Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Insuline
Uploaded by
Sikandar LodhiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Insuline
Uploaded by
Sikandar LodhiCopyright:
Available Formats
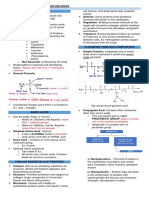
INSULINE & GLYCAGON: INSULINE:-Its a harmone that decrease the blood glucoselevel;NatureIts a Poly-peptideharmone of 51-Amino-AcidChain;STRUCTUREIts Composed of 2chain of 51-Amino-Acid;
1. 2. These 2-Chains are joined by disulphide-Bond; A. SYNTHESIS-OF-INSULINE:Its produced by the -cell of Islets Of Langerhans which present in Pancreas;
The following products are Obtain during Insuline production; 1. In Endo-Plasmic-reticiumPrepro-Insuline break intoNH3 + ProInsuline; 2. In Golgiappratus Pro-Insuline break into insuline+C-Peptide; The initial 2-reaction occurs in EndoPlasmic-reticium; The last reaction occurs in Golgiappratus;
REGULATION-OF-INSULINESECREATION: STIMULATION: 1. Folling stimuli, cause to increase( ) the secreation of insulin in blood;
a) b)
Glucose; Amino-Acid;
when Glucose & Amino-Acid increase( ) in blood it cause to secreate insulin in blood; c) GIT-HARMONES(SECREATION):Its sence the glucose & Amino-Acid in the GIT which cause to Activated the secreation of insuline in blood;
INHIBITION-OF-INSULINE: Decreased( ) of glucose & Amino-Acid in blood, causes to unactivated the secreation of the Insuline in blood by -cell in pancrease;
EPI-NEPHRINE(HARMONE): 1. When the glucose & Amino-Acid become decrease( ) in blood; 2. Then, the Supera-renal gland cause to release the activated form of Epi-nephrine-harmone into the blood; 3. Then, it cause to un-activated the secreation of insuline from to blood; METABOLIC-EFFECT-OF-INSULINE: a) EFFECT-OF-INSULINE-ONCARBOHYDRATE: -cell
A1) EFFECT-OF-INSULINE-ON-LIVER: The insuline promotes glycogen synthesis in liver; A2) EFFECT-OF-INSULINE-ON-MUSCLE: Its increase( ) Glycogen synthesis in muscle; b) EFFECT-OF-INSULINE-ON-ADIPUSETISSUES(FAT-TISSUE): Its decrease( ) the Lipolysis-process & promotes Fat storage;(OR)Its decrease( ) the uses of fat & its promotes fat storages; c) EFFECT-OF-INSULINE-ON-PROTEINE:Its increase( ) the entry of Amino-acid into the cell for synthesis of Proteinemolecule,
e). EFFECT-OF-INSULINE-ON-LIPIDMETABOLISM: Its decrease( ), the storages; INSULINE-ACTION-ON-CELL: A). MECHANISM-OF-INSULINE-ACTIONON-CELL: a) INSULINE-RECEPTORS:Its a polypeptide, having 2molecules; b) SIGNAL-TRANSDUCTION:-Binding of insuline on 2which cause in unit at insuline-receptor conformational-changes occurs & 2units, the 2Units contain binding site for a Insulinefat uses (Lypolysis-process) & its increase( ) fat
-sub-units, which activates, the
Tyrosine-kinase-enzyme;then Tyrosine-
kinase-enzyme activates, Insulinereceptors-substrate-protein(IRS); MEMBRANE-EFFECT-BY-INSULINE: Insuline produces insuline-sensitiveglucose-transpotors(GLUT-4)-Channel on cell-membrane; RECEPTOR-REGULATION:- a) Insuline bind with insulinereceptor on cell-membrane,then insuline-receptors takes insuline & move inside the cell-membrane in cytoplasm; b) when its reaches to Lysosomes,then insuline separated from its receptor & then these receptor again bind with cellmembrane;
c)Increase( ) insuline in blooddecrease( ) of its receptors on cell-membrane; & vice-verca; SHORT-TERM(SHORT-TIME)-ACTION: Its increased the transportation of glucose & Amino-acid inside the fat-cell & muscle-cell in short-interval(as in few seconds) its takes only few seconds; INTER-MEDIATED-ACTION: Activation of Tyrosine-kinase-enzyme which cause to Activate the Insulinereceptor-substrate-protein(IRS),Its takes several hours;
LONG-TERM-ACTION-OF-INSULINE: Its the increased amount of following enzyme production;
a) b) c)
Gluco-kinase; Phospho-fructo-kinase; Pyruvate-kinase;
You might also like
- Bio-Physics in Bio-medical-Engineering in PDF 1Document4 pagesBio-Physics in Bio-medical-Engineering in PDF 1Sikandar LodhiNo ratings yet
- Canadian Citizenship Test Notes From Book "Discover-Canada" (Part-1-Of-2)Document29 pagesCanadian Citizenship Test Notes From Book "Discover-Canada" (Part-1-Of-2)Sikandar Lodhi100% (5)
- Phase Lock Loop (PLL), Op-Amp, Ch-13, Signed, Part-1-OfDocument22 pagesPhase Lock Loop (PLL), Op-Amp, Ch-13, Signed, Part-1-OfSikandar LodhiNo ratings yet
- My Notes On, Heart-Physiology in Bio-Medical EngineeringDocument22 pagesMy Notes On, Heart-Physiology in Bio-Medical EngineeringSikandar LodhiNo ratings yet
- C, C++ Language For Bio-Medical Engineering CoursesDocument6 pagesC, C++ Language For Bio-Medical Engineering CoursesSikandar LodhiNo ratings yet
- Ch-8, Integrations or Anti-Derivatives 2 (PDF Rough File)Document14 pagesCh-8, Integrations or Anti-Derivatives 2 (PDF Rough File)Sikandar LodhiNo ratings yet
- Phase Lock Loop (PLL), Op-Amp, Ch-13, Signed, Part-1-OfDocument22 pagesPhase Lock Loop (PLL), Op-Amp, Ch-13, Signed, Part-1-OfSikandar LodhiNo ratings yet
- C, C++ Language For Bio-Medical Engineering CoursesDocument6 pagesC, C++ Language For Bio-Medical Engineering CoursesSikandar LodhiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Physiology All and Complete PDFDocument86 pagesRespiratory Physiology All and Complete PDFSikandar LodhiNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument5 pagesThermodynamicsSikandar LodhiNo ratings yet
- Body-Building-Guide by Sikander LodhiDocument6 pagesBody-Building-Guide by Sikander LodhiSikandar LodhiNo ratings yet
- Study Note 3 33 PDFDocument1 pageStudy Note 3 33 PDFSikandar LodhiNo ratings yet
- Transported Accross The Biological Membrane-1Document4 pagesTransported Accross The Biological Membrane-1Sikandar LodhiNo ratings yet
- Photo Chemistry of VisionDocument5 pagesPhoto Chemistry of VisionSikandar LodhiNo ratings yet
- Atp StructureDocument5 pagesAtp StructureSikandar LodhiNo ratings yet
- Structure of Protein MoleculeDocument6 pagesStructure of Protein MoleculeSikandar LodhiNo ratings yet
- 10.1+10.2, Fourier Series in PDF Completed NowDocument26 pages10.1+10.2, Fourier Series in PDF Completed NowGUIDE ON BIO-MEDICAL ENGINEERING UNDERGRADUATE PROGRAM:100% (1)
- EnzymesDocument6 pagesEnzymesSikandar LodhiNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Biochemistry Best of Five Collection For Medical StudentsDocument121 pagesBiochemistry Best of Five Collection For Medical StudentsNaji Mohamed AlfatihNo ratings yet
- DNA Gel ElectrophoresisDocument5 pagesDNA Gel ElectrophoresisTok WanNo ratings yet
- AMINO ACIDS: Classification, Properties and TypesDocument8 pagesAMINO ACIDS: Classification, Properties and Typesmukul sidhqueNo ratings yet
- Differential Roles of Nmda Receptor Subtypes Nr2A and Nr2B in Dendritic Branch Development and Requirement of Rasgrf1Document13 pagesDifferential Roles of Nmda Receptor Subtypes Nr2A and Nr2B in Dendritic Branch Development and Requirement of Rasgrf1Rosario MannsNo ratings yet
- Biotech MCQs NumanDocument28 pagesBiotech MCQs NumansajjaddrNo ratings yet
- Crispr Technology EssayDocument4 pagesCrispr Technology Essayhello annyeongNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry-MD21 and DD21-year 2, Semester 1 Lecturer: Bun SeangkhinDocument13 pagesBiochemistry-MD21 and DD21-year 2, Semester 1 Lecturer: Bun SeangkhinVathana SorNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2021Document25 pagesMark Scheme (Results) January 2021Milka RahmanNo ratings yet
- BioChemistry Syllabus and MQPs 08012018Document33 pagesBioChemistry Syllabus and MQPs 08012018rupaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Genetics Maximum Marks: 150 Time: 6 Hrs Section-A Answer All The Questions (20 1 20) Fill in The BlanksDocument5 pagesPrinciples of Genetics Maximum Marks: 150 Time: 6 Hrs Section-A Answer All The Questions (20 1 20) Fill in The BlanksRAJESHNo ratings yet
- Cell Unit of Life Question AnswerDocument8 pagesCell Unit of Life Question Answershafiahmad2014.15No ratings yet
- Student Handout 01 - Cell StructureDocument6 pagesStudent Handout 01 - Cell StructureJoslynn SlaytonNo ratings yet
- Peptidoglycan Biosynthesis: Submitted by P. Tejaswi TVM/20-18Document42 pagesPeptidoglycan Biosynthesis: Submitted by P. Tejaswi TVM/20-18Chaitanya KumarNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells Quarter 1, Module 2aDocument10 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Prokaryotic Vs Eukaryotic Cells Quarter 1, Module 2aSam KimNo ratings yet
- ISO 22119-2011 PCRDocument20 pagesISO 22119-2011 PCRSebastian Jaén Vinueza SoteloNo ratings yet
- BioCentralDogmaWorksheet 1Document3 pagesBioCentralDogmaWorksheet 1jaelajeanine326No ratings yet
- Performance Task On Nucleic AcidsDocument3 pagesPerformance Task On Nucleic AcidsPrincess Mejia De VeraNo ratings yet
- Tasks CareerNaksha Short Internship ProjectDocument23 pagesTasks CareerNaksha Short Internship ProjectDarshil DalwadiNo ratings yet
- SomatostatinDocument7 pagesSomatostatinactivnetNo ratings yet
- Levy Mwanawasa Medical University Biology AssignmentDocument5 pagesLevy Mwanawasa Medical University Biology AssignmentdianaNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM Lec 1 - Introduction To BiochemistryDocument53 pagesBIOCHEM Lec 1 - Introduction To BiochemistryThea Cheruve TomentosNo ratings yet
- Biochem Proteins ReviewerDocument4 pagesBiochem Proteins ReviewerStefany JoyNo ratings yet
- Devita Review2016 4edDocument440 pagesDevita Review2016 4edMartin GranadosNo ratings yet
- Classification of PlasmidsDocument6 pagesClassification of PlasmidsMehak KhanNo ratings yet
- Fluorescent Protein Bicistronic ExpressionDocument5 pagesFluorescent Protein Bicistronic ExpressionAlleleBiotechNo ratings yet
- s12284 019 0358 yDocument12 pagess12284 019 0358 yNi NiNo ratings yet
- Acid Phosphatase - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument3 pagesAcid Phosphatase - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaBinu GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Phytohormones and Their FunctionsDocument85 pagesPhytohormones and Their FunctionsSuvrankar Datta100% (2)
- Primary Structure of A ProteinDocument2 pagesPrimary Structure of A ProteinNkanyiso Mondli ZunguNo ratings yet
- Vce Bio 34 Chapter 2 For Early Entry Test 1 2Document30 pagesVce Bio 34 Chapter 2 For Early Entry Test 1 2YashNo ratings yet