Halogenat ion
iii) Friedel Craft s react ion
19
3. ALKYL HALI DES:
I n t his t opic, candidat e should be able t o:
a) Discuss import ance of halogenoalkanes in everyday life wit h special use of CFCs,
halot hanes, CCl
4
, CHCl
3
and Teflon
b) React ion of alkyl halides such as:
S
N
- react ions, ( React ions of alcohols wit h aqueous KOH, KCN in alcohol and wit h
aqueous NH
3
)
Eliminat ion react ion wit h alcoholic KOH t o give alkenes.
4. ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS:
I n t his t opic, candidat e should be able t o:
Discus Alcohols wit h reference to
a) Classificat ion of alcohols int o primary, secondary and t ert iary
b) Preparat ion of et hanol by ferment at ion process
c) React ion of alcohol wit h
i) K
2
Cr
2
O
7
+ H
2
SO
4
ii) PCl
5
iii) Na- met al
iv) Alkaline aqueous I odine
v) Est erificat ion
vi) Dehydrat ion
Phenols
a) Discuss react ions of phenol wit h:
i) Bromine ii) HNO
3
b) Explain t he relat ive acidit y of wat er, et hanol and phenol
20
5. ALDEHYDES AND KETONES:
I n t his t opic, candidat e should be able t o:
a) Describe t he st ruct ure of aldehyde and ket ones
b) Discuss preparat ion of aldehydes and ket ones by oxidat ion of alcohols
c) Discuss following react ions of aldehydes and ket ones
i) Common t o bot h
- 2,4- DNPH
- HCN
ii) React ions in which Aldehydes differs from ket ones
- Oxidat ion wit h K
2
Cr
2
O
7
+ H
2
SO
4
, Tollens reagent and Fehling solut ion
- Reduct ion wit h sodium boron hydride
iii) React ion which show presence of CH
3
CO group in aldehydes and ket ones
Triiodomet hane t est
(I odo form t est ) using alkaline aqueous iodine.
6. CARBOXYLI C ACI D:
I n t his t opic, candidat e should be able t o:
a) Show preparat ion of et hanoic acid by oxidat ion of et hanol or by t he hydrolysis of
CH
3
CN
b) Discuss t he react ions of et hanoic acid wit h emphasis on:
i) Salt format ion
ii) Est erificat ion
iii) Acid chloride format ion
iv) Amide format ion
c) Hydrolysis of amide in basic and acidic medium
d) Describe t he st rengt h of organic acids relat ive t o chloro subst it ut ed acids
7. AMI NO ACI DS:
I n t his t opic, candidat e should be able t o:
a) Describe t he general st ruct ure of - amino acids found in prot eins
b) Classify t he amino acids on t he basis of nat ure of R- group
c) Describe what is meant by essent ial amino acids
d) Underst and pept ide bond format ion and hydrolysis of polypept ides/ prot ein
21
8. MACROMOLECULES:
I n t his t opic, candidat e should be able t o describe and explain
a) Addit ion polymers such as polyet hene, polypropene, polyst yrene and PVC.
b) Condensat ion polymers such as polyest ers, nylon
c) St ruct ure of prot eins
d) Chemist ry of carbohydrat es
e) Chemist ry of lipids
f) Enzymes
g) St ruct ure and funct ion of nucleic acid ( DNA & RNA)
9. ENVI RONMENTAL CHEMI STRY:
I n t his t opic, candidat e should be able t o
a) Underst and causes of wat er pollut ion
b) Discuss disposal of solid wast es
c) Underst and chemist ry and causes of
i) Smog
ii) Acid rain
iii) Ozone layer
22
Table of Specif icat ion ( CHEMI STRY- 2012)
F.Sc. and Non- F.Sc.
Topic MCQs
A. Physical Chemist ry
1. Fundament al concept s 02
2. St at es of mat t er 02
3. At omic st ruct ure 02
4. Chemical bonding 02
5. Chemical energet ics 02
6. Solut ions 02
7. Elect rochemist ry 02
8. Chemical Equilibrium 02
9. React ion kinet ics 02
B. I norganic Chemist ry
1. Periods 02
2. Groups 02
3. Transit ion element s 02
4. Element s of biological import ance 04
C. Organic Chemist ry
1. Fundament al principles 02
2. Hydrocarbon 02
3. Alkyl halides 02
4. Alcohols and Phenols 04
5. Aldehydes and Ket ones 03
6. Carboxylic acid 03
7. Amino acids 06
8. Macromolecules 06
9. Environment al chemist ry 02
Tot al 58
23
SELF TEST QUESTI ONS ( CHEMI STRY)
Choose single best opt ion
Q. 1 The mass spect rum of l ead is shown:
Y
52. 3
23. 6
22. 6
1. 5
X
204 206 207 208
What quant it i es ar e repr esent ed by X- axis and Y- axis?
X- axis Y- axis
A) At omic number Relat ive abundance
B) Mass number At omic number
C) Mass number Height of peak
D) At omic number Mass number
Q. 2 Number of at oms of oxygen in 9 0g of glucose is ( C= 12, H= 1, O= 1 6) :
A) 3. 011x10
23
B) 6. 022x10
23
C) 6. 022x10
24
D) 1. 8x10
24
Q. 3 A mi xt ure of 20% NH3, 5 5% H2 and 25% N2 by volume has a pr essure of
9. 8x10
4
Nm
- 2
. What is t he par t ial pressur e of NH3 in Nm
- 2
?
A) 1. 96x10
4
B) 2. 45x10
4
C) 2. 92x10
4
D) 4. 90x10
4
Q. 4 Densit y of wat er ( H2O) is maxi mum at :
A) 100
0
C
B) 0
0
C
C) 4
0
C
D) 14
0
C
Q. 5 How many t ot al number of unpai red elect rons are shown in t he elect ronic
configur at ion of Cr:
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6
Q. 6 Energy of s, p and d sub- shells is in t he or der:
A) s> p> d
B) p> s> d
C) d> p> s
D) s> p< d
Q. 7 Hydrogen bonding pl ays a very import ant rol e in st abilizing var ious st ruct ures. I n
which of t he following case hydrogen bonding is not involved?
A) St ruct ure of ice
B) Secondary st ruct ure of pr ot ein
C) Solid st at e of iodine
D) Double helix st r uct ure of DNA
Q. 8 The shape of SnCl2 as pr edict ed by valence shell el ect ron pai r repulsi on t heory is:
A) Linear
B) Bent
C) Tet rahedral
D) Triangular pyr amidal
Q. 9 A cor rect equat ion for t he ent hal py change of format ion of NH3( g) is:
A) NH4Cl( s) NH3( g) + HCl( g)
B) N2( g) + 3H2( g) 2NH3( g)
C)
2
1
N2( g) +
2
3
H2( g) NH3( g)
D) N2O( g) + 4H2( g) 2NH3( g) + H2O( l )
Q. 10 Boiling point of wat er is 1 00
0
C. To a sampl e of 500 g of wat er 3 g of urea ( NH2) 2 CO ar e
added. The boiling point of solut ion is expect ed t o be ( N= 1 4, C= 12, O= 16, H= 1) :
A) 100
0
C
B) 100. 052
0
C
C) 99. 52
0
C
D) 99. 00
0
C
24
Q. 11 The mol e fr act ion of met hanol in a sol ut ion cont aining 90 g wat er, 92 g et hanol and
96g met hanol is ( C= 12, O= 16, H= 1) :
A) 0. 2
B) 0. 3
C) 0. 5
D) 1. 0
Q. 12 The rel evant E
o
values for 3 half cells ar e:
Mn
2+
E
o
= + 1. 49V Mn
3+
+ e
-
Fe
2+
E
o
= + 0. 77V Fe
3+
+ e
-
Co
2+
E
o
= - 0. 28V Co
3+
+ e
-
Which is t he st r ongest oxidi zing agent ?
A) Mn
3+
B) Fe
2+
C) Co
2+
D) Mn
2+
Q. 13 Sulphuric aci d is manuf act ured by cont act process. One st age in t he cont act pr ocess
involves t he react i on bet ween sulphur di oxide and oxygen.
2SO2( g) + O2( g)
2SO3( g) ; AH= - 197KJ
- 1
mol
Which st at ement about t his st ep is t rue?
A) High t emperat ure favours t he
format ion of SO3
B) High pr essure favour s t he
format ion of SO3
C) No cat alyst is used in t his st ep
D) This pr ocess is carr ied out at 200
0
C
Q. 14 Kp and Kc for a gaseous reversi bl e chemical react i on may be same or diff er ent . Sel ect
t he react ion f or which t he t wo const ant s have same numerical value:
A) N2 + 3H2 2NH3
B) PCl5 PCl3 + Cl2
C) N2 + O2 2NO
D) 2SO3 2SO2 + O2
Q. 15 The oxi dat ion of I odine i on by H2O2 t akes pl ace accor ding t o t he equat ion,
H2O2( aq) + 2H3O
+
( aq) + 2I
-
( aq)
I 2( aq) + 4H2O( l)
The rat e equat i on may be writ t en as:
Rat e = k[ H2O2]
x
[ H3O
+
]
y
[ I
-
]
z
This r eact i on t akes pl ace i n t hree st eps:
St ep 1 H2O2 + I
-
I O
-
+ H2O
St ep 2 I O
-
+ H3O
+
HI O + H2O
St ep 3 HI O + H3O
+
+
I
-
I 2 + 2H2O
What is t he value of x, y and z if st ep 1 is t he rat e det ermini ng st ep:
x y z
A) 1 1 1
B) 1 0 1
C) 1 2 0
D) 2 1 1
25
Q. 16 St at es of react ion were measur ed at differ ent init i al concent r at ion of r eact ant s A and
B. Dat a coll ect ed is given bel ow in t abular form:
[ A] [ B] I nit i al
Rat e( at m
min
- 1
)
0. 009 0. 001 0. 1
0. 018 0. 002 0. 4
0. 018 0. 001 0. 2
0. 009 0. 002 0. 2
Select t he r at e expression t hat cor responds t o t he dat a:
A) Rat e o [ A] [ B]
B) Rat e o [ A] [ B]
2
C) Rat e o [ A]
2
[ B]
D) Rat e o [ A]
2
[ B]
2
Q. 17 The periodic vari at i on in a physical pr opert y of element s wit h prot on number 1 t o 6 0
is shown in t he fi gure below:
Which propert y is shown in t he f igur e?
A) Melt ing point
B) At omic radius
C) Boiling point
D) Fir st ionisat ion energy
Q. 18 Four element s of per iod- 2 ar e given, sel ect t he el ement wit h hi ghest first i onizat ion
ener gy:
A) B
B) C
C) N
D) O
Q. 19 An el ement of group I V shows t he f ollowing pr oper t ies:
i I t is hi gh melt ing.
ii I t is lubr icant .
iii I t is used as an elect rical conduct or.
What could be t he subst ance?
A) Silicon
B) Graphit e
C) Tin
D) Lead
Q. 20 Disinfect i on of wat er by chlorine is avoided if or ganic mat t er li ke phenol or humi c
acid is pr esent in wat er. I t is due t o t he format i on of t oxic and carcinogenic product s
wit h chl ori ne. Chlorine combi nes wit h humic aci d t o for m:
A) Chlor amines
B) Nit r ogen t r ichloride
C) Chlor of orm
D) Carbon t et rachlor ide
26
Q. 21 Visibl e spect r oscopy is used t o r el at e colour of a compl ex and t he wavelengt h of
absor pt i on. The r elat ion bet ween absor bed wavelengt h and observed colour is shown
bel ow:
( nm)
Absor bed
Colour of compl ex
400 Green- Yellow
450 Yellow
490 Red
580 Blue
650 Green
The visi bl e spect rum of a compl ex is shown. What is t he col our of complex observed?
A) Green- Yellow
B) Yellow
C) Blue
D) Red
Q. 22 Transit ion el ement compl exes show colour. The col our shown by diff er ent element s is
different due t o:
A) Dif ferent number of shells
B) Energy difference of d- orbit als
varies wit h nat ure of ligand
C) Absorbance of same wavelengt h
from visible light
D) Dif ferent geomet ry of complexes
Q. 23 What is not t he use of H2SO4:
A) Paint and pigment s
B) Det ergent s
C) Food preservat ion
D) Dye st uff
Q. 24 Fert il it y of aci dic soil is r est ored by adding:
A) Lime
B) Caust ic soda
C) Baking soda
D) Milk of magnesia
Q. 25 Which pai r of t he foll owing compounds is opt ically act ive:
i. H2NCH2 CO2H
ii. HOCH2 CH2 CO2 H
iii. CH3CH( OH) CO2H
HO
iv. HO CHCH2 NHCH3
OH
A) 1 and 2
B) 2 and 3
C) 3 and 4
D) 1 and 4
Q. 26 Which one of t he foll owing r eagent s is not an elect rophil e:
A) NO2
+
B) CH3
+
C) SO3
D) CH3OH
27
Q. 27 When et hene r eact s wit h bromine in t he pr esence of a lit t l e NaCl, many el ect r ophilic
addit ion product s ar e formed. Which of t he fol lowi ng is not a possi ble product :
A) CH2CH2
Br Br
B) CH2CH2
Br OH
C) CH2CH2
Br Cl
D) CH2CH2
Cl OH
Q. 28 Chlorinat ion of met hane in t he presence of sunli ght involves mechanism of:
A) Elect rophilic subst it ut ion
B) Free radical subst it ut ion
C) Free radical addit ion
D) Free radical alkylat ion
Q. 29 Alkaline hydrolysis of bromoet hane t akes place by SN2 mechanisms as given bel ow:
CH3 CH3
CH3
OH
-
+ OH- - - - - - C- - - - - - - Br OHCH2 + Br
-
+ CH2 Br
-
H H
I nt er mediat e
What is charge on t he int er medi at e?
A) + 2
B) + 1
C) - 1
D) - 2
Q. 30 Nucleophilic subst it ut ion of t ert i ary alkyl hali de gives t ert i ary alcohol. What is t he
t ype of t his r eact i on:
A) SN1
B) SN2
C) Addit ion- eliminat ion
D) Eliminat ion- addit ion
OH
Cl Cl
Q. 31 2, 4, 6- Trichlorophenol is st r ongest ant isept ic pr esent in Det t ol. Which of t he
Cl
following r eagent is suit abl e for it s prepar at i on fr om phenol:
A) PCl5
B) SOCl2
C) HCl
D) Cl2
Q. 32 Rect ifi ed spirit cont ains 95 % et hanol in wat er. I t i s convert ed t o absolut e alcohol by:
A) Fract ional dist illat ion
B) Filt rat ion
C) Treat ing wit h lime
D) St eam dist illat ion
Q. 33 Vanilli n is a const it uent of t he vanill a bean and has t he st ruct ure:
OH
OCH3
( Vanillin)
CHO
Which of t he foll owi ng r eagent will not react wit h vanilli n?
A) 2, 4- Dinit r ophenyl hydr azine
B) [ Ag( NH3) 2]
+
( Tollens reagent )
C) Br2 in CCl4
D) Aqueous NaOH + I 2
Q. 34 Acet aldehyde and acet one can be dist inguished by:
A) Tollens t est
B) I odof orm t est
C) Bayers t est
D) 2, 4 DNPH t est
28
Q. 35 2- hydroxy propanoic aci d can be prepar ed in t he following t wo st eps st art ing from
et hanal:
St ep 1 St ep 2
CH3CHO CH3CHCN CH3CHCO2H
OH OH
What is t he reagent and condit ion for t he t wo st eps?
A) HCN, Acid hydrolysis
B) NaCN in alcohol, oxidat ion wit h
H2O2
C) HCN, basic hydr olysis
D) NaCN in alcohol, reduct ion Sn+ HCl
Q. 36 Hi ghest aci d st rengt h in aqueous medium is associ at ed wit h:
A) CH3COOH
B) ClCH2 COOH
C) Cl2CHCOOH
D) CH3CH2COOH
Q. 37 20 - amino aci ds found in prot ein are bifunct ional compounds having at l east a
car boxylic aci d gr oup and an ami no group. Which of t he fol lowing - amino acid has
t he secondary amino gr oup in it s st ruct ur e?
A) Valine
B) Alanine
C) Proline
D) Glycine
Q. 38 On hydrolysis, pr ot ei n yiel d amino aci ds. I n all pr ot ei ns about 20 diff er ent amino
acids are f ound. Which is not a char act erist ic propert y of t hese 20 ami no acids?
A) All ar e opt ically act ive
B) Those opt ically act ive have L-
conf igurat ion
C) Proline has secondary amino group
at 2- posit ion
D) They decompose bef ore melt ing
Q. 39 When an al kali is added t o t he aqueous solut ion of an amino aci d, net char ge on a
molecule of amino aci d is:
A) + ve
B) ve
C) Zero
D) May be + ve or - ve
Q. 40 A r eact i on of an addit ion polymer is shown:
What is t he st ruct ur e of t he monomer?
A) CH2CH3
B) CH= CH2
C) C CH
D) CH= CH
Q. 41 Which of t he foll owi ng f unct ional groups is present in fat s?
A) Carboxylic acid
B) Aldehyde or ket one
C) Alcohol
D) Est er
Q. 42 St arch is a mixt ur e of t wo polysacchari des, amyl ase and amylopect in. Amylase has
linear st ruct ur e wher e as amylopect in is br anched. I n amylopect in, br anching is due
t o:
A) - 1, 4 glycosidic linkage
B) |- 1, 4 glycosidic linkage
C) - 1, 6 glycosidic linkage
D) |- 1, 6 glycosidic linkage
Q. 43 Nat ural r ain wat er has a pH of 5. 6. What is t he pH of t he aci d r ain?
A) 1- 2
B) 6- 7
C) 8- 9
D) 4- 5
Q. 44 Four st at ement s regar ding t he char act erist ics of ozone ar e given, select t he
I NCORRECT:
A) Ozone is produced in most of t he
t ropical regions
B) I n polar regions it causes various
healt h pr oblems
C) I t reduces t he durabilit y of paint
D) I t is usef ul t o plant s
29
ENGLI SH
STRUCTURE OF THE SYLLABUS ( 2012)
F.Sc. and Non- F.Sc.
The English sect ion shall consist of four part s:
Part I :
- I t will be comprised of Four Quest ions in which t he candidat e will have t o select
t he appropriat e/ suit able word from t he given alt ernat ives.
Part I I :
- I t will cont ain sent ences wit h grammat ical errors and t he candidat e will have t o
ident ify t he error. There will be Six Quest ions from t his part .
Part I I I :
- There will be Ten Quest ions consist ing of a list of Four sent ences each. The
candidat e will have t o choose t he grammat ically correct sent ence out of t he given
four opt ions.
Part I V:
- I n t his part , t he candidat e will be asked t o choose t he right synonyms. Four
opt ions will be given and He/ She will have t o choose t he most appropriat e one.
There will be Ten Quest ions from t his part .
Essent ial Word Power
1. A Acupunct ure
2. Aberrat ion
3. Abnegat e
4. Aboriginal
5. Absolut i on
6. Abst ruse
7. Acclimat e
8. Accolade
9. Accrue
10. Acquiesce
11. Act uary
12. Acumen
13. Adage
14. Adamant i ne
15. Addled
16. Admonit ion
17. Adonis
18. Adroit ness
19. Aerobic- exercise
20. Aerodynamic
21. Affect
22. Affini t y
23. Af f l at us
24. Akimbo
25. Alacrit y
26. Allay
27. Alt ruist ic
28. Amazon
29. Ambulat ory
30. Ameliorat e
31. Amenit ies
32. Amorphous
33. Ampere
34. Analogue
35. Anaphyl act i c
36. Aneur ysm
37. Angi na
38. Anomaly
39. Anomie
40. Ant agonist
41. Ant ibody
42. Apocryphal
43. Apprehension
44. Aquaplane
45. Aqui f er
46. Arbit er
47. Ar bor eal
48. Arcane
49. Archives
50. Ar gosy
51. Aria
52. Armada
53. Art iculat ed
54. Art ifice
55. Ascet ic
56. Asgard
57. Askance
58. Aspersion
59. Assimilat e
60. Assume
61. At rophy
62. At t ire
63. Audacious
64. August
65. Auspicious
66. Avat ar
67. Avid Avid
68. Avoirdupois
69. Bacchanal
70. Baedeker
71. Balk
72. Bamboozl e
73. Bant am
74. Barbaric
75. Basilica
76. Bat ik
77. Bat t er
78. Bat t ery
79. Bauble
80. Bayou
81. Beguile
30
82. Behest
83. Belat ed
84. Benedict i on
85. Beneficence
86. Benign
87. Bequeat h
88. Berat e
89. Ber m
90. Beset
91. Bifurcat ed
92. Bist ro
93. Blandish
94. Blasphemous
95. Blat hering
96. Blaze
97. Bloom
98. Bonk
99. Bonsai
100. Bot anicals
101. Bouquet
102. Bowdlerize
103. Braille
104. Brambles
105. Brassy
106. Bravura
107. Bray
108. Brio
109. Broach
110. Broadside
111. Buckle
112. Buoyant
113. Burgeoning
114. Cachet
115. Caesarean
116. Caliph
117. Calist henics
118. Camber
119. Cameo
120. Candelabra
121. Capit al
122. Capsule
123. Car apace
124. Cardigan
125. Career
126. Caricat ure
127. Cart ographer
128. Cast
129. Cat acomb
130. Cat alyst
131. Cat harsis
132. Caulk
133. Cause clbre
134. Cay
135. Cent ennial
136. Cerberus
137. Chassis
138. Chast ise
139. Chiar oscuro
140. Chicane
141. Chimerical
142. Chivalry
143. Chromosome
144. Churn
145. Chut zpah
146. Clamorous
147. Claret
148. Classic
149. Classical
150. Clement
151. Close
152. Cloud nine
153. Coast
154. Cobble
155. Coccyx
156. Coercive
157. Coif
158. Collage
159. Comat ose
160. Comely
161. Commiserat e
162. Commut e
163. Compact
164. Compat ible
165. Complacent
166. Concert ed
167. Condone
168. Conciliat ory
169. Confiscat ory
170. Conf ound
171. Congeal.
172. Congruent
173. Cont emporary
174. Cont iguous
175. Cont radow
176. Cont ravent ion
177. Cont rive
178. Cont umely
179. Cont usion
180. Copacet ic
181. Coquet ry
182. Cordial
183. Cordialit y
184. Corked
185. Corollary
186. Corpuscle
187. Corroborat ing
188. Cosset
189. Cot erie
190. Covert
191. Covet ed
192. Crass
193. Craven
194. Crenelat e
195. Crescendo
196. Crescent
197. Crit erion
198. Cue
199. Cul - de- sac
200. Cut and run
201. Cuvee
202. Cygnet
203. Cynical
204. Dacha
205. Dale
206. Dam
207. Dappled
208. Dark horse
209. Dead- ender
210. Deadhead
211. Debilit y
212. Debunk
213. Debut
214. Decant
215. Decat hlon
216. Decelerat e
217. Decorum
218. Decry
219. Defenest rat ion
220. Deferent ial
221. Deferment
222. Delegat e
223. Delt a
224. Demogr aphi cs
225. Demure
226. Denominat ion
227. Deracinat e
228. Desiccat e
229. Deuce
230. Devious
231. Dext er
232. Diaspora
233. Diffidence
234. Diffident
235. Dili gence
236. Diligent
237. Diocese
238. Diorama
239. Dipt ych
240. Discombobulat e
241. Discourse
242. Discrepancy
243. Discret ion
244. Disdai n
245. Disingenuous
246. Dissension
247. Dissent
248. Dissent er
249. Dissonance
250. Diva
251. Di vagat e
252. Divulge
253. Docent
254. Dot e
255. Downy
256. Droll
257. Dryad
258. Dulcet
31
259. Dunce
260. Duplicit ous
261. Edda
262. Effect
263. Effervescent
264. El dorado
265. Elect rolyt es
266. Elicit
267. Elucidat e
268. Elusive
269. Embed
270. Embedded
271. Emblazon
272. Emblemat ic
273. Emboss
274. Emit
275. Empat hy
276. Emulat e
277. Encomi um
278. Encumber
279. Encyclical
280. Enhance
281. Ennui
282. Epicent er
283. Equipoise
284. Equivocat e
285. Ergomet er
286. Eschew
287. Espali er
288. Et hic
289. Et ude
290. Euphonious
291. Evanescent
292. Evasive
293. Evocat ive
294. Excavat e
295. Execrable
296. Exhor t at i on
297. Exonerat e
298. Exploit at ion
299. Ext emporaneous
300. Ext rapolat e
301. Ext ricat e
302. Ext ri nsic
303. Fabricat e
304. Facile
305. Facilit at e
306. Fait accompli
307. Fakir
308. Fart l ek
309. Fasci a
310. Fat eful
311. Faux
312. Fawning
313. Feasi bl e
314. Feckless
315. Felicit ous
316. Felicit y
317. Feral
318. Ferment at ion
319. Fiest a
320. Figment
321. Filigree
322. Finagle
323. Fist mel e
324. Flaunt
325. Flibbert igibbet
326. Flori d
327. Flot sam and
j et sam
328. Flux
329. Fop
330. Forswear
331. Frowsy
332. Funicular
333. Gabl e
334. Galoot
335. Galvanize
336. Gambit
337. Garnish
338. Gaudy
339. Genocide
340. Geodesic
341. Gest iculat e
342. Gesundheit
343. Gild
344. Gl aucoma
345. Glaze
346. Glib
347. Glucose
348. Gradient
349. Gr apevine
350. Green
351. Gridlock
352. Guileless
353. Guise
354. Gull
355. Guru
356. Habi li ment s
357. Hackles
358. Hail
359. Halcyon
360. Hall ux
361. Hammer and
t ongs
362. Har angue
363. Hawk
364. Hect or
365. Heinous
366. Hem and haw
367. Her bi ci de
368. Herculean
369. Hermet ic
370. Het erogeneous
371. Hiat us
372. Holist ic- medicine
373. Homeopat hy
374. Hone
375. Horse lat it udes
376. Hue and cry
377. Humane
378. Hydra
379. Hypert ension
380. Hypot hermia
381. I chor
382. I dealist
383. I lk
384. I llicit
385. I mam
386. I mmobilize
387. I mmolat e
388. I mpediment
389. I mpending
390. I mpet uous
391. I mpet us
392. I mpinge
393. I mplacable
394. I mpor t une
395. I mprecat ion
396. I mpregnable
397. I mprovise
398. I mpugn
399. I mput e
400. I nanit y
401. I ncarnat e
402. I ncent ive
403. I ncisive
404. I nculcat e
405. I ndi gent
406. I neradicable
407. I nert ia
408. I nfallible
409. I nfi del
410. I nf ract i on
411. I nfusion
412. I nherent
413. I niquit y
414. I nnocuous
415. I nnovat e
416. I nocul at e
417. I nordinat e
418. I nquisit ion
419. I nscrut able
420. I nt er
421. I nt ransigent
422. I nt rinsic
423. I r ref ut able
424. I sot roplc
425. I t inerant
426. Jackknife
427. Jaded
428. Jargon
429. Jej une
430. Jell
431. Jeopardy
432. Jeremiad
433. Jet t ison
434. Jig
32
435. Jihad
436. Jingoism
437. Jit ney
438. Jocular
439. Jocund
440. Joist
441. Journeyman
442. Joust
443. Jubilee
444. Judicial
445. Judicious
446. Juggernaut
447. Junct ure
448. Junket
449. Junt a
450. Just ify
451. Juxt apose
452. Kahuna
453. Ken
454. Kerfuffle
455. Kibit z
456. Kiln
457. Kismet
458. Lacerat ing
459. Laconic
460. Lacunae
461. Lait y
462. Lampoon
463. Lapidary
464. Largess
465. Lat ent
466. Lat he
467. Laud
468. Lee
469. Leit mot if
470. Lemming
471. Li ement
472. Li gament
473. Ligat ure
474. Lineage
475. Lion' s share
476. Li pi d
477. Lissome
478. Lit t er
479. Lit urgy
480. Lodest ar
481. Lucidit y
482. Lulu
483. Macrame
484. Magnanimous
485. Magnum
486. Malevolence
487. Mandal a
488. Maneuver
489. Mani cur ed
490. Manifest at ion
491. Mansard
492. Mat ri cul at i on
493. Mausoleum
494. Maverick
495. Mean
496. Medley
497. Melange
498. Mement o
499. Meni al
500. Ment or
501. Meri t ori ous
502. Mesa
503. Mesmerize
504. Met abol i sm
505. Micr ocosm
506. Milit at e
507. Mi nat or y
508. Mirt h
509. Misant hropy
510. Misapprehension
511. Mit igat ion
512. Modish
513. Monolit hic
514. Monot heism
515. Mont age
516. Moot
517. Morass
518. Morat orium
519. Mordant
520. Mosaic
521. Mosey
522. Mot e
523. Mot if
524. Mot ley
525. Mount ebank
526. Mulct
527. Mumbo j umbo
528. Murky
529. Muse
530. Must
531. Myriad
532. Nadir
533. Nary
534. Ne
535. Neologism
536. Nexus
537. Nibelung
538. Niche
539. Nike
540. Nip and t uck
541. Non sequit ur
542. Nuance
543. Nucl ear f amil y
544. Obeisance
545. Obi
546. Oblit erat e
547. Obsequious
548. Obst reperous
549. Obt use
550. Odomet er
551. Onerous
552. Onslaught
553. Onyx
554. Opaque
555. Oppor t une
556. Opt imum
557. Orb
558. Origami
559. Ort hodox
560. Or t hot i c
561. Ot i ose
562. Overdraft
563. Oxymoron
564. Pad
565. Paddy
566. Palat able
567. Palaver
568. Palazzo
569. Palpit at ion
570. Pampas
571. Pan
572. Pandemic
573. Paper t iger
574. Papier- mache
575. Par
576. Par adox
577. Paragon
578. Paramedic
579. Paramet er
580. Par cel
581. Pare
582. Parlous
583. Paroxysm
584. Pat hos
585. Pat isserie
586. Peccadillo
587. Pedest rian
588. Peerless
589. Pending
590. Pendulous
591. Peninsula
592. Penult imat e
593. Perfi dious
594. Perfidy
595. Perfunct ory
596. Perimet er
597. Peripheral
598. Periphery
599. Per meat e
600. Permut at ion
601. Per or at i on
602. Perpet uat e
603. Perseverance
604. Persnicket y
605. Perspicacious
606. Phalanx
607. Phlegmat ic
608. Picayune
609. Piet y
610. Pilast er
611. Placat e
33
612. Placebo
613. Plague
614. Plat onic
615. Plet hora
616. Poll ex
617. Pol yunsat ur at ed
618. Pomp
619. Porcinely
620. Port mant eau
621. Port ray
622. Post ulat e
623. Pot abl e
624. Pot pourri
625. Precipit at e
626. Prcis
627. Preclude
628. Precursor
629. Predat ory
630. Pre- empt ive
631. Premise
632. Premonit ion
633. Prepl at e
634. Prevail
635. Prevalent
636. Prig
637. Pri mal
638. Privat ion
639. Pro forma
640. Pr ocrast i nat e
641. Procure
642. Prodigious
643. Prolific
644. Proponent
645. Pr oscr i pt i on
646. Provender
647. Provident
648. Provocat ive
649. Pr owess
650. Pr une
651. Purchase
652. Put rid
653. Quadr i ceps
654. Quagmi r e
655. Quart er
656. Queasy
657. Quer ulous
658. Queue
659. Qui nt essent ial
660. Qui nt ile
661. Quorum
662. Radiant
663. Rakish
664. Rambunct ious
665. Rapacious
666. Rapport
667. Raze
668. React ionary
669. Recapit ulat e
670. Recipr ocal
671. Reclamat ion
672. Reclusive
673. Reconnoit re
674. Rect ify
675. Red herring
676. Redolent
677. Regat t a
678. Regime
679. Regnant
680. Relegat e
681. Relief
682. Remedi al
683. Renege
684. Renovat e
685. Reput e
686. Resonance
687. Resound
688. Rest it ut ion
689. Resuscit at e
690. Ret rench
691. Riff
692. Robust
693. Roil
694. Rope- a- dope
695. Rost er
696. Ruddy
697. Rue
698. Rumi nant
699. Sagacit y
700. Sampan
701. Sampler
702. Sanat orium
703. Sanct it y
704. Sandbagger
705. Sanguine
706. Sarong
707. Sat iat e
708. Sat ire
709. Scam
710. Scept ic
711. Sci at i ca
712. Score
713. Scor ned
714. Scruple
715. Scrut i nize
716. Scut work
717. Scut t le
718. Sear
719. Sec
720. Sedat e
721. Seder
722. Sediment
723. Segment
724. Seminary
725. Senescent
726. Sensibilit y
727. Sept ic
728. Serendipit y
729. Seriat i m
730. Shaman
731. Shrapnel
732. Sidle
733. Sierra
734. Siest a
735. Silhouet t e
736. Simony
737. Sinecure
738. Si nge
739. Sisyphean
740. Skept ical
741. Skew
742. Skit t ish
743. Smit hereens
744. Smorgasbord
745. Snide
746. Soj our n
747. Solvent
748. Somat ic
749. Sophist ry
750. Spa
751. Specious
752. Spect er
753. Splot ch
754. Spurious
755. Squander
756. St agft at ion
757. St alwart
758. St anch
759. St aples
760. St at ic
761. St ay
762. St ent orian
763. St eppe
764. St icky wicket
765. St ilt ed
766. St imuli
767. St ipulat e
768. St oicism
769. St rat agem
770. Subdivision
771. Succumb
772. Sui generis
773. Sunder
774. Superficial
775. Superfl uous
776. Supposit ion
777. Sur plice
778. Sur realism
779. Surrealist ic
780. Swar d
781. Swivel
782. Sycophant ic
783. Syllogism
784. Symbiosis
785. Table d' hot e
786. Taboo
787. Tact ile
788. Tai chi
34
789. Tailgat e
790. Talk t urkey
791. Tank
792. Tariff
793. Taxidermy
794. Tchot chkes
795. Telepat hy
796. Temperance
797. Tenacious
798. Tessellat e
799. Therapeut ic
800. Tinge
801. Tipping point
802. Tit an
803. Torpid
804. Tot em
805. Tot emic
806. Tract ion
807. Tranquil
808. Transcend
809. Transient
810. Tr ansmut e
811. Trash t alk
812. Treacly
813. Trepidat ion
814. Triage
815. Trifle
816. Trilogy
817. Trundle
818. Tussle
819. Uber
820. Uncanny
821. Undergird
822. Underst eer
823. Undulat e
824. Undulat ing
825. Unmit igat ed
826. Unregenerat e
827. Urbane
828. Vale
829. Val edi ct or y
830. Vanquish
831. Vascular
832. Vaud
833. Veget at e
834. Velodrome
835. Venalit y
836. Vendet t a
837. Veneer
838. Vener able
839. Venomous
840. Vent r i cl e
841. Veracit y
842. Ver t ex
843. Verve
844. Viabilit y
845. Vint age
846. Vint ner
847. Virago
848. Virulent
849. Vist a
850. Vit icult ure
851. Vit uperat ive
852. Vociferous
853. Voguism
854. Voracious
855. Voraciousness
856. Vor t ex
857. Vulcanize
858. Wadi
859. Wan
860. Wheedl e
861. Whiplash
862. Woof
863. Wry
864. Wunderkind
865. Xanadu
866. Xant hi c
867. Xant hi ppe
868. Xenophobi c
869. Xeri c
870. Xyl oi d
871. Yarmulke
872. Yin and yang
35
SELF TEST QUESTI ONS ( ENGLI SH)
Choose single best opt ion
Q. 1 He was ____ ______ _____ of all valuabl e possessi ons.
A) Robbed.
B) St olen.
C) Pinched.
D) Est ablished.
Q. 2 The pr esence of armed guar ds ____ ______ __ us f r om doing anyt hing di srupt ive.
A) Defeat ed.
B) Excit ed.
C) I rrit at ed.
D) Prevent ed.
Q. 3 Our fli ght was ___ ______ ____ f rom Lahor e t o I slamabad ai r por t .
A) Divert ed.
B) Ref lect ed.
C) Def lect ed.
D) Shift ed.
Q. 4 I am ____ ______ ___ for war d t o our picnic scheduled in next mont h.
A) Looking.
B) Planning.
C) Seeing.
D) Going.
SPOT THE ERROR: I n t he following sent ences some segment s of each
sent ence are underlined. Your t ask is t o indent ify that underlined segment of
t he sentence, which cont ains t he mist ake t hat needs t o be corrected. Fill t he
bubble / circle corresponding t o t hat lett er under t he segment in t he MCQ
Response form.
Q. 5 They did not guess how closely he had kept in t ouch wit h across t he road.
A B C D
Q. 6 He proved t hat if only germs were excluded of wounds, inf lammat ion was avert ed.
A B C D
Q. 7 The man f elt his hair f lut t er and t he t issues of his body drew t ight as if he were st anding at t he
A B C
cent re of a vacuum.
D
Q. 8 He came t o t he hurdles t hat he remember, over which once he had one so easy a vict ory.
A B C D
I n each of t he following quest ion, four alt ernat ive sent ences are given. Choose
t he CORRECT one and fill t he bubble / circle corresponding t o t hat let t er in t he
MCQ Response Form.
Q. 9
A) He lacked bot h t he t r aining and t he equipment needed in t he j ob.
B) He lacked bot h t he t r aining and t he equipment needed by t he j ob.
C) He lacked bot h t he t r aining and t he equipment needed on t he j ob.
D) He lacked bot h t he t r aining and t he equipment needed f or t he j ob.
Q. 10
A) They t r ied t o pacify him for kindness and affect ion.
B) They t r ied t o pacify him in kindness and affect ion.
C) They t r ied t o pacify him by kindness and affect ion.
D) They t r ied t o pacify him wit h kindness and affect ion.
Q. 11
A) Then he sat down in cor ner and remained queit .
B) Then he sat down in cor ner and remained quit e.
C) Then he sat down in cor ner and remain quiet .
D) Then he sat down in cor ner and remained quiet .
Q. 12
A) He was dr enched wit h t he hot ness of his f ear.
B) He was dr enched in t he hot ness of his f ear.
C) He was dr enched by t he hot ness of his fear.
D) He was dr enched of f t he hot ness of his fear.
36
I n each of the following quest ion, four alt ernat ive meanings of a word are
given. You have t o select t he NEAREST CORRECT MEANI NG of t he given word
and fill t he appropriat e Bubble / Circle on the MCQ Response Form.
Q. 13 VEXI NG
A) Annoying
B) Aggressive
C) Viable
D) Waxy
Q. 14 VAGUE
A) Respect f ul
B) Uncert ain
C) Warlock
D) Snow whit e
Q. 15 MANGLED
A) Dodged
B) Grained
C) I ndisput able
D) Damaged
Q. 16 PRODI GI OUS
A) Product ive
B) Enor mous
C) Prudent ial
D) Waddle
Q. 17 ASTOUNDED
A) Shocked
B) Discarded
C) Assured
D) At t ract ed
Q. 18 SAGACI TY
A) Foolishness
B) Large Cit y
C) Onions
D) Wisdom
Q. 19 GRI M
A) Grat is
B) Rest less
C) Severe
D) Grat er
Q. 20 I NDOLENTLY
A) Lazily
B) I ndecent ly
C) I deally
D) Gaily
Q. 21 PERI SH
A) Fur ious
B) Come t o deat h
C) Secret
D) Frust r at ed
Q. 22 DOZE
A) Dogged
B) Diet
C) Sleep
D) Medicine t o be t aken
37
BI OLOGY
STRUCTURE OF THE SYLLABUS ( 2012)
F.Sc. and Non- F.Sc.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. I nt roduct i on t o Bi ol ogy
2. Cell Bi ol ogy
3. Bi ol ogi cal Mol ecul es
4. Mi crobi ol ogy
5. Ki ngdom Animalia and Pl ant ae
6. Human Physi ol ogy
7. Bi oenerget i cs
8. Bi ot echnol ogy
9. Ecosyst em
10. Evol ut i on and Genet i cs
38
1. I NTRODUCTI ON TO BI OLOGY:
Cont ent
Branches of Biology
Learning out comes:
a) Define t he following t erms:
Ecology, Physiology, Hist ology, Genet ics, Zoogeography, Molecular Biology,
Microbiology, Marine and Fresh wat er Biology, Biot echnology, Parasit ology.
b) What are t he various levels of Biological organizat ion st art ing wit h at omic and
subat omic levels t o communit y level?
c) Define t he following t erms:
Transgenic plant s, Cloning, Biological cont rol, Biopest icides, Past eurizat ion,
Disease Cont rol ( Prevent ive measure, Vaccinizat ion, Drug t herapy)
2. CELL BI OLOGY:
Cont ent
Cell st ruct ure
St ruct ure and Funct ion of cellular organelles
Cell division
Learning out comes:
a) Compare t he st ruct ure of t ypical animal and plant cell
b) Compare and cont rast t he st ruct ure of Prokaryot ic cell wit h Eukaryot ic cells
c) Fluid mosaic model of cell membrane and t ransport at ion ( diffusion, facilit at ed
diffusion, act ive and passive t ransport ) , endocyt osis and exocyt osis.
d) Out line t he st ruct ure and funct ion of t he following organelles:
Nucleus, Endoplasmic ret iculum, Golgi apparat us, Mit ochondria, Cent rioles,
Ribosomes
e) Explain Mit osis, what is it s significance?
f) What is Meiosis, describe it in det ail.
g) Describe Meiot ic errors ( Downs syndrome, Klinefelt ers syndrome, Turners
syndrome)
h) Discuss t he t erms Karyokinesis and Cyt okinesis;
i) Discuss and explain:
- Uncont rolled cell division ( cancer)
- Programmed cell deat h (Apopt osis)
- Necrosis
39
3. BI OLOGI CAL MOLECULES:
Cont ent
Carbohydrat e
Prot eins
Lipids
Nucleic acids
Deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA)
Ribonucleic acid ( RNA)
Enzymes
Learning out comes:
a) Discuss carbohydrat es: Monosaccharides (Glucose) , Oligosacchari des ( Cane sugar,
sucrose) , Polysaccharides ( St arches)
b) Describe Prot eins: Amino acids, Primary, Secondary, Tert iary and Quat ernary
st ruct ure of prot eins
c) Describe Lipids: Acylglyceroles, waxes, Phospholipids, Terpenoids
d) Describe t he st ruct ure along it s back bone composit ion and funct ion of DNA as
heredit ary mat erial, Replicat ion of DNA (Semi-conservat ive) , Role of t riplet codons,
Transcript ion ( making up of mRNA) , Translat ion ( prot ein synt hesis: role of
ribosomes, mRNA, t RNA)
e) Give t he st ruct ure and t ypes of RNA ( mRNA, rRNA, t RNA)
f) What is enzyme and it s role in reducing act ivat ion energy?
g) Define t he following t erms:
- Enzymes, Coenzyme, Co- fact or, Prost het ic group, Apoenzyme and Holoenzyme
h) Explain t he mode/ mechanism of enzyme act ion
i) Describe t he effect s of t emperat ure, pH, enzyme concent rat ion and subst rat e
concent rat ion on t he rat e of enzyme cat alysed react ion
j ) Explain t he effect s of reversible and irreversible, compet it ive and non- compet it ive
inhibit ors on t he rat e of enzyme act ivit y
40
4. MI CROBI OLOGY:
Cont ent
Virus
Bact eria
Fungi
Learning out comes
a) Which are t he viral diseases in humans?
b) Ret eroviruses and Acquired I mmunodeficiency diseases
c) Describe t he Life cycle of Bact eriophage ( in det ail wit h it s all st eps) including:
- Lyt ic cycle
- Lysogenic cycle
d) Describe t he st ruct ure and t ypes of bact eria
e) Discuss in det ail:
- Gram + ve bact eria
- Gram ve bact eria
- Nut rit ion in bact eria
f) What are t he uses and misuses of ant ibiot ics?
g) What are molds ( fungi) ? How t hey are useful and harmful t o mankind, give
examples.
h) Describe t he Life cycle of fungus ( Rhizopus) .
5. KI NGDOM ANI MALI A AND PLANTAE:
Cont ent
Kingdom Animalia ( phyla)
Kingdom Plant ae
Learning out comes:
a) Porifera ( wit h respect t o t heir capacit y t o regenerat e)
b) Coelent erat a ( coral reefs as habit at for sea animals)
c) Plat yhelmint hes ( Harmful effect s on human beings) wit h examples
d) Aschelimint hes ( I nfect ion in humans) wit h examples
e) Art hropoda (Economic import ance of Art hropods and harmful impact s on Man)
f) Define t he following t erms:
- Coelomat a, Acoelomat a, Pseudocoele, Radiat a, Bilat eria, Diploblast ic and
Triploblast ic organizat ion.
g) Economic import ance of families wit h reference t o food and ot her usefulness:
- Cassia
- Solanaceae
- Gramineae
41
6. HUMAN PHYSI OLOGY:
Cont ent
a) Digest ive Syst em
b) Gas exchange and Transport at ion
c) Excret ion and Osmoregulat ion
d) Nervous Syst em
e) Reproduct ion
f) Support and Movement
g) Hormonal Cont rol (Endocrine Glands)
h) I mmunit y
Learning out comes:
a) Digest ive Syst em:
- Anat omy of digest ive syst em and specify t he digest ion in:
- Oral cavit y (role of t eet h, t ongue, saliva and enzymes)
- St omach ( enzymes)
- Small int est ine
- Large int est ine
b) Gas exchange and Transport at ion:
- Anat omy of respirat ory syst em (nost rils, t rachea, lungs)
- Explain t he t erm breat hing
- Discuss Blood composit ion, lymph, st ruct ure of heart , carriage of oxygen and
carbon dioxide
c) Excret ion and Osmoregulat ion:
- Describe t he st ruct ure of kidney and it s funct ions wit h respect t o homeost asis
- What are Kidney problems and cures?
- Kidney st ones, lit hot ripsy, kidney t ransplant , dialysis, renal failure
- What do you underst and by t he t erm Homeost asis?
d) Nervous Syst em:
- What is Nervous syst em and it s t ypes?
- Explain CNS ( Cent ral Nervous Syst em) including forebrain, mid brain, hind brain
and spinal cord
- Explain PNS ( Peripheral Nervous Syst em) and it s t ypes ( Aut onomic and
Sympat het ic Nervous Syst em)
- Neurons ( Associat ive, mot or and sensory neuron)
- Discuss t he Nervous disorders ( Parkinsons disease, Epilepsy and Alzheimers
disease)
- What do you underst and by Biological clock and circadian Rhyt hms?
42
e) Reproduct ion:
- Explain t he Reproduct ive syst em in male in det ail
- Explain t he Reproduct ive syst em in female / Menst rual cycle
- Explain:
- Spermat ogenesis
- Oogenesis
- Discuss t he following Diseases in det ail which are sexually t ransmit t ed:
- Gonorrhea, Syphilis, Genit al Herpes, AI DS and how t hese diseases can be
cont rolled (t reat ment is not required)
f) Support and Movement :
- Explain t he role of Human skelet on and skelet al muscles in locomot ion
- Explain t he process of muscle cont ract ion
- What is Muscle fat igue, Tet ani, Cramps?
- Describe t he st ruct ure and funct ions of involunt ary, volunt ary and cardiac
muscles
g) Hormonal control ( Endocrine glands) :
- What are hormones?
- Describe Hypot halamus wit h it s hormones.
- Describe Pit uit ary gland wit h hormones secret ed from it s Ant erior, Median and
Post erior lobe
- Describe adrenal gland wit h it s hormones.
- What are I slet s of langerhans?
- What are t he hormones of aliment ary canal (Gast rin, secret in) ?
- The hormones of ovaries and t est es
h) I mmunit y:
- I mmune syst em and define it s component s:
- Ant igen
- Ant ibody (st ruct ure of ant ibody)
- Lymphocyt es ( B and T cells)
- What is cell mediat ed response and humoral immune response?
- Types of I mmunit y:
- Act ive immunit y
- Passive immunit y
- What do you mean by vaccinat ion?
43
7. BI OENERGETI CS:
Cont ent
Phot osynt hesis and cellular respirat ion
Learning out comes
a) Phot osynt het ic pigment s and t heir absorpt ion spect rum
b) Light dependent st age
c) Light independent st age
d) Describe t he respirat ion at cellular level including:
- Glycolysis, Krebs cycle, Elect ron Transport Chain
8. BI OTECHNOLOGY:
Cont ent
DNA t echnology
Learning out comes
a) Explain Recombinant DNA Technology
b) Discuss Polymerase Chain React ion ( det ailed procedure)
c) What do you underst and by t he following t erms:
- Gene t herapy
- Transgenic animals
9. ECOSYSTEM:
Cont ent
Component s of Ecosyst em
Biological succession
Energy flow in ecosyst em
I mpact s of Human act ivit y on ecosyst em
Learning out comes:
a) Abiot ic and biot ic component s of ecosyst em
b) What is succession, give various st ages of succession on land.
c) Explain t he following t erms:
- Predat ion, parasit ism, symbiosis, mut ualism, commensalism, grazing
d) Describe t he flow of energy in an ecosyst em
- Food chain
- Food web
e) What is t he significance of Human act ivit y on ecosyst em as populat ion, deforest at ion,
ozone deplet ion, at mospheric pollut ion, Green house effect , indust rial effluent s
( insect icides and herbicides) .
44
10. EVOLUTI ON AND GENETI CS:
Cont ent
Darwins t heory
Lamarcks t heory
Evidences of evolut ion
Genet ics
Learning out comes
a) Theory of Darwin and Lamarck, also discuss t he merit s and demerit s
b) Evidences of evolut ion from paleont ology and comparat ive embryology
c) Sex det erminat ion and sex linkage in humans
d) Define t he following t erms:
- Mut at ions, Epist asis, Gene, Allele, Mult iple allele, Pleiot ropy.
45
Table of Specif icat ion ( Biology- 2012)
( For F.Sc. and Non- F.Sc.)
Topic MCQs
1. I nt roduct ion to Biology 04
2. Cell Biology
10
3. Biological Molecules
a) Carbohydrat es 02
b) Prot eins 01
c) Lipids 01
d) Nucleic Acids 01
e) Enzymes 04
4. Microbiology
a) Virus
01
b) Bact eria 02
c) Fungi 01
5. Kingdom Animalia and Plant ae
05
6. Human Physiology
a) Digest ive Syst em 04
b) Gas exchange and Transport at ion 04
c) Excret ion and Osmoregulat ion 05
d) Nervous Syst em 04
e) Reproduct ion 05
f) Support and Movement 05
g) Hormonal Cont rol ( Endocrine Glands) 04
h) I mmunit y 05
7. Bioenerget ics
05
8. Biot echnology
05
9. Ecosyst em
05
10. Evolut ion and Genet ics
05
Tot al 88
46
SELF TEST QUESTI ONS ( BI OLOGY)
Choose single best opt ion
Q. 1 The br anch of biology t hat deals wi t h cell funct ions is call ed:
A) Hist ology.
B) Physiology.
C) Molecular biology.
D) Micr obiology.
Q. 2 Different t issues having r el at ed funct ions t oget her form:
A) Organ.
B) I ndividual.
C) Organelles.
D) Molecules.
Q. 3 St at ement made by a sci ent ist t hat may or may not be t rue is:
A) Theory.
B) Hypot hesis.
C) Scient if ic law.
D) St at ement .
Q. 4 The met hod by which pest s ar e dest royed by using some living or ganisms is call ed:
A) Bio- pest icide.
B) I nt egrat ed management .
C) Biological cont rol.
D) Past eurizat ion.
Q. 5 Robert Hook was t he first person t o see cells in:
A) Various plant s.
B) Animals.
C) Fungi.
D) Cork.
Q. 6 The concept OMNI S cell ula- e- cell al a means t hat , new cells ar e formed fr om:
A) Non living mat erials.
B) Dead organic mat t er.
C) Pre- exist ing living cells.
D) As t he result of chemical react ions.
Q. 7 I n gener alized plant cell t he nucleus is:
A) Present in middle of t he cell.
B) Displaced t o t he side of t he cell.
C) Absent .
D) Modified int o endoplasmic
ret iculum.
Q. 8 Plasma membrane is f ound in t he cells of :
A) Animals only.
B) Plant s only.
C) Bot h in plant s and animals.
D) Bact er ia only.
Q. 9 The semici rcular channels and syst em of t ubes found in cyt oplasm ar e known as:
A) Ribosomes.
B) Glyoxisomes.
C) Endoplasmic ret iculum.
D) Vacuoles.
Q. 10 The st ruct ures t hat ar e involved in t he manufact ure and supply of ener gy t o t he cell
ar e:
A) Cent r ioles.
B) Plast ids.
C) Nucleolus.
D) Mit ochondr ia.
Q. 11 I n a pl ant cell chl orophyll is pr esent in:
A) Chr omoplast s.
B) Leucoplast s.
C) St roma.
D) Chlor oplast s.
Q. 12 Cyt okinesis is a division of:
A) Cyt oplasm.
B) Chr omosomes.
C) Nucleus.
D) Nucleolus.
Q. 13 Duri ng cell division t he plant cell is not seen t o have:
A) Spindle f iber s.
B) Chr omat ids.
C) Cent r omer e.
D) Cent r ioles.
Q. 14 Which human disease is due t o mei ot ic er rors:
A) Typhoid.
B) Cholera.
C) Measles.
D) Downs syndrome.
Q. 15 The basic el ement of all or ganic compounds is:
A) Oxygen.
B) Nit r ogen.
C) Hydrogen.
D) Carbon.
Q. 16 The most abundant car bohydrat e in nat ur e is:
A) Cellulose.
B) Glycogen.
C) Fruct ose.
D) St arch.
47
Q. 17 Ter penoi ds ar e i mport ant group of compounds t hat are made up of simple r epeat ing
unit s:
A) Acylglycerols.
B) I soprenoids.
C) Phospholipids.
D) Ket ones.
Q. 18 The number of t ypes of ami no acid t hat ar e found t o occur i n cells are:
A) 20.
B) 25.
C) 100.
D) 170.
Q. 19 Biochemically enzymes are:
A) Carbohydrat es.
B) Fat t y acids.
C) Hor mones.
D) Prot eins.
Q. 20 The pr esence of enzymes:
A) Slows down t he rat e of react ion.
B) I ncreases t he rat e of react ion.
C) Does not show any change.
D) Complet ely st ops t he react ion.
Q. 21 Lock and key model of enzyme react ing wit h subst rat e was ori gi nally proposed by:
A) Emil Fisher.
B) Koshland.
C) Robert Hook.
D) Robert Br own.
Q. 22 The maj or RNA in t he cell is ribosomal RNA. I t makes up:
A) 80% of t ot al RNAs.
B) 58% of t ot al RNAs.
C) 90% of t ot al RNAs.
D) 40% of t ot al RNA.
Q. 23 Opt i mum pH for pepsin t o wor k efficient ly is:
A) 4. 50
B) 2. 00
C) 6. 80
D) 9. 00
Q. 24 Viruses are simplest organisms and:
A) Have t heir own enzymes.
B) Have cell membrane but not cell
wall.
C) Undergo cell division.
D) Are only DNA or RNA part icles
wit hout cellular st ruct ure.
Q. 25 The most ancient bact eri a ar e:
A) Eubact eria.
B) Archaeobact er ia.
C) Escher ichia coli.
D) St rept ococci.
Q. 26 The bact er ia t hat cause diseases in human bei ngs, ar e cal led:
A) Phot osynt het ic bact er ia.
B) Chemosynt het ic bact er ia.
C) Facult at ive bact eria.
D) Pat hogenic bact eria.
Q. 27 The mut ualist ic associ at ion bet ween cer t ai n fungi and root s of vascul ar pl ant s is
called:
A) Lichens.
B) Parasit ism.
C) Budding.
D) Mycorrhizae.
Q. 28 Sponges which bel ong t o phyl um Porif er a have:
A) Maximum capacit y t o regenerat e.
B) Very lit t le capacit y t o regenerat e.
C) Moderat e capacit y t o regenerat e.
D) No regener at ion capacit y.
Q. 29 The pl at yhelmint hes l iver fluke is:
A) Ect oparasit e in humans.
B) Blood parasit e.
C) Parasit e of respirat ory t ract .
D) Parasit e in t he bile duct .
Q. 30 Which of t he foll owi ng is of economic import ance t o man:
A) Daphnia.
B) Millipede.
C) Silkwor m.
D) Scorpion.
Q. 31 The name Nicot i ana t abacum is given t o:
A) Pot at o.
B) Tomat o.
C) Red pepper.
D) Tobacco.
Q. 32 Family Gramineae has:
A) Only wheat .
B) Only cor n.
C) Only rice.
D) All of t he above.
Q. 33 Duri ng swal lowing t he food t r avels from or al cavit y t o t he st omach by way of
oesophagus:
A) Very quickly.
B) By ant i- per ist alsis.
C) Pushed down by pharynx.
D) Moving due t o per ist alsis.
48
Q. 34 The pancr eas is a:
A) Part of St omach.
B) Part of Small int est ine.
C) Part of Large int est ine.
D) Separat e gland.
Q. 35 The t er m chyme is appl ied t o:
A) Semi- digest ive food in oral cavit y.
B) Semi- solid food in st omach.
C) Semi- digest ed food in t he small
int est ine.
D) Complet ely digest ed f ood in t he
last part of small int est ine.
Q. 36 Villi and micr o villi are pr esent :
A) I n pharynx.
B) I n small int est ine ( j ej unum) .
C) I n oesophagus.
D) I n large int est ine.
Q. 37 Exchange of gases duri ng or ginismic respi rat ion is car ried out by:
A) Dif fusion.
B) Act ive t ransport .
C) Osmosis.
D) Facilit at ed dif fusion.
Q. 38 The opening in t he oral cavi t y ( t hr oat ) t hrough which ai r ent ers t he wind pi pe is
called:
A) Glot t is.
B) Bronchus.
C) Larynx.
D) Pharynx.
Q. 39 The doubl e l ayer of t hin membranes which line and cover lungs ar e call ed:
A) Diaphragm.
B) Alveoli.
C) Pleura.
D) Bronchioles.
Q. 40 Transport at i on of oxygen f rom lungs t o t he t issue cells is by means of:
A) Complet e blood.
B) Lymph.
C) Red blood cells.
D) Whit e blood cells.
Q. 41 Podocyt es ar e pr esent in:
A) Epit helium of renal capsule.
B) Endot helium of blood capillary.
C) Basement membrane of blood
capillary.
D) Epit helium of t he PCT.
Q. 42 Which of t he foll owi ng are t he f unct ions of proxi mal convolut ed t ubule:
A) Ult raf ilt rat ion and reabsorpt ion.
B) Select ive reabsorpt ion and
ret ent ion of wat er.
C) Select ive reabsorpt ion and act ive
t ubular secr et ion.
D) Reabsorpt ion of wat er by t he help
of ADH.
Q. 43 The wal ls of descending li mb of loop of Henl e ar e:
A) Permeable t o wat er as well as t o
sodium and chlor ide.
B) Permeable t o wat er but
imper meable t o salt s.
C) I mpermeable t o wat er and
permeable t o sodium and chloride.
D) I mpermeable t o bot h wat er and
salt s.
Q. 44 ADH aff ect s which of t he f ollowing for ret ent i on of wat er:
A) Walls of collect ing duct .
B) Walls of loop of Henle.
C) Glomer ulus.
D) Proximal convolut ed t ubule.
Q. 45 The count er- cur r ent mult i pli er mechanism is shown by which of t he foll owi ng:
A) Loop of Henle.
B) Proximal convolut ed t ubule.
C) Dist al convolut ed t ubule.
D) Bowmans capsule.
Q. 46 Mechanorecept ors det ect st imulus of :
A) Smell.
B) Light .
C) Pressure ( t ouch) .
D) Cold and warmt h.
Q. 47 The eff ect ors in t he human body which r espond t o a st imulus ar e:
A) Glands only.
B) Muscles only.
C) Bot h muscles and glands.
D) Bones.
Q. 48 Loss of memory ( Dement i a) is also known as:
A) Alzheimer s disease.
B) Epilepsy.
C) Parkinsons disease.
D) Graves disease.
Q. 49 A mi x nerve consist s of:
A) Mot or and sensory nerve fiber s.
B) Sensory and associat ive nerve
fiber s.
C) Mot or and associat ive nerve f iber s.
D) Dendrons and dendrit es.
49
Q. 50 Which one of t he fol lowing hormones is essent ial for t he successful pr oduct ion of
sperms:
A) LH ( Lut einizing Hor mone) .
B) Gonadot r opin hor mone.
C) Test ost er one.
D) Follicle st imulat ing hor mone ( FSH) .
Q. 51 Treponema palli dum cause a disease ( sexually t ransmit t ed) call ed:
A) Genit al Herpes.
B) AI DS.
C) Gonorrhoa.
D) Syphilis.
Q. 52 The fert ili zat ion of ovum t akes place in t he proximal part of t he:
A) Ut erus.
B) Oviduct .
C) Placent a.
D) Uret hra.
Q. 53 Pregnancy is mai nt ai ned by t he:
A) LTH ( Lut eot r opic hormone) .
B) Progest erone.
C) Cort icost eroids.
D) LH and FSH.
Q. 54 At which mont h of pr egnancy t he human embryo is ref er red t o as t he fet us:
A) 3
r d
mont h.
B) 4
t h
mont h.
C) 6
t h
mont h.
D) 2
nd
mont h.
Q. 55 Muscle f at i gue is due t o accumulat i on of :
A) Lact ic acid.
B) ATP.
C) Glucose.
D) Fat s.
Q. 56 Diamet er of skel et al muscl e fi ber is:
A) 2- 50 m.
B) 30- 90 m.
C) 10- 100 m.
D) 1- 80 m.
Q. 57 Lining of di gest ive syst em cont ain t he:
A) Skelet al muscles.
B) Skelet al and car diac muscles.
C) Cardiac muscles.
D) Smoot h muscles.
Q. 58 The vert ebr al column consist s of ______ _ vert ebrae:
A) 33
B) 30
C) 28
D) 38
Q. 59 The most abundant t ype of bone found on moveabl e j oi nt s is:
A) Bone.
B) Hyaline cart ilage.
C) Fibr o- cart ilage.
D) Bone and f ibr o- cart ilage.
Q. 60 Which of t he foll owi ng is a hormone:
A) Gast r ic j uice.
B) Pancreat ic j uice.
C) Bile.
D) I nsulin.
Q. 61 The hor mones in t he human body ar e pr oduced by:
A) Brain only.
B) Liver only.
C) Pancreas only.
D) Dif ferent endocrine glands.
Q. 62 I nsulin is a hor mone pr oduced by:
A) Thyroid gland.
B) Parat hyr oid.
C) Adrenaline gland.
D) Pancreas.
Q. 63 The hor mone call ed Par at hormone r egulat es calcium level in t he bl ood. This hor mone
is produced by:
A) Gonads.
B) Gut .
C) Thyroid gland.
D) Parat hyr oid.
Q. 64 The chemical nat ure of ant i body is:
A) Glycopr ot eins.
B) Glycolipids.
C) Lipopr ot eins.
D) Polysacchar ides.
Q. 65 Which chemicals are secr et ed by T- hel per cel ls t o st imul at e B- pl asma cells t o divi de:
A) I nt erfer ons.
B) Cyt okines.
C) Hist amines.
D) Fibr in.
Q. 66 Which of t he foll owi ng is descr ibed as vaccinat ion:
A) Art if icial act ive immunit y.
B) Nat ural act ive immunit y.
C) Art if icial passive immunit y.
D) Nat ural passive immunit y.
Q. 67 B- lymphocyt es and T- lymphocyt es ar e formed:
A) Befor e birt h in bone marrow.
B) Befor e birt h in t hymus gland.
C) Aft er mat ur it y in blood.
D) Aft er birt h in blood.
50
Q. 68 The ant i bodi es provi ded t o inf ant t hr ough mot hers mil k is an exampl e of:
A) Nat ural passive immunit y.
B) Art if icial passive immunit y.
C) Nat ural act ive immunit y.
D) Art if icial act ive immunit y.
Q. 69 Which of t he foll owi ng is not t he end pr oduct of glycolysis:
A) Pyruvat e.
B) ATP.
C) Oxaloacet at e.
D) Reduced NAD.
Q. 70 Which of t he foll owi ng process does occur for t he for mat ion of acet yl Co- A from
pyr uvat e:
A) Decarboxylat ion.
B) Hydrogenat ion.
C) Carboxylat ion.
D) Deaminait on.
Q. 71 At t he beginning of Kr ebs cycle, acet yl Co- A combines wit h which subst ance t o form
cit rat e ( 6- C) :
A) Oxaloacet at e.
B) Oxoglut arat e.
C) Fumarat e.
D) Succinat e.
Q. 72 Which of t he following ar e t he end product s of l ight dependent st age, used in t he
Calvi n cycle t o change glycer at e- 3- phosphat es i nt o t riose phosphat es:
A) NADPH + ATP
B) NADH + ATP
C) RuBp + ATP
D) O2 + NADPH
Q. 73 Which of t he foll owi ng is not t he end pr oduct of non- cyclic phot ophosphoryl at ion:
A) Reduced NADP.
B) ATP.
C) O2.
D) CO2.
Q. 74 Enzymes r est rict ion endonucleases wer e isol at ed f rom:
A) Viruses.
B) Bact er ia.
C) Fungi.
D) Prot ozoan.
Q. 75 Duri ng polymer ase chai n r eact i on, how DNA doubl e hel ix is separ at ed:
A) By heat t reat ment .
B) By use of enzyme DNA Polymerase.
C) By use of enzyme DNA Helicase.
D) By use of enzyme DNA Ligase.
Q. 76 Which enzyme is used t o j oin t he desir ed gene int o t he pl asmi d DNA during genet ic
engineer ing:
A) DNA Helicase.
B) DNA Ligase.
C) DNA Polymerase.
D) Taq Polymerase.
Q. 77 Which of t he following is an exampl e of benefit s of t ransgenic or ganisms pr oduced
t hrough genet ic engi neeri ng:
A) Product ion of ant ibiot ics.
B) Product ion of insulin.
C) Product ion of ant i- rabies vaccine.
D) Product ion of ant i- malarial drugs.
Q. 78 I n cyst ic fibrosis t ransport at ion of which ion is f ault y, result ing int o t he product i on of
disease:
A) Chlor ide.
B) Fluor ide.
C) Calcium.
D) Magnesium.
Q. 79 A group of int er- breeding indivi duals occurri ng t oget her in a space and t i me is call ed:
A) Communit y.
B) Populat ion.
C) Niche.
D) Species.
Q. 80 Which of t hese is bi ot ic fact or of t he ecosyst em:
A) Air.
B) Wat er.
C) Soil.
D) Phot osynt het ic plant s.
Q. 81 An associat i on bet ween or ganisms which bri ngs benefit t o bot h t he or ganisms i s
known as:
A) Predat ion.
B) Commensalism.
C) Grazing.
D) Symbiosis.
Q. 82 When successi on is complet ed, a gr eat diversit y of plant s and a st able communit y i s
seen, which is call ed:
A) Hydrosphere.
B) Pioneer s.
C) Climax communit y.
D) Secondary succession.
Q. 83 A t hin l ayer of eart h in which all living or ganisms exist s is called:
A) Ecosyst em.
B) Biosphere.
C) Habit at .
D) Xerosere.
51
Q. 84 The br anch of biology t hat provi de evi dence t hr ough fossil recor d is cal led:
A) Vest igial st r uct ur es.
B) Comparat ive anat omy.
C) Biogeogr aphy.
D) Palaeont ology.
Q. 85 One of t he f act ors given below does not eff ect gene fr equency:
A) Mut at ion.
B) Migrat ion.
C) Genet ic dr ift .
D) Food.
Q. 86 Charl es Dar wi n gave t he:
A) Theory of special cr eat ion.
B) Theory of Nat ural select ion.
C) I nher it ance of acquired charact er s.
D) Cell t heory.
Q. 87 A gene which has mult i ple phenot ypic effect is call ed:
A) Pleiot r opic.
B) Epist asis.
C) Mult iple allele.
D) Locus.
Q. 88 Change in t he nat ur e of gene is known as:
A) I ncomplet e dominance.
B) Pleiot r opy.
C) Mut at ion.
D) Polygenic t rait .
APTI TUDE FEEDBACK FOR ENTRANCE TEST 2012
A compul sory feedback shall be admini st ered t o all candi dat es
aft er t he complet i on of Ent rance Test 2012, coll ect i on and secure
packing of t he Quest i on Papers and Response Forms. The feedback i s
for Uni versit y and Government use onl y and SHALL NOT I N ANY WAY
affect t he meri t of t he candi dat es.
You might also like
- UHS MCAT Entry Test Syllabus 2014Document55 pagesUHS MCAT Entry Test Syllabus 2014medicalkidunya100% (1)
- Syllabus: Entrance TestDocument55 pagesSyllabus: Entrance TestMalikXufyanNo ratings yet
- UHS MCAT Entry Test Syllabus 2015Document36 pagesUHS MCAT Entry Test Syllabus 2015Shawn Parker89% (9)
- Syllabus & Model Paper: Entrance TestDocument60 pagesSyllabus & Model Paper: Entrance TestTanzil RahmanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Physics June 2013 (2010)Document4 pagesEngineering Physics June 2013 (2010)Prasad C MNo ratings yet
- Vtu Be 1st Year Physics Question PaperDocument4 pagesVtu Be 1st Year Physics Question PapermidhunmathewNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper 2Document3 pagesPractice Paper 2shrirahulambadkarNo ratings yet
- UHS Lahore Entrance Test Syllabus 2011Document37 pagesUHS Lahore Entrance Test Syllabus 2011Junaid AlamNo ratings yet
- Engg Physics June 2012 NewDocument4 pagesEngg Physics June 2012 NewPrasad C MNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For General Chemistry Atoms First 2Nd Edition by Mcmurry Fay Isbn 0321809262 978032180926 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesTest Bank For General Chemistry Atoms First 2Nd Edition by Mcmurry Fay Isbn 0321809262 978032180926 Full Chapter PDFrex.henderson212100% (13)
- Phy 111Document5 pagesPhy 111Oyari felixNo ratings yet
- Question Bank CHEM 1201Document12 pagesQuestion Bank CHEM 1201SHASHANK VISHWAKARMANo ratings yet
- Chemistry OverviewDocument33 pagesChemistry OverviewKarim HakimNo ratings yet
- Phy XDocument4 pagesPhy XMuhammad SaadNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1 1Bittu rajaNo ratings yet
- ALL QB's PDFDocument36 pagesALL QB's PDFanimesh0gargNo ratings yet
- Revision QuestionsDocument7 pagesRevision QuestionsShazia FarheenNo ratings yet
- Resource 20210531095551 Enrichment Work ChemistryDocument4 pagesResource 20210531095551 Enrichment Work ChemistryAditya SallyNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy (MCQ) - : YogeshDocument16 pagesSpectroscopy (MCQ) - : YogeshYUGI SINGH100% (1)
- Topic 1 Introduction To Atomic Structure 2012-1Document58 pagesTopic 1 Introduction To Atomic Structure 2012-1Arjun RavalNo ratings yet
- Therapy Physics - Review - Part 1 PDFDocument62 pagesTherapy Physics - Review - Part 1 PDFcarlosqueiroz7669100% (3)
- Ai Interview QuestionsDocument31 pagesAi Interview QuestionsmohanapriyaNo ratings yet
- 10th Phy 1st Half BookDocument3 pages10th Phy 1st Half BookIbrahim FarooqiNo ratings yet
- Physics EngDocument8 pagesPhysics EngPrasad C MNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper Set 2017 SA 1Document4 pagesChemistry Paper Set 2017 SA 1Daulot SarmaNo ratings yet
- CentralDocument10 pagesCentralwondimuNo ratings yet
- Quantum Physics Review QuestionsDocument3 pagesQuantum Physics Review QuestionswondimuNo ratings yet
- Laser and Its Application MCQDocument50 pagesLaser and Its Application MCQChudaman Mahajan100% (2)
- ChemistryDocument5 pagesChemistryTirupal PuliNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Exam 1Document10 pagesGeneral Chemistry Exam 1Bethany Wong100% (1)
- 2022 Puc I Chem Imp QuestionsDocument13 pages2022 Puc I Chem Imp QuestionsCHAKRI BABLUNo ratings yet
- MCQs For Chapter 7-12 KeyDocument11 pagesMCQs For Chapter 7-12 KeyismahijNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document18 pagesChapter 7roxy8marie8chanNo ratings yet
- Half Yearly Revision ImarksDocument1 pageHalf Yearly Revision ImarksJagan EashwarNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 of 12 Class-1Document3 pagesUnit - 1 of 12 Class-1kopperumsingh875No ratings yet
- Test Bank For General Organic and Biochemistry 8th Edition Katherine Denniston DownloadDocument15 pagesTest Bank For General Organic and Biochemistry 8th Edition Katherine Denniston Downloadankledsisterlydaazg100% (26)
- Modern Physics Mcqs and Fill in The Blanks 2023Document8 pagesModern Physics Mcqs and Fill in The Blanks 2023LakshmiNo ratings yet
- C1100E-TDDocument27 pagesC1100E-TDghadirtaleb4No ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) On Nuclear PhysicsDocument150 pagesMultiple Choice Questions (MCQ) On Nuclear PhysicsChudaman MahajanNo ratings yet
- Class11 T2 2023Document7 pagesClass11 T2 2023SA M MYNo ratings yet
- Physics Question Bank TitleDocument6 pagesPhysics Question Bank TitlePATIL NISHANT SUNILNo ratings yet
- HP Board Class XII Physics Model Question PaperDocument5 pagesHP Board Class XII Physics Model Question PaperJack DourNo ratings yet
- 102 Fundamentals of Radiology and ImagingDocument15 pages102 Fundamentals of Radiology and ImagingShivani YadavNo ratings yet
- 02 - Test - FinalDocument3 pages02 - Test - FinalHarshitha KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Physics fundamentals and concepts MCQ practice testDocument2 pagesPhysics fundamentals and concepts MCQ practice testUsman ChughtaiNo ratings yet
- CH 7 PTDocument14 pagesCH 7 PTaaron.hartmanNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Applied Physics, Sem-1, BS-105Document5 pagesQuestion Paper Applied Physics, Sem-1, BS-105Kartik AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Page 1 of 2Document0 pagesPage 1 of 2Pratyush MishraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages From The CosmosDocument12 pagesChapter 5 Light and Matter: Reading Messages From The CosmosThangaVeluNo ratings yet
- The Navigator Science School and College Thatta: PHY-2 CH#6TH & 7TH: Date: 03-10-2020Document2 pagesThe Navigator Science School and College Thatta: PHY-2 CH#6TH & 7TH: Date: 03-10-2020FatehNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter QuestionsDocument13 pagesDual Nature of Radiation and Matter QuestionsRohit Karandikar0% (1)
- 102 Fundamentals of Radiology and ImagingDocument14 pages102 Fundamentals of Radiology and ImagingManisha khan100% (2)
- Grade 12 Chemistry Model ExamsDocument11 pagesGrade 12 Chemistry Model ExamsErmias100% (1)
- 12 TH STD Physics Important Questions S.Y.J.C. March 2022Document8 pages12 TH STD Physics Important Questions S.Y.J.C. March 2022jhanvi.rmNo ratings yet
- 24-10-17 - Assignment 3 Question PoolDocument1 page24-10-17 - Assignment 3 Question PoolPranavSharmaNo ratings yet
- Optics: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyFrom EverandOptics: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Theoretical Solid State Physics: International Series in Natural Philosophy, Volume 1From EverandTheoretical Solid State Physics: International Series in Natural Philosophy, Volume 1Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Quantitative Coherent Imaging: Theory, Methods and Some ApplicationsFrom EverandQuantitative Coherent Imaging: Theory, Methods and Some ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Solid State Physics: International Series of Monographs in Natural Philosophy, Volume 2From EverandTheoretical Solid State Physics: International Series of Monographs in Natural Philosophy, Volume 2No ratings yet
- Law No. 116 of 2013 For Promoting Foreign Direct Investment in KuwaitDocument18 pagesLaw No. 116 of 2013 For Promoting Foreign Direct Investment in KuwaitMohammad RNo ratings yet
- Cyberoam Registration & Subscriptin GuideDocument14 pagesCyberoam Registration & Subscriptin GuideMohammad RNo ratings yet
- Configure Gateway Load Balancing and Failover PDFDocument5 pagesConfigure Gateway Load Balancing and Failover PDFMohammad RNo ratings yet
- Trend MicroDocument18 pagesTrend MicroMohammad RNo ratings yet