Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology Ws
Uploaded by
ananthOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology Ws
Uploaded by
ananthCopyright:
Available Formats
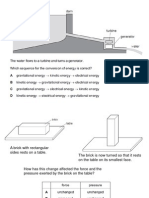
1.The diagram below shows the main vessels of the blood circulation system of a mammal.
a) Add the following labels to the diagram below: caudal vena cava; cranial vena cava; aorta; hepatic portal vessel pulmonary artery; pulmonary vein; renal artery b) Add arrows to show the direction in which the blood flows c) Colour the vessels that carry oxygen rich blood "red" and oxygen poor blood "blue".
2. Arrange the following types of blood vessel in the correct order as blood would flow down them from the heart to the body and back to the heart again.
A. other veins; B. venules; C. capillaries; D. arterioles; E. other arteries. F. vena cava; G. aorta ...... ...... ...... ...... ...... ...... ...... ...... ...... ...... ...... ...... ...... ......
He art
He art
3. Fill in the blanks in the following table on arteries, veins and capillaries.
Arteries
Capillaries
Veins
Structure of wall
3 layers
Thickness of wall
...................
Very thin
...................
Retain shape or collapse when no blood passes ................... ................... ...................
Direction of blood flow
......................
......................
Towards heart
Speed of blood flow?
...................
..................
..................
Blood pressure
High
.................
.................
Valves present?
..............
No
..............
Pulse present?
..............
..............
..............
Carry oxygenated/deoxygenated blood?
...................
...................
...................
4. The photo below shows cross sections through an artery and a vein.
a. Label which vessel is the artery and which the vein. b. Give 2 reasons for your answer. Reason 1.. Reason 2..
5. True or false? If false give the correct answer. Mammals have a double open blood system. T / F Arteries only carry oxygenated blood. T / F Artery walls have many more layers of tissue in them than the walls of veins. T / F The pulse is only felt in arteries. T / F
Capillaries have valves in them to stop the blood flowing backwards. T / F Blood leaks out of capillaries so that the oxygen and glucose etc. can reach the cells. T / F Diastole is the phase between pulses. T / F Blood flows along veins back to the heart because of gravity. T / F
6. The diagram below shows the blood pressure during the passage of the pulse along an artery.
Add labels to the diagram to
show: the pulse; diastole; systole.
7. As there is no pulse in veins, what moves the blood along them? (Give at least 2 methods) 1. ................................................. 2................................................... 8. Name the vessel that:
Carries oxygenated blood to the heart muscle............................... Supplies the brain with oxygenated blood............................... Carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs............................... Carries blood from the intestines to the liver.............................. Carries deoxygenated blood away from the kidneys...............................
a. Which is the blood capillary? b. How thick is the wall of the capillary? c. What is happening to the blood pressure as the blood flows along the capillary? d. What substances pass out of the capillary walls to surround the tissues? e. What is tissue fluid? f. Which vessel is the lymphatic vessel? g. How do lymphatic vessels differ from capillaries? h. What passes into the lymphatic vessel? i. How does lymph differ from tissue fluid? j. Why does the fluid leave the capillary at the beginning of the capillary bed and flow back in at the other end?
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Treasures Book 1 Unit 1Document33 pagesTreasures Book 1 Unit 1Janinne AbuegNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Biology Notes For O LevelDocument36 pagesBiology Notes For O LevelAhmad Barrun Nidhom92% (158)
- Biology Notes For O LevelDocument36 pagesBiology Notes For O LevelAhmad Barrun Nidhom92% (158)
- The Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesThe Nervous SystemananthNo ratings yet
- Foreclosing Modifications - How Servicer Incentives Discourage Loan ModificationsDocument86 pagesForeclosing Modifications - How Servicer Incentives Discourage Loan ModificationsRicharnellia-RichieRichBattiest-CollinsNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesLesson PlanNunette SenilloNo ratings yet
- Sale DeedDocument3 pagesSale DeedGaurav Babbar0% (1)
- NOGALES Math Files for Elementary SchoolDocument3 pagesNOGALES Math Files for Elementary SchoolMl Phil100% (6)
- FeuersteinDocument13 pagesFeuersteinCognitiveSkillsMeka100% (2)
- California Clothing Vs QuinonesDocument4 pagesCalifornia Clothing Vs QuinonesLily MondaragonNo ratings yet
- IQ PHysics 1Document20 pagesIQ PHysics 1ananthNo ratings yet
- What Do You Know Already About The Hole' in The Ozone Layer? Jot Down Your Notes HereDocument2 pagesWhat Do You Know Already About The Hole' in The Ozone Layer? Jot Down Your Notes HereananthNo ratings yet
- Fact and Opinion Climbing BlindlyDocument2 pagesFact and Opinion Climbing Blindlyananth0% (1)
- IQ PHysics 2Document24 pagesIQ PHysics 2ananthNo ratings yet
- Additive What The Additive Does E Number: ColoursDocument1 pageAdditive What The Additive Does E Number: ColoursananthNo ratings yet
- DweckshortDocument4 pagesDweckshortananthNo ratings yet
- Gibbs Exercise FiveDocument3 pagesGibbs Exercise FiveananthNo ratings yet
- IQ PHysics 1Document20 pagesIQ PHysics 1ananthNo ratings yet
- Gibbs Exercise Four ReadingDocument8 pagesGibbs Exercise Four ReadingananthNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet On CirculationDocument2 pagesWork Sheet On CirculationananthNo ratings yet
- Effective teaching of study skills strategiesDocument4 pagesEffective teaching of study skills strategiesMohamad Hafiz SalehNo ratings yet
- Paper 3 Marking Scheme Nov 2009Document3 pagesPaper 3 Marking Scheme Nov 2009MSHNo ratings yet
- Complete The Sentences 6 Bgb75Document1 pageComplete The Sentences 6 Bgb75ananthNo ratings yet
- W S Grade 8 EnzymesDocument2 pagesW S Grade 8 EnzymesananthNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse EffectDocument3 pagesGreenhouse EffectananthNo ratings yet
- Enzymes in IndustryDocument4 pagesEnzymes in IndustryananthNo ratings yet
- Asexual ReproductionDocument6 pagesAsexual ReproductionananthNo ratings yet
- 5090 w09 Ms 6Document3 pages5090 w09 Ms 6mstudy123456No ratings yet
- Enzymes: The Effect of Temperature EnzymesDocument2 pagesEnzymes: The Effect of Temperature EnzymesananthNo ratings yet
- Reflex ArcDocument6 pagesReflex ArcananthNo ratings yet
- Reflex ArcDocument6 pagesReflex ArcananthNo ratings yet
- 50 Interesting FactsDocument1 page50 Interesting FactsJela ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Bacteria:: Classification and StructureDocument12 pagesBacteria:: Classification and StructureananthNo ratings yet
- Accenture 2014 Celent Claims ABCD Acn Duck Creek Dec14Document28 pagesAccenture 2014 Celent Claims ABCD Acn Duck Creek Dec14Ainia Putri Ayu KusumaNo ratings yet
- ECEg 241 Chapter 2 Particle Properties of WavesDocument5 pagesECEg 241 Chapter 2 Particle Properties of WavesYITBAREKNo ratings yet
- TQM 2 MARKSDocument12 pagesTQM 2 MARKSMARIYAPPANNo ratings yet
- TQM Study of Quality Practices at Unicast AutotechDocument32 pagesTQM Study of Quality Practices at Unicast AutotechAkshay Kumar RNo ratings yet
- Meena ResumeDocument3 pagesMeena ResumeAnonymous oEzGNENo ratings yet
- PROJECT REPORT Personal Selling PDFDocument19 pagesPROJECT REPORT Personal Selling PDFHimaja GharaiNo ratings yet
- Year 9 Autumn 1 2018Document55 pagesYear 9 Autumn 1 2018andyedwards73No ratings yet
- Book Report Template 02Document3 pagesBook Report Template 02JaredNo ratings yet
- Holy Trinity University: Puerto Princesa City Basic Education DepartmentDocument2 pagesHoly Trinity University: Puerto Princesa City Basic Education DepartmentBrian Reyes GangcaNo ratings yet
- Healthy Horizons-Butler University Ambulatory Care Appe Rotation SyllabusDocument13 pagesHealthy Horizons-Butler University Ambulatory Care Appe Rotation Syllabusapi-316593964No ratings yet
- 1201 CCP Literature ReviewDocument5 pages1201 CCP Literature Reviewapi-548148057No ratings yet
- Webquest Biotechnology RubricDocument2 pagesWebquest Biotechnology Rubricapi-556285637No ratings yet
- SDSDDocument114 pagesSDSDbhatiasabNo ratings yet
- One, Two and Three PerspectiveDocument10 pagesOne, Two and Three PerspectiveNikko Bait-itNo ratings yet
- B1 Mod 01 MathsDocument152 pagesB1 Mod 01 MathsTharrmaselan VmanimaranNo ratings yet
- Chronology of TLM Event in The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesChronology of TLM Event in The PhilippinesTheus LineusNo ratings yet
- Coordinates: Primary Practice QuestionsDocument10 pagesCoordinates: Primary Practice QuestionsJames KeruNo ratings yet
- Compulsive Buying Tendency As A Predictor of Attitudes and PerceptionsDocument4 pagesCompulsive Buying Tendency As A Predictor of Attitudes and PerceptionsvsharanyaNo ratings yet
- (PC) Brian Barlow v. California Dept. of Corrections Et Al - Document No. 4Document2 pages(PC) Brian Barlow v. California Dept. of Corrections Et Al - Document No. 4Justia.comNo ratings yet
- Wildlife Ecology - Unit 14 - Week (12) - RevisionDocument1 pageWildlife Ecology - Unit 14 - Week (12) - RevisionAdityaNo ratings yet
- Sugar Cane White FlyDocument13 pagesSugar Cane White Flyvishnu0751No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 SQL Complex QueriesDocument51 pagesChapter 8 SQL Complex QueriesJiawei TanNo ratings yet