Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Networking Plus 2005 Notes 1. Standard Topologies
Uploaded by
eyenstynOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Networking Plus 2005 Notes 1. Standard Topologies
Uploaded by
eyenstynCopyright:
Available Formats
Networking Plus 2005 Notes 1.
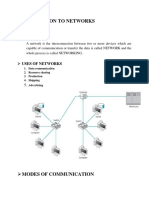
Standard Topologies Bus - A single cable (trunk) that connects all computers in a single line. Star - Computers connect to a centralized hub via cable segments. Ring - Connects all computers on a single cable. Ends are not terminated, but form a full Mesh - Commonly used in WAN configurations. Routers are connected to multiple links for redundancy and to give the ability to determine the quickest route to a destination. 2. Access Methods Accessing Network Media Token Ring Deterministic access method Ethernet Contention based method CSMA/CD - Collision Detection; listens to cable prior to sending data. (Ethernet) CSMA/CA - Collision Avoidance; Announces intention to send data. (AppleTalk) Token-Passing - Token revolves around ring, computer which has token is permitted to data. (Token Ring) One device designated media administrator. Secondary device waits to be polled by primary device to check if it has data to be sent. 3. IBM Cabling System RG stands for Radio Guide Thinnet Coaxial - .25 inches thick carries signal 185 meters. Known as RG-58 family and has a 50 ohm impedance. RG-58 /U - Solid Copper Core RG-58 A/U - Stranded Wire Core RG-58 C/U - Military Specification of RG-58 A/U RG-59 - Broadband transmission (Television Cable) RG-62 - ArcNet Network Cable - When troubleshooting thinnet coaxial cable, the cable terminator must read 50 ohms, and the cable and connector must measure infinite. Thicknet Coaxial - .5 inches thick, carries signal 500 meters. A transceiver (Vampire Tap) is used to make a physical connection with the Thicknet core. Unshielded Twisted Pair - Twisted pair wiring, carries signal 100 meters. Is susceptible to crosstalk. Shielded Twisted Pair - Twisted pair wiring, carries signal 100 meters. Has foil or braided jacket around wiring to help reduce crosstalk and to prevent electromagnetic interference. Attenuation - The degrading of a signal as it travels farther from its origination. Crosstalk - Signal overflow from one wire to another adjacent wire. Jitter - Instability in a signal wave. Caused by signal interference or an unbalanced FDDI ring or Token Ring. 4. UTP/STP Category Speeds Cat 2 - 4 mbps Cat 3 - 10 mbps Cat 4 - 16 mbps Cat 5 - 100 mbps Fiber-Optic - Carries light pulse signals through glass core at speeds of between 100 Mbps - 200,000 Mbps. 5. Ethernet Specifications Type Cable types 10Base2 - RG-58 thinnet coaxial cable 10Base5 - Thicknet coaxial cable 10BaseT - Category 3, 4, or 5 UTP cable 100BaseT - Category 5 UTP cable Connection Type BNC T Connector DIX/AUI RJ-45 RJ-45 Max Length 185 meters (607 ft) 500 meters (1640 ft) 100 meters (328 ft) 100 meters (328 ft)
6. Signal Transmissions Baseband - Uses digital signaling over a single frequency. Transmits bi-directionally. Broadband - Uses analog signaling over a range of frequencies. Transmits unidirectionally and uses amplifiers for signal regeneration.
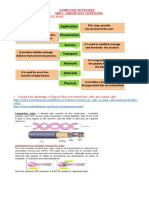
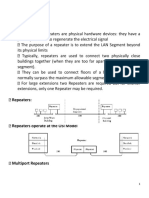
7. OSI Model Application Layer - Allows applications to use the network. Handles network access, flow control and error recovery. Presentation Layer - Translates data into a form usable by the application layer. The redirector operates here. Responsible for protocol conversion, translating and encrypting data, and managing data compression. Session Layer - Allows applications on connecting systems to establish a session. Provides synchronization between communicating computers. Transport Layer - Responsible for packet handling. Ensures error-free delivery. Repackages messages into smaller packets, and handles error handling. Network Layer - Translates system names into addresses. Responsible for addressing, determining routes for sending, managing network traffic problems, packet switching, routing, data congestion, and reassembling data. Data Link Layer - Sends data from network layer to physical layer. Manages physical layer communications between connecting systems. LLC - (802.2) Manages link control and defines SAP's (Service Access Points). Checks ACK, CRC MAC - (802.3, 802.4, 802.5, 802.12) Communicates with adapter card. Responsible for Carrier Sense and Token Passing Physical Layer - Transmits data over a physical medium. Defines cables, cards, and physical aspects. 7a. OSI layer Protocols residing here Application SMB, NCP Presentation NCP Session None Transport TCP, SPX, NWLink, NetBEUI NetworkIP, IPX, NetBEUI, DLC, DecNET Data Link None Physical None 8. IEEE 802 Specifications 802.1 Internetworking 802.2 LLC (Logical Link Control) 802.3 CSMA/CD - Ethernet 802.4 Token Bus LAN 802.5 Token Ring LAN 802.6 MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) 802.7 Broadband Technical Advisory Group 802.8 Fiber-Optic Technical Advisory Group 802.9 Integrated Voice/Data Networks 802.10 Network Security 802.11 Wireless Networks 802.12 Demand Priority Access LAN, 100 Base VG - AnyLAN 8a. LAN Enhancement Components Repeater - regenerates signals for retransmission. Moves packets from one physical media to another. Will pass broadcast storms. Cannot connect different network topologies or access methods. Bridges - are used to segment networks. They forward packets based on address of destination node. Uses RAM to build a routing table based on hardware addresses. Will connect dissimilar network topologies. Will forward all protocols. Regenerates the signal at the packet level. Routers - packets across multiple networks. Uses RAM to build a routing table based on network addresses (i.e. TCP address). Shares status and routing information to other routers to provide better traffic management and bypass slow connections. Will not pass broadcast traffic. Are slower than bridges due to complex functions. Strips off Data Link Layer source and destination addresses and then recreates them for packets. Routers can accommodate multiple active paths between LAN segments. Will not pass unroutable protocols. Brouter - Will act as a router for specified protocols and as a bridge for other specified protocols. Gateway - Used for communications between different NOS's (i.e. Windows NT and IBM SNA). Takes the packet, strips off the old protocol and repackages it for the receiving network. Basically converts data between incompatible sstems for different networks.
Multiplexer Device - that can divide transmissions into two or more channels. Switches - Hub with bridging capabilities. Switch filters traffic through MAC addresses. Creates sessions on ports within the hub. Used when upgrading to 100mb Fast Ethernet. Repeater Physical Bridge Data Link (MAC Sublayer) Remote Bridge Data Link (MAC Sublayer) Router Network Brouter Data Link and Network Gateway Transport, Session, Presentation and Application Multiplexer Physical Switch Data Link Spanning Tree Algorithm - was developed for bridges to determine the most efficient network in path when there are multiple paths to choose from. Multiplexing - Several signals from different sources are collected into the component and are fed into one cable for transmission. 8b. Protocols Routable - TCP/IP, IPX/SPX, OSI, AppleTalk, DecNET, XNS. Non-routable - NetBEUI, DLC NetBEUI - Microsoft protocol designed for small LANs; non-routable. Not compatible with UNIX networks. IPX/SPX - Fast protocol for small and large Novell networks; is routable. Also known in NT as NWLink. TCP/IP - Internet protocol; is routable. Used by UNIX networks. Remember IP is connectionless DecNET - Defines communications over FDDI MANs; is routable. AppleTalk - Apple protocol designed for small LAN file and print sharing; is routable. RIP (Routing Information Protocol) - Routers use this to communicate with each other to determine the least busy and shortest network routes. NDIS (Microsoft) and ODI (Novell) are used to bind multiple protocols to a network adapter. SLIP (Serial Line IP) - Provides dial-up communications, but is unable to simultaneously transfer multiple protocols. PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) - Performs dynamic IP addressing, multi-protocol support, password login and error control. Common TCP/IP problems are caused by incorrect subnet masks and default gateways. Incorrect frame types will cause problems between two systems using IPX/SPX. 8c. Protocols within TCP/IP FTP File Transfer connection oriented TFTP is connectionless SMTP Simple Mail Transfer Proto HTTP this is a stateless protocol meaning each command is executed independently POP3 Remember it is mail delivery ONLY it does not handle sending messages. Port 110 Telnet port 23 ICMP control, uses PING DNS port 53 DHCP need to allow DHCP relay agents in order to send broadcasts over routers (which by design do not normally accept ANY broadcasts). Basically DHCP is a form of broadcast Remember DORA which stands for the lease process and menas Discover, Offer, Request, ACK NOTE: DHCP uses ARP to assign IP addresses to clients SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol consists of two components, an agent and SNMP mgmt console (according to a MIB). Uses READ, WRITE, TAVERSAL and TRAP commands. These are set up with GET requests (GET is actually a READ command)Most common way of security in SNMP is community names. Port 161 and 162 Consists of three elements: 1. SNMP Mgmt Console (OpenView, Tivoli, etc) 2. Agent 3. MIB
9. Computer Name Resolution DNS (Domain Name Services) - Used to translate a host name to an IP address. Default gateways and sbnets can also be assigned by DNS. Remember that FQDN is fully qualified domain WINS (Windows Internet Naming Service) - Used to resolve NetBIOS computer name to an IP address. Similari to DNS except that it only works on a Microsoft network. WINS can be combined with DNS. WINS has both a server and a client component HOSTS - File which contains mappings between DNS host names and their IP addresses. LMHOSTS - File which contains mappings between NetBIOS computer names and their IP addresses. Packet Switching - Packets are relayed across network along the best route available. Beaconing - Computers are used to detect network faults, then transmit the fault signal to the server. Packet Switching Networks (sent in burst over the network in asynchronus meaning not in any order). QoS is nearly non-existent versus circuit switched Type Function X.25 Designed to connect remote terminals to mainframe host systems. Is very slow due to constant error-checking. Frame Relay Point-to-point system which uses digital leased lines. Will provide bandwidth as needed. Requires frame relay capable bridge or router for transmission. Frame is roughly equivalent to ISDN in performance. This is a connectionless service ATM OPERATES AT DATA LINK LAYER and is connection-oriented Advanced implementation of packet switching. Asynchronus Transfer Mode. Transmits at speeds of 155Mbps to 622Mbps with capabilities of higher speeds. Transmits data in 53 byte (48 application, 5 header) cells. Uses switches as multiplexers to permit several computers to simultaneously transmit data on a network. Great for voice and video communications. ATM can prioritize data ISDN Transmits at 128k/sec. Has three data channels - 2 B channels @ 64k/sec & 1 D channel @ 16k/sec. The B channels carry data while the D channel performs link management and signaling. PRI is roughly equivalent to T-1 One D channel and 23 B channels FDDI 100 Mbps token-passing ring network which uses fiber-optic media. Uses a dual-ring topology for redundancy and in case of ring failure. Each ring is capable of connecting 500 computers over 100 kilometers (62 miles). Can be used as a network backbone. Uses beaconing for ring troubleshooting. Cable and DSL Cable modems are not really modems at all. They use coax cable. DSL has a max distance of 18,000ft with the most popular flavor of DSL bing ADSL Circuit-Switching Networks use ONE consistent circuit. Can be either a physical circuit or a virtual circuit. ISDN is a virtual circuit The communication is usually a DEDICATED circuit. 10. Network Diagnostic Tools Tool Function Digital Volt Meters (DVM) Measures voltage passing through a resistance. Primarily used for network cable troubleshooting. Time-Domain Reflectors (TDRs) Sends sonar-like pulses to look for breaks, shorts or crimps in cables. Can locate a break within a few feet of actual fault. Oscilloscope Measures amount of signal voltage per unit of time. Displays crimps, shorts, opens, etc. Network Monitor Examines packet types, errors and traffic to and from each computer on a network. Protocol Analyzer Look inside the packet to determine cause of problem. Contains built in TimeDomain Port Scanner Scans for open TCP/UDP ports 11. Multiple Disk Sets Fault Tolerant Systems protect data by duplicating data or by placing data in different physical sources. RAID Function Level 0 Disk Striping-Divides data into 64k blocks and spreads it equally among all disks in the array. Is not fault tolerant. Level 1 Disk Mirroring -Duplicates a partition on another physical disk. Level 1 Disk Duplexing -Duplicates a partition on another physical disk that is connected to another Hard Drive Controller. Level 2 Disk Striping w/ECC -Data blocks are broken up and distributed across all drives in array with error checking.
Level 3 Disk Striping w/ ECC stored as parity -Data blocks are broken up and distributed across all drives in array with one drive dedicated to storing parity data. Level 4 Disk Striping with large blocks -Complete blocks of data are distributed across all drives in the array. Level 5 Disk Striping with parity -Distributes data and parity information across all disks in the array. The data and the parity information are arranged so they are always on separate disks. A parity stripe block exists for each row across the disk. The parity stripe is used for disk reconstruction in case of a failed disk. Supports a minimum of three disks and a maximum of thirty-two disks. Windows NT supports RAID Levels 0, 1, and 5. Sector Sparing - Automatically adds sector-recovery capabilities to the files system while the computer is running. Available when using RAID methods. Only available with SCSI drives. 12. Upgrading the network. To upgrade a network to 100 mbps Ethernet, you must perform the following: - Upgrade all hubs to switches or 100 mbps hubs. - Upgrade the wiring to CAT 5 UTP/STP. - Upgrade all network cards to 100 mbps. 13. Reliable Packet Delivery Methods and Checks - Parity Checks you add an additional BIT to both ends - CRC (Cyclical Redundancy Check) - EDAC Error Detection and Correction - EXAM Tip SQUELCH is the signal sent by recvg node to slow down transmission of data from sender 14. TCP Command Line Utilities arp- Arp.exe is used to resolve an IP address to its hardware (MAC address). Local Arp cache is checked first before initiating an ARP request broadcast arp switches -a - View the contents of the local ARP cache table -s - Add a static Arp entry for frequent accessed hosts -d - Delete a entry ipconfig - The ipconfig is a command line tool for NT that shows how the computer's IP stack is configured.C:\ipconfig ipconfig switches /all - Extra information is revealed; IP host name, DNS, WINS server /release - If DHCP is enabled, you release the lease with this switch. /renew - The renew switch will update and renew DHCP lease information from the DHCP Server. winipcfg - The winipcfg is a GUI version for ipconfig netstat - The netstat tool displays protocol statistics and the state of current TCP/IP connections C:\WINDOWS>netstat /? Displays protocol statistics and current TCP/IP network connections. netstat [-a] [-e] [-n] [-s] [-p proto] [-r] [interval] -a Displays all connections and listening ports. -e Displays Ethernet statistics. This may be combined with the -s option. -n Displays addresses and port numbers in numerical form. -p proto Shows connections for the protocol specified by proto; proto may be TCP or UDP. If used with the -s option to display per-protocol statistics, proto may be TCP, UDP, or IP. -r Displays the routing table. -s Displays per-protocol statistics. By default, statistics are shown for TCP, UDP and IP; the -p option may be used to specify a subset of the default. interval Redisplays selected statistics, pausing interval seconds between each display. Press CTRL+C to stop redisplaying statistics. If omitted, netstat will print the current configuration information once. nbtstat The nbtstat checks the state of NetBIOS over TCP/IP connections and returns NetBIOS session and name resolution statistics. This tool can also be used to update the local NetBIOS name cache. Displays protocol statistics and current TCP/IP connections using NBT(NetBIOS over TCP/IP). nbtstat [-a RemoteName] [-A IP address] [-c] [-n] [-r] [-R] [-s] [S] [interval] ] -a (adapter status) Lists the remote machine's name table given its name
-A (Adapter status) Lists the remote machine's name table given its IP address. -c (cache) Lists the remote name cache including the IP addresses -n (names) Lists local NetBIOS names. -r (resolved) Lists names resolved by broadcast and via WINS -R (Reload) Purges and reloads the remote cache name table -S (Sessions) Lists sessions table with the destination IP addresses -s (sessions) Lists sessions table converting destination IP addresses to host names via the hosts file. RemoteName Remote host machine name. IP address Dotted decimal representation of the IP address. interval Redisplays selected statistics, pausing interval seconds between each display. Press Ctrl+C to stop redisplaying statistics. Note: Netstat works for TCP/IP connections, and Nbtstat works for NetBIOS connections. nslookup The Nslookup tool is used to trace DNS queries from start to finish ping- Ping.exe verifies configurations and tests connectivity If you can ping a hostname but cannot connect to a share point in Explorer, then the LMHOST file does not have an entry for that hostname or WINS is not working. Conversely, if you CAN connect to a share in Explorer yet cannot ping the hostname, then either the HOST file entry is wrong or DNS is not working. NetBIOS-problems are due to problems with WINS or LMHOST file. DNS- problems are due to HOST file errors or DNS server problems. Tracert - The tracert tool shows the route a packet will take over a network from one computer to another. 15. Port Numbers Number Description Number 21 FTP 69 23 Telnet 80 25 SMTP 110 53 DNS 137 161 SNMP 389 1494 Citrix 22 123 NTP(network time prot) 1723 443 HTTPS 143 16. Address Classes: Decimal Class A:1-126 Class B:128-191 Class C:192-223 Class D:224-239 Class E:240-255 Binary 00000001-01111111 10000000-10111111 11000000-11011111 11100000-11101111 11110000-11111111 Description TFTP HTTP POP WINS LDAP SSH PPTP (Microsoft VPN) IMAP4
The 127.0.0.0 network is reserved for loopback testing of the TCP/IP Stack within your system. Class D is used for Multicast Class E is reserved for experimental purposes 17. Routing Algorithms Distance Vector aka Gossiping RIP, IGRP, EIGRP Only allows for up to 15 routers in a network Transfers its entire table to its neighbors translates the WHOLE table IGRP adds 6 diff metrics over RIP EIGRP- supports VLSM
Link State IS-IS, OSPF a. Larger metrics b. Allows for thousands of routers (actually 65,535) c. Helo packerts every 30 seconds d. Rapds convergence 18. Data Link Protocols for Point to Point Links SLIP (Serial Line IP) Support ONLY IP (not IPX) Encapsulation not much else PPP (Point to Point Protocol) has error detection SLIP does NOT Successor to SLIP. Uses a serial connection Used for dial-in and high speed routers HDLC (High Level Data Link) Default protocol for serical links on Cisco routers NAT NAT is a router function which enables hosts on a private network to communicate with hosts on internet. Used for pooling of addresses. The duh of it all says that it connects multiple computers to other IP networks using only ONE single IP address. 5:4:3 Law 5 segments, 4 repeaters and 3 nodes Default Gateway has three elements: IP address Sugnet Mask Default gateway itself Troubleshooting Always REMEMBER: If its broke, its probably DNS 19. Firewalls Packet-filtering firewalls (transparent , cost-effective, no user authentication application based firewalls (clients do not connect directly to outside network, has user authen, all transaction are logged however this is not cost effective for small networks REMEMBER: a packet filtering firewall looks at the source address AND the port number of a packet 20. VPN and Tunneling methods: L2TP combines PPP from Microsoft and L2F from Cisco. Uses LNS and LAC PPTP enables remote users to log in to a secure server. It will seem like the network is accessed by local means since it hides the routing and switching process from users. Provides security for file transfer via encryption. IPSec (IP Security) implemted at Network layer like SSL and L2TP but does not require IPSec aware applications. The IPSec SUBprotocols are AH(auth header) and ESP(encapsulating security protocol). In order to authenticate clients and servers IPSec uses and automated key-management system called IKE (internet key exchange) CHAP (challenge handshake authentication RAS - Remote Access Service for Windws NT/2000 The actual VPN protocols are: GRE, L2F, PPTP, L2TP (used for IPSec), MPPE (used for Windows dial-up networks ONLY) and IPSec PPTP ports you can configure 16,384 ports 21. Digital Carrier Services DS0 64 DS1 1.544 24 channels DS3 45 672 channels
21a. OPTICAL Carrier Services OC1 51.84 mbps OC-3 155mbps OC-12 622 mbps OC-192 10gbps 22. ICA Independent Computing Architecture (CITRIX) Thin client computing. The ICA protocol uses less than 20K. The thin clients connect ot a server and that server starts the application executes the app transfers only the apps interface to the client Uses a boot ROM to attach to server Needs a network connection Emulates complete PC environment OS is embedded in a ROM 23. Security Protocols Non-repudiation (spoofing) handled by digital signatures Ciphertext/hash Make the distinction between ciphers (arrangement of codes) and codes which are just 1s and 0s Two types of cryptography, Secure key and PKI Encryption Methods DES Digital Encrypt in 64k blocks Diffie-Hellman PK and session key RSA uses PKI and SSL SOCKETS defined as a connection from a client to an endpoint SSL is the main protocol that uses sockets. Runs at network layer SSL is NOT and encryption method it IS a security PROTOCOL SSL uses BOTH public-key and secret-key cryptogoraphy Tunnels are actually big sockets Has two sub-protocols: SSL record protocol and SSL handshake protocol Kerberos uses a ticketing system 24. Network Operating Systems Two types :Client/Server and Peer to Peer Windows and Linux can operate as Peer to Peer but Netware cannot EXAM tip EXAM tip all NOS use Administrator, root (or superuser) to signifiy Admin users Directory services and X.500 the X.500 Dir Services is called the global white pages NetWare ALERT: netware is a network operating systems ONLY it has NO client version EXAM tip Multiprocessor kernel, NLMs (netware loadable modules), PCI Hotplus Netware 3.x has a bindery feature a big database, which ea user needed a login for EACH server!- UGH NetWare PROTOCOLS: IPX (internetwork packet exchange) similair to IP in that it is connectionless and SPX(sequenced packert exchange) similair to TCP in that it is connectioned oriented EXAM Netware File Attirbutes: Archive(A), Execute Only(X), Hidden (H), Read-Only(RO, Read-Write(RW) and Shareable (SH). UNIX/Linux - Multipupose operating system meaning it is considered both a client and a network operating system It has protected multitasking, POSIX (portable operating system interface) compliance, shell interface, support for dumb terminals EXAM tip: versions f UNIX: HP-UX, AIX, Solaris, IRIX, Redhat, Slackware, SuSE, Debian GNU UNIX Basics (EXAM tip) root user is all powerful. U is user who owns, g is group, r read access, w is write access and x is execution permission. So basically if you have RWX it grants permission to do everything. UNIX protocols: UDP, ICMP, NIS, LDAP 25. Network Implementation Windows NT Domains and Controllers: Windows uses an organizational concept called domains to spearate members of a network, including users, printers and servers. Domain organization is logical, the physical location DOESNT matter. It involves PDCs and BDCs (primary and backup domain controllers)
The PDC stores the SAM (Security Accounts Manager) Windows 2000 Active Directory becomes available which can handle parent/child domain AD sets trust relationships Macintosh Apple abandon AppleTalk after Mac OS8 in favor of TCP/IP VLANS 802.1q: A logical LAN within a physical LAN Benefits and Basics Fewer switches Traffic isolated by groups Can overlap one another Three Major Types of VLANS Port-based VLANS (if a repeater is installed in any place it segments by repeater Mac-address-based VLANS (routed by MAC address Protocol-based VLANS (Layer 3 Based) The IEEE 802.1q standard defines VLANs using explicit technology rather than implicit. Meaning, that explicit VLANs are either port-based or protocol based (NOT Mac-based) Data Storage Network Attached Storage be able to note the main characteristics. TAPE: DAT (Digital Audio), DLT (Digital Linear), DDS (Digital Data Sortage) Storage Controller Interfaces: a. IDE (Integrated Data Environment) slave/master dive relationship, b. SCSI (higher transfer rates than IDE). Note that SCSI has tweo possible types of terminators (Passive and Active) Fiber Channel (faster than SCSI has transfer rates up to 4gbps) 1. Benefits of NAS: Cross-platforms file sharing, Easy backups (using RAID- and NAS can support at least RAID 5) 2. How NAS operates: a. Operates on client/server premise access granted via Ethernet b. NAS devices are usually hard disks using SCSI 26. Data Availability Fault tolerance concepts Load balancing: one way is to route each request to a different, identicial server host address in a DNS table Latency MTBF (mean time between failures Failover RAID: Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks Parity: a bit in the data to determine if it is corrupt Striping: basically a way of partitioning raid disks into what appears to be the operating systems as on logical drive. STRIPED data is written in order and NOT randomly Disk duplexing: also known as AKA RAID 1 involves storing (mirrored) data on not just diff disks BUT also on diff controllers/channels RAID 1 = duplexing, RAID 2 = striping with error correction(rearely used), RAID3 striping with Parity on a single drive, RAID 4 = block by block on multiple drives and RAID 5 = striping with parity AND supported by Windows EXAM tip: When trying to remember how many disk with each RAID just remember that RAID 3 is the FIRST class that requires 3 disks all others above it also require at least 3 and the ones below it require two 27. Configuring Remote Connectivity RAS Connection methods: PPP SLIP (mainly used with UNIX) does require a static IP Microsoft RAS protocol Encryption: RAS uses CHAP CHAP uses MD5 (message diget) for Hash
Installing and Configuring RAS Hardware reqd: NIC with NDIS driver, Modem, If you need more than 254 addresses youll need to span across subnets You can configure up to 16,384 ports Remember that L2F encapsulates packets into PPP b/4 transmitting them Remember that PAP just send stuff in cleartext so is is pretty USELESS Remember that netsh ras add registeredserver is the COMMAND to addRAS and IAS to Windows Active Directory. Firewalls, Proxy Servers and Security Methods: Packet filters (low security), Application Gateways (aka proxy server firewalls good security), circuit level (poorest security) and Stateful Inspection(good security) A note on Stateful it keeps a state-table of connections whereby it monitors the state of a TCP connection and allows traffic accordingly One of the more popular proxy servers is Wingate and the other (for Linus) is www.squid-cache.com 28. Network Configuration Settings Nonroutable Protocols DLC (data Link Control : for printers), NetBEUI Routable IPX, TCP/IP Windows Internet Naming Service (WINS) used with Microsoft NetBIOS. Enables clients to register NetBIOS names at startup, and request name resolution DNS it is a hierarchical naming system. Resolves hotnames to an IP address DHCP automagically assigns IP addresses and cal also provide the addresses of routers, WINS servers, DNS servers , etc Uses a form of BOOTP (BOOTPAS protocol) 29. Private IP addresses these are not routable addresses thru the Internet 10.0.0.0 10.255.255.255 172.16.0.0 172.31.255.255 192.168.0.0 192.168.255.255 30. Linux NFS Network Files System #killall this command kills the running process on the computer 31. Novell Netware Can configure it for both IP and IPX GSNW (gateway services for Netware) enables Win NT/2000 32.Troubleshooting by Topology Ring: one error can bring down the entire ring Star: the main error issues reside in cabling Bus: must ensure that cable is properly terminated if a computer/device is brought out of the network. 33. Guidelines for Assigning IP addresses 1. All devices on subnet must have the same Network ID 2. Node IDs on local subnet must be unique 3. 127.0.0.1 is reserved for loopback 4. Node addresses cannot be all 1s or 0s Subnet What is masking used for? It masks what you dont want to touch (if you have a car, you mask the chrome to avoid painting it) If a user tells you the IP address without the subnet you have nothing Subnet masks determine local or remote addresses
10
You might also like
- Module 1-2 TakenotesDocument9 pagesModule 1-2 TakenotesAries VenturaNo ratings yet
- Fast Ethernet Standards: Fiber OpticsDocument5 pagesFast Ethernet Standards: Fiber OpticsHimanshu GouravNo ratings yet
- Networking ConceptDocument81 pagesNetworking ConceptMaghairNo ratings yet
- Comptia Network+ Study SheetDocument30 pagesComptia Network+ Study SheetDan Sheets100% (5)
- Exam Objectives - 1-4 NotesDocument62 pagesExam Objectives - 1-4 NotesDesoukyNo ratings yet
- NetworksDocument31 pagesNetworksGlan DevadhasNo ratings yet
- Basic Networking Concepts: 2. Protocols 3. Protocol Layers 4. Network Interconnection/InternetDocument29 pagesBasic Networking Concepts: 2. Protocols 3. Protocol Layers 4. Network Interconnection/InternethemendraNo ratings yet
- Ccna Interview QuestionsDocument25 pagesCcna Interview QuestionsDinesh SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- CCNA Study NotesDocument13 pagesCCNA Study NotesAminata KondehNo ratings yet
- Network+ Certification Study Guide 2000Document39 pagesNetwork+ Certification Study Guide 2000SuryaNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication and Computer Networking Lab ManualDocument66 pagesDigital Communication and Computer Networking Lab ManualJoey TribianniNo ratings yet
- Dell EMC 2000 Networking 2020Document30 pagesDell EMC 2000 Networking 2020abdulmuizzNo ratings yet
- Basic Networking Concepts: 2. Protocols 3. Protocol Layers 4. Network Interconnection/InternetDocument28 pagesBasic Networking Concepts: 2. Protocols 3. Protocol Layers 4. Network Interconnection/InternetAbdinasir RobleNo ratings yet
- Basic Networking ConceptsDocument28 pagesBasic Networking Conceptsapi-3832232100% (2)
- Dist 03 4 PDFDocument28 pagesDist 03 4 PDFTazar phyo waiNo ratings yet
- Basics of NetworkingDocument19 pagesBasics of NetworkingtestNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Networks: Modes of CommunicationDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Networks: Modes of CommunicationamitNo ratings yet
- CCNET Handbook - Good Summary For Networking IdeasDocument42 pagesCCNET Handbook - Good Summary For Networking IdeasAnas ElgaudNo ratings yet
- Network ReviewDocument29 pagesNetwork ReviewMuhammad AteeqNo ratings yet
- Network+ Notes 01Document25 pagesNetwork+ Notes 01joes sloppyNo ratings yet
- 3 Basic Network Topologies ExplainedDocument4 pages3 Basic Network Topologies ExplainedJomariPrimeroNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For MID I CNDocument14 pagesImportant Questions For MID I CN20H51A0540-NAKKA SREEKAR B.Tech CSE (2020-24)No ratings yet
- Cisco 1 Review Lecture Notes OSI ModelDocument97 pagesCisco 1 Review Lecture Notes OSI ModelGirmaNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworksDocument17 pagesComputer NetworksInban DhasNo ratings yet
- Cse ComputernetworkDocument22 pagesCse ComputernetworkLakshmi BaskarNo ratings yet
- NetworksDocument8 pagesNetworksGaby MbuguaNo ratings yet
- Daystar University ACS 351 A Computer Networks 1Document12 pagesDaystar University ACS 351 A Computer Networks 1Marilene Soulfly MercyNo ratings yet
- Networking: Instructor: S.D.BanerjeeDocument70 pagesNetworking: Instructor: S.D.BanerjeeAnkur Chattopadhayay100% (1)
- CCNA Study GuideDocument5 pagesCCNA Study Guideasmith2112No ratings yet
- Twisted Pair: Networking Devices, Media and Connector Common Network Cables 1Document3 pagesTwisted Pair: Networking Devices, Media and Connector Common Network Cables 1Vincent TayagNo ratings yet
- LAN and WAN Topologies ExplainedDocument50 pagesLAN and WAN Topologies ExplainedJohn Dustin SaintsNo ratings yet
- IPv4 - Quick GuideDocument21 pagesIPv4 - Quick GuidemispanshieNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Networking FundamentalsDocument50 pagesIntroduction to Networking Fundamentalsarif420_999No ratings yet
- Computer Network Lab FileDocument27 pagesComputer Network Lab FileVinayak KanherkarNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Networking Communication Modes and MediaDocument50 pagesIntroduction to Networking Communication Modes and MediaMuhammad Osama RazaNo ratings yet
- Network GlossaryDocument8 pagesNetwork Glossarysandeep kumarNo ratings yet
- LAN and Ethernet Basics - Deepak George: OSI Network LayersDocument12 pagesLAN and Ethernet Basics - Deepak George: OSI Network LayersUseful Videos DevotionalNo ratings yet
- Ethernet NetworkingDocument5 pagesEthernet NetworkingEfti ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Chap 1Document47 pagesChap 1hafiz youngNo ratings yet
- SYN CH - 1 and 2Document20 pagesSYN CH - 1 and 2IG TECHNo ratings yet
- Ccna Notes FullDocument35 pagesCcna Notes FullSudhir MaherwalNo ratings yet
- What Is A Protocol?: OSI Layer Name Common ProtocolsDocument24 pagesWhat Is A Protocol?: OSI Layer Name Common ProtocolsPrashank SinghNo ratings yet
- IST220 CH 1-11, 13, 14 Final Exam Review QuestionsDocument8 pagesIST220 CH 1-11, 13, 14 Final Exam Review Questionsamelio518No ratings yet
- Assignment: SUBMITTED FROM: Yousra Nur Obaid ID:19204025 Submitted To: Md. HasanuzamanDocument17 pagesAssignment: SUBMITTED FROM: Yousra Nur Obaid ID:19204025 Submitted To: Md. HasanuzamanFahad RuhulNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document9 pagesLesson 5Kean Rafael MarianoNo ratings yet
- Basic Networking Guide: Topologies, OSI Model, TCP/IP & MoreDocument40 pagesBasic Networking Guide: Topologies, OSI Model, TCP/IP & MorePrateek Persistently PreciousNo ratings yet
- Cisco: Sritrusta SukaridhotoDocument34 pagesCisco: Sritrusta SukaridhotoAhmad SahalNo ratings yet
- SemSim CCNA Cram SheetsDocument9 pagesSemSim CCNA Cram SheetsMohan KumarNo ratings yet
- Other Technologies & Network Architecture: Session 7Document23 pagesOther Technologies & Network Architecture: Session 7Aravind BhomboreNo ratings yet
- Networks, Part 1: What Is A Network?Document4 pagesNetworks, Part 1: What Is A Network?Mohammad Hammad RashidNo ratings yet
- NetworkingDocument4 pagesNetworkingDheeraj KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Computer CommunicationDocument7 pagesComputer Communicationsaravanamuthaly1397No ratings yet
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1From EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Introduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyFrom EverandIntroduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Cisco Network Administration Interview Questions: CISCO CCNA Certification ReviewFrom EverandCisco Network Administration Interview Questions: CISCO CCNA Certification ReviewRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- HPLaserJetProMFPM426fdn PDFDocument2 pagesHPLaserJetProMFPM426fdn PDFOpština LebaneNo ratings yet
- Pinza Prova 5601Document2 pagesPinza Prova 5601Sublimec San RafaelNo ratings yet
- F Pv28T: PR EN 2714-013A/B/C/DDocument2 pagesF Pv28T: PR EN 2714-013A/B/C/DFredNo ratings yet
- FC102 Pid PDFDocument1 pageFC102 Pid PDFKwameOpareNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 - Managing Personal CommunicationDocument37 pagesChapter 19 - Managing Personal CommunicationAmit Thapa100% (2)
- 66 67wvh8m8dall BLL-2936104Document50 pages66 67wvh8m8dall BLL-2936104ManunoghiNo ratings yet
- Animal-Cube-Puzzle I e LTR PDFDocument3 pagesAnimal-Cube-Puzzle I e LTR PDFJose Oswaldo Sierra MatheusNo ratings yet
- Experimental Design and Optimization of Free EnergDocument5 pagesExperimental Design and Optimization of Free Energesubalew tadesseNo ratings yet
- Sample Solar Permit Plan - 1 Line Drawing PDFDocument1 pageSample Solar Permit Plan - 1 Line Drawing PDFSAEL SOLARNo ratings yet
- ASME B31.3 2020 CambiosDocument10 pagesASME B31.3 2020 CambiosJosé Juan Jiménez AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Finaldc 2Document10 pagesFinaldc 2Noel BactonNo ratings yet
- Catalog Filters PDFDocument53 pagesCatalog Filters PDFAlexandre Hugen100% (1)
- Telepo SDK Develop Guide (Linux For TPS300) - v1.0Document10 pagesTelepo SDK Develop Guide (Linux For TPS300) - v1.0VKM2013No ratings yet
- CMM49 14 01 MtocDocument2 pagesCMM49 14 01 MtocMichail K100% (1)
- Digital Vision Installation PDFDocument2 pagesDigital Vision Installation PDFnikola5nikolicNo ratings yet
- Netapp Simulator - Installation Steps UbuntuDocument2 pagesNetapp Simulator - Installation Steps UbuntukodurumanojkumarNo ratings yet
- II BTECH - I SEM - ECE - EDC - THEORY & QUIZ QUESTIONS - MID 2 - Students PDFDocument19 pagesII BTECH - I SEM - ECE - EDC - THEORY & QUIZ QUESTIONS - MID 2 - Students PDFK SrinuNo ratings yet
- AlarmsReference ME-B 1212 PDFDocument130 pagesAlarmsReference ME-B 1212 PDFNAGENDRA KUMAR DNo ratings yet
- Microstation GuideDocument158 pagesMicrostation GuideMishra KirtiwardhanNo ratings yet
- CIRCULAR WATER TANK DESIGN-Layout1 AkhilDocument1 pageCIRCULAR WATER TANK DESIGN-Layout1 AkhilVENKAT KALYANNo ratings yet
- Techsheet ZerowasteDocument2 pagesTechsheet ZerowastesunillimayeNo ratings yet
- ZZZXDocument14 pagesZZZXJay R DenostaNo ratings yet
- Sadi Mohammad Naved: Duties/ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesSadi Mohammad Naved: Duties/ResponsibilitiesNick SanchezNo ratings yet
- Class XII Computer Science: HOTS (High Order Thinking Skill)Document14 pagesClass XII Computer Science: HOTS (High Order Thinking Skill)JanakiNo ratings yet
- SWOT) Analysis, Marketing Process, Marketing PlanDocument24 pagesSWOT) Analysis, Marketing Process, Marketing PlanSagar Patil100% (2)
- Gulf Harmony AW 46 Data SheetDocument1 pageGulf Harmony AW 46 Data SheetRezaNo ratings yet
- StradaDocument4 pagesStradayzk14No ratings yet
- Why Geomechanical Reservoir KpiDocument43 pagesWhy Geomechanical Reservoir KpiKevin MusterNo ratings yet
- Nano Particle Characterization MethodsDocument32 pagesNano Particle Characterization MethodsVignesh Raja PNo ratings yet