Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CHN
Uploaded by
Gilleen Megan BungaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CHN
Uploaded by
Gilleen Megan BungaCopyright:
Available Formats
1. Which is the primary goal of community health nursing? A.
To support and supplement the efforts of the medical profession in the promotion of health and prevention of illness B. To enhance the capacity of individuals, families and communities to cope with their health needs C. To increase the productivity of the people by providing them with services that will increase their level of health D. To contribute to national development through promotion of family welfare, focusing particularly on mothers and children.
2. CHN is a community-based practice. Which best explains this statement? A. The service is provided in the natural environment of people. B. The nurse has to conduct community diagnosis to determine nursing needs and problems. C. The services are based on the available resources within the community. D. Priority setting is based on the magnitude of the health problems identified.
3. Population-focused nursing practice requires which of the following processes? A. Community organizing B. Nursing process C. Community diagnosis D. Epidemiologic process
4. R.A. 1054 is also known as the Occupational Health Act. Aside from number of employees, what other factor must be considered in determining the occupational health privileges to which the workers will be entitled? A. Type of occupation: agricultural, commercial, industrial B. Location of the workplace in relation to health facilities C. Classification of the business enterprise based on net profit D. Sex and age composition of employees
5. A business firm must employ an occupational health nurse when it has at least how many employees? A. 21 B. 101 C. 201 D. 301
6. When the occupational health nurse employs ergonomic principles, she is performing which of her roles? A. Health care provider B. Health educator C. Health care coordinator D. Environmental manager
7. A garment factory does not have an occupational nurse. Who shall provide the occupational health needs of the factory workers? A. Occupational health nurse at the Provincial Health Office B. Physician employed by the factory C. Public health nurse of the RHU of their municipality D. Rural sanitary inspector of the RHU of their municipality
8. Public health services are given free of charge. Is this statement true or false? A. The statement is true; it is the responsibility of government to provide basic services. B. The statement is false; people pay indirectly for public health services. C. The statement may be true or false, depending on the specific service required. D. The statement may be true or false, depending on policies of the government concerned.
9. According to C.E.Winslow, which of the following is the goal of Public Health? A. For people to attain their birthrights of health and longevity B. For promotion of health and prevention of disease C. For people to have access to basic health services D. For people to be organized in their health efforts
10. We say that a Filipino has attained longevity when he is able to reach the average lifespan of Filipinos. What other statistic may be used to determine attainment of longevity? A. Age-specific mortality rate B. Proportionate mortality rate C. Swaroops index
D. Case fatality rate
11. Which of the following is the most prominent feature of public health nursing? A. It involves providing home care to sick people who are not confined in the hospital. B. Services are provided free of charge to people within the catchment area. C. The public health nurse functions as part of a team providing a public health nursing services. D. Public health nursing focuses on preventive, not curative, services.
12. According to Margaret Shetland, the philosophy of public health nursing is based on which of the following? A. Health and longevity as birthrights B. The mandate of the state to protect the birthrights of its citizens C. Public health nursing as a specialized field of nursing D. The worth and dignity of man
13. Which of the following is the mission of the Department of Health? A. Health for all Filipinos B. Ensure the accessibility and quality of health care C. Improve the general health status of the population D. Health in the hands of the Filipino people by the year 2020
14. Region IV Hospital is classified as what level of facility? A. Primary B. Secondary C. Intermediate D. Tertiary
15. Which is true of primary facilities? A. They are usually government-run. B. Their services are provided on an out-patient basis. C. They are training facilities for health professionals. D. A community hospital is an example of this level of health facilities.
16. Which is an example of the school nurses health care provider functions? A. Requesting for BCG from the RHU for school entrant immunization B. Conducting random classroom inspection during a measles epidemic C. Taking remedial action on an accident hazard in the school playground D. Observing places in the school where pupils spend their free time
17. When the nurse determines whether resources were maximized in implementing Ligtas Tigdas, she is evaluating A. Effectiveness B. Efficiency C. Adequacy D. Appropriateness
18. You are a new B.S.N. graduate. You want to become a Public Health Nurse. Where will you apply? A. Department of Health B. Provincial Health Office C. Regional Health Office D. Rural Health Unit
19. R.A. 7160 mandates devolution of basic services from the national government to local government units. Which of the following is the major goal of devolution? A. To strengthen local government units B. To allow greater autonomy to local government units C. To empower the people and promote their self-reliance D. To make basic services more accessible to the people
20. Who is the Chairman of the Municipal Health Board? A. Mayor B. Municipal Health Officer C. Public Health Nurse D. Any qualified physician
21. Which level of health facility is the usual point of entry of a client into the health care delivery system? A. Primary B. Secondary C. Intermediate D. Tertiary
22. The public health nurse is the supervisor of rural health midwives. Which of the following is a supervisory function of the public health nurse? A. Referring cases or patients to the midwife B. Providing technical guidance to the midwife C. Providing nursing care to cases referred by the midwife D. Formulating and implementing training programs for midwives
23. One of the participants in a hilot training class asked you to whom she should refer a patient in labor who develops a complication. You will answer, to the A. Public Health Nurse B. Rural Health Midwife C. Municipal Health Officer D. Any of these health professionals
24. You are the public health nurse in a municipality with a total population of about 20,000. There are 3 rural health midwives among the RHU personnel. How many more midwife items will the RHU need? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. The RHU does not need any more midwife item.
25. If the RHU needs additional midwife items, you will submit the request for additional midwife items for approval to the A. Rural Health Unit B. District Health Office C. Provincial Health Office
D. Municipal Health Board
26. As an epidemiologist, the nurse is responsible for reporting cases of notifiable diseases. What law mandates reporting of cases of notifiable diseases? A. Act 3573 B. R.A. 3753 C. R.A. 1054 D. R.A. 1082
27. According to Freeman and Heinrich, community health nursing is a developmental service. Which of the following best illustrates this statement? A. The community health nurse continuously develops himself personally and professionally. B. Health education and community organizing are necessary in providing community health services. C. Community health nursing is intended primarily for health promotion and prevention and treatment of disease. D. The goal of community health nursing is to provide nursing services to people in their own places of residence.
28. Which disease was declared through Presidential Proclamation No. 4 as a target for eradication in the Philippines? A. Poliomyelitis B. Measles C. Rabies D. Neonatal tetanus
29. The public health nurse is responsible for presenting the municipal health statistics using graphs and tables. To compare the frequency of the leading causes of mortality in the municipality, which graph will you prepare? A. Line B. Bar C. Pie D. Scatter diagram
30. Which step in community organizing involves training of potential leaders in the community? A. Integration B. Community organization C. Community study D. Core group formation
31. In which step are plans formulated for solving community problems? A. Mobilization B. Community organization C. Follow-up/extension D. Core group formation
32. The public health nurse takes an active role in community participation. What is the primary goal of community organizing? A. To educate the people regarding community health problems B. To mobilize the people to resolve community health problems C. To maximize the communitys resources in dealing with health problems D. To maximize the communitys resources in dealing with health problems
33. An indicator of success in community organizing is when people are able to A. Participate in community activities for the solution of a community problem B. Implement activities for the solution of the community problem C. Plan activities for the solution of the community problem D. Identify the health problem as a common concern
34. Tertiary prevention is needed in which stage of the natural history of disease? A. Pre-pathogenesis B. Pathogenesis C. Prodromal D. Terminal
35. Isolation of a child with measles belongs to what level of prevention? A. Primary B. Secondary C. Intermediate D. Tertiary
36. On the other hand, Operation Timbang is _____ prevention. A. Primary B. Secondary C. Intermediate D. Tertiary
37. Which type of family-nurse contact will provide you with the best opportunity to observe family dynamics? A. Clinic consultation B. Group conference C. Home visit D. Written communication
38. The typology of family nursing problems is used in the statement of nursing diagnosis in the care of families. The youngest child of the de los Reyes family has been diagnosed as mentally retarded. This is classified as a A. Health threat B. Health deficit C. Foreseeable crisis D. Stress point
39. The de los Reyes couple have a 6-year old child entering school for the first time. The de los Reyes family has a A. Health threat B. Health deficit C. Foreseeable crisis D. Stress point
40. Which of the following is an advantage of a home visit? A. It allows the nurse to provide nursing care to a greater number of people. B. It provides an opportunity to do first hand appraisal of the home situation. C. It allows sharing of experiences among people with similar health problems. D. It develops the familys initiative in providing for health needs of its members.
41. Which is CONTRARY to the principles in planning a home visit? A. A home visit should have a purpose or objective. B. The plan should revolve around family health needs. C. A home visit should be conducted in the manner prescribed by the RHU. D. Planning of continuing care should involve a responsible family member.
42. The PHN bag is an important tool in providing nursing care during a home visit. The most important principle of bag technique states that it A. Should save time and effort. B. Should minimize if not totally prevent the spread of infection. C. Should not overshadow concern for the patient and his family. D. May be done in a variety of ways depending on the home situation, etc.
43. To maintain the cleanliness of the bag and its contents, which of the following must the nurse do? A. Wash his/her hands before and after providing nursing care to the family members. B. In the care of family members, as much as possible, use only articles taken from the bag. C. Put on an apron to protect her uniform and fold it with the right side out before putting it back into the bag. D. At the end of the visit, fold the lining on which the bag was placed, ensuring that the contaminated side is on the outside.
44. The public health nurse conducts a study on the factors contributing to the high mortality rate due to heart disease in the municipality where she works. Which branch of epidemiology does the nurse practice in this situation? A. Descriptive B. Analytical C. Therapeutic
D. Evaluation
45. Which of the following is a function of epidemiology? A. Identifying the disease condition based on manifestations presented by a client B. Determining factors that contributed to the occurrence of pneumonia in a 3 year old C. Determining the efficacy of the antibiotic used in the treatment of the 3 year old client with pneumonia D. Evaluating the effectiveness of the implementation of the Integrated Management of Childhood Illness
46. Which of the following is an epidemiologic function of the nurse during an epidemic? A. Conducting assessment of suspected cases to detect the communicable disease B. Monitoring the condition of the cases affected by the communicable disease C. Participating in the investigation to determine the source of the epidemic D. Teaching the community on preventive measures against the disease
47. The primary purpose of conducting an epidemiologic investigation is to A. Delineate the etiology of the epidemic B. Encourage cooperation and support of the community C. Identify groups who are at risk of contracting the disease D. Identify geographical location of cases of the disease in the community
48. Which is a characteristic of person-to-person propagated epidemics? A. There are more cases of the disease than expected. B. The disease must necessarily be transmitted through a vector. C. The spread of the disease can be attributed to a common vehicle. D. There is a gradual build up of cases before the epidemic becomes easily noticeable.
49. In the investigation of an epidemic, you compare the present frequency of the disease with the usual frequency at this time of the year in this community. This is done during which stage of the investigation? A. Establishing the epidemic
B. Testing the hypothesis C. Formulation of the hypothesis D. Appraisal of facts
50. The number of cases of Dengue fever usually increases towards the end of the rainy season. This pattern of occurrence of Dengue fever is best described as A. Epidemic occurrence B. Cyclical variation C. Sporadic occurrence D. Secular variation
1. This STD is characterized by greenish yellow, frothy musty odorous vaginal discharge accompanied with vaginal itchiness and painful urination? a. Trichomoniasis b. Chancroid c. Moniliasis d. Chlamydia Ans. A. Trichomoniasis 2. DOTS is a comprehensive strategy to detect and cure TB. The primary element of DOTS is a. Health workers counsel and observe their patients swallow each anti-TB medication and monitor progress until cures b. Regular drug supply c. Political will in terms of manpower and funding d. Sputum microscopy services Ans. A. The main strategy of the NTP is Directly Observed Treatment, short course (DOTS). This is a comprehensive strategy to control TB which primary health services around the world are using in the detection and cure TB 3. What is the mode of transmission of Pulmonary Tuberculosis? a. Fecal-oral b. Direct contact c. Airborne, droplet d. Blood borne Ans. C. (Martinez, D. Intensive Final Coaching Primary Health Care, Legazpi City: A1 Review Center, 06, question 36) 4. Standard examination in detecting PTb: a. X-ray b. Sputum Exam c. Ultrasound d. Tuberculin Test Ans. B.
5. In Catergory II of the TB treatment regimen all are prescribed BUT one: a. Relapse case b. New pulmonary smear (+) cases c. Failure cases d. Other (smear +) Ans. B. Category I: Prescribed for a) new pulmonary smear (+) cases, b) new seriously ill pulmonary smear(-) cases with extensive parenchymal involvement and c.) new severely ill extrapulmonary TB cases; Category II: Prescribed for a.) failure cases, b) relapse cases; c) RAD (smear +), and OTHER (smear+); Category III Prescribed for a.) new smear (-) but with minimal pulmonary TB on radiography as confirmed by medical officer and b) new extrapulmonary TB (not serious). 6. Malaria can be prevented by the following EXCEPT: a. Avoiding outdoor night time activities b. Use of mosquito repellants c. Planting of herbal plants which can be mosquito repellants d. Spending leisure time in the forest Ans. D. Preventive activities against malaria include all but not limited to the following: 1. Avoid going outdoor between 9pm to 3 am , the peak biting hours of female anopheles mosquitoes 2. Prophylaxis: taking chloroquine every week starting one to two weeks before traveling 3. Using mosquito net or curtain treatment by soaking the mosquito net in insecticidal solution and allow to dry before using 4. House spraying of insecticide inside the house 5. Wearing clothes that cover arms and legs at night 7. During this stage the H fever is said to cause severe abdominal pain, vomiting and frequent bleeding from GI tract: a. Invasive Stage b. Toxic stage c. Convalescent Stage d. Febrile Stage Ans. B. Toxic Stage A. Invasive stage or febrile stage starts abruptly as high fever, abdominal pain and headache; later flushing which maybe accompanied by vomiting and epistaxis; B. Toxic or hemorrhagic stage is the time where severe abdominal pain, vomiting and frequent bleeding from the GI is observed; C. Convalescent or recovery stage most of the vital signs are stable.
8. What is the etiologic agent of Diptheria? a. Klebs-Loffler bacillus b. Bordet Gengou Bacillus c. Vibrio El Tor d. Filterable virus Ans. A. Klebs-Loffler bacillus
9. An example of this route of transmission is the dust particles with infectious agent and residue of evaporated droplets that remain suspended in the air: a. Vectorborne transmission c. Contact transmission b. Airborne transmission d. Droplet transmission Ans. Ans. B. Airborne transmission A. Vectorborne transmission examples are flies, ticks, mosquitoes and flies; B. Airborne transmission includes droplet nuclei, dust particles with infectious agent and organisms shed into the environment from the skin, hair or perineal area; C. Contact transmission includes direct contact, indirect contact and droplet contact; D. theres no such thing as droplet transmission only droplet contact.
10. This chain of infection allows the microorganisms to move from reservoir to host: a. Portal of Exit c. Portal of entry b. infectious agent d. susceptible host Ans. A. Portal of exit A. Some examples of movement from reservoir to host are excretions, secretions and skin droplets; B. The common site for the portal of entry is mucous membranes, GI tract and non-intact skin; C. Examples of infectious agents are bacteria and virus; D. susceptible host are the immunosuppressed patient, fatigued, elderly and other hospitalized patient.
11. Inflammatory processes provided by the WBC (leukocytes), whose main purpose is to limit the effect of harmful bacteria or injury by destroying or neutralizing the organism, and by limiting its spread throughout the body: a. First line of defense b. Second line of defense c. Third line of defense d. Fourth line of defense Ans. B. Second line of defense A. First line of defense include the skin and mucus membrane; B. Second line of defense involves leukocytes; C. Third line of defense include the antibodies
12. The immune response is considered to be: a. First line of defense b. Second line of defense c. Third line of defense d. Fourth line of defense Ans. C. Third line of defense A. First line of defense include the skin and mucus membrane; B. Second line of defense involves leukocytes; C. Third line of defense includes the antibodies.
13. Nurse Angelika believed that the complete destruction of all microorganisms, including the spores is:
a. Disinfection b. Sterilization c. Cleaning d. all of these Ans. B. Sterilization 14. When asked about the risk of transmitting agents through large particles (5 micrometer or more) Crizelda refer this type of precaution to her clients as: a. Airborne precaution b. Contact precaution c. Standard precaution d. Droplet precaution Ans. D. Droplet precaution 15. It is an upper respiratory condition characterized by escalating fever (peaks 3-5 days), conjunctivitis and coryza: a. Measles b. German Measles c. chicken pox d. Varicella Ans. Measles 16. A day biting female mosquito that breeds in household or standing clean water: a. Female anopheles b. Male anopheles c. Aedes aegypti d. None of these Ans. C. Aedes aegypti 17. The following are the major causes of intestinal parasitic infections in the Philippines, EXCEPT: a. Trichuris trichiura b. Ascaris lumbricoides c. Hookworm d. none of these Ans. D. All of them are the three major causes of intestinal parasitic infections 18. What is the period of communicability of the epidemic parotitis? a. Begins before the glands are swollen and presumed to last as long as localized glandular swelling remains b. Begins after the glands are swollen especially when the localized glandular swelling remains c. Begins before the glands are swollen and after the glands are swollen even when the glandular swelling is not observed. d. except c Ans. A. Begins before the glands are swollen and presumed to last as long as localized glandular swelling remains 19. Which his TRUE regarding Filariasis? a. Microfilarie rate increases with age and then levels off during the acute stage b. Men have higher micronlariae rate than women
c. During the chronic stage the disease develops 2-5 years from the onset of attack d. Hydrocoele is evident in men during the acute stage A. It is not during the acute stage but during the asymptomatic stage: B True that men have higher micronlariae rate than women; C. The disease develops from 10-15 years from the onset of attack; D. It is during the chronic stage when hydrocoele will be noted. 20. Which is FALSE about Tuberculosis? a. The most hazardous period for development of clinical disease is the first 6-12 months after infection b. The risk of developing the disease is highest in children under 3 years old. c. The degree of communicability depends on the virulence of the bacilli, adequacy of ventilation with no direct exposure of bacilli to the sun or UV light d. Susceptibility of the disease is markedly increased in those with HIV infection and other forms of immunosuppression Ans. C. All are true except C because the degree of communicability always involves exposure of the bacilli to the sun or UV light. 21. Which of the following tetanus immunization is given to a mother to prevent from a neonatal tetanus and provide 10 years protection for the mother? a. TT1 b.TT2 c. TT3 d. TT4 Ans. C. Schedule of TT immunization: VACCINATION SCHEDULE PROTECTION DURATION OF PROTECTION TT1 As early as possible during pregnancy 80% TT2 4 weeks after TT1 80% Infants protected from neonatal tetanus. Provides 3 year protection to the mother TT3 6 months after TT2 90% Infants protected from neonatal tetanus. Provides 5 year protection to the mother TT4 1 year after TT3 99% Infants protected from neonatal tetanus. Provides 10 year protection to the mother TT5 1 year after TT4 99% Infants protected from neonatal tetanus. Provides lifetime protection to the mother.
22. Which of the following vaccines is not recommended by IM injection? a. Measles vaccine c. Hepa B vaccine b. Tetanus toxoid d. DPT Ans. A. Measles vaccine 23. The following are vaccines which are less sensitive to heat: a. oral polio, DPT b. Measles, Hep B c. BCG, TT d. BCG, oral polio Ans. C. BCG and TT Most sensitive to heat: oral polio and measles; least sensitive to heat: DPT, Hep B, BCG, TT
24. OPV should be stored in a freezer with a temperature of: a. 2-8 degrees C b. -15 to -25 degrees C c. -2 to -8 degrees C d. none of these Ans. B. -15 to -25 degrees C 25. Hepa B is given at birth with 6 weeks interval from the 1st dose to 2nd dose, 8 weeks interval from the 2nd to 3rd dose. It is given intramuscularly in the: a. outer part of upper arm b. gluteus maximus c. vastus lateralis d. deltoid region Ans. C. vastus lateralis 26. It is the principle practiced in order to assure that all vaccines are utilized before its due date: a. First expiry and first out b. First used and first contained c. First expiry and last out d. First used and last contained Ans. A. First expiry and First out
27. When reconstituting the freeze dried BCG vaccine the nurse must always keep the diluents in the room temperature by sustaining with the BCG vaccine ampules in the clinic table: a. TRUE b. FALSE c. TRUE in Hep B and DPT d. except A Ans. A. FALSE The BCG vaccine must always be kept in cold temperature and sustaining it in the refrigerator or vaccine carrier. 28. What is the classification of disease when the level of management is urgent referral in hospital? a. mild b. moderate c. severe d. most severe Ans. C. Severe. 29. What is the color presentation to children whose level of management is home care. a. yellow b. red c. green d. pink
Ans. C. Green. 30. The following BUT one is part of the danger signs that needs to be checked in assessing the child using the integrated case management process? a. vomits everything b. convulsions c. unable to drink/breastfeed d. difficulty breathing Ans. D. Difficulty of breathing is part of the main symptoms that needs to be assessed not the danger signs. The missing danger sign is abnormality sleepy or difficult to awaken.
You might also like
- How To Open Nfo FilesDocument1 pageHow To Open Nfo FilesCristian TuturoiNo ratings yet
- Ched Memorandum Order (Cmo) No. 14 Series of 2009: Republic of The Philippines Commission On Higher EducationDocument213 pagesChed Memorandum Order (Cmo) No. 14 Series of 2009: Republic of The Philippines Commission On Higher EducationGilleen Megan BungaNo ratings yet
- Credibility Perception of TV and Radio Broadcasters Towards Print News and Online NewsDocument84 pagesCredibility Perception of TV and Radio Broadcasters Towards Print News and Online NewsGilleen Megan Bunga100% (1)
- Calayan Educational Foundation Inc. Red-V Lucena City: Course Code Course Title Units GradesDocument4 pagesCalayan Educational Foundation Inc. Red-V Lucena City: Course Code Course Title Units GradesGilleen Megan BungaNo ratings yet
- InternetDocument1 pageInternetGilleen Megan BungaNo ratings yet
- 2 (Final N Tlga)Document71 pages2 (Final N Tlga)Gilleen Megan BungaNo ratings yet
- Ched Memorandum Order (Cmo) No. 14 Series of 2009: Republic of The Philippines Commission On Higher EducationDocument213 pagesChed Memorandum Order (Cmo) No. 14 Series of 2009: Republic of The Philippines Commission On Higher EducationGilleen Megan BungaNo ratings yet
- 30 1 EngDocument1 page30 1 EngGilleen Megan BungaNo ratings yet
- M Usculo Skeletal System Assessm EntDocument39 pagesM Usculo Skeletal System Assessm EntGilleen Megan BungaNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
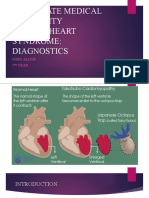
- Broken Heart Syndrome: DiagnosticsDocument25 pagesBroken Heart Syndrome: DiagnosticsOlga Goryacheva100% (1)
- Test Bank Alexanders Care of The Patient in Surgery 16th Edition RothrockDocument4 pagesTest Bank Alexanders Care of The Patient in Surgery 16th Edition RothrockCarlton Caughey100% (33)
- Daftar PustakaDocument4 pagesDaftar PustakajhnaidillaNo ratings yet
- DENGUE CS NCP 1Document8 pagesDENGUE CS NCP 1Karyl SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Journal ClubDocument12 pagesJournal ClubAnonymous ibmeej9No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For "Herniated Nucleus Pulposus Ruptured Inter Vertebral Disc"Document9 pagesNursing Care Plan For "Herniated Nucleus Pulposus Ruptured Inter Vertebral Disc"jhonroks100% (7)
- Health The Complimentry Way - Hiten PatelDocument96 pagesHealth The Complimentry Way - Hiten PatelManish Goel100% (2)
- Research Paper DiabetesDocument8 pagesResearch Paper Diabetesapi-359023534No ratings yet
- IMCIDocument21 pagesIMCIAnonymous h2EnKyDbNo ratings yet
- Ultraspund in Pediatric EmergencyDocument22 pagesUltraspund in Pediatric EmergencyAli Akbar RahmaniNo ratings yet
- WLP Health Makatao Q1 W5Document13 pagesWLP Health Makatao Q1 W5Rosemarie Mañabo RamirezNo ratings yet
- PSY 22 ABPSYCH 1st Exam REVIWERDocument14 pagesPSY 22 ABPSYCH 1st Exam REVIWERCresiel PontijonNo ratings yet
- Indian List-Of-HospitalsDocument564 pagesIndian List-Of-HospitalsPinder BaiNo ratings yet
- Psychosis 2020Document10 pagesPsychosis 2020moebius70No ratings yet
- NSE121 - Care PlanDocument7 pagesNSE121 - Care Planramyharoon2004No ratings yet
- Schizophrenia Presentation by Dr. MORAHDocument39 pagesSchizophrenia Presentation by Dr. MORAHChikezie OnwukweNo ratings yet
- Lifestyle DiseasesDocument44 pagesLifestyle Diseaseskyro draxNo ratings yet
- Ds Pedia WardDocument2 pagesDs Pedia WardRhea Mae Valles - ReyesNo ratings yet
- Elephantiasis: Report AboutDocument8 pagesElephantiasis: Report AboutAmjadRashidNo ratings yet
- Asepsis and Aseptic Practices in The Operating RoomDocument6 pagesAsepsis and Aseptic Practices in The Operating RoomMichelle ViduyaNo ratings yet
- College Nursing Exam ReviewDocument8 pagesCollege Nursing Exam ReviewKenneth NovenoNo ratings yet
- 12 OET Sample Referral Letter (Nurse) WritingDocument43 pages12 OET Sample Referral Letter (Nurse) WritingAL ' ARIS98% (41)
- Reyes Et Al. (2004) - Validation of A Modified Version of The Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) in Spanish PDFDocument11 pagesReyes Et Al. (2004) - Validation of A Modified Version of The Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) in Spanish PDFjonas1808No ratings yet
- ScccvyDocument7 pagesScccvyDavy JonesNo ratings yet
- Inter Disciplinary Periodontics A Multi Disciplinary Approach To Complex Case Planning and TreatmentDocument17 pagesInter Disciplinary Periodontics A Multi Disciplinary Approach To Complex Case Planning and TreatmentInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- The Blood Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesThe Blood Circulatory SystemListiyani IsmailNo ratings yet
- Title: Congenital Hypothyroidism: A Ran Sacker Escaping Under The Nose AbstractDocument6 pagesTitle: Congenital Hypothyroidism: A Ran Sacker Escaping Under The Nose AbstractKavita KhannaNo ratings yet
- Patient HIV and Urine Test ResultsDocument5 pagesPatient HIV and Urine Test ResultsPsyche's CupidoNo ratings yet
- Rajiv Gandhi College of Nursing BSC Nursing 1St Year 2020 Fundamental of Nursing Pathology SetbDocument3 pagesRajiv Gandhi College of Nursing BSC Nursing 1St Year 2020 Fundamental of Nursing Pathology SetbNeenu RajputNo ratings yet
- Edema Por Destete Teboul - MonnetDocument8 pagesEdema Por Destete Teboul - MonnetLuis Felipe Villamarín GranjaNo ratings yet