Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AP Physics B Equation Reference Sheet
Uploaded by
jaintanyaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
AP Physics B Equation Reference Sheet
Uploaded by
jaintanyaCopyright:
Available Formats
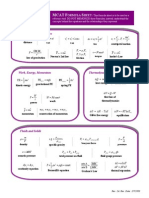
Kevin Jiempreecha's AP Physics B Equation Reference Sheet Kinematics in One Dimension and Two Dimensions (Plane) Average Velocity:
v=
d t a= d t
Average Acceleration:
v f =v i +at 1 v= ( v f +v i ) 2 1 d = ( v f + vi ) t 2 1 2 d = at +v i t 2 2 v f =v 2 +2ad i
Range:
R=
v 0 sin2 g
Motion and Force: Dynamics Force: F =ma Summation of Forces: F x =ma x Weight: Wt=mg Force of Friction: F f = F n Circular Motion and Gravitation Period:
F y =ma y
T=
2 r v f= 1 T T= 1 f ac= v2 r mv2 F c= r
Frequency:
Centripetal Acceleration:
Centripetal Force: F c=ma c
Period of Pendulum:
T =2
l g
Gravitational Force:
F =G
m1 m2 r2
Work and Energy
W =Fd W Power: P= t
Work: Kinetic Energy:
P=Fv 1 2 E k = mv 2
Potential Energy due to Gravity: U =E pg =mgh Law of Conservation of Energy:
E total =E pi + E ki =E pf + E kf
E total =E p + E k + Q
Hooke's Law (Force of Spring): F =kx Period of Spring:
T =2
m k
Potential Energy of Spring: Momentum Momentum: p=mv Impulse: J = p= F
1 2 U =E ps = kx 2
t=m v p i= p f mv i=mv f
m1 v 1+ m2 v 2=m1 v 1 +m2 v 2
1 1
Law of Conservation of Momentum: Elastic Collision:
E k1 + E k2=E 1 +E 1 k1 k2
1
2 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 m1 ( v 1 ) + m2 ( v 2 ) = m 1 ( v 1) + m2 (v 1 ) 1 2 2 2 2 2 1
Head-On Elastic Collision: Torque Torque: =Fr
v 1 +v 1=v 2+ v 2
Fluids Density:
m V F A
Pressure:
P=
P= g h Pressure Varying with Depth (Sealed): P= g h P= P0 + g h Pressure Varying with Depth (Exposed): P=P 0 + g h
Pascal's Principle:
P=P out
F F out = A Aout F net= F B W
Buoyant Force: F B = f V f g Net Force due to Buoyancy:
F o o = FB f
Continuity Equation: Bernoulli's Equation:
A1 v 1= A2 v 2 P 1+ 1 1 2 v1 + g h1 =P 2+ v 2+ g h 2 2 2 2
Vibrations and Waves Hooke's Law: F =kx Frequency:
f=
1 T
T=
1 f 1 U =E ps = k x 2 2
Potential Energy of Spring:
Period of Pendulum:
T =2
l g
Velocity of Wave: v= f Law of Reflection: Sound
i = r
FT ( m/ L ) Speed of Sound Varying with Temperature: v=( 331+0.6T ) m/ s
Speed of Sound Varying with Tension: v=
Temperature and Kinetic Theory Thermal Expansion:
L= Lo T
Boyle's Law: P 1 V 1 =P 2 V 2 Charles' Law:
V1 V2 = T1 T2 P1 V 1 P 2 V 2 = Combined Gas Law: T1 T2
Ideal Gas Law (Universal Gas Constant): PV =nRT Ideal Gas Law (Boltzmann's Constant): PV = N K B T Average Kinetic Energy of Molecules in Gas Sample:
P V =nR T P V = N K B T 3 Ek = k B T 2 v rms = v 2= 3RT 3k b T = M
Root-Mean-Square Velocity of Molecules in Gas Sample: Heat Internal Energy of an Ideal Gas:
3 U = nRT 2
3 U = nR T 2
Q=mc T
Heat Transfer by Conduction: Thermodynamics
H=
Q kA T = t L
U =Q+ W
Work Done During Thermodynamic Processes:
W = P V
Q H =W +Q L
Engine Efficiency:
e=
W QH ec= T H T L TH
Carnot (Maximum) Engine Efficiency:
Electric Charge and Electric Field Coulomb's Law:
F=
k Q1 Q2 r
2
Electric Field Intensity:
E=
F Q
E=
kQ r2
Electric Potential, Electric Energy, and Capacitance Voltage (Electric Potential Difference; Electric Potential; Potential Difference):
V=
W Q
V = Ed kQ Voltage due to Point Charge: V = r
Voltage Between Charged Plates: Capacitor Charge: Q=VC Capacitance (Vacuum):
C= 0
A d C=K 0 A d
Parallel-Plate Capacitance (Dielectric):
Energy Stored in Capacitor: Electric Currents Current:
(1/ 2 ) Q2 1 1 U =E p= QV = CV 2= 2 2 C
I=
Q t I= V R
V = IR
Current due to Resistance:
Resistance:
R=
L A V P=IV = I R= R
2 2
Power of Electricity: Circuits Terminal Voltage:
V ab=V n Ir C p= Ci
i=1 n
Equivalent Capacitance (Parallel): Equivalent Capacitance (Series):
1 1 = C s i=1 C i
Magnetic Fields Magnetic Field Strength:
B=
Force on Current in Magnetic Field: F =BILsin Force on Charged Particle in Magnetic Field: F =QvBsin Path of Electron in Uniform Magnetic Field: Electromagnetic Induction Magnetic Flux:
0 I 2 r
r=
mv qB
B =B A=BAcos = N B t
Faraday's Law of Induction (Induced EMF due to Magnetic Flux): Induced Electromotive Force (EMF): =Blv Light and Electromagnetic Waves
1 1 1 = + f do di So do = Si di
Magnification of Mirror:
M= c v
S i d i = So do
Index of Refraction:
n=
Snell's Law (Law of Refraction):
n 1 sin 1=n2 sin 2
n2 v 1 1 = = n1 v 2 2 m L d dsin =m xm =
Maxima (Constructive Interference) in Double-Slit Diffraction: dsin =m Minima (Destructive Interference) in Double-Slit Diffraction: Maxima (Constructive Interference) in Single-Slit Diffraction: Minima (Destructive Interference) in Single-Slit Diffraction:
dsin = m+
( 1) 2 1 dsin =( m+ ) 2
dsin =m
Quantum Theory, Nuclear Physics, and Elementary Particles Energy of Photon:
E photon=hf = p=
hc
Momentum of Photon:
hf h = c = h h = mv p E=mc2
De Broglie Wavelength of Particle:
Energy from Contact Between Matter and Antimatter:
You might also like
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsFrom EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNo ratings yet
- AP Physics B Equation Reference SheetDocument7 pagesAP Physics B Equation Reference SheetKevin JiempreechaNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet PhysicsDocument4 pagesData Sheet PhysicsBernice JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Ap Physics 2 - Equation SheetDocument3 pagesAp Physics 2 - Equation Sheetapi-275404928No ratings yet
- University Physics Equation SheetDocument2 pagesUniversity Physics Equation SheetKyle OberleNo ratings yet
- Practice FinalDocument26 pagesPractice Finalchaseutd123No ratings yet
- Equations Sheet For FYS1120: Electric Fields Maxwell's EquationsDocument3 pagesEquations Sheet For FYS1120: Electric Fields Maxwell's EquationsLeseat NocaNo ratings yet
- Bütün Fizik FormülleriDocument13 pagesBütün Fizik Formüllerimhasan13No ratings yet
- Physics Formulas: G G (1-d) RDocument6 pagesPhysics Formulas: G G (1-d) RAitazaz AhsanNo ratings yet
- ThePhysicsCafe Summary of JC PhysicsDocument2 pagesThePhysicsCafe Summary of JC PhysicsLim Zer HeanNo ratings yet
- MCAT FormulasDocument2 pagesMCAT Formulasdjanisz2100% (3)
- AE1104 Physics 1: List of EquationsDocument24 pagesAE1104 Physics 1: List of EquationssmithastellaNo ratings yet
- Physics 1 Honors Formula SheetDocument11 pagesPhysics 1 Honors Formula SheetCody JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet: Electricity and MagnetismDocument3 pagesFormula Sheet: Electricity and MagnetismThivagar RajasekaranNo ratings yet
- Study MaterialDocument42 pagesStudy MaterialWhite DevilNo ratings yet
- Science Formula SheetDocument2 pagesScience Formula Sheetrhemaksha78% (9)
- Formula Sheet PHYS 157Document1 pageFormula Sheet PHYS 157Carmen YangNo ratings yet
- Physics A Level Formula Sheet 2Document4 pagesPhysics A Level Formula Sheet 2Ahmad HussainNo ratings yet
- Adapted Reference TablesDocument4 pagesAdapted Reference Tablesapi-327660250No ratings yet
- Physics EquationsDocument5 pagesPhysics EquationsMichael CollinsNo ratings yet
- Phys 122 Equation Sheet Exam 3Document3 pagesPhys 122 Equation Sheet Exam 3zxc100311No ratings yet
- Category: Physics FormulasDocument24 pagesCategory: Physics FormulasKalpana ShankarNo ratings yet
- Things To Know For The Physics GRE: Daniel Beller October 28, 2009Document20 pagesThings To Know For The Physics GRE: Daniel Beller October 28, 2009Arif SolmazNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument4 pagesFormula SheetLegacyGrade12No ratings yet
- Formula Sheet - Engineering Physics II - Electricity and Magnetism - PHY 303L UT AustinDocument2 pagesFormula Sheet - Engineering Physics II - Electricity and Magnetism - PHY 303L UT AustinJeremy Priest100% (2)
- POE Formula Sheet Rev 3-24-12Document6 pagesPOE Formula Sheet Rev 3-24-12poignantNo ratings yet
- HKDSE Physics Formulae List (English Version)Document5 pagesHKDSE Physics Formulae List (English Version)flowerinsnowNo ratings yet
- EquationsDocument1 pageEquationsmyassisitchyNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Physics Equation SheetDocument2 pagesConceptual Physics Equation SheetjeremytimmonsNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument4 pagesPhysicstim94leeNo ratings yet
- 2018 PU3 H2 PHY PE2 Mark Scheme: Paper 1 (30 Marks)Document3 pages2018 PU3 H2 PHY PE2 Mark Scheme: Paper 1 (30 Marks)Kok Soon ChongNo ratings yet
- Physics Formulas: G G (1-d) RDocument6 pagesPhysics Formulas: G G (1-d) Ronewing949No ratings yet
- Fis 24Document6 pagesFis 24syafrina novitaNo ratings yet
- Part 1 - Physics: L B A G 2Document7 pagesPart 1 - Physics: L B A G 2bindaaz301No ratings yet
- 72 ReviewerDocument17 pages72 ReviewerGeronimo Allan Jerome AcostaNo ratings yet
- Phys 1004 - Cheat - Sheet. Electromagnetism and WavesDocument2 pagesPhys 1004 - Cheat - Sheet. Electromagnetism and WavesNadya B.No ratings yet
- 1 Formulae ElectrostaticsDocument21 pages1 Formulae ElectrostaticsNathanianNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 2 Equations TableDocument3 pagesAP Physics 2 Equations TableHorizonAcademy100% (1)
- Physics Reference TableDocument4 pagesPhysics Reference Tablegoncstate93No ratings yet
- Physics Class 9 FormulasDocument13 pagesPhysics Class 9 FormulasJatin Gupta73% (63)
- Formulas To Remember in PhysicsDocument5 pagesFormulas To Remember in PhysicsBliss JullienneNo ratings yet
- Physics Class 9 FormulasDocument13 pagesPhysics Class 9 FormulasEKLABAY SONINo ratings yet
- Data & FormulaeDocument2 pagesData & FormulaeMaheerNo ratings yet
- Formule Iz FizikeDocument5 pagesFormule Iz FizikeАлександар ДимитријевићNo ratings yet
- THERMO1 - 2 Energy and The First Law of Thermodynamics - Sample Problems PDFDocument14 pagesTHERMO1 - 2 Energy and The First Law of Thermodynamics - Sample Problems PDFEdmark AldeaNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet For PhysicsDocument6 pagesFormula Sheet For PhysicsAsim ButtNo ratings yet
- University Physics Equation SheetDocument2 pagesUniversity Physics Equation SheetDipesh BhandariNo ratings yet
- M e M M C N G R G K: Table of Information For 2010 and 2011Document3 pagesM e M M C N G R G K: Table of Information For 2010 and 2011mys85No ratings yet
- Lecture 31Document15 pagesLecture 31Milian PeresNo ratings yet
- Forces and MotionDocument4 pagesForces and MotionMu'iz RahmanNo ratings yet
- 2 PDFDocument5 pages2 PDFDre ParkerNo ratings yet
- Physics FormulasDocument23 pagesPhysics FormulasViral AssassinNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document7 pagesAssignment 1debabrata chowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandMathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- 5.3 ElectromagnetDocument8 pages5.3 ElectromagnetYee Jiea PangNo ratings yet
- MSD AssignmentDocument16 pagesMSD AssignmentNanda KishoreNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Electricity and MagnetismDocument18 pagesFundamental of Electricity and MagnetismVedant KamlaskarNo ratings yet
- Question BankeemcDocument8 pagesQuestion BankeemcapurvaNo ratings yet
- Electro Magnetic FieldDocument42 pagesElectro Magnetic FieldKapil_1983No ratings yet
- Vdoc - Pub Electromagnetic Fields in Electrical EngineeringDocument305 pagesVdoc - Pub Electromagnetic Fields in Electrical EngineeringFaisal JavaidNo ratings yet
- Carr Technology (OTC X1) by Julio C. GobbiDocument30 pagesCarr Technology (OTC X1) by Julio C. GobbiSavouretNo ratings yet
- Experiment 31: Magnetic Force: PurposeDocument7 pagesExperiment 31: Magnetic Force: PurposeValeria MendozaNo ratings yet
- Physics Revision Notes Term 1Document6 pagesPhysics Revision Notes Term 1prachi guptaNo ratings yet
- Physics (A-Level) Revision WorksheetDocument142 pagesPhysics (A-Level) Revision WorksheetAmmara AJ88% (8)
- Gambi CADocument28 pagesGambi CAishan0588No ratings yet
- Ionospheres Physics Plasma Physics and Chemistry Cambridge Atmospheric and Space Science SeriesDocument569 pagesIonospheres Physics Plasma Physics and Chemistry Cambridge Atmospheric and Space Science SeriesMushi82100% (2)
- Week 9 - Chap28Document27 pagesWeek 9 - Chap28Viet PhamNo ratings yet
- Oldfinalsolution PDF PDFDocument20 pagesOldfinalsolution PDF PDFguardian12No ratings yet
- EE6604-Design of Electrical MachinesDocument12 pagesEE6604-Design of Electrical MachinesGokul ChandrasekaranNo ratings yet
- Konstantin P. Shamrai and Shunjiro Shinohara - Modeling Electromagnetic Field Excitation and RF Power Absorption in A Large Helicon PlasmaDocument4 pagesKonstantin P. Shamrai and Shunjiro Shinohara - Modeling Electromagnetic Field Excitation and RF Power Absorption in A Large Helicon PlasmaHimaszNo ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument13 pagesMagnetismPriyan PriyanNo ratings yet
- Magnetic MaterialsDocument26 pagesMagnetic MaterialsVinit VikasNo ratings yet
- Physics 28th June Shift-2Document20 pagesPhysics 28th June Shift-2Suman KumariNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus Primer Crash CourseDocument136 pagesVector Calculus Primer Crash CourseArijit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ieee TemplateDocument7 pagesIeee TemplateJasmin NukicNo ratings yet
- SSPC-PA 2 (2004) - Measurement of DFT With Magnetic Gages PDFDocument11 pagesSSPC-PA 2 (2004) - Measurement of DFT With Magnetic Gages PDFkhuramilyas100% (1)
- Assignment 1 - Dariusz Zielinski: Heffield Allam Niversit YDocument28 pagesAssignment 1 - Dariusz Zielinski: Heffield Allam Niversit YzielinskidrNo ratings yet
- What Is The Electron SpinDocument92 pagesWhat Is The Electron SpinTomás Andres Veliz Campos100% (1)
- Introduction To NDT For PT 1Document50 pagesIntroduction To NDT For PT 1mangsureshNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Field (EMF)Document30 pagesElectromagnetic Field (EMF)juliaNo ratings yet
- NTSE SAT Stage 2 Solved Paper 2016Document22 pagesNTSE SAT Stage 2 Solved Paper 2016Anirudh Agarwal100% (1)
- ELF Measurement IEC 106 - 108 - CDDocument41 pagesELF Measurement IEC 106 - 108 - CDIan GairNo ratings yet
- EEB1073/EDB2013 Electromagnetic Theory: Project Title: Maglev Train Group Number: 7Document25 pagesEEB1073/EDB2013 Electromagnetic Theory: Project Title: Maglev Train Group Number: 7bunny beeNo ratings yet