Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ac Ckts Formulae Sheets
Uploaded by
Gaurav ShrimaliCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ac Ckts Formulae Sheets
Uploaded by
Gaurav ShrimaliCopyright:
Available Formats
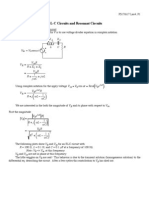
ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS 104 FORMULA SHEET 1. DC CIRCUITS (Resistive) (i) Ohms Law: V = R.I or I = G.
.V (ii) Delta to Y Transformations (Ra, Rb, Rc) to (R1, R2, R3): 3. SWITCHED CIRCUITS (First and Second Order Transient Responses) (i) (ii) (iii) First Order DE: Solution:
d dt 1 y + T y = f (t ) where T = RC or T = L/R
t T
R1 =
(iii) (iv)
Rb Rc R1 R2 + R2 R3 + R3 R1 .. Ra = Ra + Rb + Rc R1
2 2
y (t ) = A + B.e
d2 dt 2
where A & B from boundary conditions
d dt 2 y + o y = f (t ) where
Power: P = V .I = V G = I Operational Amplifier Model:
Second Order DE:
y + 2
o = 1 / LC (natural freq) and is the damping factor
(iv) (v) (vi) Overdamped Solution: Critically Damped: Underdamped : Solution : 4.
y (t ) = ( A.e 1t + B.e 2t ) + forced Response
d
y (t ) = ( A.e .t + B.t.e .t ) + forced Response = K
2 s = j d = 2 + d tan 1
y (t ) = A.e .t cos( d .t ) + B.e .t sin( d .t ) + forced R
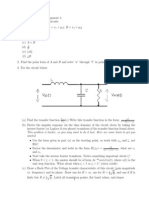
APPLICATIONS (frequency response, filters, 2-port networks) (i) (ii)
V out = H ( j ) H ( j ) V in The Magnitude Response can be expressed in dB = 20 log H ( j )
Transfer Function:
H ( j ) =
where Ri 2.
Ro 0
A
b a
(iii) (iv) (v)
AC CIRCUITS (Phasors and Impedances) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) Complex Number:
a + jb = a 2 + b 2 tan 1 A + B cos( tan
2 2
The half-power bandwidth is defined between 2 frequencies at which the response drops down by -3dB (i.e. 0.707 of Maximum value). Band-pass Filters are characterised by the centre frequency () and the halfpower bandwidth ( ) . Quality factor, Q = o / . z-parameters are defined as: V1 = z11 I1 + z12 I2 and V2 = z21 I1 + z22 I2 Transmission parameters are defined as: V1 = a11 V2 - a12 I2 and I1 = a21 V2 - a22 I2 Hybrid parameters are defined as: V1 = h11 I1 + h12 V2 and I2 = h21 I1 + h22 V2 Conditions for Reciprocity: z12 = z21, (a11.a22 - a12.a21) = 1, h12 = -h21. Additional Conditions for Symmetry: z11 = z22, a11 = a22, (h11.h22 - h12.h21) = 1 Converting [Z] to [A]: a11
A cos + B sin = sin = cos( ) 2
1 B A
(vi) (vii) (viii) (ix) (x)
v(t ) = Vm cos( .t + ) V = Vm = Vm cos + jVm sin Z = R + jX , Y = G + jB , Z L = j .L , Z c = j 1C .
Mutual Inductance:
v1 = L
di1 1 dt
di2 dt
and
k = M / L1 L2
V1 = ( j .L1 ) I 1 ( j .M ) I 2
(vii) (viii) (ix)
2 2 Pav = Vrms I rms cos = I rms R = Vrms G where Vrms = Vm / 2
Complex Power:
S = V .I = Vrms I rms cos + jVrms I rms sin Wc = 1 CV 2 ; inductor, WL = 1 LI 2 . 2 2
(xi)
z z 1 = 11 , a12 = z , a 21 = , a 22 = 22 z 21 z 21 z 21 z 21 z z 1 Converting [Z] to [H]: h11 = z , h12 = 12 , h21 = 21 , h22 = z 22 z 22 z 22 z 22
Energy stored: capacitor,
You might also like
- Fundamentals of AC Circuit AnalysisDocument24 pagesFundamentals of AC Circuit AnalysisAldeline SungahidNo ratings yet
- COMMUNICATIONS Formulas and Concepts V3 PDFDocument24 pagesCOMMUNICATIONS Formulas and Concepts V3 PDFHector Ledesma IIINo ratings yet
- 2M EIC1999 Exam Answers: Part ADocument2 pages2M EIC1999 Exam Answers: Part Aaaroncete14No ratings yet
- Solutions Manual: Electric Motor DrivesDocument12 pagesSolutions Manual: Electric Motor DrivesMedo Sabah100% (2)
- Nptel Control Engineering Assignment 1 McqsDocument4 pagesNptel Control Engineering Assignment 1 McqsDharaniChintaNo ratings yet
- Things To Know For The Physics GRE: Daniel Beller October 28, 2009Document20 pagesThings To Know For The Physics GRE: Daniel Beller October 28, 2009Arif SolmazNo ratings yet
- 2006 ISRO ECE Question Paper PDFDocument19 pages2006 ISRO ECE Question Paper PDFKD0% (1)
- MECE232 2018 2019 Spring MidtermDocument3 pagesMECE232 2018 2019 Spring MidtermNeslihan YılmazNo ratings yet
- GATE Study Material, Forum, Downloads, Discussions & More!Document17 pagesGATE Study Material, Forum, Downloads, Discussions & More!Ajay NarvariyaNo ratings yet
- AP PGECET 2015 EC Question Paper & Answer Key DownloadDocument16 pagesAP PGECET 2015 EC Question Paper & Answer Key DownloadpavaniNo ratings yet
- The Transfer Function PDFDocument15 pagesThe Transfer Function PDFArnav KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Frequency Response of CircuitDocument14 pagesFrequency Response of Circuitpra_zara2637100% (1)
- ENAD Formula SheetDocument7 pagesENAD Formula SheetRachel TanNo ratings yet
- Gate - in 2007Document30 pagesGate - in 2007prabhjot singh1No ratings yet
- COMMUNICATIONS Formulas and ConceptsDocument24 pagesCOMMUNICATIONS Formulas and ConceptsAllan Paul Lorenzo Abando76% (17)
- 08 Differential Equations - Second Order LDE ApplicationsDocument25 pages08 Differential Equations - Second Order LDE ApplicationsRemo Rubian EvangelistaNo ratings yet
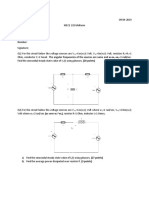
- Electronic Circuits 1 Mid-Term Exam 1Document5 pagesElectronic Circuits 1 Mid-Term Exam 1정연종No ratings yet
- Week 1 Assignment SolutionsDocument5 pagesWeek 1 Assignment SolutionsMuskan JainNo ratings yet
- PID Buck-BoostDocument8 pagesPID Buck-BoostIvan RahmanNo ratings yet
- 2labman lcr7Document8 pages2labman lcr7RufosNo ratings yet
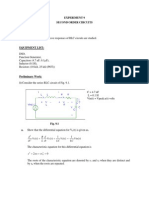
- Experiment 9 Second Order Circuits: F),, 25 K (POT) )Document3 pagesExperiment 9 Second Order Circuits: F),, 25 K (POT) )zito_marcoNo ratings yet
- Gate Ece 1998Document9 pagesGate Ece 1998Janmejay OjhaNo ratings yet
- 1091 Circuit Theory HW1 Solution: Tera T Giga G (Femto FDocument5 pages1091 Circuit Theory HW1 Solution: Tera T Giga G (Femto F曾燒餅No ratings yet
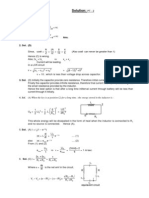
- Solution:: DT DQ e RC C V BDocument5 pagesSolution:: DT DQ e RC C V BAritra LahiriNo ratings yet
- Gate Ece 2010Document16 pagesGate Ece 2010Abhinav RajNo ratings yet
- Et M Zulassungspruefung PDFDocument5 pagesEt M Zulassungspruefung PDFmuhammad bilalNo ratings yet
- Q. No. 1 - 25 Carry One Mark Each: DNX NX 0 DX LDocument17 pagesQ. No. 1 - 25 Carry One Mark Each: DNX NX 0 DX LChangal Reddy Yarrapu ReddyNo ratings yet
- Gate 2015 PDFDocument81 pagesGate 2015 PDFsameer meshramNo ratings yet
- Summary From Previous Lecture: - Laplace TransformDocument16 pagesSummary From Previous Lecture: - Laplace Transformgunawan refiadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Transmission LineDocument87 pagesChapter 1 Transmission LinePhamHungNo ratings yet
- (WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - GATE Instrumentation Engineering Sample Paper 1Document13 pages(WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - GATE Instrumentation Engineering Sample Paper 1Rajni KantNo ratings yet
- Final Power Electronics Formulas ListDocument8 pagesFinal Power Electronics Formulas ListJuan RaoofNo ratings yet
- JEE 2016 Online 10th APRIL 2016 PDFDocument67 pagesJEE 2016 Online 10th APRIL 2016 PDFRamesh BadamNo ratings yet
- Power Systems With MATLABDocument156 pagesPower Systems With MATLABJuan Alex Arequipa ChecaNo ratings yet
- Signals and SystemsDocument69 pagesSignals and Systemsanand_kkrNo ratings yet
- HW 1Document5 pagesHW 1BrimwoodboyNo ratings yet
- Subject: Signals & SystemsDocument27 pagesSubject: Signals & SystemsNaga VardhanNo ratings yet
- Final Report Buck ConverterDocument30 pagesFinal Report Buck Converter015Maulana Malik IbrahimNo ratings yet
- A4 SolDocument35 pagesA4 Solanshikamittal1807No ratings yet
- Electronics Sample Paper 1Document13 pagesElectronics Sample Paper 1krish_cvr2937No ratings yet
- 2023 (I) Ing Mec Matematica III (List 08)Document3 pages2023 (I) Ing Mec Matematica III (List 08)Cristopher SalazarNo ratings yet
- Network Functions and S-Domain AnalysisDocument22 pagesNetwork Functions and S-Domain AnalysispowerdeadlifterNo ratings yet
- Gate Ece 2006Document12 pagesGate Ece 2006mgitecetechNo ratings yet
- Lec 4Document9 pagesLec 4Jura PateregaNo ratings yet
- BookkkkDocument207 pagesBookkkkNadin NirvanaNo ratings yet
- GATE-Electronics & Comm (ECE) - 2009Document21 pagesGATE-Electronics & Comm (ECE) - 2009Rajendra PrasadNo ratings yet
- Walker, J., Halliday, D., & Resnick, R. (2011) - Fundamentals of Physics. 6th Edition, Page 837. Hoboken, NJ, WileyDocument8 pagesWalker, J., Halliday, D., & Resnick, R. (2011) - Fundamentals of Physics. 6th Edition, Page 837. Hoboken, NJ, WileyBigBluesterNo ratings yet
- Second Order TransientsDocument6 pagesSecond Order Transientsmusy1233No ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 3Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Exercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsFrom EverandExercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Tables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27From EverandTables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27No ratings yet
- Mathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandMathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1From EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1No ratings yet
- Hpa Phenol Toxicological Overview v2Document12 pagesHpa Phenol Toxicological Overview v2Gaurav ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- MPPDocument7 pagesMPPGaurav ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- FS Calendar 2014 Wall ENGDocument17 pagesFS Calendar 2014 Wall ENGGaurav ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- Acc 2Document3 pagesAcc 2Gaurav ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- Life D2013 KeyDocument11 pagesLife D2013 KeyGaurav ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- Birth, Life and Death of The EgoDocument18 pagesBirth, Life and Death of The EgoBuddhist Publication SocietyNo ratings yet
- SPMCILHRDocument1 pageSPMCILHRGaurav ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: India'S Best Institute For EngineersDocument6 pagesSyllabus: India'S Best Institute For EngineersGaurav ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- AnswersDocument51 pagesAnswersGaurav ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- New Rev Peh II Manual 15 Aug 2013Document187 pagesNew Rev Peh II Manual 15 Aug 2013Gaurav ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- D 8805 Paper IiDocument12 pagesD 8805 Paper IirahulpelectronicsNo ratings yet
- ACE Engineering Academy - Online Test:: Test-1 On Communications, Topic: Analog Communication SystemDocument1 pageACE Engineering Academy - Online Test:: Test-1 On Communications, Topic: Analog Communication SystemGaurav ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- D 8804 Paper IiDocument12 pagesD 8804 Paper IiRamkrishna ChittooriNo ratings yet
- Ugc Keys PDF 2005Document2 pagesUgc Keys PDF 2005Gaurav ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- Am 1Document1 pageAm 1Gaurav ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- Cut-Off: India's Best Institute For EngineersDocument1 pageCut-Off: India's Best Institute For EngineersGaurav ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- Electronics: Venue:-Destination Academy, Garh Road Near Hotel Harmony S2S Restaurant MeerutDocument1 pageElectronics: Venue:-Destination Academy, Garh Road Near Hotel Harmony S2S Restaurant MeerutGaurav ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- Am 3Document1 pageAm 3Gaurav ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- TimeDocument5 pagesTimeGaurav ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- Am 3Document1 pageAm 3Gaurav ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- Am 14Document1 pageAm 14Gaurav ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- ACE Engineering Academy - Online Test:: Test-1 On Communications, Topic: Analog Communication SystemDocument1 pageACE Engineering Academy - Online Test:: Test-1 On Communications, Topic: Analog Communication SystemGaurav ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- Am 14Document1 pageAm 14Gaurav ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- Am 14Document1 pageAm 14Gaurav ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- Am 14Document1 pageAm 14Gaurav ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- Am 14Document1 pageAm 14Gaurav ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- Data Card FR Offshore PDFDocument4 pagesData Card FR Offshore PDFGaurav ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- Income Tax PrerequisiteDocument4 pagesIncome Tax PrerequisiteGaurav ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- AllowanceDocument5 pagesAllowanceGaurav ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- Ongc PdfsDocument1 pageOngc PdfsGaurav ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- Control Valve Inspection RequirementDocument1 pageControl Valve Inspection RequirementGeekyard Geeks GNo ratings yet
- Cloud ChartDocument2 pagesCloud ChartmcwoodlandsNo ratings yet
- Substation LayoutDocument23 pagesSubstation LayoutMahendra KammaNo ratings yet
- Carbogran: Material Innovations in CompositesDocument1 pageCarbogran: Material Innovations in CompositesvinayksNo ratings yet
- MRC-107T Tadiran RADIO PALLET TMDocument74 pagesMRC-107T Tadiran RADIO PALLET TMΒΕΗΣ ΣΤΕΛΙΟΣ Veis Stelios0% (1)
- Sniffer For Detecting Lost MobilesDocument14 pagesSniffer For Detecting Lost MobilesSandeep SangaNo ratings yet
- Well Log Interpretation Neutron Log: Earth & Environmental Science University of Texas at ArlingtonDocument12 pagesWell Log Interpretation Neutron Log: Earth & Environmental Science University of Texas at ArlingtonDeny Fatryanto EkoNo ratings yet
- Heent ExaminationDocument1 pageHeent ExaminationJudrelle Krizia MarianoNo ratings yet
- Gatt Declaration FormDocument1 pageGatt Declaration FormUtsav Ethan PatelNo ratings yet
- Dead LoadsDocument3 pagesDead Loadsezarul fitriNo ratings yet
- Case Summary of A.1. Steak SauceDocument2 pagesCase Summary of A.1. Steak SauceAbhinitMahtoNo ratings yet
- QSB Audit1Document1 pageQSB Audit1meca2aNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis-YUM Power PointDocument9 pagesCase Analysis-YUM Power PointKsenia ProkopienkoNo ratings yet
- Safety Alert: Tong Incident Results in A FatalityDocument1 pageSafety Alert: Tong Incident Results in A FatalityVimal SinghNo ratings yet
- Batteries enDocument1 pageBatteries enRogelio MolinaNo ratings yet
- 2.5x1.5 Fire Hose Rack AssembliesDocument1 page2.5x1.5 Fire Hose Rack AssembliesMostafa El-BalashonyNo ratings yet
- AE 221tutorial 3Document2 pagesAE 221tutorial 3animeshkumarvermaNo ratings yet
- CIMPLICITY VirtualMachineDocument1 pageCIMPLICITY VirtualMachineJuan Carlos Sanchez CastilloNo ratings yet
- Mrunal (Economy Q) GDP at Factor Cost and Market Price (GDPFC & GDPMP), NNPFC, NNPMP PrintDocument2 pagesMrunal (Economy Q) GDP at Factor Cost and Market Price (GDPFC & GDPMP), NNPFC, NNPMP PrintAkash Singh Chauhan0% (2)
- ECE 2C Mid-Term Exam May 6, 2010: and Approximately Justifying ThemDocument12 pagesECE 2C Mid-Term Exam May 6, 2010: and Approximately Justifying Themjack monetNo ratings yet
- The Immortal Rooster and Other Stories by Diane de AndaDocument74 pagesThe Immortal Rooster and Other Stories by Diane de AndaArte Público Press67% (3)
- The Turning Circle of VehiclesDocument2 pagesThe Turning Circle of Vehiclesanon_170098985No ratings yet
- Form CoefficientsDocument5 pagesForm CoefficientsjishnusajiNo ratings yet
- ECE 131 FOTEX Laboratory 1.finalDocument7 pagesECE 131 FOTEX Laboratory 1.finalDonna AmbalongNo ratings yet
- Primavera Project Planner Sample Project: Prepared By: Luay Dwaikat, Msc. Construction ManagementDocument3 pagesPrimavera Project Planner Sample Project: Prepared By: Luay Dwaikat, Msc. Construction ManagementkrajeshkumarxNo ratings yet
- Role of Energy Conservation in Spinning MillsDocument15 pagesRole of Energy Conservation in Spinning MillsMufaddal BagwalaNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice ExercisesDocument1 pagePassive Voice ExercisesSimona SymonyciNo ratings yet
- ST1 Grease TrapDocument4 pagesST1 Grease Trap21smithNo ratings yet
- Gelatin Film Lysis TestDocument2 pagesGelatin Film Lysis TestSuryakant HayatnagarkarNo ratings yet
- Chem100 - ThermochemDocument12 pagesChem100 - ThermochemEdrick RamoranNo ratings yet