Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Plant Structure
Uploaded by
Yoga Trista MajidOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Plant Structure
Uploaded by
Yoga Trista MajidCopyright:
Available Formats
PLANT STRUCTURE
Plant has structure like animal and human. The plant has organ:
1. Root
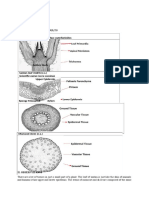
The function or root: Absorbing water and mineral salt Supporting plant body Storage of food Helping respiration Generally root has structure like this figure:
Root hair
Root cap
Dicotyledonous and monocotyledonous have different root type. Dicotyledonous has tap rot but monocotyledonous has fibrous root. Tap root has mainly roots but fibrous root does not have mainly roots, all of roots are fibrous.
Mainly root
Tap root
Fibrous root
OUTER MOST STRUCTURE a. Root hairs, absorbs mineral and water. b. Root cap, keeps cap of root. It has soft and damaged easily. It produces enzyme to help root penetrates soil so the roots can enter easily.
INNER MOST STRUCTURE
From outer into inner layer
a. b. c. d. Epidermis, outer layer. It keeps tissues under this layer. It consists of one layer, thin wall and semipermiable. Cortex, is composed many layers, inter cell gaps for exchanging gas. It also consists parenchyma tissues for storing food and water. Endodermis, one layer under cortex. it controls mineral and water. It has casparian strip. This part blocks fluid passed from soil by passing cell wall, so it flows by passing cytoplasm. Stele, it consists pericycle and vascular bundles (phloem and xylem). The pericycle is composed parenchyma tissue. In dicotyledonous regular vascular bundles but monocotyledonous has spread vascular bundles. Between phloem and xylem it has cambium. The function of phloem carries the product of photosynthesis and xylem carries mineral and water.
The structure of root
The function of stem: Transporting mineral and water to leave Storing food The structure of stem: a. OUTER MOST STRUCTURE Woody stem has characters like woody, brown, hard. It has lenticels. The function of lenticels is changing gas in plant. Herbaceous plant, softly, has chlorophyll. b. INNER MOST STRUCTURE The structure likes root The layer from outer into inner: Epidermis cortex endodermis stele Dicotyledonous and monocotyledonous have different stem structure The character dicotyledonous Monocotyledonous Location of vascular bundles regular Spread cambium presence Nothing Growth lengthen and enlargement lengthen
2. Stem
Dicotyledonous stem
Monocotyledonous stem
3. Leaf
The function of leaf Having photosynthesis Exchanging gas The structure of leave a. OUTER MOST STUCTURE
The outermost structure of leaf
Generally leaf has characters like flat, width, and green. Many of plant has leaf like needle (pine and cactus)
The morphology of leaf:
According to its amount of leave a. Simple leaf, one leaf in one petiole b. Compound leaf, many leave in one petiole
Simple leaf
Compound leaf
According to shape According to vein According to margin
The morphology of leaf
b.
INNER MOST STUCTURE
The structure of leaf
The structure of innermost leaf
a. Epidermis, the outer layer. The epidermis has upper epidermis and lower epidermis. It has stomata for place that exchanged gas from environment and its body. b. Palisade, the cell is long. It contains of chloroplast so it can get photosynthesis. c. Spongy tissue, the shape likes spongy and it is happen photosynthesis. d. Vascular bundles, it is located in spongy tissue.
4. FLOWER
The function of flower Reproductive organ The structure of flower
The structure of flower
a. Sepal, one circle of sepal is called calyx The function keeps flower still bud and its organs b. Petal, one circle of petal is called corolla The function interests insects. c. Stamen, male organ reproductive. It consists of filament and anther d. Pistil, female organ reproductive. It consists style, ovarian, and ovule.
5. FRUIT
The function is being embryo for plant The type of fruit: a. Right fruit, is formed by all of ovary. Ex: papaya, durian b. False fruit, is formed not only ovary but also other organ. Ex: pineapple (is formed by ovary and sepal), apple (is formed ovary and sepal). The inner structure of fruit contains of three layer: a. Epicarp (outer layer), it is hard b. Mesocarp (middle layer), thick, many fibrous c. Endocarp (inner layer), thin layer
6. SEED
The function seed: organ reproductive. It comes from fertilization. The structure of seed:
The structure of seed consists of two layers: a. Outer layer, seed coat. Generally dry and hard b. Inner layer, endosperm TRANSPORTATION IN PLANT 1. Transpiration is less of water vapour from the leaves and other aerial parts of plant 2. The three sites of transpiration, stomata, cuticle, and lenticels 3. External condition, air movement, light intensity, and relative humidity 4. If a stem is cut it will be amount of water exude from it cut. It is caused by root pressure.
You might also like
- Structure N Function of PlantDocument36 pagesStructure N Function of Plantndzani_latifaturNo ratings yet
- 03-Flowering PlantsDocument45 pages03-Flowering PlantsMaku MichaelNo ratings yet
- Laporan Pengamatan Falisha - Jaringan TumbuhanDocument12 pagesLaporan Pengamatan Falisha - Jaringan Tumbuhanfalisha adelia putriNo ratings yet
- Parts of Plant and Their FunctionsDocument23 pagesParts of Plant and Their Functionssarahbaharudin85No ratings yet
- Network Structure in Root, Stem, and LeafDocument5 pagesNetwork Structure in Root, Stem, and LeafMarwana SuaibNo ratings yet
- Botany RootsDocument49 pagesBotany RootsCudal, Estephanie RoseNo ratings yet
- Section B-Introduction To Crop ProductionDocument3 pagesSection B-Introduction To Crop ProductionDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Report SheetDocument6 pagesReport SheetMikhail LandichoNo ratings yet
- Welcome 10 Sci To Distance Learning 2021: Your Guide: MR KhooDocument20 pagesWelcome 10 Sci To Distance Learning 2021: Your Guide: MR KhooAariz KhanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Plant Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument37 pagesLesson 4 - Plant Anatomy and PhysiologyReuth Thessalonica Dela VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Plant PhysiologyDocument5 pagesLab Report Plant Physiologysarahyahaya100% (1)
- Anatomy and MorphologyDocument8 pagesAnatomy and MorphologyminichelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10 Parts of A PlantDocument6 pagesLecture 10 Parts of A PlantkedeshiaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of StemDocument15 pagesAnatomy of StemMonica LumbantobingNo ratings yet
- Cluster Biology of PlantsDocument48 pagesCluster Biology of Plantsapi-452104023100% (1)
- Report SheetDocument11 pagesReport SheetMikhail LandichoNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity 5: Plant Morphology: StemDocument5 pagesLab Activity 5: Plant Morphology: StemPaulNo ratings yet
- Plant Physiology PPT 9Document53 pagesPlant Physiology PPT 9sargonsielaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 21 The Stem (Primary Structure of Flowering Plant Body)Document9 pagesLecture 21 The Stem (Primary Structure of Flowering Plant Body)maheen akramNo ratings yet
- Quisao Lab Act 4Document3 pagesQuisao Lab Act 4PaulNo ratings yet
- Plant Anatomi-Plant OrgansDocument70 pagesPlant Anatomi-Plant OrgansHambaukaiNo ratings yet
- Botany 101Document7 pagesBotany 101Gladdin ChloeNo ratings yet
- Parts and Function of Plants and Animal CellDocument3 pagesParts and Function of Plants and Animal CellPrince AbraganNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1A.1 Plant Form and Function-1Document26 pagesMODULE 1A.1 Plant Form and Function-1Althea Angela BulaclacNo ratings yet
- Post Lab Discussion IIDocument64 pagesPost Lab Discussion IIJeli Mae Ysabel PerezNo ratings yet
- Villanueva - Bot01 Lab Act #4Document14 pagesVillanueva - Bot01 Lab Act #4Kath ErineNo ratings yet
- Botany RootsDocument49 pagesBotany Rootsartadiel28No ratings yet
- Plant Anatomy: Angiosperm CategoriesDocument5 pagesPlant Anatomy: Angiosperm CategoriesRizka Apriliana KumalasariNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument29 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantssaleemNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants Revision NotesDocument72 pagesCBSE Class 11 Biology Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants Revision Noteschakrabortytrisha.2006No ratings yet
- Andamun Tle106 ReportDocument34 pagesAndamun Tle106 ReportNaharia RangirisNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science - G11 - John Mark de SagunDocument48 pagesEarth and Life Science - G11 - John Mark de SagunsailorNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER III Tree Physiology 2.15.22Document2 pagesCHAPTER III Tree Physiology 2.15.22Cassandra AlexisNo ratings yet
- II1 IB RevisionDocument3 pagesII1 IB RevisionMedinaNo ratings yet
- Alido, Charlito VDocument5 pagesAlido, Charlito VCharlito AlidoNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet TutorDocument4 pagesWork Sheet TutorNuni Rismayanti NurQalbiNo ratings yet
- Plant Parts and Its Function: Module 1 For CollegeDocument9 pagesPlant Parts and Its Function: Module 1 For CollegeYan DechosNo ratings yet
- Plant and Their Systems, Gr-7, AdyalaDocument15 pagesPlant and Their Systems, Gr-7, AdyalaSidra UsmanNo ratings yet
- 1osc03 PlantkingdomDocument4 pages1osc03 PlantkingdomIrene AragonesesNo ratings yet
- Agric Ultur E Scienc E Proje CT ON Leave S and Stems: Name: Asher Greaves Form: 1 Room 2 Teacher: Date: 18/2/2020Document6 pagesAgric Ultur E Scienc E Proje CT ON Leave S and Stems: Name: Asher Greaves Form: 1 Room 2 Teacher: Date: 18/2/2020Sheniqua GreavesNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants For PrintDocument17 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants For PrintOjobo Blessing100% (1)
- Dokumen - Tips Lab 3 Report Plant AnatomyDocument11 pagesDokumen - Tips Lab 3 Report Plant AnatomyAin SufizaNo ratings yet
- Leaf Anatomy: Cells (E), and They Create A Circle Around The Xylem and The Phloem. On TheDocument3 pagesLeaf Anatomy: Cells (E), and They Create A Circle Around The Xylem and The Phloem. On TheANo ratings yet
- Science Second Quarter GuideDocument6 pagesScience Second Quarter GuideLuis Ureña HurtadoNo ratings yet
- Sitologi Dan Histologi TumbuhanDocument14 pagesSitologi Dan Histologi TumbuhanMonica Roly VonitaNo ratings yet
- Plant MorphologyDocument7 pagesPlant MorphologyTiken SinghNo ratings yet
- CropSci101 Module 3Document11 pagesCropSci101 Module 3Jetro Neil GapasinNo ratings yet
- Activity 7 Angiosperm Plant BodyDocument13 pagesActivity 7 Angiosperm Plant BodyHerlyn SabulaanNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY II NotesDocument8 pagesBIOLOGY II NotesDarwin SawalNo ratings yet
- Seeds (Semen)Document11 pagesSeeds (Semen)johanes manaluNo ratings yet
- PLC 7 and 8Document21 pagesPLC 7 and 8rheyukijNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Plantae: Phylum Bryophyta (Moss)Document10 pagesKingdom Plantae: Phylum Bryophyta (Moss)Naduku EridadNo ratings yet
- Earth & Life Science: How Plants SurviveDocument9 pagesEarth & Life Science: How Plants Survivejames bonfNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Plant TissuesDocument8 pagesLab Report Plant TissuesMOHD MU'IZZ BIN MOHD SHUKRI100% (6)
- k12 Bio1 Exer6 RootsDocument3 pagesk12 Bio1 Exer6 RootsJohn Matthew Jobo100% (1)
- Botany Report - Chap 7Document35 pagesBotany Report - Chap 7Seannel CruzNo ratings yet
- 6 ThscicenceDocument4 pages6 Thscicencelearn4chatgptNo ratings yet
- Structure of PlantsDocument17 pagesStructure of PlantsJillian Lao100% (5)
- Morphology of Flowering Plants51 - PPTDocument54 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants51 - PPTPemmasaniSrinivasNo ratings yet
- How Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersFrom EverandHow Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersNo ratings yet
- EuglenidDocument4 pagesEuglenidx456456456xNo ratings yet
- Personal Development Lesson 2Document54 pagesPersonal Development Lesson 2Ysay FranciscoNo ratings yet
- (The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry 42) Antoni Munné, Antoni Ginebreda, Narcís Prat (eds.)-Experiences from Surface Water Quality Monitoring_ The EU Water Framework Directive Implementation in th.pdfDocument337 pages(The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry 42) Antoni Munné, Antoni Ginebreda, Narcís Prat (eds.)-Experiences from Surface Water Quality Monitoring_ The EU Water Framework Directive Implementation in th.pdfChris JamesNo ratings yet
- 1st Summative Exam in General Biology 2Document1 page1st Summative Exam in General Biology 2Eula Pacifico100% (1)
- CROSS TREE - Sorte I Selekcije Voćaka I Vinove Loze Iz Severozapadne Srbije I Istočne Hrvatske PDFDocument153 pagesCROSS TREE - Sorte I Selekcije Voćaka I Vinove Loze Iz Severozapadne Srbije I Istočne Hrvatske PDFrraattaarrrraattaaNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT 3.6: Determining The Concentration of An External Solution Which Is Isotonic To The Cell Sap of A PlantDocument2 pagesEXPERIMENT 3.6: Determining The Concentration of An External Solution Which Is Isotonic To The Cell Sap of A PlantAmsyidi AsmidaNo ratings yet
- Allen and Hightower Population Dynamics Chapter IFM3Document38 pagesAllen and Hightower Population Dynamics Chapter IFM3Emily HaugNo ratings yet
- CAPE Bio Mark SchemeDocument4 pagesCAPE Bio Mark Schemeron97150% (2)
- Artikel SkripsiDocument12 pagesArtikel SkripsiSari RofiqohNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument570 pagesPDFEshaal FatimaNo ratings yet
- Social Institutions - Kinship, Family&Marriage PDFDocument47 pagesSocial Institutions - Kinship, Family&Marriage PDFAbhijith KNo ratings yet
- Contoh Rencana Studi LPDPDocument3 pagesContoh Rencana Studi LPDPZahid ZainNo ratings yet
- Accessory Organ of The AbdomenDocument58 pagesAccessory Organ of The AbdomenOgundipe olorunfemiNo ratings yet
- A Review On Potential Toxicity of Artificial Sweetners Vs Safety of SteviaDocument13 pagesA Review On Potential Toxicity of Artificial Sweetners Vs Safety of SteviaAlexander DeckerNo ratings yet
- Using STADEN For Sequence AssemblyDocument5 pagesUsing STADEN For Sequence AssemblyChristen Rune StensvoldNo ratings yet
- Biological Induced CorrosionDocument22 pagesBiological Induced CorrosionHemanth100% (1)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyPREFACEDocument3 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyPREFACEtortenhumNo ratings yet
- Staar Eoc 2016test Bio F 7Document39 pagesStaar Eoc 2016test Bio F 7api-293216402No ratings yet
- The Truth About Honey - White Paper PDFDocument5 pagesThe Truth About Honey - White Paper PDFSergio PérezNo ratings yet
- Determination of Formaldehyde in Tofu From Ciputat Traditional Market With Colorimetry MethodDocument6 pagesDetermination of Formaldehyde in Tofu From Ciputat Traditional Market With Colorimetry Methodhali taekookNo ratings yet
- Noncanonical Transnitrosylation Network Contributes To Synapse Loss in Alzheimer's DiseaseDocument18 pagesNoncanonical Transnitrosylation Network Contributes To Synapse Loss in Alzheimer's DiseasedmitworNo ratings yet
- Blood Doping PPT PresentationDocument26 pagesBlood Doping PPT Presentationee4254100% (1)
- The Ethics of Respect For Nature - Paul W. Taylor PDFDocument22 pagesThe Ethics of Respect For Nature - Paul W. Taylor PDFArtur P. CoelhoNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Your Results 5/5Document5 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Your Results 5/5Pearl PascuaNo ratings yet
- Indira Renganathan 2018 18Document1,992 pagesIndira Renganathan 2018 18shubham vedakNo ratings yet
- Skin and Body Membranes: EssentialsDocument43 pagesSkin and Body Membranes: EssentialsJohn Rex Lloyd TunaNo ratings yet
- 19 - Lipid MetabolismDocument35 pages19 - Lipid MetabolismcheckmateNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions FinalDocument32 pagesPractice Questions FinalpsdantonioNo ratings yet
- 8610 - 1 Maham AslamDocument21 pages8610 - 1 Maham AslamMuhammad BasitNo ratings yet
- Update On Perioperative Fluid Therapy DR Y Narendra, SPBDocument36 pagesUpdate On Perioperative Fluid Therapy DR Y Narendra, SPBnafisyarifahNo ratings yet