Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Learning
Uploaded by
yousuf adilOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Learning
Uploaded by
yousuf adilCopyright:
Available Formats
ILR Cornell
Micro-Organizational Behavior: Perception and Learning
Copyright 1999 by Brent Smith, Ph.D.
ILR Cornell
Stereotypes
Beliefs that all members of specific groups share similar traits and are prone to behave in the same way. Why do we rely on stereotypes?
Copyright 1999 by Brent Smith, Ph.D.
ILR Cornell
Overcoming Biases
Dont overlook external causes of others behavior Identify and confront your stereotypes Evaluate people based on objective factors Avoid making rash judgments
Copyright 1999 by Brent Smith, Ph.D.
ILR Cornell
Learning
A relatively permanent change in knowledge or behavior that results from practice or experience.
Copyright 1999 by Brent Smith, Ph.D.
ILR Cornell
Classical Conditioning
Learning that takes place when the learner recognizes the connection between an unconditioned stimulus and a conditioned stimulus.
Copyright 1999 by Brent Smith, Ph.D.
ILR Cornell
Stimulus
Conditioned Stimulus: A neutral stimulus that, as a result of being paired with an unconditioned stimulus, elicits a response.
Unconditioned Stimulus: Anything that produces an unconditioned response.
Copyright 1999 by Brent Smith, Ph.D.
ILR Cornell
Response
Unconditioned Response: A response that occurs naturally in the presence of a given stimulus.
Conditioned Response: A response that is called forth by a previously neutral stimulus (the conditioned stimulus.)
Copyright 1999 by Brent Smith, Ph.D.
ILR Cornell
Operant Conditioning
Learning that takes place when the learner recognizes the connection between a behavior and its consequences.
Behaviors with positive consequences are acquired. Behaviors with negative consequences are eliminated
Law of Effect: tendency for behaviors leading to desirable consequences to be strengthened and for behaviors leading to undesirable consequences to be weakened
Copyright 1999 by Brent Smith, Ph.D.
ILR Cornell
Operant Conditioning
Copyright 1999 by Brent Smith, Ph.D.
ILR Cornell
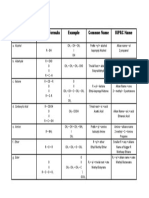
An Example
Example of the Operant Conditioning Process
Manager shows employee how to do a job
Employee performs job properly
Manager praises employee
Copyright 1999 by Brent Smith, Ph.D.
ILR Cornell
Operant Conditioning Keys
Antecedents: Anything that tells workers about desired and undesired behaviors and their consequences.
Behaviors: Desirable organizational behaviors and undesirable organizational behaviors.
Copyright 1999 by Brent Smith, Ph.D.
ILR Cornell
Operant Conditioning Keys
Consequences of Behavior: Include positive reinforcement and negative reinforcement for desirable organizational behaviors; and extinction and punishment for undesirable organizational behaviors.
Copyright 1999 by Brent Smith, Ph.D.
ILR Cornell
Consequences of Behavior
Positive Reinforcement: Administering positive consequences to workers who perform the desired behavior.
Negative Reinforcement: Removing negative consequences to workers who perform the desired behavior.
Copyright 1999 by Brent Smith, Ph.D.
ILR Cornell
Consequences of Behavior
Extinction: Removing whatever is currently reinforcing the undesirable behavior.
Punishment: Administering negative consequences to workers who perform the undesirable behavior.
Copyright 1999 by Brent Smith, Ph.D.
ILR Cornell
Operant Conditioning
Copyright 1999 by Brent Smith, Ph.D.
ILR Cornell
Reinforcement Strategies
Immediate Reinforcement Delayed Reinforcement Continuous Reinforcement Partial Reinforcement
Copyright 1999 by Brent Smith, Ph.D.
ILR Cornell
Reinforcement Schedules
Fixed-Interval Schedule Variable-Interval Schedule Fixed-Ratio Schedule Variable-Ratio Schedule
Copyright 1999 by Brent Smith, Ph.D.
ILR Cornell
Shaping
The reinforcement of successive and closer approximations to a desired behavior.
Copyright 1999 by Brent Smith, Ph.D.
ILR Cornell
Organizational Behavior Modification (O.B. Mod.)
The systematic application of the principles of operant conditioning for teaching and managing important organizational behaviors.
Copyright 1999 by Brent Smith, Ph.D.
ILR Cornell
The Basic Steps of O.B. Mod.
Identify the behavior to be learned. Measure the frequency of the behavior. Establish a criterion or goal. Choose a reinforcer. Selectively reward the desired behavior. Measure the frequency of the behavior.
Copyright 1999 by Brent Smith, Ph.D.
ILR Cornell
Social Learning Theory
A learning theory that takes into account the fact that thoughts and feelings influence learning. Necessary components include vicarious learning, self-control, and selfefficacy.
Copyright 1999 by Brent Smith, Ph.D.
ILR Cornell
Social Learning Theory
Observational Learning (Modeling): people can learn new behaviors by observing the rewards and punishments given to others.
Copyright 1999 by Brent Smith, Ph.D.
You might also like
- Leadership in OrganizationDocument39 pagesLeadership in Organizationyousuf adilNo ratings yet
- Leadership & Management: Discussion For Lesson 9: Transactional and Transformational LeadershipDocument9 pagesLeadership & Management: Discussion For Lesson 9: Transactional and Transformational Leadershipyousuf adilNo ratings yet
- Leadership: Presentation in PSY/SOA 131 "Social Psychology" K. D. KappusDocument12 pagesLeadership: Presentation in PSY/SOA 131 "Social Psychology" K. D. Kappusyousuf adilNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Organization StructureDocument22 pagesFoundations of Organization Structureyousuf adilNo ratings yet
- Agriculture Sector of PakistanDocument51 pagesAgriculture Sector of Pakistanyousuf adil100% (3)
- Statutory Meeting of CompanyDocument38 pagesStatutory Meeting of Companyyousuf adil0% (1)
- Delivering The Presentation: Chapter 13-AdlerDocument6 pagesDelivering The Presentation: Chapter 13-Adleryousuf adilNo ratings yet
- Monetary Aggregates: M1, M2 and M3Document1 pageMonetary Aggregates: M1, M2 and M3yousuf adilNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- CR-7iA CR-4iA Installation and Setup Guide (B-83774JA-1 01)Document1 pageCR-7iA CR-4iA Installation and Setup Guide (B-83774JA-1 01)lidiia.pavlkukNo ratings yet
- Sathyamangalam Chennai MR Sivakumar N: Rolsun TravelsDocument2 pagesSathyamangalam Chennai MR Sivakumar N: Rolsun TravelsGayu carita catoNo ratings yet
- 56.vocal Warmup Log For Belt Your FaceDocument5 pages56.vocal Warmup Log For Belt Your FaceAlinutza AlinaNo ratings yet
- Random FactsDocument353 pagesRandom FactsSergio Rivas100% (1)
- Gulayan Sa Barangay OrdinanceDocument2 pagesGulayan Sa Barangay OrdinancekonsinoyeNo ratings yet
- Calamansi: Soil and Climatic RequirementsDocument4 pagesCalamansi: Soil and Climatic Requirementshikage0100% (1)
- Linkage 2 Lab ReportDocument25 pagesLinkage 2 Lab Reportapi-25176084883% (6)
- EV-H-A1R 54C - M - EN - 2014 - D - Heat Detector SalwicoDocument2 pagesEV-H-A1R 54C - M - EN - 2014 - D - Heat Detector SalwicoCarolinaNo ratings yet
- Articulo de Las 3 Tesis Por BrowDocument30 pagesArticulo de Las 3 Tesis Por BrowJHIMI DEIVIS QUISPE ROQUENo ratings yet
- The Ethics of CloningDocument5 pagesThe Ethics of CloningUpai MbembNo ratings yet
- Information Technology Solutions: ADMET Testing SystemsDocument2 pagesInformation Technology Solutions: ADMET Testing Systemskrishgen biosystemsNo ratings yet
- Level 9 - Unit 34Document7 pagesLevel 9 - Unit 34Javier RiquelmeNo ratings yet
- SCL NotesDocument4 pagesSCL NotesmayaNo ratings yet
- ASHRAE52Document8 pagesASHRAE52ImranAtheeqNo ratings yet
- MODEL 1332 MODEL 1432: Slide LengthDocument8 pagesMODEL 1332 MODEL 1432: Slide LengthFabian FragosoNo ratings yet
- Adhi Wardana 405120042: Blok PenginderaanDocument51 pagesAdhi Wardana 405120042: Blok PenginderaanErwin DiprajaNo ratings yet
- Dolor Postoperatorio y Efectos Secundarios de La Uvulo Palstia Con Radiofrecuencia en Roncopatia Primaria.Document5 pagesDolor Postoperatorio y Efectos Secundarios de La Uvulo Palstia Con Radiofrecuencia en Roncopatia Primaria.Alejandro RuizNo ratings yet
- Stepanenko DermatologyDocument556 pagesStepanenko DermatologySanskar DeyNo ratings yet
- ARI 700 StandardDocument19 pagesARI 700 StandardMarcos Antonio MoraesNo ratings yet
- Vulnerability of The Urban EnvironmentDocument11 pagesVulnerability of The Urban EnvironmentKin LeeNo ratings yet
- PL 806aDocument45 pagesPL 806acesar luis gonzalez rodriguezNo ratings yet
- 30356-Article Text-56848-1-10-20210201Document14 pages30356-Article Text-56848-1-10-20210201Mel FaithNo ratings yet
- Audio AmplifierDocument8 pagesAudio AmplifierYuda Aditama100% (2)
- Naming Alcohols, Aldehydes. EtcDocument1 pageNaming Alcohols, Aldehydes. Etcim_mikezNo ratings yet
- Stas Final ReviewerDocument8 pagesStas Final ReviewerShane SaynoNo ratings yet
- VSR 411 QB AnaesthesiaDocument7 pagesVSR 411 QB Anaesthesiavishnu dathNo ratings yet
- Recognizing Fractures and Dislocations: Corpuz, Rachella Nicole PDocument46 pagesRecognizing Fractures and Dislocations: Corpuz, Rachella Nicole PRachella Nicole CorpuzNo ratings yet
- 134.4902.06 - DM4170 - DatasheetDocument7 pages134.4902.06 - DM4170 - DatasheetVinicius MollNo ratings yet
- SCI Fayette Greene..2007-2009 ViolationsDocument10 pagesSCI Fayette Greene..2007-2009 ViolationsHRCFedUpNo ratings yet
- Chem Sba 2019-2020Document36 pagesChem Sba 2019-2020Amma MissigherNo ratings yet