Professional Documents
Culture Documents
International Law June 2012 Syllabus
Uploaded by
poodleistOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
International Law June 2012 Syllabus
Uploaded by
poodleistCopyright:
Available Formats
San Beda College Alabang
College of Arts and Sciences Accountancy & Legal Management Department
Catholic Christian in Principle, Benedictine in Orientation, and Filipino in Character
Course Syllabus Course Code / Title Credit Units / Hours Course Description : : : LM143N/PRINCIPLES OF INTERNATIONAL LAW 3 UNITS / 3 hours per week
This course provides an introduction to the basic principles in international law and modes of settling disputes between and among nations. It also deals with international organizations, primarily the United Nations, its principles, purposes, compositions, organs and what it does for peace, justice, human rights, international law, humanitarian assistance and development. Some crises which the UN tried to resolve will also be evaluated. Course Objectives : At the end of the semester, the students are expected to: 1. Identify the basic principles in international law, determine the sources of international law and different organizations created to maintain world peace; 2. Describe the systems and structure of the United Nations, including its principal organs and specialized agencies and other international organizations, and enumerate and explain the powers and jurisdiction of the United Nations over its members and non-members; 3. Evaluate the success or failure of the United Nations in light of conflicts the organization has tried to settle based on the methods under its Charter; 4. Acknowledge the adjustments and settlements made by international organizations in any international dispute to achieve lasting world peace; 5. Appreciate the values of having a unified organization not only to settle international disputes but also to take care of justice, human rights and development and other humanitarian concerns; 6. Strongly support the initiatives and activities of the United Nations to foster brotherhood of nations and promote lasting peace and order throughout the world, human rights and sustainable development beneficial to all mankind. 7. Share the significance of the United Nations and other international organizations and how they contribute to pacific settlement of disputes and sustainable development not only for nations but also for individuals. 8. Practice the value of peace, cooperation, justice and friendship among nations with their respective citizens; and 9. Identify and apply in the course of learning the Benedictine core values of mutually respectful way of praying, of mutual love, of global community service and commitment to work discipline
Page 1 of 8
Grading System : Midterm Grade 60% Partial Class Standing (includes all aggregate CS grades prior to the midterm exam) 40% Midterm Exam Final Course Grade 50% Final Class Standing (includes all aggregate CS grades for the whole semester) 20% Midterm Exam 30% Final Exam Class Standing (CS) Components - Quizzes (inclusive of Long Tests), Assignments, Seatwork, Research/Reaction Papers, Class Activities and Class Participation/Recitation
SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES
CONTENTS / TOPICS
SUGGESTED STRATEGIES / METHODS Lecture, Recitation, Discussion, Reporting
NUMBER OF WEEK / HOURS Weeks 1-2
MODE OF EVALUATION / ASSESSMENT Quiz, Seatwork, Homework
At the end of the subject matter, General Principles the student should be able to : 1.1. Nature and Scope 1.2. Divisions of International Law Identify and explain the basic 1.3. Distinctions with Municipal Law principles in international law 1.4. Relations with Municipal law 1.5. Constitution vs. Treaty 1.6. Basis of International Law Compare and contrast municipal law and international1.7. Sanctions of International Law 1.8. Enforcement of International Law law 1.9. Functions of International Law 1.10. Distinctions with Other Concepts Evaluate the interplay of Present State of International Law municipal law and international1.11. law
Enumerate and describe the
2. Sources of International Law 2.1. Primary Sources primary and secondary sources 2.2. Secondary Sources of international law 3. The International Community 3.1. Subject and Object Distinguished various the components of the 3.2. Development of the International Community international community 3.3. States
Group Discussion, Lecture, Reporting
Week 3
Quiz, Assignment, Recitation
Describe and explain the
Group Discussion, Lecture, Reporting
Quiz, Assignment, Recitation
Page 2 of 8
3.4. The United Nations 3.5. The Vatican City organizations and identify and 3.6. Colonies and Dependencies 3.7. explain the history of the United Mandates and Trust Territories 3.8. Belligerent Communities Nations, its composition, 3.9. International Administrative Bodies objectives, functions and systems and structure and its 3.10.Individuals role in international community Enumerate the principal organs 4. The United Nations 4.1. The United Nations of the United nations, and 4.2. explain the mandate, functions, The U.N. Charter 4.2.1. The Preamble to the Charter powers, structure and 4.2.2. Purposes membership of these organs 4.2.3. Principles and agencies 4.2.4. Membership Identify the specialized 4.2.5. Suspension of Members agencies which are linked to the 4.2.6. Expulsion of Members UN through special agreements 4.2.7. Withdrawal of Members and how they contribute to the 4.3. Organs of the United Nations attainment of the objective of 4.3.1. The General Assembly UN 4.3.2. The Security Council Evaluate the peacekeeping 4.3.3. The Economic and Social Council efforts of UN in recent conflicts 4.3.4. The Trusteeship Council and determine the challenges 4.3.5. The International Court of Justice that UN encounters as it 4.3.6. The Secretariat evolves into a dynamic international organization to MIDTERM EXAMINATION address the growing demands of the international community
Define international
Lecture, Group Discussion, News Reporting, Sharing of Observations, Film Showing (Documentaries)
Week 4-7
Quiz, Assignment, Recitation, Reaction Paper
Define and explain the concept5.1. Creation of State
of the state
5. The Concept of State
Lecture, Recitation, Group Discussion
Week 8
Quiz, Seatwork, Homework
5.2. The Principle of State Continuity 5.3. Extinction of the State 5.4. Succession of State 5.5. Consequences of State Succession Lecture, Reporting, Recitation Week 9 Quiz, Seatwork, Homework
Explain the concept of
6. Recognition recognition of states, 6.1. Object of Recognition governments, and belligerency6.2. Kinds of recognition
Page 3 of 8
and determine their effects
6.3. Recognition of States 6.4. Recognition of Governments 6.5. Effects of Recognition of States and Governments 6.6. Recognition of Belligerency 6.7. Consequences of Recognition of Belligerency
Describe and explain a states
7. Rights of a State right of existence and how this 7.1. Right to Existence and Self Defense 7.1.1. Requisites of Rights is maintained or preserved 7.1.2. Regional Arrangements 7.1.3. The Balance of Power Describe and explain a states 7.1.4. Aggression Defined right of independence and 7.2. Right of Independence extent of intervention by other 7.2.1. Ideal of Independence states 7.2.2. Nature of Independence 7.2.3. Intervention Describe and explain a states 7.2.4. The Drago Doctrine right of equality and discuss its 7.3. Right of Equality essence and implications 7.3.1. Essence of Equality 7.3.2. Legal Equality vs. Factual Equality Determine and explain how 7.4. Territory territory is acquired or lost, 7.4.1. Acquisition and Loss of Territory including its components and 7.4.1.1. Discovery and Occupation extent 7.4.1.2. Prescription 7.4.1.3. Cession 7.4.1.4. Subjugation 7.4.1.5. Accretion 7.4.2. Components of Territory 7.4.2.1. The Terrestrial Domain 7.4.2.2. The Maritime and Fluvial Domain 7.4.2.3. The Aerial Domain Enumerate and explain the 7.5. Jurisdiction types of jurisdiction of a state 7.5.1. Personal Jurisdiction 7.5.2. Territorial Jurisdiction 7.5.3. Land Jurisdiction 7.5.4. Maritime and Fluvial Jurisdiction 7.5.4.1. The Contiguous Zone 7.5.4.2. The Continental Shelf 7.5.4.3. The Patrimonial Sea
Lecture, Recitation, Reporting
Weeks 10-12
Quiz, Seatwork, Homework
Page 4 of 8
7.5.4.4. The Open Sea 7.5.5. Aerial Jurisdiction 7.5.6. Outer Space 7.5.7. Other Territories 7.6. Right of Legation Define and explain the nature of 7.6.1. Agents of Diplomatic Intercourse right of legation, the privileges 7.6.1.1. The Head of State and immunities accorded to the 7.6.1.2. The Foreign Secretary agents of diplomatic 7.6.1.3. Diplomatic Envoys intercourse, and how it is 7.6.1.4. The Diplomatic Corps terminated. 7.6.2. Appointment of Envoys 7.6.3. Commencement of Diplomatic Missions 7.6.4. Diplomatic Functions 7.6.5. Conduct of Diplomatic Mission 7.6.6. Diplomatic Immunities and Privileges 7.6.6.1. Personal Inviolability 7.6.6.2. Immunity from Jurisdiction 7.6.6.3. Inviolability of Diplomatic Premises 7.6.6.4. Inviolability of Archives 7.6.6.5. Inviolability of Communication 7.6.6.6. Exemption from Testimonial Duties 7.6.6.7. Exemption from Taxation 7.6.6.8. Other Privileges 7.6.7. The Diplomatic Suite or Retinue 7.6.8. Duration 7.6.9. Termination of Diplomatic Mission 8. Consuls 8.1. Consuls Define the functions of consuls,8.2. Kinds and Grades enumerate their kinds, grades 8.3. Appointment 8.4. Functions and functions 8.5. Immunities and Privileges 8.6. Termination of Consular Mission 9. Treaties 9.1. Functions of Treaties 9.2. Essential Requisites of a Valid Treaty Describe treaties, explain the 9.2.1. Treaty-making Capacity requisites and outline the treatyLecture, Recitation, Reporting, Group Discussion Week 13-14 Quiz, Seatwork, Homework
Page 5 of 8
9.2.2. Authorized Representatives 9.2.3. Freedom of Consent Identify the treaties entered into 9.2.4. Lawful Subject Matter 9.2.5. Compliance with Constitutional Processes by the government and 9.3. Treaty-making Process appreciate the value of a treaty, its observance and termination 9.4. Binding Effect of Treaties 9.5. Observance of Treaties by signatory states 9.6. Treaty Interpretation Explain how treaties should be 9.7. Termination of Treaties interpreted in light of existing municipal laws 10. Nationality and Statelessness 10.1. Nationality and Statelessness 10.2. Acquisition of Nationality 10.3. Multiple Nationality 10.4. Loss of Nationality 10.5. Conflict Nationality Laws 10.6. Statelessness Lecture, Recitation, Group Discussion, Reporting Weeks 15-16 Quiz, Seatwork, Homework
making process
Describe nationality and
statelessness, and how nationality is acquired and lost
11. Treatment of Aliens 11.1. Treatment of Aliens 11.2. The Doctrine of State Responsibility Explain how aliens should be 11.3. The International Standard of Justice treated based on international 11.4. Failure of Protection or Redress standard of justice and the 11.5. Exhaustion of Local Remedies doctrine of state responsibility 11.6. Resort to Diplomatic Protection 11.7. Enforcement of Claim Determine how an alien can 11.8. Avoidance of State Responsibility resort to diplomatic protection 11.9. Exclusion of Aliens 11.10. Extradition Outline and explain the principles 11.10.1.Basis of Extradition of extradition and the procedure 11.10.2.Fundamental Principles of Extradition to be adopted 11.10.3.Procedure of Extradition 12. Settlement of International Disputes 12.1. Settlement of International Disputes 12.2. Methods of Settling Disputes 12.3. The United Nations
Enumerate and explain the
modes of settling international disputes, including the
Page 6 of 8
13. War 13.1. War 13.1.1. Outlawry of War 13.1.2. Law of War Describe the nature, rules, and 13.1.3. Commencement of War effects of war, and its 13.1.4. Effects of the Outbreak of War termination 13.1.5. Combatants and Non-combatants 13.1.6. Conduct of Hostilities 13.1.7. Kinds of Warfare 13.2. Belligerent Occupation 13.3. Postliminium 13.4. Non-Hostile Intercourse 13.5. Suspension of Hostilities 13.6. Termination of War 13.7. Aftermath of War 14. Neutrality 14.1. Neutrality 14.1.1. Neutrality and Neutralization 14.1.2. Laws of Neutrality 14.1.3. Relations of Belligerent States and Neutral States 14.2. Use of Neutral Territories 14.3. Use of Neutral facilities and Services 14.4. Relations of Belligerent State with Nationals of Neutral States 14.5. Visit and Search 14.6. Contraband 14.7. Unneutral Service 14.8. Angary 14.9. Termination of Neutrality FINAL EXAMINATION
mechanisms under the United Nations
Lecture, Recitation, Group Discussion, Reporting
Weeks17-18
Quiz, Seatwork, Homework
Describe and explain the
concept, nature, laws, and effects of neutrality
Page 7 of 8
San Beda College Alabang
College of Arts and Sciences Accountancy & Legal Management Department
TEXT BOOK
Cruz, Isagani A. International Law. Central Book Supply, Inc., 2003 .
REFERENCES
Agpalo, Ruben. Public International Law. Manila: Rex Book Store, 2006. Bernas, Joaquin. An Introduction to Public International Law. Manila: Rex Book Store, 2002. Santiago, Miriam D. International Law with Philippine Cases and Materials and ASEAN Instruments. Quezon City: Central Professional Books, 1999. Magallona, Merlin M. International Law Issues in Perspective. Quezon City: Law Center University of the Philippines, 1996. Paras, Edgardo L. International law and World Politics. Manila: Rex Book Store, 1994. Coquia, Jorge, and Santiago, Miriam D. International Law. Quezon City: University of the Philippines Law Complex. 1993. Schoenbaum, Thomas J. International Relations-The Path Not Taken: Using International Law to Promote World Peace and Security. New York: Cambridge University Press, 2006. Joyne, Christopher (editor). United Nations and International Law. New York: Cambridge University Press, 1997. 1987 Constitution http://www.un.org Prepared by:
Accountancy & Legal Management Department
That in all things God may be glorified.
Page 8 of 8
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Arms Rules 1924 PDFDocument88 pagesArms Rules 1924 PDFshoaib87% (23)
- NEBOSH HSE Certificate in Process Safety Management - NEBOSHDocument8 pagesNEBOSH HSE Certificate in Process Safety Management - NEBOSHamra_41No ratings yet
- Component of SpeakingDocument3 pagesComponent of SpeakingDian Miranda75% (8)
- CV RahulGoswamiDocument4 pagesCV RahulGoswamiRahul GoswamiNo ratings yet
- 11 Humss Philippine Politics and Governance 3RD Summative NewDocument5 pages11 Humss Philippine Politics and Governance 3RD Summative Newmichelle garbinNo ratings yet
- Berger J - Ways of Seeing, BBC and Penguin Books 1972Document79 pagesBerger J - Ways of Seeing, BBC and Penguin Books 1972Yao DajuinNo ratings yet
- Navy Traffic Safety Program 5100 12gDocument21 pagesNavy Traffic Safety Program 5100 12gTravis BroussardNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Development AdministrationDocument17 pagesCurriculum Development AdministrationNAZRUL ISLAM MONDALNo ratings yet
- Combat Aircraft 2020 09 SepDocument100 pagesCombat Aircraft 2020 09 SepSérgio SantanaNo ratings yet
- The Role of Hungarian Capital in Foreign MediaDocument39 pagesThe Role of Hungarian Capital in Foreign MediaatlatszoNo ratings yet
- AMPH Brochure 2022 31august UpdatedDocument16 pagesAMPH Brochure 2022 31august Updated9980139892No ratings yet
- Queensland Asia Tourism Strategy 2016 2025Document56 pagesQueensland Asia Tourism Strategy 2016 2025Lijo DavisNo ratings yet
- 3 Background: Coffee Production in Papua New GuineaDocument10 pages3 Background: Coffee Production in Papua New GuineamiriamNo ratings yet
- Physical Literacy Is The Development of A Range of Basic Human MovementsDocument15 pagesPhysical Literacy Is The Development of A Range of Basic Human MovementsFRANCIS FRANCISCO. CLIMACONo ratings yet
- Internship Report 21-22 - Pravin JagtapDocument8 pagesInternship Report 21-22 - Pravin JagtapPravin JagtapNo ratings yet
- Elizabeth Holmes Body Language ReportDocument6 pagesElizabeth Holmes Body Language ReportAmmajan75% (4)
- TAI 9 - LatestDocument8 pagesTAI 9 - LatestNur Afifah ShahrizalNo ratings yet
- Jonathan D. Lovitz: Professional SummaryDocument2 pagesJonathan D. Lovitz: Professional SummaryAnonymous 0RkNbGPesNo ratings yet
- Using Drama To Teach English Language inDocument18 pagesUsing Drama To Teach English Language inSafiah MadriNo ratings yet
- Standards of Medical Care For Nursing Home Residents in EuropeDocument3 pagesStandards of Medical Care For Nursing Home Residents in EuropeAida MawaddahNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Engineering IN Civil Engineering: Visvesvaraya Technological University Jnana Sangama, BelagaviDocument3 pagesBachelor of Engineering IN Civil Engineering: Visvesvaraya Technological University Jnana Sangama, Belagavianon_591012339No ratings yet
- Verified Complaint - Ball & Chain Case - 1st Amendment ViolationsDocument48 pagesVerified Complaint - Ball & Chain Case - 1st Amendment ViolationsMichael PancierNo ratings yet
- Oposa v. Factoran (G.R. No. 101083 July 30, 1993)Document12 pagesOposa v. Factoran (G.R. No. 101083 July 30, 1993)Claire CaceresNo ratings yet
- Last Clear Chance - A Transitional Doctrine PDFDocument20 pagesLast Clear Chance - A Transitional Doctrine PDFBANanaispleetNo ratings yet
- Implementing Rules and Regulations (IRR) of R. A. No. 10931 (NORSU)Document50 pagesImplementing Rules and Regulations (IRR) of R. A. No. 10931 (NORSU)Euro AccessNo ratings yet
- Mary Joy V. OliciaDocument10 pagesMary Joy V. OliciaImel Sta Romana100% (1)
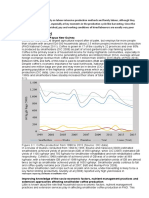
- Auto & Auto Components - Sector BrochureDocument7 pagesAuto & Auto Components - Sector BrochureSanyaNo ratings yet
- YNHPROP AnnualReport2012Document126 pagesYNHPROP AnnualReport2012tycoonshan24No ratings yet
- Delegated LegislationDocument19 pagesDelegated LegislationAli Miqdad SyedNo ratings yet
- Art Appreciation: Learning OutcomesDocument13 pagesArt Appreciation: Learning OutcomesJohn Vincent EstoceNo ratings yet