Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Disgestive System Flow
Uploaded by
sabinehaqOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Disgestive System Flow
Uploaded by
sabinehaqCopyright:
Available Formats
Please use this study guide along with your book and notes.
Make sure you understand what the enzymes involved in mechanical digestion are. STUDY A little bit each night (20 minutes or so).
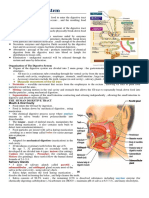
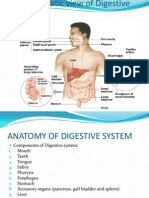
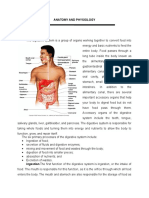
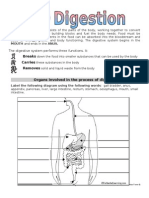
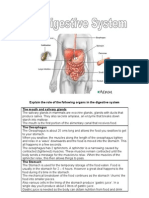
Pathway of Food Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small Intestine Large Intestine (colon) Rectum Anus
DIGESTION- STUDY GUIDE
Digestive Helpers Send things to the food, but the food doesnt send things to them 1. Pancreas 2. Liver 3. Gall Bladder Appendix has no purpose in body Mechanical vs. Chemical Digestion Mechanical Digestion - physically breaking food into smaller pieces occurs in the: Mouth chew with teeth and tongue Stomach churns food into chyme (a blended liquid) Small Intestine - receives bile from gall bladder. Bile is produced in the Liver and stored in the gall bladder. Bile breaks up large droplets of fat into tiny drops of fat. Tiny droplets will then be easier to chemically digest.
Chemical Digestion chemically changes food into simpler ( soluble) substances Examples: starches protein fats sugars animo acids fatty acids
(insoluble)
(soluble)
Why chemically digest food? ~Nutrients cannot diffuse into the bloodstream unless they can dissolve in water Soluble able to dissolve; Insoluble unable to dissolve Enzymes change insoluble nutrients into soluble nutrients During Digestion Mouth - Begin the breakdown of starches In saliva, there is an enzyme called ptyalin [tile-in] (also called amylase) which begins the chemical digestion STARCH MECHANICAL (chewing) AND CHEMICAL (ptyalin) Esophagus - Transports food to stomach Peristalsis rhythmic muscular contractions that push food through esophagus
Stomach begins the breakdown of PROTEIN into amino acids Food is churned into CHYME blended liquid (MECHANICAL) Gastric juice hydrochloric acid + pepsin break down protein (CHEMICAL) Sphincter muscles seal the entrance and exit to the stomach and only open to allow food through Mucus lines your stomach to protect it from its own Acids. An ulcer occurs when the acids get through the mucus, and begins to digest in the lining of the stomach
Small intestine about 20 feet long. In the first foot or so, most CHEMICAL digestion takes place. Enzymes from the small intestine and pancreas chemically break down fats, proteins, and carbs. The duodenum is the name for this section of the small intestine. Receives bile from gall bladder. Bile is produced in the liver and stored in the gall bladder. Bile breaks up large droplets of fat into tiny drops of fat. (PHYSICAL) Tiny droplets will then be easier to chemically digest. Pancreatic and intestinal enzymes CHEMICALLY digest Protein, starches, and fats. The remainder of the small intestine is mainly for absorption. Villi line the small intestine to absorb nutrients into its capillaries (diffusion). Peristalsis rhythmic muscular contractions that push food through intestines. Large Intestine (colon) takes leftover food and absorbs the water from it. Rectum Stores feces (waste)
Anus Opening through which feces exits the body Dont forgetknow the diagram of the digestive system!!
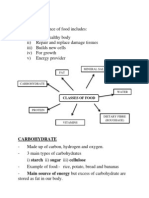
Nutrient Notes Nutrients are the useable portion of the food we eat. The digestive system processes the food we eat into a form that is useable by the bodys cells. Macronutrients: Nutrients used in large amounts Carbohydrates Proteins Fats Water Micronutrients: Nutrients used in small amounts Vitamins Minerals ~Carbohydrates: Major energy source for cells. Two major types: starches and sugars a. Starches - large chains of b. Sugars - smaller molecules that diffuse quickly into the bloodstream There are 4 calories of fuel in each gram of carbohydrates. Calorie - measurement of the energy a particular food contains. High carbohydrate foods: breads, pasta, cereal, fruits, grains, vegetablesplant products.
~Proteins: Build and repair cells, produce enzymes, hormones, etc. Proteins are chains of amino acids. Your body produces some essential animo acids. The rest must be gotten from your diet. There are 4 calories of energy per gram of protein
High protein foods: meats, fish, nuts, soy, tofu, eggs ~Fats: - Major energy source for cells Fat helps to cushion your organs, and provide under-the-skin insulation Fats are chains of fatty acids. There are 9 calories of energy per gram of fat. Foods high in fat: bacon, nuts, red meat, dairy products. Animal fats are usually solid at room temperature, while plant fats (oils) are usually liquid at room temperature. ~Water: Most essential nutrient of all. -Body is 55%-75% water. -Water is the base of your cells cytoplasm as well as the plasma of your blood. Many of the chemical reactions that happen within your body are also based in water. -Water also helps to maintain a constant body temperature, as sweating cools an overheated body. -Water has NO calories, and almost all foods contain some degree of water. Vitamins and Minerals You are to choose any three vitamins and any three minerals from the charts in your textbook. You should know what purpose they have in the body as well as what foods contain them. Vitamins and minerals are referred to as micronutrients because they are used in tiny amounts for very specific cellular purposes.
You might also like
- TG 24 Crowded House - Don't Dream It's Over 1Document1 pageTG 24 Crowded House - Don't Dream It's Over 1ubaldo100% (1)
- 2004 Polaris Parts ManualDocument67 pages2004 Polaris Parts ManualAngela TullochNo ratings yet
- Human & Social Biology 4th FormDocument23 pagesHuman & Social Biology 4th Formhedasdudh100% (1)
- Drums Alive Routine 1Document3 pagesDrums Alive Routine 1Erin Sandberg100% (1)
- High-Yield Anatomy Notes For FCPS Part 1 (MUST HAVE)Document12 pagesHigh-Yield Anatomy Notes For FCPS Part 1 (MUST HAVE)Dr-Sanjay SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System MODULEDocument3 pagesThe Digestive System MODULEBen Moldenhaur100% (2)
- Gastrointestinal System Ppt.-NewDocument117 pagesGastrointestinal System Ppt.-NewFatima Syed100% (3)
- BearingsDocument20 pagesBearingsMuhammad AsadNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System Final 1Document34 pagesThe Digestive System Final 1Jam DabalosNo ratings yet
- Uman Digestive System Structure and Function: DR Neelam SharmaDocument37 pagesUman Digestive System Structure and Function: DR Neelam SharmaBishal Khaidem0% (1)
- Calamba Doctors' College: Digestion, Absorption, and Metabolism Lesson 5Document13 pagesCalamba Doctors' College: Digestion, Absorption, and Metabolism Lesson 5Melody DoriaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Digestive SystemJesrel DelotaNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument30 pagesDigestive SystemImneil Jeanne Melendres-PerezNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Digestive SystemDocument26 pagesWeek 1 - Digestive Systemlau dashNo ratings yet
- The Liver Healing Diet: The Nutritional Plan to Fight Toxins, Reverse Fatty Liver Disease and Promote Good HealthFrom EverandThe Liver Healing Diet: The Nutritional Plan to Fight Toxins, Reverse Fatty Liver Disease and Promote Good HealthNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument26 pagesDigestive Systemapi-208253906100% (1)
- Digestion: The Digestive SystemDocument66 pagesDigestion: The Digestive SystemTonique Gordon100% (1)
- How I Cured My Chronic Back Pain in 48Hours: with Best Herbal Medicines, Diets Plan, Aromatherapy…and Many Others That Give Quick and Permanent Relief of Back PainFrom EverandHow I Cured My Chronic Back Pain in 48Hours: with Best Herbal Medicines, Diets Plan, Aromatherapy…and Many Others That Give Quick and Permanent Relief of Back PainNo ratings yet
- WWW - Incar.tw-Cat 3066 Engine Repair Manual PDFDocument5 pagesWWW - Incar.tw-Cat 3066 Engine Repair Manual PDFlilik50% (4)
- England Abc BookDocument28 pagesEngland Abc Bookapi-251681514No ratings yet
- Essay PlanDocument3 pagesEssay PlanSherbet SpenceNo ratings yet
- Yr 10 WK 3 NoteDocument5 pagesYr 10 WK 3 Notesedrick ocheNo ratings yet
- Digestion HandoutDocument4 pagesDigestion HandoutStephanie ZammitNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive System-Note NewDocument7 pagesHuman Digestive System-Note Newtinsae tewodrosNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Digestive SystemDocument31 pagesUnit 4 - Digestive SystemAbdullah MohammedNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument26 pagesDigestive Systemshahrulafzanizam79No ratings yet
- m6 Digestive SystemDocument23 pagesm6 Digestive Systemapi-464344582No ratings yet
- DigestionDocument22 pagesDigestionapi-200177496No ratings yet
- Human Digestive SystemDocument39 pagesHuman Digestive SystemSha KhinaNo ratings yet
- Human Nutrition Review CORDocument4 pagesHuman Nutrition Review COReshal mobeenNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Digestion and Absorption: Digestion of Food MoleculesDocument24 pages6.1 Digestion and Absorption: Digestion of Food MoleculesWILSON KosheyNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Diagram: Salivary GlandsDocument35 pagesDigestive System Diagram: Salivary GlandsJoyce DometitaNo ratings yet
- 6 Human PhysiologyDocument29 pages6 Human PhysiologyRaynaahNo ratings yet
- Human Digestion PresentationDocument35 pagesHuman Digestion PresentationYamyang Galay-BañoNo ratings yet
- Diet Assessment NBDocument6 pagesDiet Assessment NBnbaker2108No ratings yet
- DigestionDocument6 pagesDigestionWriddhi MononNo ratings yet
- AbsorbtionDocument2 pagesAbsorbtionÁšhlëy Ålïãh GhåñįęNo ratings yet
- 2.6 Digestive SystemDocument3 pages2.6 Digestive SystemOke AdasenNo ratings yet
- SBI3U Digestive SystemDocument4 pagesSBI3U Digestive SystemMario AttallaNo ratings yet
- Modular Handout and Worksheet For April 19-21-2023Document5 pagesModular Handout and Worksheet For April 19-21-2023ccam88743No ratings yet
- Biology 11 - June Final Exam NotesDocument15 pagesBiology 11 - June Final Exam NotesagbavaNo ratings yet
- Diet Assessment 2Document6 pagesDiet Assessment 2NorrisRyanNo ratings yet
- 21 DigestiveDocument23 pages21 DigestivesaqibNo ratings yet
- Diet Assessment 1 0Document7 pagesDiet Assessment 1 0DanRenwickNo ratings yet
- Digestive System NotesDocument10 pagesDigestive System NotesSumit SinghNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument36 pagesDigestive SystemNyasha RumhezaNo ratings yet
- Diet Assessment AFDocument6 pagesDiet Assessment AFAdamFerris94No ratings yet
- K. Nutrition and DigestionDocument23 pagesK. Nutrition and DigestionMary Rose Bobis VicenteNo ratings yet
- Human Digestion1Document23 pagesHuman Digestion1joshua.brussell100% (2)
- Sistem Pencernaan ManusiaDocument8 pagesSistem Pencernaan ManusiaJovan Bimaa PramanaNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System Powerpoint 1227698045024899 8Document44 pagesThe Digestive System Powerpoint 1227698045024899 8Julia Rae Delos Santos100% (1)
- Digestive SystemDocument48 pagesDigestive SystemAlyanna Marie CarilloNo ratings yet
- Updated Presentation Note - 091343Document3 pagesUpdated Presentation Note - 091343Joshua AladenikaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System ReviewerDocument2 pagesDigestive System ReviewerDivino BauzonNo ratings yet
- The Digestive SystemDocument5 pagesThe Digestive SystemFarheen AmerNo ratings yet
- Digestive System - An Overview: How We SurviveDocument45 pagesDigestive System - An Overview: How We SurviveKirubel FekaduNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Key Terms:: Nutrition Quiz NotesDocument8 pagesChapter 1 Key Terms:: Nutrition Quiz NotesThomas AssisNo ratings yet
- The Digestive SystemDocument7 pagesThe Digestive SystemnurmeenNo ratings yet
- LN Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesLN Digestive SystemCasey Dkaye MorrisNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument63 pagesDigestive Systemxander.aguiwasNo ratings yet
- Nutrition: Mineral Salts FATDocument10 pagesNutrition: Mineral Salts FATZirctheace NowxNo ratings yet
- Part I: Anatomy and Physiology of The Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesPart I: Anatomy and Physiology of The Digestive SystemLleana TanNo ratings yet
- HCPCSDocument1 pageHCPCSsabinehaqNo ratings yet
- Trading Forex What Investors Need To KnowDocument24 pagesTrading Forex What Investors Need To KnowTanoj PandeyNo ratings yet
- Single Molecule's Electric Charges Seen in First ImageDocument2 pagesSingle Molecule's Electric Charges Seen in First ImagesabinehaqNo ratings yet
- Skin Transformed Into Brain CellsDocument2 pagesSkin Transformed Into Brain CellssabinehaqNo ratings yet
- AnimesDocument4 pagesAnimeskosali4061No ratings yet
- Nissan Kicks Digital Report V1.0 18 Nov 2020Document4 pagesNissan Kicks Digital Report V1.0 18 Nov 2020Galih PnNo ratings yet
- PVC BowsDocument9 pagesPVC BowsAaronNo ratings yet
- Saab 900 Convertible 86 93 (Opt)Document4 pagesSaab 900 Convertible 86 93 (Opt)mnbvqwertNo ratings yet
- Request For MeetingDocument6 pagesRequest For MeetingMARY JUSTINE SIENNE D. CORPORALNo ratings yet
- Anthonys Resume-2Document2 pagesAnthonys Resume-2api-366419156No ratings yet
- Physiology of The Elite RowerDocument8 pagesPhysiology of The Elite RowerLuky PratamaNo ratings yet
- Danglam: Isua Ka Hmu Ta !!Document4 pagesDanglam: Isua Ka Hmu Ta !!bawihpuiapaNo ratings yet
- ObrasDocument34 pagesObrasandy hernandez0% (1)
- The Thorax and LungsDocument3 pagesThe Thorax and LungsAdellia PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- List of Breath of Fire III AbilitiesDocument22 pagesList of Breath of Fire III AbilitiesDuniesky Trujillo GarcíaNo ratings yet
- YMA Chu Tanpui Ngaite Tanpuitu A NiDocument4 pagesYMA Chu Tanpui Ngaite Tanpuitu A NibawihpuiapaNo ratings yet
- Cheat Downhill DominationDocument9 pagesCheat Downhill DominationDodi KusumaNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Momentum EquationDocument45 pagesTopic 6 Momentum EquationHeyyydayyya HzNo ratings yet
- Reversible Plate Compactor CatalougeDocument4 pagesReversible Plate Compactor CatalougeDeep ZaveriNo ratings yet
- BANSBACH Gas Springs Quick Ship Catalogue 2011enDocument10 pagesBANSBACH Gas Springs Quick Ship Catalogue 2011enGustavo BermudezNo ratings yet
- IKC 4 Rule BookDocument24 pagesIKC 4 Rule BookJee RyNo ratings yet
- Paper AeroplaneDocument19 pagesPaper Aeroplanejkb SudhakarNo ratings yet
- The Avengers Workout: Build A Superhero Physique in Six WeeksDocument1 pageThe Avengers Workout: Build A Superhero Physique in Six WeeksefidjozaNo ratings yet
- Marketing 2Document5 pagesMarketing 2Inam Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- War Commander Codes UpgradeDocument2 pagesWar Commander Codes UpgradeRahul Dogra100% (1)
- Ip TVDocument58 pagesIp TVArisNo ratings yet
- A Health and Safety Guideline For Your Workplace - Manual Materials HandlingDocument6 pagesA Health and Safety Guideline For Your Workplace - Manual Materials HandlingJames UgoNo ratings yet