Professional Documents
Culture Documents
English
Uploaded by
Neha Chourey SharmaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
English
Uploaded by
Neha Chourey SharmaCopyright:
Available Formats
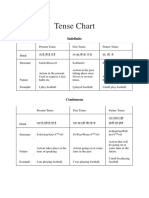
1
Steps for an effective introduction
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Greeting, name, age, born and brought up, sun sign Work experience Academic qualification Professional Qualification Ambition of life Family Introduction Favourite---- Music, Food, Place, Clothes Strengths and Weakness Ideal and inspirations
Introduction to Words CLASSES
1. Noun 2. Pronoun 3. Adjective 4. Verb 5. Adverb 6. Preposition 7. Conjunction 8. Interjection Naming Words (Ram, Ujjain) Words used in place of noun (He, She, It) words used to Qualifying noun or pronoun (Good, small) Action Words (Run, sleep) words Qualifying verb and adjective (fast, very) words showing relation of noun with rest of the sentences Joining Words Words used for sudden feelings
Basic Rule st 1. Always use Verb 1 form with To th 2. Always use Verb 4 form with For th 3. Always use Verb 4 form with After, Before, At the Time ( ), While ( ), Start. Use of Here
The meaning of here is () it shows the near place, it can be use anywhere in sentence. Ex. Affirmative Here is your friend Here is your watch Do not come here. Use of There The meaning of there is () It shows the far place or used for things There are books on the table. There is a girl in that class. Do not go there. There is no vacancy. Use of This The meaning of this is () it shows position of person, place or thing This is my pen This is a good story This is not my job This is not easy to carry
The meaning of that is (), it shows the position of person, place or thing which is far Ex.
Use of That
That is a good book. That is your bicycle. That is your office. That was my computer. Use of It The meaning of it is (), it is used as subject in sentence for season, air, rain, experience, non living things , animals and for those things that we feel. It is use for singular. The plural form of it is they. Ex. It is raining. Its my friend It is not my duty Different use of have
It is very essential to learn the use have before learning English, because it is use not even as a principal verb but as a helping verb too. Had is a past tense of have and has. Have/Has (, )/ had (, ) I have a pen. He had a beautiful idea. Have (, ) I have a cup of tea. I like to have a cup of tea. Has got to, Have got to, had got to, ( , , , ) I have got to go to school daily. She has got to go to cook food daily. I had got to study daily. Has..on, Have..on, Had..on ( , ) She has beautiful earrings on. Inspector had civil dress on at the party. Has to / Have to / Had to ( , , ) I have to go. Ram had to visit bring some books for me. Has / Have / Had ( , ) Always use verb 3rd form with {Has / Have / Had} Ram has come. She have visited to the doctor. I had gone to the field. Should have + Verb 3rd form. ( ) He should have gone to the market. I should have completed the lesson. Could have + Verb 3rd form. ( ) I could have gone. She could have given some new ideas to me. Will have / Shall Have + Verb 3rd form. ( ) He will have seen the movie.
We shall have finished the job. Might have + Verb 3rd form. ( ) He might have reached. She might have finished her work. Use of there in translating sentence It is used when there is no subject and main verb There + is/are + noun+ place There are fifty teachers in my school. There is no ink in my ink pot. Are there 63 passengers in bus? There was very rush in fair yesterday. There was no taste in food. Was there no any priest in temple.
Verb
There are two types of verbs 1. helping verb 2. Main verb There are 24 Helping verbs. If we know how and where to use them then no one can challenge your English Is Am Are Do Does Has Have Was Were Did Had Will Shall Can May Might Could Would Should Ought to Used to Must Need Dare
USED FOR SENTENCES IN PRESENT TIMEZONE
USED FOR SENTENCES IN PAST TIMEZONE USED FOR SENTENCES IN FUTURE TIMEZONE
USED FOR SENTENCES IN GENERAL TIMEZONE
Gender
There are 4 types of gender 1. Masculine Gender (Male sex) Example, tiger, Father, Boy.. 2. Feminine Gender (Female Sex) Example, Tigress, Mother, Girl 3. Common Gender (use for both sex) Example, Baby, Child, Teacher 4. Neutral (non living thing) Example, Copy, Book, Room.
Sentence
Sentence is a group of words which gives complete sense Subject Predicate Example controller, examiner, and doer of action. the part of sentence, which tells about the subject john goes to the market (sub) (verb) (predicate)
Kinds of sentences Assertive/ affirmative. interrogative sentence exclamatory sentence imperative sentence Assertive sentence are the simple statements, also used in daily life Interrogative sentence are the question asking sentences Exclamatory sentence are the Sentences spoken out of sudden Imperative sentence are sentences in which we give command, take request or permission
PERSONS
1 persons I, We Numbers
2 persons You
3 persons He, she, It, Name, They, My father, My Mother
Singular number I You She, He It Brother
Plural number We You They It Brothers
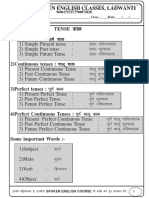
Helping Verb chart
FOR Present Tense
Helping verb Is, am, are Has / have Has / Have been S or es Condition Present continuous tense Present perfect tense Present perfect continuous tense Present indefinite Tense (singular no third person)
FOR Past Tense
Helping verb Was / Were Had Had Been Condition Past continuous tense Past perfect tense Past perfect continuous tense
FOR Future Tense
Helping verb Will, Shall (Will / Shall) be Will, Shall Have Will shall have been Condition Future Indefinite tense Future Contentious tense Future perfect tense Future perfect continuous
Verb Chart
Verb 1 Verb 2 Verb 3 Verb 4 Present & Future Indefinite (Simple) Tense Past Indefinite Tense Present, Past, Future Perfect Tense Present, Past, Future Continuous and Perfect Continuous Tense
Tenses
Present tense Present indefinite tense Formula 1 Sub + V (S or Es) + object Rules
1. 2.
We use S or Es only with sing. no 3rd person.
If the verb ends with ss, o, z, x, ch, sh so we use Es and apart from this we use S If the verb ends with Y and the second last alphabet is consonant so we replace Y with Ies
3.
Example Mai jata hu Mai likhta hu Mai rota hu
I go I write I cry Negative and Interrogative
Negative: Interrogative: Interrogative Negative sentence Affirmative I Play chess. Negative
Sub + do/does not + V + object Do/Does + Sub + V + Object? Do/Does + Sub + not + V1 + object? Interrogative Do I play chess Interrogative Negative Do I not play chess
1
I do not play chess
10
He goes to office
He does not go to Does he office office
go
to Does he not go to office
Present Continuous Tense This tense shows that the work is in progress Sub + is am are + V + object Rule 1. 2. 3. Use is with he, she, it(singular no. third person) am with I are with we, you, they(plural) I am teaching I am going to market
4
Example Mai pada raha hu Mai bazar ja raha hu
Negative and Interrogative sentences Negative Interrogative Affirmative I am writing They are playing Sub + is/am/are + not + V + object is/am/are+ Sub + V + object? Negative I am not writing They are not playing Interrogative Negative Sentence is/am/are + sub + not + V + object? Affirmative I am going to hospital It is raining Interrogative Negative Am I not going to hospital? Is it not raining?
4 4 4
Interrogative Am I writing Are they playing
11
Present perfect tense This tense shows that some work is done in present Formula 3 Sub + has/ have + V + object Rule 1. Use Has with He, She, It, Name, my brother(singular no. Third person) 2. We use Have with 1st and 2nd person and with plural no. (I, we, they, you, etc) Example Train aa chuki hai The train has arrived
Negative and Interrogative sentences Negative Interrogative Affirmative I have taken lunch They have gone Sub + has/have + not + V + object Has/ have + sub + V + object Negative I have not taken lunch They have not gone Interrogative Have I taken lunch? Have they gone?
3 3
Negative Interrogative sentences Has / have + Sub + Not + V + Object Affirmative He has taken food I have done my work Interrogative Has he taken food? Have I not done my work
3
12
Present perfect continuous tense Tense shows that work which is in process and mentioned with specific time Formula 4 Sub + has/have + been + V + Object + Since/For. Rule 1. We use since/for to show time in Present Prefect Continuous Tense 2. We use for in period of time example for 15 days, for a long time, for some time 3. Since in Point of time Example: since 1997, since Morning, Since January 4. Has been is use with singular no 3rd person (he, she, it, name, my brother, my friend) 5. Have been is use with 1st and 2nd person and with plural no. (I, we, we, they, you, etc) Example Ram ek mahine se kitab likh raha hai Ram has been writing a book for a month. Negative and Interrogative sentences Negative: Interrogative Sub + has/have + not + been + V4 + Object + Since/for Has/have + Sub + been + V4 + Object + since/for..... Negative I have not been swimming for two hours He has not been playing since morning Interro. Have I been swimming for two hours? Has he been playing since morning?
Affirmative I have been swimming for two hours He has been playing since morning
Negative Interrogative sentences Has/ have + sub + not been + V4 + object + since/for..
13
Affirmative He has been playing for two hours.
negative-Interrogative Has he not been playing for two hours They have been making a noise since Have they not been making noise morning. since morning
PAST TENSE
Past Indefinite Tense This tense shows that some work is done past time zone Formula Sub + V + Object Example Sita ne Ram ko patr likha Whe football khele Sita Wrote a letter to Ram. They played football.
2
Negative and Interrogative sentences Negative: Interrogative Affirmative He wrote She went Sub + did not + V + Object Did sub + V + Object? Negative He did not write She did not go Negative Interrogative sentences Did + Sub + Not + V + Object? Affirmative He watched TV He went to market Negative Interrogative sentences Did he not watch TV Did he not go to market
1 1 1
Interrogative Did he write? Did she go?
14
Past Continuous Tense This shows the work is continue from the past Formula: 4 Sub + Was/ Were + V + Object Rule. 1. 2. Was used for singular no. Were used for plural no.
Example Ram patr likh raha tha Tum kapde dho rahi thi Ram was writing a letter. you were washing clothes.
Negative and Interrogative sentences Negative: Interrogative Affirmative He was playing They were smoking Sub + Was/ Were Not + V + Object Was/ Were + sub + V + Object? Negative He was not playing They were not smoking Interrogative Was he playing? Were they smoking?
4 4
Negative and Interrogative sentences Was/ Were + Sub + Not + V + Object? He was going to market They were playing was he not going to market? were they not playing?
4
15
Past Perfect Tense This shows that some work is done in past time zone. If two work were done in same time zone so we use past perfect for the first one and past indefinite for the second one Formula Sub + Had + V3. (before) . (past Indefinite) (Past indefinite) . (after) .sub +had+V3 Rule 1. In past PERFECT use Had with V 3rd form. Example Mere station pahuch ne se purv train ja chuki thi The train had departed before I reached the station. Tum hare so jane ke bad sita yaha aai thi Sita came here after you had slept. Gdai aane ke bad wah station pahucha tha He reached the station after the train had arrived Doctor ke aane se purv marrij mar chukka tha The pecient had died before the doctor came. Uske collage pahuchne se purv chatra class se ja chuke the I The student had left the class before he reached college.
16
Negative and Interrogative sentences Negative: Interrogative: Sub + had + Not + V3 + object Had + sub + V3 + Object?
Affirmative Negative Interrogative She had written a She had not written a Had she written a novel? novel novel Ram had gone to Ram had not gone to Had Ram gone to Agra? Agra Agra Negative Interrogative sentences Formula Had + Sub + Not + V3 + Object I had already visited Agra Had I not already visited Agra The train had departed before I reached there Had the train not departed before I reached there?
17
Past Perfect Continuous tense We use past perfect continuous tense when at the time of speaking the work should be in progress from the past time Formula Subject + had been + V4 +..+ since/for + Time Ram do ghante se TV dekh raha tha Ram had been watching TV for two hours. Ram do baje se TV dekh raha tha Ram had been watching TV since 2 O Clock. Negative and Interrogative sentences 4 Negative:Sub + had + not + been + V + Object. Interrogative:Had + Sub + been + V + object.
4
Affirmative Negative Interrogative He had been waiting for He had not been waiting Had he been waiting her since morning for her since morning for her since morning? She had been writing She had not been writing Had she been letters for two hours letters for two hours writing letters for two hours? Sita had been crying since Sita had not been crying Had sita been crying morning since morning since morning? Negative Interrogative sentences Had + sub + not + been + V4 + object? I had been flying kites since morning.
18
Had I not been flying kites since morning?
Future tense
Future Indefinite tense Formula 1 Sub + will/shall/can/may etc. + V + object.
We can use will with I & we but as per the british English we have to use shall with it.
Rule 1 We use shall with I and we (First person) 2 Will with He, She, They, it, you, etc. (Second and third person) wah Jaipur jayega He will go to Jaipur. Sita gana gaye gi Sita will sing a song. Negative and Interrogative sentences Negative:Interrogative:sub + will / shall + not + V + object will/ shall + subject + V + object? Negative I shall not buy a T.V. He will not go to Agra Negative Interrogative sentences Will/ shall + subject + not + V + object? I shall buy a T.V Shall I not but a T.V?
1 1 1
Affirmative I shall buy a T.V. He will go to Agra
Interrogative Shall I buy a T.V? Will he go to Agra
19
He will go to market. Will he not go to market? Future Continuous Tense We use this tense when work is progress in future. Formula:4 Sub + will/ shall be + V + OBJECT Hum raat ko T.V dekh rahe hoge We shall be watching T.V in the night Who kapde dho rahi hogi She will be washing cloths Negative and Interrogative sentences Negative:Interrogative sub + will/ shall + not + be + V object will / shall + sub + be + V4 + object?
4
Note 1. In negative sentence we put not after will / shall and before be. 2. In interrogative sentence we put will / shall before subject and rest structure will be same Affirmative I shall be going She will be washing Negative interrogative Will / shall + sub + not + be + V4 + Object/ Example Affirmative I shall be playing tomorrow Interrogative negative Shall I not be playing tomarrow? Negative I shall not be going She will not be washing Interrogative Shall I be goin go Will she be washing
20
They will be washing cloths
Will they not be washing cloths?
Future perfect tense This tense show that some work is done at any specific time or it will finish before the second work start Formula Sub + will/shall + have + V3 + object. Rule 1. In future perfect use only have 2. use by instead of in (in future tense for time reference)
Example :
Wah agle versh tak yah project kahatam kar chuge ga He will have competed this project by next year Sarita agle mah ghar wapas aa jaye ga Sarita will have returned home by next year Ghanti bajne se purv mai school pahuch jauga I shall have reached school before the bell rings.
Negative interrogative Negative Interrogative Note 1. in negative sentence use not after will / shall and before have 2. in interrogative sentence use shall / will before subject? Interrogative negative Shall / will + subject + not +have + V3 + Object? sub + shall / will + have not + V3 object shall / will + subject + have + V3 + object?
21
Future perfect continuous Formula Subject + will / shall + have been + V4 + .+ object + since/ for.. Rule 1. In this type of sentence we use have been with will / shall 2. we use by for time reference but some time we use on as per the sentence Example: Sat baje ve do ghante se khel rahe hoge They will have been playing for two hours by 7O clock. Vah agle mah mai es office mai char versh se kaam kar rahi thi She will have been working in this office for five years by the next month. Versh 2005 mai ramesh es makan mai 5 versh se rah raha hoga Ramesh will have been living in this house for 5 years by the year 2005. Agle Monday ko hum subhh se patag uda rahe hoge We shall have been flying kites since morning on next Monday. Negative and interrogative Negative Interrogative:Affirmative I shall have been playing football. They will have been working Interrogative negative Will / shall + sub + not + have been + V4 + Object? Affirmative Interrogative negative I shall have been playing match since Shall I not have been playing match morning since morning? Sub + shall / will + not + have been + V4 + .. Shall / Will + subject + have been + V4 + .? Negative I shall not been playing football. They will have not been working Interrogative Shall I have been playing football? Will they have been working?
22
He will have been watching T.V. for two Will he not have been watching hours. T.V. for two hours?
Article
There are two types of articles
1. 2.
Indefinite article (A, An) Definite article (The) Use of A, An
1.
We use A, An before singular Countable noun
2. In Exclamatory sentences after What, Such if singular, countable noun is there so we use A, An Example: What a grand Building!, What a pretty Girl!
3.
Before profession / designation we use A, An
Example He is an MP, MLA, SDO. He is a manager. After Many, Rather, Quite, Such if there is singular noun so we have to use A, An
4.
Example Quite an easy question,
Use of The
With previously discussed matter. we use the Example: - I found a bag. The bag contained a coin. The coin was made of gold. She bought a saree. The saree was very costly.
1.
23
2. Before parts of the body Example: - He was wounded in the arm. 3. Mythological communities, historical events, political parties, rivers and oceans name. Example: - The Hindus, the Muslims 4. Before unique things (Dont use article before hell, Heaven, God, Parliament) Example: - The sun sets in the west, The earth revolves round the sun 5. 6. 7. Before Ramayan, Kuran, Bible we have to use the. Before the persons post we have to use The Before those words who express the nationality we have to use the
8. Before ordinals we have to use the. First, second, third.ordinals and one, two, threecardinals 9.
10.
Before musical instruments, or any inventions we have to use The
We cant use the in front of the countrys name. But if the some words like Republic, kingdom, states are added to the countrys name so we have to use The Before east, west, north, south we have to use the, but if the places name stuck with it or with northern, western, eastern, southern. So, we cant use The with them 12. With this type of sentence structure: the + Name + of +we have to use the Example:- The bank of America is a big bank. The Great Wall of China
11.
Modals
Use of Can
24
Can is used in present and future only Can is used to express ABILITY, or asking PERMISSION. Can in Positive 1. I can give only ten Rupees 2. They can speak English 3. He can ride a bicycle 4. I can clean the clothes 5. He can sing
Use of could Could is used in present and future tense only
Could is used to express ABILITY or asking PERMISSION but more politely. Could in Affirmative Sentence Could I speak to Mr. Sharma? Could you not come early? (Permission) (Ability)
Use of should
Should is used for
Giving suggestions / advice
25
Expressing social obligations Should is used for giving suggestions / Advice 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. You should work hard You should exercise daily You should earn more You should take care of yourself You should come in time
Should is used to express social obligations 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. You should help the poor. You should keep your city clean You should listen to elders You should keep good company You should obey traffic rules
Use of would
26
Would is the past tense of will Would alone has no definite meaning in the past If Have is added to would it becomes would have The meaning of would have is past imaginary action.
1.
If be is added to would it become would be The meaning of would be the action to be done in future.
2.
Would have is used in past conditional sentences
1. 2.
I would have paid the fees yesterday, if I had the money I would have married the girl last year, if she had proposed to me.
Would be is used in future for work to be done
1. 2. 3. The director would be checking the letter. The lessons would be reaching in time. They would be coming late in the evening
Use of MAY
MAY is used in present and future only
27
May is used 1. 2. To express possibility if some action. For taking permission with respect from elders
May to express possibility of action 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. We may go out. He may rum fast They may sing songs I may write a book She may study more
May is used for talking permission with respect
1.
2. 3. 4. 5.
May I go to the party, daddy? May I borrow your pen, sir? May I go out, sir? May we study together, sir? May I come in, sir?
Use of might
Might is used in the past, present & future Might has many implications as per the additions of other verbs to might
28
1. 2. 3.
By addition of now to it, the sentence becomes present tense. By addition of tomorrow to the sentence, it becomes future tense. By addition of have to might, the sentence becomes past.
Note the difference He might come now. He might come tomorrow. He might have come.
1. 2. 3.
Use of might
Might is used to express possibility of action in the past 1. 2. 3. I might have informed him I might have seen the movie I might have married my friend
Might is used for less possibility In present 1. 2. 3. It might rain He might come She might go
Might is used for low possibility in future a.
b.
c. NOTE:
I might go there They might visit us next year She might sing on stage tomorrow
When the possibility is very high so we use MAY instead of MIGHT
Use of used to
29
Used To for Past Routine Action To express Action Repeatedly Done in The Past Time Zone Note Only Verbs 1st form is going to use For example: last summer, When I was in America_ _ _ _ _
1. I used to go for a walk every morning. 2. I used to take juice everyday 3. I used to read the newspaper once a day. With Used To we usually use Often, sometime, occasionally and frequently When I was In Paris, ----------I often used to attend parties in the evening 2. I used to visit restaurants frequently. 3. I generally used to stay at home in the afternoon. 4. I used to feel home sick, Sometime. 5. I used to go by air, occasionally.
1.
Use of Ought to ()
Subject + ought to + V1
To express duty or moral obligation towards Nation, Elders, Community and Animals
The key to make questions with W / H family
Word Used for Examples
30
Who What Where Why
Which
How
When Whom
Asking about the 1. Who are you? identity of a person 2. Who is she? 3. Who has sung this song Asking something 1. What is your name? about a person or 2. What are they drinking? thing 3. What has he done? Asking about some 1. Where are my balls? place, person, or 2. Where is your bag? thing 3. Where has she gone? Asking the reason 1. Why is he late? cause etc. 2. Why are you crying? 3. Why have they come here? 4. Why will he tease you? Asking about person 1. Which is my room? or thing in a group 2. Which dress should you wear? 3. Which group are you joining? Inquiring about 1. How are you? things related to 2. How is your headache? somebody 3. How can he do this? 4. How will they come hear? Asking about the 1. When is your birthday? time of incident 2. When will you come back? 3. When are we going there? Whom is used for 1. Whom you are waiting for? indicating unknown 2. Whom do you want to see? persons
Introduction to Prepositions
31
Prepositions are the words that show the relationship of noun or pronoun with rest of the sentences. Generally preposition comes immediately before the noun like: After Class At home By Tulsidas On fire There are certain expectations to the above said rule like 1. In case where Determiners (a, an, The) are used like: After THE storm, under the old regimes 2. In case where Adjectives are used like: On the horse With colour shirt.
Guide Pattern For Use Of Prepositions
a.
Usage of on:-
It is used for place and as well as time.
32
Ex. The book is on table I will see you on Sunday.
b.
Usage of in:For expressing duration of time I will see you in few hours. I will be there in two hours Usage of over:- Used for things, which are positioned above something without having contact with the surface? The fan is over the table Usage of above:-To express thing placed higher comparatively. It is used in case of rank. Anand is above average in class Usage of up:- To express the upward indication and position. I will climb up the tree Usage if upper:- Position of higher comparatively with respect to something He lives in the ground floor and his office is on upper storey Usage of Below: It indicates anything under the mark/ standard/ surface. It is below his dignity to work like a clerk Usage of Under :To express lower position or placing beneath something The basket is lying under the table. Usage of Down :Refers to standard, position, surface comparatively lower. In the morning temperature came down by 2 degrees Usage of By :- It indicates time & Position both, refers to the possible (round) ending time of action. I am standing by the bridge (position) He will reach America by 7.00 pm (time) Usage of Aside:-Mean to keep away. He brushed aside all the questions. Beside :It expresses placing by said of some people or something.
c.
d.
e.
f.
g.
h.
i.
j.
k.
l.
33
On the annual day, I sat beside the chief guest.
m.
Along :Means parallel, in the same line The traveller moved along the railway line. Against :Mainly used for opposition, it is used to indicate support. I am against dishonesty (opposition) He is standing against the wall (support)
n.
o. With : Indicates: 1. Association or union of two or more. 2. To express agreeability & disagreeability. 3. To express result. Ex : The rain is accompanied with strong winds (associated of two) I disagree with what you say I am satisfied with your performance (result) p. Within : To express specified limitation oftime and amount. I can go from Delhi to Mumbai within 2 hours. Arrange your necessities within Rs. 700/q. In / At: Indicates time, place and whereabouts of thing. To mention the end of the period. To differenciate between main place and sub place. 1. Main place, 2. Sub place. E.g. in India at Delhi. Use to placing used to indicate presence or existence within a place Ex. the books are in the rack.
*** Words of Grammar 1***
34
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Ever means Never means Seldom means Oftenmeans Usually means
Always At No Time Very Rarely repeatedly generally
Words of grammar in use
Ever Never Seldom Often Usually
1. 2. 3.
1. 2. 3. 1. 2. 3. 1. 2. 3. 1. 2. 3.
I will care of you forever. No one lives forever. Joy is not forever. Never will I trouble you One should Never flight Never hurt anyone. He seldom watches movies They will seldom do it. They seldom right. I often go there. We often attend meetings They often go for shopping They usually meet in the club Some people usually sleep late. I usually take tea in the morning.
Words Of Grammar2
35
Use of A Few, Few, Little, A Little
A few means LESS NUMBER used for countable things Few means NO NUMBER used for countable things LITTLE means nothing used for things cannot be counted A LITTLE means SOME QUANTITY used for things cant be counted
Words of grammar in use
A FEW Few A Little LITTLE
1. A few books are left now. 2. A few children are in the room 3. She has A FEW sweets. 1. She has FEW friends. 2. FEW birds are in the cage. 3. FEW onions are in the plate. 1.A LITTLE work was done by him. 2.There A LITTLE rice in the plate. 3.A LITTLE exercise is good for health. 1.LITTLE work was done by him. 2.Little play makes you dull. 3.LITTLE study is not good.
Words of Grammar--3
Use of WHEREVER, WHENEVER, WHATEVER
36
Wherever Whenever Whatever Wherever Whenever Whatever
means means means
At Any Place at any time Any THING Wherever you go, Ill follow He spend money whenever he gets Take whatever you want
WORDS OF GRAMMAR4
Use of Someone, somebody, anyone, anybody Somebody Anybody Someone Anyone Everybody means means means means means some unknown person any unknown persons some persons out of any group known persons all persons
You might also like
- English Grammar in HindiDocument14 pagesEnglish Grammar in HindiYogendra Uikey88% (8)
- TriPac EVOLUTION Operators Manual 55711 19 OP Rev. 0-06-13Document68 pagesTriPac EVOLUTION Operators Manual 55711 19 OP Rev. 0-06-13Ariel Noya100% (1)
- English GrammarDocument16 pagesEnglish GrammarAman SharmaNo ratings yet
- A Complete Solution of EnglishDocument94 pagesA Complete Solution of Englishsarvesh kumar100% (1)
- All Verbs in English GrammarDocument93 pagesAll Verbs in English GrammarAbdul Ahad R-02100% (1)
- 2-in-1 Book Series: Teacher King’s English Beginner Course Book 1 & English Speaking Course Book 1 - Croatian EditionFrom Everand2-in-1 Book Series: Teacher King’s English Beginner Course Book 1 & English Speaking Course Book 1 - Croatian EditionNo ratings yet
- English Verb Tenses 1: Affirmative: Negative: InterrogativeDocument11 pagesEnglish Verb Tenses 1: Affirmative: Negative: InterrogativeEvita KoenNo ratings yet
- 16) ALL 12 Verb Tenses in English EXPLAINED!Document5 pages16) ALL 12 Verb Tenses in English EXPLAINED!Laura Pujol100% (1)
- Grammar BookDocument119 pagesGrammar BookBetsabe Tejada100% (3)
- English GrammarDocument160 pagesEnglish GrammarBabu Bhosale100% (4)
- Grammar RulesDocument11 pagesGrammar RulesAkshay Shukla100% (1)
- Hindhi BasicsDocument23 pagesHindhi BasicsSreenivasan Gopalakrishnamurthy100% (1)
- Spoken English EbookDocument452 pagesSpoken English EbookAnadi Gupta100% (1)
- CHAPTER 1 (For Tutor)Document15 pagesCHAPTER 1 (For Tutor)Diễm NgọcNo ratings yet
- Present Continuous Tense in Urdu by EA Spoken English With Emran Ali Rai On YouTubeDocument15 pagesPresent Continuous Tense in Urdu by EA Spoken English With Emran Ali Rai On YouTubeEA Spoken English100% (1)
- English Book Grammar NewDocument100 pagesEnglish Book Grammar NewMuslim Physicist100% (1)
- Basic English GrammarDocument49 pagesBasic English GrammarthaniaNo ratings yet
- English Translation TensesDocument104 pagesEnglish Translation TensesP Eng Suraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Verbs in English Grammar PDFDocument93 pagesVerbs in English Grammar PDFLotus100% (1)
- Tense Chart Hindi To EnglishDocument1 pageTense Chart Hindi To EnglishVikas Singla68% (22)
- Leadership Styles-Mckinsey EdDocument14 pagesLeadership Styles-Mckinsey EdcrimsengreenNo ratings yet
- Past Continuous Tense in Urdu by EA Spoken English With Emran Ali Rai On YouTubeDocument13 pagesPast Continuous Tense in Urdu by EA Spoken English With Emran Ali Rai On YouTubeEA Spoken EnglishNo ratings yet
- IEC TC 56 Dependability PDFDocument8 pagesIEC TC 56 Dependability PDFsaospieNo ratings yet
- Inside:: Issue 4 - February 2004 Bi-Monthly Warhammer E-ZineDocument40 pagesInside:: Issue 4 - February 2004 Bi-Monthly Warhammer E-ZineJoe BloggsNo ratings yet
- English Grammar Topics List PDF Free Download PDF HunterDocument4 pagesEnglish Grammar Topics List PDF Free Download PDF HunterRamin ShamsNo ratings yet
- Namma Kalvi General English Grammar Study MaterialDocument9 pagesNamma Kalvi General English Grammar Study MaterialdeviNo ratings yet
- VerbsDocument59 pagesVerbsVinceNo ratings yet
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense in Urdu by EA Spoken English On YouTubeDocument24 pagesPresent Perfect Continuous Tense in Urdu by EA Spoken English On YouTubeEA Spoken English100% (6)
- Impact of Pantawid Pamilyang Pilipino Program On EducationDocument10 pagesImpact of Pantawid Pamilyang Pilipino Program On EducationEllyssa Erika MabayagNo ratings yet
- English Grammar NotesDocument32 pagesEnglish Grammar NotesYash PatelNo ratings yet
- March Forward Spoken English Lecture#01Document6 pagesMarch Forward Spoken English Lecture#01Mahmudul Hassan Jony100% (1)
- General EnglishDocument169 pagesGeneral EnglishSanthosh Kumar100% (1)
- Conditional Sentence in Hindi - YouTube - EnglishGuru PDFDocument4 pagesConditional Sentence in Hindi - YouTube - EnglishGuru PDFSunil YadavNo ratings yet
- English TenseDocument39 pagesEnglish TenseTesso RarNo ratings yet
- How To Learn Hindi (With Pictures) - WikiHowDocument1 pageHow To Learn Hindi (With Pictures) - WikiHowImaadh IfthikarNo ratings yet
- Spoken English Guru - YouTubeDocument21 pagesSpoken English Guru - YouTubeSyed Hassan TariqNo ratings yet
- Tense Chart: IndefiniteDocument2 pagesTense Chart: IndefiniteAbhimanyu SinghNo ratings yet
- Q&R EnglishToTeluguMeaningsDocument286 pagesQ&R EnglishToTeluguMeaningsmouse.lenova mouseNo ratings yet
- English Grammar BookDocument128 pagesEnglish Grammar BookAkash MaharanaNo ratings yet
- Tenses in Hindi PDF by Ajay Sir Accent Hisar 1 PDFDocument25 pagesTenses in Hindi PDF by Ajay Sir Accent Hisar 1 PDFbanwari Lal SharmaNo ratings yet
- ENG11Document45 pagesENG11Suresh SV100% (2)
- Verbs & Related Words S. No. Present Past Past Participle Verb+ing S/esDocument14 pagesVerbs & Related Words S. No. Present Past Past Participle Verb+ing S/es101010121212No ratings yet
- Formal Words and PhraseDocument2 pagesFormal Words and PhraseJopie Aranda100% (1)
- All TensesDocument16 pagesAll TensesAntonia AntoNo ratings yet
- Hindi Lesson Fruits and VegetableDocument12 pagesHindi Lesson Fruits and VegetableSubashini Jaganathan100% (1)
- English Practice BookDocument120 pagesEnglish Practice BookTarak Palavalasa100% (1)
- GujaratiDocument29 pagesGujaratiPiyush ShahNo ratings yet
- Spoken EnglishDocument1 pageSpoken EnglishPrabha KaruppuchamyNo ratings yet
- Day 8 - Noun PhrasesDocument28 pagesDay 8 - Noun PhrasesNorman Chen100% (2)
- 85 English Grammer Rules and Shortcuts For CDS NDA AFCATDocument4 pages85 English Grammer Rules and Shortcuts For CDS NDA AFCATAnchorNo ratings yet
- Past Indefinite Tense in Urdu by EA Spoken English With Emran Ali Rai On YouTubeDocument14 pagesPast Indefinite Tense in Urdu by EA Spoken English With Emran Ali Rai On YouTubeEA Spoken EnglishNo ratings yet
- Communicative English: Listen, Learn, ApplyDocument180 pagesCommunicative English: Listen, Learn, ApplySindhu Manja100% (1)
- Personal Mantra From PenokondaDocument1 pagePersonal Mantra From PenokondaSrinathvrNo ratings yet
- Urdu Words List in English Watch Video & Download PDF Book - Grammareer PDFDocument34 pagesUrdu Words List in English Watch Video & Download PDF Book - Grammareer PDFLyla AamirNo ratings yet
- All Grammar PDFDocument160 pagesAll Grammar PDFprasadzeal100% (1)
- 3 Essential Grammar Rules For Spoken EnglishDocument7 pages3 Essential Grammar Rules For Spoken EnglishbhaskarNo ratings yet
- Aug Ca Hindi 45 PDFDocument29 pagesAug Ca Hindi 45 PDFPrashank GuptaNo ratings yet
- Basic Sentence Patterns in EnglishDocument16 pagesBasic Sentence Patterns in Englishsalwa296No ratings yet
- Preview JVREnglish Grammar 10536Document15 pagesPreview JVREnglish Grammar 10536N Bhagya VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Basic Sentence PatternDocument3 pagesBasic Sentence PatternAdmiryNo ratings yet
- Preposition PDFDocument17 pagesPreposition PDFLuckysachin100% (1)
- Teacher King’s English Speaking Course Book 1: Italian EditionFrom EverandTeacher King’s English Speaking Course Book 1: Italian EditionNo ratings yet
- Shishtachar Evam Vyaktitva Vikas: Parsonality Development CourseFrom EverandShishtachar Evam Vyaktitva Vikas: Parsonality Development CourseNo ratings yet
- Teaching Profession - Educational PhilosophyDocument23 pagesTeaching Profession - Educational PhilosophyRon louise PereyraNo ratings yet
- Perancangan Crushing Plant Batu Andesit Di PT Nurmuda Cahaya Desa Batujajar Timur Kecamatan Batujajar Kabupaten Bandung Barat Provinsi Jawa BaratDocument8 pagesPerancangan Crushing Plant Batu Andesit Di PT Nurmuda Cahaya Desa Batujajar Timur Kecamatan Batujajar Kabupaten Bandung Barat Provinsi Jawa BaratSutan AdityaNo ratings yet
- CV & Surat Lamaran KerjaDocument2 pagesCV & Surat Lamaran KerjaAci Hiko RickoNo ratings yet
- FuzzingBluetooth Paul ShenDocument8 pagesFuzzingBluetooth Paul Shen许昆No ratings yet
- Heimbach - Keeping Formingfabrics CleanDocument4 pagesHeimbach - Keeping Formingfabrics CleanTunç TürkNo ratings yet
- Jakub - BaZi CalculatorDocument3 pagesJakub - BaZi Calculatorpedro restinxNo ratings yet
- Module 2 MANA ECON PDFDocument5 pagesModule 2 MANA ECON PDFMeian De JesusNo ratings yet
- Winter CrocFest 2017 at St. Augustine Alligator Farm - Final ReportDocument6 pagesWinter CrocFest 2017 at St. Augustine Alligator Farm - Final ReportColette AdamsNo ratings yet
- How To Configure PowerMACS 4000 As A PROFINET IO Slave With Siemens S7Document20 pagesHow To Configure PowerMACS 4000 As A PROFINET IO Slave With Siemens S7kukaNo ratings yet
- PFEIFER Angled Loops For Hollow Core Slabs: Item-No. 05.023Document1 pagePFEIFER Angled Loops For Hollow Core Slabs: Item-No. 05.023adyhugoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 SolvedDocument3 pagesTutorial 5 SolvedAshutoshKumarNo ratings yet
- Kiritsis SolutionsDocument200 pagesKiritsis SolutionsSagnik MisraNo ratings yet
- Escaner Electromagnético de Faja Transportadora-Steel SPECTDocument85 pagesEscaner Electromagnético de Faja Transportadora-Steel SPECTEdwin Alfredo Eche QuirozNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 (Automatic Transmission)Document26 pagesChapter 13 (Automatic Transmission)ZIBA KHADIBINo ratings yet
- postedcontentadminuploadsFAQs20for20Organization PDFDocument10 pagespostedcontentadminuploadsFAQs20for20Organization PDFMohd Adil AliNo ratings yet
- An Annotated Bibliography of Timothy LearyDocument312 pagesAn Annotated Bibliography of Timothy LearyGeetika CnNo ratings yet
- 2011-2012 - Medical - DirectoryDocument112 pages2011-2012 - Medical - DirectoryЈелена КошевићNo ratings yet
- NCP - Major Depressive DisorderDocument7 pagesNCP - Major Depressive DisorderJaylord Verazon100% (1)
- Systems Analysis and Design in A Changing World, Fourth EditionDocument41 pagesSystems Analysis and Design in A Changing World, Fourth EditionKoko Dwika PutraNo ratings yet
- 6GK74435DX040XE0 Datasheet enDocument3 pages6GK74435DX040XE0 Datasheet enLuis CortezNo ratings yet
- Bullshit System v0.5Document40 pagesBullshit System v0.5ZolaniusNo ratings yet
- Close Enough To Touch by Victoria Dahl - Chapter SamplerDocument23 pagesClose Enough To Touch by Victoria Dahl - Chapter SamplerHarlequinAustraliaNo ratings yet
- PresentationDocument27 pagesPresentationMenuka WatankachhiNo ratings yet
- Sveba Dahlen - SRP240Document16 pagesSveba Dahlen - SRP240Paola MendozaNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Arts in Theology: Christian Apologetics/ Seventh-Day Adventist Contemporary IssuesDocument13 pagesBachelor of Arts in Theology: Christian Apologetics/ Seventh-Day Adventist Contemporary IssuesRamel LigueNo ratings yet