Professional Documents
Culture Documents
20 Variance Analysis
Uploaded by
achutagvkrao0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
291 views29 pagesMaterial Cost Variance (MCV) is the difference between The Total Standard Material Costs (TSMC) and The Total Actual Material Cost (TAMC). Material Mix Sub Variance (MMSV) is useful when there is a possibility of changing the mix of various materials used in the production of the final unit.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMaterial Cost Variance (MCV) is the difference between The Total Standard Material Costs (TSMC) and The Total Actual Material Cost (TAMC). Material Mix Sub Variance (MMSV) is useful when there is a possibility of changing the mix of various materials used in the production of the final unit.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
291 views29 pages20 Variance Analysis
Uploaded by
achutagvkraoMaterial Cost Variance (MCV) is the difference between The Total Standard Material Costs (TSMC) and The Total Actual Material Cost (TAMC). Material Mix Sub Variance (MMSV) is useful when there is a possibility of changing the mix of various materials used in the production of the final unit.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 29
Variance Analysis
Material Cost Variances
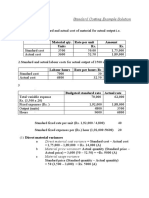
Material Cost Variance (MCV) is the difference between The Total Standard Material Costs (TSMC) and The Total Actual Material Cost(TAMC). MCV = (SQ x SP x AO) (AQ x AP x AO) MCV = TSMC TAMC
SQ = Standard Quantity of Usage per unit SP = Standard Price of Material per unit AO = Actual Output AQ = Actual Quantity of Usage per unit AP = Actual Price of Material per unit
2
Material Cost Variances
Material Costs Material Usage per Unit (kg) Price per Unit (kg) in Rs. Standards 2 14 Actuals 2.2 15
Actual Units Produced
100
MCV = (SQ x SP x AO)-(AQ x AP x AO) MCV = (2 x 14 x 100) (2.2 x 15 x 100) MCV = Rs.2800 Rs. 3300 = - Rs.500
3
Material Cost Variances
Material Cost Variance is due to Material Price Variance (MPV) & Material Usage Quantity Variance (MUV) MCV = MPV + MQV MPV = (SP AP) x AQ x AO = (14 15) x 2.2 x 100 = - Rs.220 MUV = (SQ AQ) x SP x AO = (2 2.2) x 14 x 100 = - Rs.280 MCV = - 220 + ( - ) 280 = - Rs.500
4
Material Usage Variance
The Material Usage Variance could (only if required) be further analyzed into Material Mix Sub Variance (MMSV) & Material Yield Sub Variance (MYSV). MUV = MMSV + MYSV Material Mix Sub Variance is useful when there is a possibility of changing the mix of various materials used in the production of the final unit.
5
Material Mix Sub Variance v/s Material Yield Sub Variance
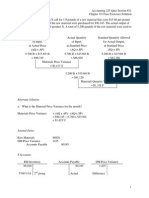
MMSV = (Standard Mix of Actual Total Quantity of Materials Used Actual Mix of Actual Quantity Used ) x Standard Price of each Material. The Std mix to make 1 drum of 100 Kg sauce is 50 Kg Mat. X @ 2.00 + 30 Kg Mat. Y @ 3.00 + 20 Kg Mat. Z @ 4.00 The Act. input used to make 1 drum of 100 Kg sauce is: 60 Kg Mat. X + 40 Kg Mat. Y + 10 Kg Mat. Z.
6
Material Mix Sub Variance
1. Std Mix is 50 : 30 : 20 for 1 drum of 100 Kgs
I.e. 5:3:2
2. Actual Input Quantity is 110 Kgs. So Standard
Mix for Actual Input Quantity should have been
55:33:22
3. MMSV =
1. Mat.X = (55 60) x 2 = - Rs.10 2. Mat.Y = (33 40) x 3 = - Rs.21 3. Mat.Z = (22 10) x 4 = + Rs.48 Net MMSV = - Rs.10 Rs.21 + Rs.48 = + Rs.17
7
Material Yield Sub Variance
The MUV in this Case is MUV = (SQ AQ) x SP x AO Here AO = 1 as we are considering only One drum of sauce MUV = for Mat.X (50 60) x 2 x 1 = - Rs.20 + for Mat.Y (30 40) x 3 x 1 = - Rs.30 + for Mat.Z (20 10) x 4 x 1 = + Rs.40 MUV = - Rs.10 MUV = MMSV + MYSV. - 10 = + 17 + MYSV i.e. MYSV = - Rs.27
8
Material Yield Sub Variance
Materials Std. Actual Standard Total Quantity Quantity Price Std. Cost (A) (B) ( C) (AxC) Mat.X 50 60 2 100 Mat.Y Mat.Z Total 30 20 100 40 10 110 3 4 2.70 90 80 270
9
Material Yield Sub Variance
The Weighted Average Standard Price of Material is Rs 2.70 & Standard Quantity is 100 Kgs. MYSV = (SQ AQ) x SP (wtd Avg.) = (100 110) x 2.70 = - Rs.27 MUV = MMSV + MYSV - 10 = +17 + ( -) 27
10
Labor Cost Variance
Labor Cost Variance (LCV) is the difference between The Total Standard Labor Costs (TSLC) and The Total Actual Labor Cost (TALC). LCV = (SH x SR x AO) (AH x AR x AO) LCV = TSLC TALC
SH = Standard Labor hours per unit SR = Standard Rate of Labor per hour AO = Actual Output AH = Actual Labor hours per unit AR = Actual Rate of Labor per hour
11
Labor Cost Variance
Labor Costs Labor Hours Usage per Unit Labor Rate per Hour Actual Units Produced Standards 2 14 100 Actual 2.2 15
LCV = (SH x SR x AO)-(AH x AR x AO)
LCV = (2 x 14 x 100) (2.2 x 15 x 100) LCV = Rs.2800 Rs. 3300 = - Rs.500
12
Labor Cost Variances
Labor Cost Variance is due to Labor Rate Variance (LRV) & Labor Efficiency Variance (LEV) LCV = LRV + LEV LRV = (SR AR) x AH x AO = (14 15) x 2.2 x 100 = - Rs.220 LEV = (SH AH) x SR x AO = (2 2.2) x 14 x 100 = - Rs.280 LCV = - 220 + ( - ) 280 = - Rs.500
13
Labor Efficiency Variance
The Labor Efficiency Variance could (only if required) be further analyzed into Labor Mix Sub Variance (LMSV) & Labor Yield Sub Variance (LYSV). LEV = LMSV + LYSV Labor Mix Sub Variance is useful when there is a possibility of changing the mix of various class of laborers used in the production of the final unit.
14
Labor Mix Sub Variance v/s Labor Yield Sub Variance
LMSV = (Standard Mix of Actual Labor Hours Worked Actual Mix of Actual Labor hours worked) x Standard Rate of each Class of Laborers. The Std Labor mix to make 1 drum of 100 Kg sauce is 50 Hrs Lbr X @ 2.00 + 30 Hrs Lbr Y @ 3.00 + 20 Hrs Lbr Z @ 4.00 The Act. Labor used to make 1 drum of 100 Kg sauce is: 60 Hr of Lbr X + 40 Hrs of Lbr Y + 10 Hrs of Lbr Z.
15
Labor Mix Sub Variance
1. Std Lbr Mix is 50 : 30 : 20 for 1 drum of 100
Kgs i.e. 5:3:2 2. Actual Labor hours worked is 110 hours. So Standard Lbr Mix for Actual Labor hours worked should have been
55:33:22
3. LMSV =
1. Lbr X = (55 60) x 2 = - Rs.10 2. Lbr Y = (33 40) x 3 = - Rs.21 3. Lbr Z = (22 10) x 4 = + Rs.48 Net LMSV = - Rs.10 Rs.21 + Rs.48 = + Rs.17
16
Labor Yield Sub Variance
The LEV in this Case is LEV = (SH AH) x SR x AO Here AO = 1 as we are considering only One drum of sauce LEV = for Lbr X (50 60) x 2 x 1 = - Rs.20 + for Lbr.Y (30 40) x 3 x 1 = - Rs.30 + for Lbr.Z (20 10) x 4 x 1 = + Rs.40 LEV = - Rs.10 LEV = LMSV + LYSV. - 10 = + 17 + LYSV i.e. LYSV = - Rs.27
17
Labor Yield Sub Variance
Laborers Std. Hours to be Worked (A) Lbr X 50 Lbr Y Lbr Z Total 30 20 100 Actual Hours Worked (B) 60 40 10 110 Standard Rate per Labor Hour ( C) 2 3 4 2.70 Total Std. Labor Cost (AxC) 100 90 80 270
18
Labor Yield Sub Variance
The Weighted Average Standard Rate of Laborers is Rs 2.70 per hour & Standard Labor Hours to be worked is 100 Kgs. LYSV = (SH AH) x SR (wtd Avg.) = (100 110) x 2.70 = - Rs.27 LEV = LMSV + LYSV - 10 = +17 + ( -) 27
19
Variable Overhead Cost Variances
The Variable Overhead Cost Variances
(VOCV) is similar in treatment to the Material & Labor Cost Variances. It is the difference between the Standard Variable Overhead Costs from the Actual Variable Overhead Costs.
20
Variable Overhead Cost Variances
VOCV = (SVOC AVOC ) x AO VOCV = TSVOC TAVOC VOCV = VOEV + VOSV
21
Variable Overhead Cost Variances
Where
SVOC = Standard Variable Overhead Costs per Unit AVOC = Actual Variable Overhead Costs per Unit TSVOC = Total Standard Variable Overhead Costs TAVOC = Total Actual Variable Overhead Costs VOEV = Variable Overhead Efficiency Variance VOSV = Variable Overhead Spending Variance
22
Variable Overhead Cost Variances
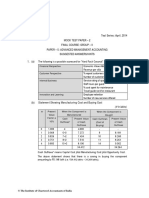
Std Labor Hours allowed: Rs.2 per unit Std Variable Costs allowed: Rs.3 per
direct labor hour Actual Production: 80 units Actual Direct Labor Hours: 165 units Actual Overheads incurred: Rs.518 Determine the VOCV ; VOEV & VOSV
23
Variable Overhead Cost Variances
VOCV = (Standard Variable Overhead Costs Actual Variable Overhead Costs incurred. Standard Variable Overhead Costs = (Standard Labor Hours per Unit x Standard Variable Costs allowed per labor hour x Actual Output) Please note that here we have taken labor hours only because the cost factor used to allocate the variable overheads is labor hours !! Please use the relevant cost factor for each type of variable overhead VOCV = (2 x 3 x 80) 518 = - Rs.38
24
Variable Overhead Cost Variances
The Variable Overhead Cost Variance could be due to Efficiency or Spending Variances ( Similar to Material / Labor Variances.) VOEV = {(Std. Labor Hours per Unit x Actual Output) Actual Hours } x Std. Variable Overhead Rate. { ( 2 x 80) 165 } x 3 = - Rs.15
25
Variable Overhead Cost Variances
VOSV = (Actual Labor Hours Worked x
Std. Variable Overhead Rate per hour) Actual Variable Overhead costs VOSV = ( 165 x 3 ) Rs.518/- = Rs 23
Thus VOCV = VOEV + VOSV Rs.38 = Rs.15 + Rs.23
26
Fixed Overhead Cost Variances
Fixed Overheads do not vary with volume of production. They are allocated at a predetermined standard fixed
overhead rate. (SFOR) SFOR = Budgeted Fixed Overhead Budgeted Volume of Activity Fixed Overhead Cost Variance (FOCV) = Total Actual Fixed Overhead Costs (TAFOC) (SFOR per hour x Std Hours per Unit (SH) x Actual Output (AO)) FOCV = FOSV + FOEV + Volume Variance FOSV = Fixed Overhead Spending Variance FOEV = Fixed Overhead Efficiency Variance
27
Fixed Overhead Cost Variances
Actual Fixed O/heads = Rs.530/ Budgeted Fixed O/heads = Rs.500/ Budgeted Level of Activity = 100 units or
200 Labor Hours Std. Labour Hours allowed per unit = 2 hours per unit Actual Production = 90 units Actual Labor Hours = 190 hours.
28
Fixed Overhead Cost Variances
FOCV = Rs.530 (Rs.500 /(2 x 100)units x 2x 90 units) = Rs.530
(500/200) x 2x90 = Rs.80 (unfavorable) FOSV = Total Actual Overheads Total Budgeted Overheads = Rs.530 Rs.500 = Rs.30 FOEV = [(Std. Hrs per Unit x AO) Actual Hrs Wrkd] x SFOR = [(2 x 90) 190] x 500 / (2x100) = - Rs.25 Volume Variance = (Bud.Volume - Actual Volume) x SFOR = 100 units 90 units x (500/(2x100)) =10x2.5=Rs.25. FOCV (Rs.80) = FOSV (Rs.30) + FOEV (Rs.25) + Vol. Variance (Rs.25)
29
You might also like
- Topic 4231Document3 pagesTopic 4231Richard mwanaNo ratings yet
- Labour Cost VarianceDocument30 pagesLabour Cost VarianceSunita BasakNo ratings yet
- Cost VarianceDocument10 pagesCost VariancesurendarNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing ProblemsDocument16 pagesStandard Costing ProblemsSanket PanwalkarNo ratings yet
- Overhead Variances FinalDocument12 pagesOverhead Variances FinalKella PradeepNo ratings yet
- Assignment #2 DM&DL L Variance With SolutionDocument9 pagesAssignment #2 DM&DL L Variance With SolutionJeannet LagcoNo ratings yet
- Stand CostingDocument38 pagesStand CostingaydhaNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing and Variance AnalysisDocument7 pagesStandard Costing and Variance AnalysisaKSHAT sHARMANo ratings yet
- Variance AnalysisDocument36 pagesVariance AnalysisParesh JhaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument9 pagesUntitledAhmad GilaniNo ratings yet
- Review QuestionsDocument22 pagesReview QuestionsJustus MusilaNo ratings yet
- Variances Analysis - ExerciesDocument14 pagesVariances Analysis - Exerciesashish6784No ratings yet
- Unit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsDocument14 pagesUnit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsRuchi pariharNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsDocument14 pagesUnit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsDerrick de los ReyesNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsDocument14 pagesUnit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsShruti BannerjeeNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsDocument14 pagesUnit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsShubham NamdevNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsDocument14 pagesUnit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsAlbsNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsDocument14 pagesUnit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsyanbladeNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsDocument14 pagesUnit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical Problemskiran shettyNo ratings yet
- 18 10 SA V1 S1 Solved Problems SC PDFDocument14 pages18 10 SA V1 S1 Solved Problems SC PDFTheVagabond HarshalNo ratings yet
- 18-10-SA-V1-S1 Solved Problems SC PDFDocument14 pages18-10-SA-V1-S1 Solved Problems SC PDFAlbsNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsDocument14 pagesUnit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsAfsahNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsDocument14 pagesUnit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsNeelima Varma NadimpalliNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical ProblemsDocument14 pagesUnit 6 Module 10 Standard Costing: Practical Problemsyousuf AhmedNo ratings yet
- Standard CostingDocument19 pagesStandard CostingWong Mei KunNo ratings yet
- 8 Standard CostingDocument22 pages8 Standard CostingNeha KhalidNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing Example SolutionDocument2 pagesStandard Costing Example SolutionVikas KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Derivatives - Ahmed SamyDocument5 pagesDerivatives - Ahmed SamyMostafa KaghaNo ratings yet
- Costing Ans 2Document16 pagesCosting Ans 2Shikha SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit 7-Standard CostingDocument5 pagesUnit 7-Standard Costingkevin75108No ratings yet
- Break Even Analysis, Systems of Linear EquationsDocument29 pagesBreak Even Analysis, Systems of Linear EquationsTareq IslamNo ratings yet
- Costing Notes Chapter - Standard Costing: MCV Muv + MPV and Muv Myv + MMVDocument12 pagesCosting Notes Chapter - Standard Costing: MCV Muv + MPV and Muv Myv + MMVSocial SectorNo ratings yet
- Ch09 - Standard Costing A Managerial Control ToolDocument46 pagesCh09 - Standard Costing A Managerial Control Toolachmad rezaNo ratings yet
- ECON 301 Homework Chapter 5 1. A Firm Can Manufacture A Product According To The Production FunctionDocument8 pagesECON 301 Homework Chapter 5 1. A Firm Can Manufacture A Product According To The Production FunctionFachrizal AnshoriNo ratings yet
- Ma Chapter 3 Standard Costing - LabourDocument60 pagesMa Chapter 3 Standard Costing - LabourMohd Zubair KhanNo ratings yet
- Q. No. 1 (Material Variances) Part - 1Document2 pagesQ. No. 1 (Material Variances) Part - 1HelplineNo ratings yet
- VariancesDocument16 pagesVariancesaroridouglas880No ratings yet
- Perilaku Produsen: Teori Produksi Dan Biaya ProduksiDocument14 pagesPerilaku Produsen: Teori Produksi Dan Biaya ProduksiRizki Nur FitriyaniNo ratings yet
- Process CostingDocument16 pagesProcess CostingvijayNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Part 3 - Standard CostingDocument8 pagesUnit 3 Part 3 - Standard CostingPrarthana R Industrial EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Cha (Ter 3 ContDocument2 pagesCha (Ter 3 ContMindy PhanNo ratings yet
- 21 Costing BestDocument23 pages21 Costing BestAkash GuptaNo ratings yet
- Hilton CH 10 Select SolutionsDocument24 pagesHilton CH 10 Select SolutionsRaza Ze0% (1)
- 09 - Marginal AnalysisDocument35 pages09 - Marginal AnalysisLyka Garcia100% (1)
- CHAPTER 9 StandardDocument6 pagesCHAPTER 9 Standardsarahayeesha1No ratings yet
- Economia Mineral: I N I N N NDocument10 pagesEconomia Mineral: I N I N N NClaudio Herman CHNo ratings yet
- QS11 - Class Exercises SolutionDocument8 pagesQS11 - Class Exercises Solutionlyk0tex100% (2)
- DocumentDocument5 pagesDocumentCurrent ShirtsNo ratings yet
- Chapter Nine: Standard Costing: A Managerial Control ToolDocument26 pagesChapter Nine: Standard Costing: A Managerial Control ToolGirlshey 26No ratings yet
- Process Costing and Joint Product and byDocument4 pagesProcess Costing and Joint Product and byGeetika BhattiNo ratings yet
- Afm AssignmentDocument4 pagesAfm AssignmentNISHANo ratings yet
- Standard Costing and Balanced ScorecardDocument25 pagesStandard Costing and Balanced ScorecardMary Joy BalangcadNo ratings yet
- Finalcosting NiyazDocument29 pagesFinalcosting Niyazakramshaikh87No ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document13 pagesChapter 12mikeNo ratings yet
- Standard Costing - Problem SolutionsDocument10 pagesStandard Costing - Problem Solutionsallen1191919No ratings yet
- Production & Operations Management: Facility Location StrategyDocument8 pagesProduction & Operations Management: Facility Location StrategyRomesh SomaniNo ratings yet
- 22.02.2017 Models For Location ProblemsDocument8 pages22.02.2017 Models For Location ProblemsRomesh SomaniNo ratings yet
- MBA ACTG 5101 FINAL EXAM DEC 2022 PROBLEMS STUDENT Renee Nerissa GuerraDocument34 pagesMBA ACTG 5101 FINAL EXAM DEC 2022 PROBLEMS STUDENT Renee Nerissa GuerraSheila ArjonaNo ratings yet
- Visual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsFrom EverandVisual Financial Accounting for You: Greatly Modified Chess Positions as Financial and Accounting ConceptsNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionFrom EverandMathematical Formulas for Economics and Business: A Simple IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Consultant Digital & Data (Stage)Document3 pagesConsultant Digital & Data (Stage)Dharmavir KatbaNo ratings yet
- Assignment On HR of AarongDocument6 pagesAssignment On HR of AarongFarzana KhanNo ratings yet
- The Importance of VideoDocument3 pagesThe Importance of VideoPaul ChadwickNo ratings yet
- III Sem - Marketing ManagementDocument20 pagesIII Sem - Marketing ManagementAzra MuftiNo ratings yet
- Online Marketplace Analysis: Micro-EnvironmentDocument17 pagesOnline Marketplace Analysis: Micro-EnvironmentsahafyNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On Employee EngagementDocument121 pagesA Project Report On Employee EngagementSumit RpNo ratings yet
- Obj and Questionnaire PatanjaliDocument3 pagesObj and Questionnaire PatanjaliVaibhav PatilNo ratings yet
- SlidesDocument237 pagesSlidesMansur KhamitovNo ratings yet
- Vdo SwitchDocument1 pageVdo SwitchjengandxbNo ratings yet
- Liquid DetergentDocument6 pagesLiquid Detergentmayanksarin23100% (1)
- Financial Template RsDocument11 pagesFinancial Template Rsginish12No ratings yet
- ProgramDocument8 pagesProgramMichille Piquero DE LeonNo ratings yet
- CLV Tutorial PDFDocument11 pagesCLV Tutorial PDFjegosssNo ratings yet
- CH 6Document31 pagesCH 6Hesham AbdallaNo ratings yet
- SWOT and PEST Analysis of Southwest AirlinesDocument6 pagesSWOT and PEST Analysis of Southwest AirlinesAmmara LatifNo ratings yet
- Danone CaseDocument16 pagesDanone Caseprashanthc85100% (2)
- Study - ISO 13485 PDFDocument15 pagesStudy - ISO 13485 PDFAnonymous 78Ezy46qvNo ratings yet
- Book Review On Money Marketing by Jessie PaulDocument13 pagesBook Review On Money Marketing by Jessie PaulKunal ParekhNo ratings yet
- Allison James Business Plan Real TrendsDocument9 pagesAllison James Business Plan Real TrendsAllison JamesNo ratings yet
- AT List of Centres PDFDocument128 pagesAT List of Centres PDFKushal DaveNo ratings yet
- Distribution: DefinitionDocument25 pagesDistribution: Definitiontheanuuradha1993gmaiNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Marketing Strategies of Milktea Shops On The Preference of The ConsumersDocument5 pagesThe Influence of Marketing Strategies of Milktea Shops On The Preference of The ConsumersRose Ann Callada100% (1)
- WWW - Pocketful.in: About Pocketful ( - Under Construction)Document3 pagesWWW - Pocketful.in: About Pocketful ( - Under Construction)Korra Akshitha KeerthiNo ratings yet
- Beer GameDocument5 pagesBeer GameUnni KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Business EnvironmentDocument21 pagesChapter 2 - The Business EnvironmentPui YanNo ratings yet
- KodakDocument21 pagesKodakPrabhjot Seehra83% (6)
- Assignmentclovis Repaired) by EmmaDocument20 pagesAssignmentclovis Repaired) by EmmaClovis DjoumessiNo ratings yet
- Sales and Distributtion of Itc - SunfeastDocument27 pagesSales and Distributtion of Itc - SunfeastSiddharth GuptaNo ratings yet
- BBA 4year Termsystem PDFDocument44 pagesBBA 4year Termsystem PDFMuhammad SaadNo ratings yet
- Alpecin Caffeine Shampoo - 250ml Amazon - Com.auDocument1 pageAlpecin Caffeine Shampoo - 250ml Amazon - Com.auasankaNo ratings yet